Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Index of Economic Freedom
Annual index and ranking created in 1995 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Index of Economic Freedom is an annual index and ranking created in 1995 by The Heritage Foundation and The Wall Street Journal to measure the degree of economic freedom in the world's nations. The creators of the index assert that they take an approach inspired by Adam Smith's The Wealth of Nations, that "basic institutions that protect the liberty of individuals to pursue their own economic interests result in greater prosperity for the larger society".[1][2][page needed]
Parts of this article (those related to Ranking and scores section) need to be updated. (October 2025) |
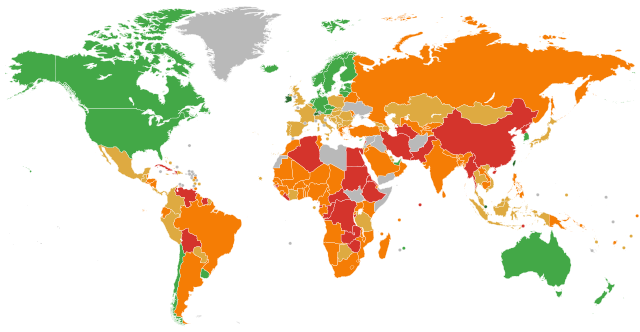
Free (100–80)
Mostly free (79.9–70)
Moderately free (69.9–60)
Mostly unfree (59.9–50)
Repressed (49.9–0.00)
Remove ads
Purpose
Summarize
Perspective
The Heritage Foundation's Index of Economic Freedom states that, "Economic freedom is the fundamental right of every human to control his or her own labor and property. In an economically free society, individuals are free to work, produce, consume, and invest in any way they please. In economically free societies, governments allow labor, capital, and goods to move freely, and refrain from coercion or constraint of liberty beyond the extent necessary to protect and maintain liberty itself."[3] By publishing the Index annually, the foundation attempts to highlight where such freedoms do and do not exist.
The Heritage Foundation reports that the top 20% on the Index have twice the per capita income of those in the second quintile, and five times that of the bottom 20%.[4]
Carl Schramm, who wrote the first chapter of the 2008 Index, states that cities of Medieval Italy and those of the mid-19th century Midwestern United States both flourished proportionate to their possessed economic fluidity and institutional adaptiveness created by economic freedom.[5]
According to Will Wilkinson of the libertarian think tank Cato Institute, studies show that higher economic freedom correlates strongly with higher self-reported happiness.[6] According to economists Tomi Ovaska and Ryo Takashima, economic freedom research suggests "that people unmistakably care about the degree to which the society where they live provides them opportunities and the freedom to undertake new projects, and make choices based on one's personal preferences."[7]
According to the Cato Institute, higher economic freedom promotes participation and collaboration.[8] Also claimed is that higher economic freedom is extremely significant in preventing wars; according to their calculations, freedom is around 54 times more effective than democracy (as measured by Democracy Score) in diminishing violent conflict.[9]
Remove ads
Ratings
Summarize
Perspective
Between 1995, the first edition of the Index, and 2008, the score for world economic freedom has increased, rising 2.6 points, according to the Index.[10]
Between 2008 and 2011, however, the score decreased 60.2 to 59.7, though the 2011 score represents an increase of 2.2 points since the first edition in 1995. The economic freedom score improved for 117 countries, the majority of countries included in the index, which were mainly developing and emerging market economies. In 2011, with the exception of Europe and North America, there were increased levels of freedom recorded in all regions, with the greatest improvement shown in Sub-Saharan Africa. The top five "free" economies identified by the 2011 index were Hong Kong, Singapore, Australia, New Zealand, and Switzerland, each scoring over 80 on the economic freedom grading scale.[11]
Also in 2011, the United States dropped to 9th place in the Index, falling behind Denmark, Canada, and first-place Hong Kong, which ranked first in every issue of the Index from 1995 until 2019.[11] The Heritage Foundation pointed to increases in government spending as a primary reason for the United States' decline in its ranking. According to data from the 2011 Index, the growth rates of countries with the highest levels of government spending were 4.5 points lower, on average, than countries where government spending was under control.[12] In their "Executive Highlights" of index results in 2011, the Heritage Foundation wrote that, "high levels of government spending in response to the global economic turmoil have not resulted in higher economic growth".[11]
In 2012, results from the Index showed an overall decline in global economic freedom; according to The Heritage Foundation, the average score in its ranking was the second- lowest of the last ten years.[13] The U.S. dropped to 10th place in the 2012 ranking, falling three places since 2008, when it was seventh.[14] A report issued by the Heritage Foundation stated that government spending was the cause of many countries' declines, and that the spending had "not only failed to arrest the economic crisis, but also – in many countries – seems to be prolonging it".[15] According to the report, activity in the private sector is threatened by the greater government spending, which has increased public debt and led to more bureaucracy.[13]
Hong Kong
For 25 consecutive years, from 1995 to 2019, Hong Kong was ranked the world's most free economy by the Index.[11][16][failed verification]
In 2021, however, after the Hong Kong national security law was implemented, the Heritage Foundation dropped Hong Kong and Macau as independent entities in the Index, writing that, "developments in recent years have demonstrated unambiguously that those policies are ultimately controlled from Beijing". The 2019 Index ranked the level of economic freedom in China low, 107th among the 178 ranked in the report.[17]
Remove ads
Methodology
The Index evaluates 184 countries in four broad policy areas that affect the economic freedom, which are rule of law, government size, regulatory efficiency, and open markets.[18][19] It also takes into consideration some specific categories like property rights, judicial effectiveness, government integrity and tax burden.[20] The ranking scores aspects of economic freedom between 0 and 100, with 0 meaning "no economic freedom" and 100 meaning "total economic freedom". There are twelve aspects divided into four categories.[21]
Reception
Summarize
Perspective
In 2001, Freedom House, a human rights group, wrote that, "there is a high and statistically significant correlation between the level of political freedom as measured by Freedom House and economic freedom as measured by The Wall Street Journal/Heritage Foundation survey."[22]
In his 2005 book The End of Poverty, Jeffrey Sachs graphed countries' ratings on the Index against per capita GDP growth between 1995 and 2003, claiming to demonstrate that there was no correlation between a country's rating and its rate of economic growth. As examples, Sachs cited countries with good ratings in the Index, such as Switzerland and Uruguay, which had sluggish economic performances while others, like China, with poorer ratings in the Index were experiencing strong economic growth.[23]
In January 2005, Stefan Karlsson of the Ludwig von Mises Institute challenged the usefulness of the Index due to the fuzziness of many of the categories used to determine freedom.[24]
In March 2005, John Miller criticized the Index, writing in Dollars & Sense, "In the hands of the Wall Street Journal and the Heritage Foundation, Washington's foremost right-wing think tank, however, an economic freedom index merely measures corporate and entrepreneurial freedom from accountability. Upon examination, the index turns out to be a poor barometer of either freedom more broadly construed or of prosperity."[25] According to Left Business Observer, growth in Index accounts for 10% of the variation in the growth of GDP.[26]
In September 2007, the Millennium Challenge Account, a U.S. government foreign aid program, used the Index in determining which countries will receive their performance-based compacts.[27]
In January 2008, United Arab Emirates questioned its rating in the Index, comparing its average rating with the high rating they had received from other economic freedom indexes, such as Transparency International and Moody's. UAE argued, calling the Index "unreliable", arguing that its methodology changed twice over the prior two years.[28]
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
