Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
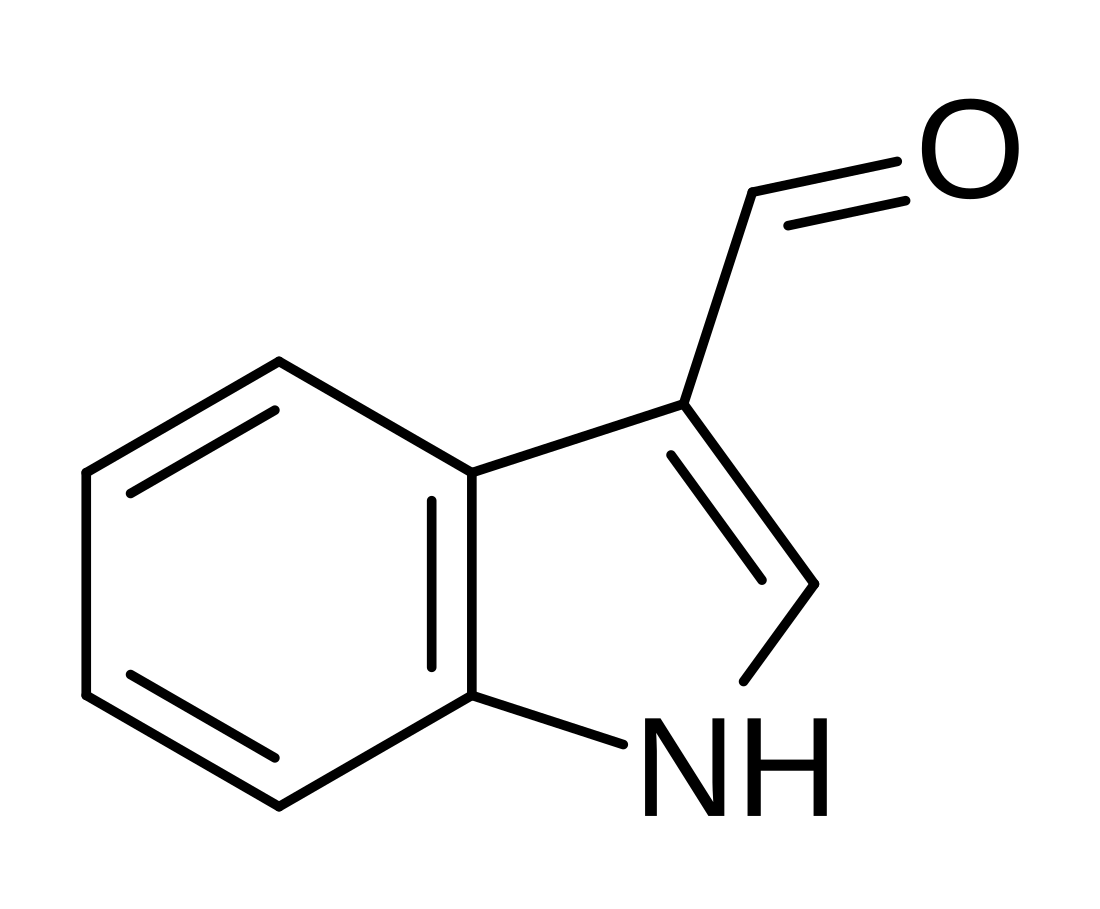
Indole-3-carbaldehyde
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Indole-3-carbaldehyde (I3A), also known as indole-3-aldehyde and 3-formylindole, is a metabolite of dietary L-tryptophan which is synthesized by human gastrointestinal bacteria, particularly species of the Lactobacillus genus.[2][3] I3A is a biologically active metabolite which acts as a receptor agonist at the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in intestinal immune cells, in turn stimulating the production of interleukin-22 which facilitates mucosal reactivity.[4][3][2]
Remove ads
Biosynthesis in humans and cellular effects
Tryptophan metabolism by human gut microbiota ()
|
Remove ads
Chemistry
Indole-3-carbaldehyde has reactivity typical of aromatic aldehydes. It can is easily oxidized to indole-3-carboxylic acid. It condenses with nitromethane in a Henry reaction to give 3-nitrovinyl indole.
Antifungal properties
Indole-3-carbaldehyde has antifungal properties, and partially accounts for the protection from chytridiomycosis seen in amphibian species which carry Janthinobacterium lividum on their skin.[8]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads