Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
January–March 2022 in science
Overview of the events of 2022 in science From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
This article lists a number of significant events in science that have occurred in the first quarter of 2022.
Events
January
- 1 January – Israel reports, for the first time, a case of flurona, a rare mixture of coronavirus and influenza infections.[1][2][3][4]

The graphs visualize recent developments of science based on this data.[5]

- 3 January – OpenAlex, a free online index of over 200 million scientific documents – each with metadata such as sources, citations, author information and research topics – is launched. The API and open source website can be used for metascience, scientometrics and novel tools that query this semantic web of papers.[6][7][8]
- 5 January – Scientists show how antibiotic resistance also evolves naturally, without and before the use of antibiotics.[9][10]
- 6 January
- The global atmospheric methane concentration exceeds 1,900 parts per billion (ppb) for the first time in human history.[11]
- Astronomers report the first direct detection of pre-supernova activity in a red supergiant star before a Type II supernova (SN 2020tlf).[12][13]
- Scientists report the development of sensors to gather and identify DNA of animals from air (airborne eDNA).[14][15][16]
- 7 January – Progress in cancer pre-screening, screening and early detection is reported: metabolomic biomarkers in blood (4 J.),[17][18] circulating protein biomarkers (7 J.),[19][20] and an optical biopsy system with a fine-needle probe (6 J.).[21][22]
- 10 January
- The first successful xenogeneic heart transplant, from a genetically modified pig to a human patient, is reported in the United States.[23][24]
- Researchers build upon previous studies documenting biodiversity loss to confirm that a sixth mass extinction event, entirely caused by anthropogenic activity, is currently underway.[25][26]
- A study quantifies climate change mitigation potentials of 'high-income' nations shifting diets – away from meat consumption – and restoration of the land.[27][28]
- 11 January
- The first known deformation of an exoplanet is detected by the CHEOPS mission, which finds that WASP-103b is being strongly influenced by its parent star's close proximity, making the planet shaped like an ellipsoid instead of a sphere.[29][30]
- A study reports the likely detection of an extreme SEP event that hit Earth ~9000 years ago and, unlike known Solar storms, unexpectedly happened near a Solar minimum.[31][32]

- 12 January
- A team reports the fastest ever sequencing of a human genome, accomplished in just five hours and two minutes.[33][34]
- Molecular biologists show that the common assumption that mutations are "random" is wrong – mutation frequency can vary across regions of the genome, with such DNA repair- and mutation-biases being associated with various factors.[35][36]
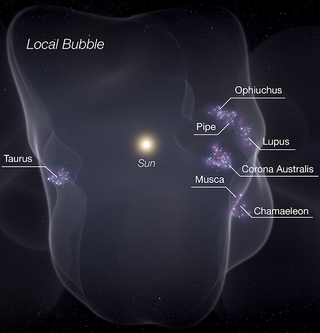
- Astronomers report, based on new spatial and dynamical constraints, that the Local Bubble, a ~1,000-light-years wide superbubble, is driving nearly all recent star formation near the Sun and that it originates ~14 Myr ago.[37][38]
- 13 January
- NASA reports that Earth's global average surface temperature in 2021 was tied with 2018 as the sixth warmest on record, while the past eight years were collectively the warmest years since modern recordkeeping began in 1880.[39]
- A study, based on data of millions of military personnel, suggests that the common Epstein-Barr virus is the leading cause of multiple sclerosis.[40][41]
- 18 January
- Europe's first quantum annealer with more than 5,000 qubits is launched in Jülich, Germany.[42]
- A study suggests and defines a 'planetary boundary' for novel entities such as plastic- and chemical pollution and finds that it has been crossed.[43][44]
- A study for the first time attempts to assess and quantify complete societal costs of cars (i.e. car-use, etc).[45]
- Microbiologists demonstrate an individually adjusted phage-antibiotic combination as an antimicrobial resistance treatment,[46][47] calling for scaling up the research[48] and further development of this approach.[49]

- 19 January
- In a first global assessment, scientists report, based on medical records, that antibiotic resistance may have contributed to ~4.95 million deaths (1.3 M directly attributed) in 2019, more than e.g. AIDS.[50][51] Increased antibiotic use during the COVID-19 pandemic may exacerbate this global health challenge.[52][53]
- A report recommends a number of measures such as, broadly described, building resilience to scientific misinformation and a healthy online information environment and not having offending content removed.[54]
- 20 January – UNESCO announces a major new coral reef off the coast of Tahiti, stretching 3 km and in "pristine" condition, discovered by marine biologists as part of the Seabed 2030 Project.[55][56]
- 22 January – According to a space monitoring company, a Chinese satellite, SJ-21, grabs an unused satellite and throws it into an orbit with a lower risk for the space debris to collide.[57][58]
- 24 January
- A chip with molecular circuit components in single-molecule (bio)sensors is demonstrated.[59][60]
- The James Webb Space Telescope arrives at its destination, Lagrange Point 2.[61]
- 25 January
- Chinese scientists at the Wuhan University and other institutions report in a preprint the detection of the closest MERS-CoV relative in bats to date, NeoCoV, and PDF-2180-CoV that can efficiently use bats' ACE2 for cell-entry. The to-date unreviewed preprint finds that one mutation could result in a 'MERS-CoV-2' that, like SARS-CoV-2, can use humans' ACE2 receptor and has both a very high fatality (MERS-CoV had a mortality of around 35%)[62] and high transmission rate, and hence represents a risk to biosafety and of potential zoonotic spillover.[63][64] According to one report, the WHO stated that further study would be required to find out "whether the virus detected in the study will pose a risk for humans".[65] The study also emphasizes the need for pathogen/spillover surveillance.[66][64]
- Neuroscientists confirm an unknown type of communication between neurons in the healthy brain – the transfer of proteins (TNTPs). Here between RGC and excitatory LGN neurons.[67][68]
- The CDC confirms the Omicron variant causes less severe disease than previously dominant variants.[69] The novel Omicron subtype 'BA.2' did not initially show an increase over this lower virulence.[70][71][72] Nevertheless, in the U.S., the daily new COVID-19 deaths were higher during Omicron dominance than during Delta's during fall[73] and the high volume of hospitalizations can cause indirect harm via local health care system strains[69] beyond less severe but non-mild disease effects.[73]
- 26 January
- Scientists regrow the missing legs of adult frogs, which are naturally unable to regenerate limbs, within 1.5 years using a five-drug mixture applied for a day via a silicone wearable bioreactor.[74][75]
- The first laparoscopic surgery performed entirely by a robot is reported.[76][77]
- Astronomers at the ICRAR report the discovery of a repeating transient with an unusually slow spin, occurring just three times an hour. It is believed to be a new class of neutron star or a white dwarf, located ~4,000 light-years away.[78][79]
- Researchers report the development of a technology that enables searching the planetary collection of nucleic acid sequences. The open source supercomputing-based Serratus Project identified over 130,000 RNA-based viruses, including 9 coronaviruses. While such and related endeavors and data are reportedly risky themselves as of 2021,[80][81] the project aims to improve pathogen surveillance, the understanding of viral evolutionary origins and enable quickly connecting strange emerging illnesses to recorded viruses.[82][83]
- 31 January – Researchers find evidence that reading on electronic devices can reduce comprehension. Reading text on a smartphone was found to promote overactivity in the prefrontal cortex and reduce sighing frequency compared to reading text on paper.[84]
February

- 1 February – The American Geophysical Union reports, based on a study by Chinese scientists published in November, that climate change has likely begun to suffocate the world's fisheries, passing a critical threshold of oxygen loss in 2021.[85][86]
- 2 February
- Progress in cancer screening is reported: DNA methylation biomarkers for breast cancer (WID-BC-index; 1 Feb.)[87][88] and ovarian cancer (WID-OC-index; 1 Feb.)[87][89] as well as lipidomics biomarkers for lung cancer (MS-based rapid targeted assay[specify] for levels of nine lipids in blood; 2 Feb.).[90][91]
- The IAU announces the Centre for the Protection of the Dark and Quiet Sky from Satellite Constellation Interference to coordinate or aggregate measures to mitigate the detrimental effects of satellite constellations on astronomy.[92][93][94]
- 3 February
- The first comprehensive non-public global map of oil and gas "ultra-emitters" of the potent greenhouse gas methane based on satellite data, first reported in 2020,[95] is published.[96][97][98]
- Scientists report the development of artificial tooth enamel from aligned assembled hydroxyapatite nanowires, a biomimetic material that has superior properties to natural tooth enamel and shows potential for use in dentistry (if found, made or further developed to be compatible with the mouth environment).[99][100][101]
- Scientists report the detection of anomalous unknown-host SARS-CoV-2 lineages with wastewater surveillance.[102][103]
- 4 February – COVID-19 pandemic: A study by the CDC finds that surgical masks worn at indoor public venues can reduce the chances of testing positive for COVID-19 by 66%, while tightfitting N95 and KN95 masks can reduce the odds of infection by 83%.[104][105]
- 7 February – Researchers demonstrate a spinal cord stimulator that enables patients with spinal cord injury to walk again via epidural electrical stimulation (EES) with substantial neurorehabilitation-progress during the first day.[106][107] On the same day, a separate team reports the first[108] engineered functional human (motor-)neuronal networks derived from iPSCs from the patient for implantation to regenerate injured spinal cord showing success in tests with mice.[109][110]
- 8 February
- A study integrates meta-analyses and data in a tool that shows populations' relative general life extension potentials of different food groups.[111][112]
- The largest and most accurate computer simulation to date of the local Universe is presented. It covers a volume of 600 million light-years from Earth and includes over 130 billion simulated particles, spanning its complete history from the Big Bang to the present.[113][114][115]
- The first evidence of a planet within the habitable zone of a white dwarf is reported, based on data from the star WD 1054–226, which lies 117 light-years from Earth.[116][117]
- 9 February
- Researchers report the development of a viable flash JH-based process to recover rare-earth elements used in modern electronics from industrial wastes.[118][119]
- A breakthrough in fusion energy is reported at the Joint European Torus in Oxford, UK, with 59 megajoules produced over five seconds (11 megawatts of power), more than double the previous record set in 1997.[120][121]

- 10 February
- A third planet is detected orbiting Proxima Centauri, the nearest known star to the Sun. Proxima d, with only a quarter of Earth's mass, is one of the lightest exoplanets ever found.[122][123]
- Results from the first controlled trial of caloric restriction in healthy non-obese humans, CALERIE, are published, confirming benefits and identifying a key protein that could be harnessed to extend health in humans.[124][125][126][127]
- 11 February
- The Australian government changes the conservation status of the koala from vulnerable to endangered, due to its rapidly shrinking habitats and climate change.[128][129]
- Astronomers report the discovery of Alcyoneus, the largest known galaxy, 5 million parsecs (16.3 million light-years) in diameter.[130][131]
- 14 February
- A study shows how immune training via a mix of molecules extracted from certain bacteria could potentially protect infants against pervasive severe lower respiratory tract infections.[132][133]
- The most comprehensive study of pharmaceutical pollution of the world's rivers finds that it threatens "environmental and/or human health in more than a quarter of the studied locations".[134][135]
- 15 February – NASA publishes its latest Sea Level Rise Technical Report, an update of the 2017 edition, which includes projections for sea-level rise through to the year 2150. The agency warns that sea levels may rise as much over the next 30 years as during the previous 100.[136][137]
- 16 February – A study models the system of coupled feedback processes (including potential mitigation tipping points) that may shape the trajectory of global greenhouse gas emissions over the century in the contemporary socioeconomic system if it both persists as is and its components remain largely unreformed. Broad factor-domains include public perceptions of climate change, future mitigation technologies' characteristics, and the responsiveness of political institutions.[138][139]
- 17 February – Bionanotechnologists report the development of a viable biosensor, ROSALIND 2.0, that can detect levels of diverse water pollutants.[140][141]
- 18 February – Neurobiologists demonstrate a Wnt7a-based approach to repair the blood–brain barrier, via GPR124/RECK agonists, as a treatment for diseases of the brain in mice.[142][143]

- 21 February – A new therapy called CINDELA is reported by scientists in South Korea, which uses CRISPR-Cas9 to kill cancer cells without harming normal tissues.[144][145][146]
- 22 February – A study uses 'years of potential life lost' (YPLL) to show that firearms have become the largest co-cause of traumatic death (or are associated with its causes) in the U.S. in 2017 and 2018 (1.42 M YPLL), slightly more than from motor vehicle crashes.[147][148] One year earlier, a study suggested the global 'mean loss of life expectancy' (LLE) from all forms of direct violence is about 0.3 years, while air pollution accounts for about 2.9 years.[149]
- 23 February
- Researchers report the development of a quantum gravity-gradiometer – an atom interferometer quantum sensor – which could be used to map and investigate subterraneans.[150][151]
- UN researchers publish a comprehensive study about climate change impacted wildfires with projections (e.g. a 31–57% increase of extreme wildfires by 2100) and information about impacts and countermeasures.[152][153]
- Astronomers report that M81, a grand design spiral galaxy about 12 million light-years away, may be the source of FRB 20200120E, a repeating fast radio burst.[154][155]
- 24 February – The 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine begins, causing impacts on science and on scientists and reactions from scientists such as condemnation, science-related sanctions, calls and measures for accelerating renewable energy transitions/decarbonization (i.e. for Russian fossil fuels sanctions) and Web-based coordination tools.[156][157][158]
- 25 February
- Scientists report the largest detailed human genetic genealogy, unifying human genomes from many sources for insights about human history, ancestry and evolution. It demonstrates a novel computational method for estimating how human DNA is related via a series of 13 million linked trees along the genome, a tree-sequence, described as the largest global family tree.[159][160][161]
- A study shows a range of commercial products to have formulations that are detrimental to human health: floor cleaners with certain fragants (certain monoterpenes) that cause indoor air pollution equivalent or exceeding the harm to respiratory tracts when the time is spent near a busy road.[162][163]
- 28 February
- A study shows annual carbon emissions (or carbon loss) from tropical deforestation have doubled during the last two decades and continue to increase.[164][165]
- One of the first scientific reviews about the association between strength training and mortality indicates that such activities are associated with a "10–17% lower risk of all-cause mortality, cardiovascular disease (CVD), total cancer, diabetes and lung cancer".[166][167]
- The IPCC releases the second part of its Sixth Assessment Report on climate change. It suggests that any further delay in concerted global action would mean missing the rapidly closing window to secure human wellbeing and the planet's health against cascading impacts of which some would become "irreversible".[168][169]
March
- 1 March
- Researchers report the development of a solar panel integrated system that, using a hydrogel, cools the panel or produces fresh water to irrigate enclosed crops beneath.[170][171]
- Atmospheric scientists report that the 2022 volcano eruption in Tonga, Pacific Ocean – the largest recorded volcanic eruption since 1991 which eruption reportedly cooled global climate by ~0.6°C during 15 months[172] – did not have a cooling effect (volcanic winter) of significance to global climate change (i.e. a cooling of ~0.004°C during the first year).[173][174]
- 2 March – Researchers report the development of a system that combines the MOST solar thermal energy storage system with a chip-sized thermoelectric generator to generate electricity from it.[175][176]
- 4 March – A study using brain-scans of 36,678 UK Biobank participants shows that negative associations between alcohol intake and brain macrostructure and microstructure are apparent in individuals consuming an average of "one to two daily alcohol units" that some may consider light or moderate consumption.[177][178] A study of 371,463 UK Biobank participants' cardiovascular health published on 25 March shows that while "light to moderate alcohol consumption was associated with healthier lifestyle factors" than in alcohol-abstainers, adjustment for such factors suggests that in principle minimizing alcohol intake could lower risks for (or negative effects towards) hypertension and coronary artery disease for everybody.[179][180]
- 7 March
- Pig calls are decoded into positive or negative emotions, using an algorithm based on ~7,000 audio recordings classified by an artificial neural network for potential use in farms.[181][182]
- A new cellular rejuvenation therapy of bursts of iPSC reprogramming is reported, which can reverse aspects of aging in mice, without causing cancer or other health problems.[183][184]
- Researchers report that more than three-quarters of the Amazon rainforest has been losing resilience due to deforestation and climate change since the early 2000s as measured by recovery-time from short-term perturbations ("critical slowing down" (CSD)), reinforcing the theory that it is approaching a critical transition.[185][186] On March 11, INPE reports satellite data that show record-high levels of Amazon deforestation in Brazil for a February (199 km²).[187]
- Scientists report how COVID-19 impacts the brain at least temporarily based on brain-scans and cognitive tests of 785 UK Biobank participants (401 positive cases), including grey matter thickness- and brain size-reductions.[188][189]
- Researchers report the first artificial parthenogenesis in mammals (viable mice offspring born from unfertilized eggs).[190][191]
- A study suggests that half of the US population has been exposed to substantially detrimental lead levels in early childhood – mainly from car exhaust whose lead pollution peaked in the 1970s.[192][193][United States-centric]
- Researchers report the development of 3D-printed nano-"skyscraper" electrodes that house cyanobacteria for extracting substantially more sustainable bioenergy from their photosynthesis than before.[194][195]
- Researchers report that the widely used supplements glycine and NAC when combined as "GlyNAC", which previously showed various beneficial effects in humans i.a. in a small trial by the authors,[196] can extend lifespan by 24% in mice when taken at old age.[197][198]
- Progress in biomarkers-based cancer screening is reported: researchers estimate risks for prostate cancer based on age, PSA and hK2 (7 Mar).[199][200] Researchers achieve high prediction accuracy for pancreatic cancer using faecal microbiota biomarkers (8 Mar).[201][202] A cancer test that checks for more mutations than ever before in one tissue sample is launched by a biotech-company (15 Mar).[203] The first clinical test of a technology to detect early-stage cancer via novel[204] biomarkers of extracellular vesicles concludes with promising results, possibly reaching screening-relevant sensitivities at high specificity at least for pancreatic cancer (17 Mar).[205][206]
- Using drug discovery artificial intelligence algorithms, researchers generate 40,000 potential chemical weapon candidates,[207][208] which may be relevant to timely regulation of chemicals and related products that can be used to manufacture the fraction of viable candidates and either illustrates or proves that such software is dual-use technology.[citation needed]
- 8 March – Researchers report SARS-CoV-2 variant recombinant viruses that contain elements of Delta and Omicron – Deltacron (also called "Deltamicron").[209][210][211] Recombination occurs when a virus combines parts from a related virus with its genetic sequence as it assembles copies of itself. It is unclear whether Deltacron – which is not to be confused with "Deltacron" reported in January – will be able to compete with Omicron and whether that would be detrimental to health.[212]
- 9 March
- Researchers in the Antarctic announce they have found Endurance, one of the greatest ever undiscovered shipwrecks, which sank in 1915 during Ernest Shackleton's exploration.[213]
- Doctors report that an antiseptic drug reduced recurring urinary tract infections in a trial as effectively as antibiotics whose prevalent use is implicated in antimicrobial resistance.[214][215]
- Researchers report that, on average, the elderly played "a leading role in driving up GHG emissions in the past decade and are on the way to becoming the largest contributor" due to factors such as demographic transition, low informed concern about climate change and high expenditures on carbon-intensive products like energy which is used i.a. for heating rooms and private transport.[216][217]
- Results from a study imply "that all living cells probably possess a common mechanism of [methane] formation". This universal mechanism is based on interactions among ROS, iron and methyl donors.[218][219][220]
- Scientists demonstrate limits and the scale of challenge of genetic-editing-based de-extinction, suggesting resources spent on more comprehensive de-extinction such as of the woolly mammoth may currently not be well allocated and substantially limited.[221][222]
- Using graphene and molybdenum disulfide, Chinese scientists create a transistor gate with a length of 0.34 nm, equivalent to just one carbon atom, by exploiting the vertical aspect of the device.[223][224]
- 10 March
- A study estimates that "relocating current croplands to [environmentally] optimal locations, whilst allowing ecosystems in then-abandoned areas to regenerate, could simultaneously decrease the current carbon, biodiversity, and irrigation water footprint of global crop production by 71%, 87%, and 100%", with relocation only within national borders also having substantial potential.[225][226]
- A study reports that excess mortality data suggests that between Jan 1, 2020, and Dec 31, 2021, ~18.2 million people died worldwide because of the COVID-19 pandemic (compared to 5.94 million reported deaths). It notes that further research could help distinguish the proportions directly caused by COVID-19 from those caused by indirect consequences of the pandemic.[227][228]
- 11 March – Researchers demonstrate electrostatic dust removal from solar panels.[229][230]
- 12 March – Biomedical gerontologists demonstrate a mechanism of anti-aging senolytics, in particular of Dasatinib plus Quercetin (D+Q) – an increase of α-Klotho as shown in mice, human cells and in a human trial.[231][232]
- 14 March – Impact and reactions to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine in science: at least one journal enacts a immediate publishing boycotts against Russia-located researchers or institutions (before 14 Mar).[233] Researchers caution that a surge of various diseases is to be expected due to the war (15 Mar).[234] Scientists warn that policy-makers should not abandon sustainable farming practices to increase grain production in response to resulting food insecurity, but change "the demand side which can lead to both a more resilient and more sustainable global food system" (18 Mar)[235] – such as limiting the import of animal feed (10 Mar)[236] – and e.g. expanding wheat production in high-productivity areas (22 Mar).[237] Scientists explain why the Ukraine biolabs conspiracy theory is disinformation (11 Mar).[238] Scientists describe dangers of nuclear energy facilities within war-zones and bombing/shelling of or near them – as well as of waste-sites[239] – by Russia.[240][241]
- 15 March – Neuroscientists report that mutations that enable people to naturally sleep as short as five hours reduce Alzheimer's pathology in mice.[242][243] On 17 March, a study reports that longer and more frequent daytime naps appears to be associated with higher risk of Alzheimer's dementia.[244][245]
- 16 March
- Researchers report that over 80% of the growth of methane emissions during 2010–2019 was caused by tropical terrestrial emissions.[246][247]
- Results of a study suggest that many earlier brain–phenotype studies ("BWAS") produced invalid conclusions as reproducibility of such studies requires samples from thousands of individuals due to small effect sizes.[248][249]
- 18 March
- Neuroscientists report that in mice suppression of claustrum appears to attenuate anxiety/stress and increase chronic stress-resistance.[250][251]
- Scientists report evolution experiments of self-replicating RNA showing a segment of how life may have emerged on Earth (abiogenesis) e.g. from RNA world conditions – from the long self-replicating RNA chemicals to diverse complex molecules.[252][253]
- 21 March
- The number of confirmed exoplanets exceeds 5,000.[254]
- Before formal publication of the 'Global Carbon Budget 2021' preprint,[255] scientists report, based on Carbon Monitor[256] data, that after COVID-19-pandemic-caused record-level declines in 2020, global CO2 emissions rebounded sharply by 4.8% in 2021, indicating that at the current trajectory, the 1.5 °C carbon budget would be used up within 9.5 years with a 2⁄3 likelihood.[257]

- 23 March – A far-UVC (ultraviolet light) air purification system is demonstrated by scientists, which can reduce levels of an airborne pathogen by 98% within minutes. This is equivalent to 184 air changes per hour – better than HEPA air cleaners – and is proposed as a solution for COVID-19 and other future pandemics.[258][259] On 9 March, a study reports promising results of tests of durably biocide treated air filters for preventing the spread of airborne pathogens like SARS-CoV-2, including of field trials onboard public rail transport.[260][261]
- 24 March
- A physical speed limit for electronic computers, optoelectronics, of approximately one petahertz (1015 Hz) is reported. This theoretical maximum is about 100,000 times faster than modern transistors.[262][263]
- Scientists review the biophysical mechanisms by which forests influence climate, showing that beyond 50°N large scale deforestation leads to a net global cooling, that tropical deforestation leads to substantial warming from non-CO2-impacts, and that as well as how standing tropical forests help cool the average global temperature by more than 1 °C.[264][265]
- Researchers report the development of the first prototype, photonic, quantum memristive device for neuromorphic (quantum-)computers/artificial neural networks.[266][267]
- 25 March – Genetic engineers report field test results that show CRISPR-based gene knockout of KRN2 in maize and OsKRN2 in rice increased grain yields by ~10% and ~8% and did not find any negative effects.[268][269]
- 30 March – WHL0137-LS, also known as Earendel, is reported as the farthest individual star ever discovered, its light having taken 12.9 billion years to reach Earth.[270][271]
- 31 March
- Astronomers report the discovery of K2-2016-BLG-0005Lb as the most distant exoplanet found by Kepler to date, at 17,000 light years.[272][273]
- Depletion of ozone in the stratosphere and, more importantly (60%), ozone increase in the troposphere is shown to be responsible for ~30% of upper Southern Ocean interior warming between 1955 and 2000.[274][275]
Remove ads
Deaths
- 18 January – Sir David Cox, English statistician (b. 1924)[276]
- 15 March – Eugene Parker, American solar and plasma physicist (b. 1927)
- 20 March – Wen Shengchang, Chinese oceanographer and member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (b. 1921)
- 23 March – Arthur Riggs, American geneticist (b. 1939)
- 27 March – Martin Pope, American physical scientist (b. 1918)
- 27 March – James Vaupel, American demographer and aging researcher (b. 1945)
- 29 March – Paul Benioff, American physicist of quantum computing (b. 1930)
- 30 March – Kenneth Walters, British mathematician and rheologist (b. 1934)
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads