Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
IRF1
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Interferon regulatory factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IRF1 gene.[4][5]
Remove ads
Function
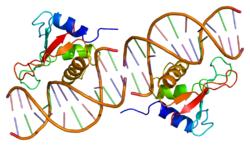
Interferon regulatory factor 1 was the first member of the interferon regulatory transcription factor (IRF) family identified. Initially described as a transcription factor able to activate expression of the cytokine Interferon beta,[6] IRF-1 was subsequently shown to function as a transcriptional activator or repressor of a variety of target genes. IRF-1 regulates expression of target genes by binding to an interferon stimulated response element (ISRE) in their promoters. The IRF-1 protein binds to the ISRE via an N-terminal helix-turn-helix DNA binding domain,[7] which is highly conserved among all IRF proteins.
Beyond its function as a transcription factor, IRF-1 has also been shown to trans-activate the tumour suppressor protein p53 through the recruitment of its co-factor p300.[8]
IRF-1 has been shown to play roles in the immune response, regulating apoptosis, DNA damage and tumor suppression.[9]
Remove ads
Regulation
It has been shown that the extreme C-terminus of IRF-1 regulates its ability to activate transcription, nanobodies targeting this domain (MF1) are able to increase IRF-1 activity.[10]
Interactions
IRF1 has been shown to interact with:
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads