Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Ludic language
Finnic language of southern Karelia, Russia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
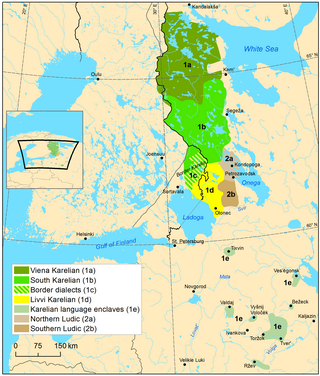
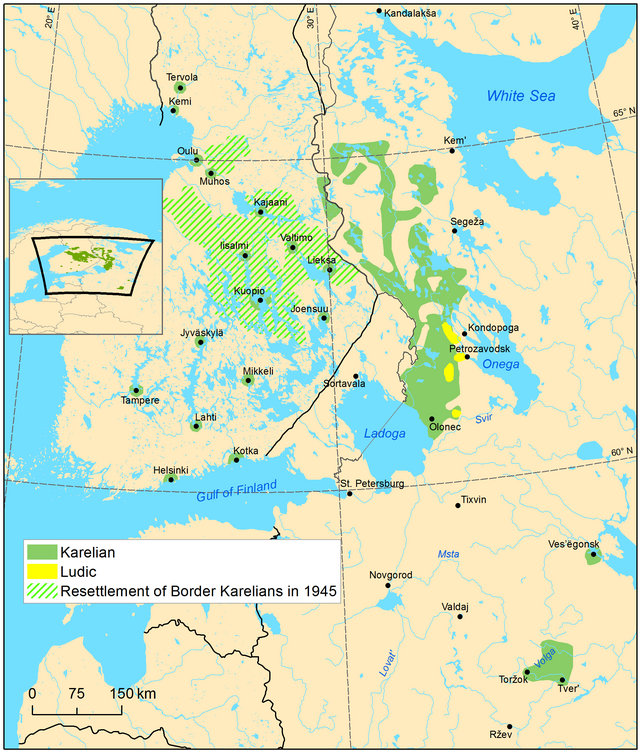
Ludic, Ludian, or Ludic Karelian (Luudi, Lyydi or lüüdi), is a Finnic language in the Uralic language family or a third supradialect of Karelian. It is transitional between the Olonets Karelian language and the Veps language.[1] It is spoken by 300 Karelians in the Republic of Karelia in Russia, near the southwestern shore of Lake Onega, including a few children.[5]
Remove ads
Classification

In the Finnish research tradition, Ludic has been considered a transitional dialect area between Karelian and Veps,[6] while in the Russian research tradition it is, on ethnographic grounds, normally considered a dialect of Karelian. A status as an independent language has been proposed in recent times.[7] Ludic is characterised by a specific mixture of Karelian-like traits (such as the diphthongisation of the Proto-Finnic non-open long vowels: e.g. *pää > piä 'head', *soo > suo 'swamp', contrast Veps pä, so)[8] and Veps-like traits (such as an almost complete loss of consonant gradation).[9] Like Veps, Ludic has also partially lost vowel harmony.
Dialects
Ludic comprises three main dialect groups:[7]
- Ludic
- Northern (Lake) Ludic, at the northwestern shores of Lake Onega
- Central (River) Ludic, at settlements along river Shuya and near the city of Petrozavodsk
- Kujärv (Forest) Ludic, in the Mikhaylovskoye (Kujärv) rural locality
The strongest Karelian resemblance is found in Northern Ludic, while the Kujärv dialect shares the most features with Veps.
Remove ads
Phonology
Vowels
- Vowel length may also be distinctive.
Consonants
- Sounds /f, fʲ, bʲ, pʲ, vʲ, mʲ/ only occur in recent borrowings.
- /h/ can also be heard as a velar [x].
- /n/ is heard as velar [ŋ] when preceding velar consonants.
- /ɡ/ can be lenited as a fricative [ɣ] in intervocalic positions.
Remove ads
Written language
Summarize
Perspective
The modern development of Ludic as a written language began during Perestroika in 1989, when the Petrozavodsk literary journal Carelia published the first poems in Ludic, based on the Kujärv dialect. At the same time, Lidia Potašova started teaching Ludic at the Kujärv school, using a Latin-based alphabet developed by Miikul Pahomov. The writing system was initially tested in literary texts before being applied to educational materials. In 1991, Potašova translated a Veps primer into Kujärv Ludic. Potašova and Pahomov later prepared the first proper Ludic primer ABC-kird' Kujärven lüüdin kielel (2003), which also included a grammar sketch and a small Kujärv Ludic dictionary. This was followed by the reader Tervheks! (2007) by Potašova and Pahomov.[10]
Subsequent publications have used two slightly different written norms. One is the Kujärv-based literary variety employed in primers, readers, and children's literature, while the other is a broader "general Ludic" standard that draws on central and northern Ludic dialects in an attempt to reduce dialectal differences. Pahomov himself experimented with this broader norm in works such as Lüüdiland (2000), Ehtsluužb (2005), and Ukon bembel (2010), where both orthographic tendencies are represented.[10]
In early Ludic publications the vowel /y/ was written either as Y, following the unified Karelian alphabet, or as Ü, by analogy with the Veps alphabet. This variation preceded the later standardization in primers and schoolbooks.
| Majuscule Forms (also called uppercase or capital letters) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | B | C | Č | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | R | S | Š | Z | Ž | T | U | V | Y (Ü) | Ä | Ö | ʹ |
| Minuscule Forms (also called lowercase or small letters) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a | b | c | č | d | e | f | g | h | i | j | k | l | m | n | o | p | r | s | š | z | ž | t | u | v | y (ü) | ä | ö | ʹ |
Phrases
- Ken sina oled? = Who are you?
- Mi tämä on? = What is this?
- Kudam teiš on Onni? = Which one of you is Onni?
- Mikš sina nagrad? = Why are you laughing?
- Kudam čuas on? = What time is it?
- Konz hyö tuldah kodih? = When are they coming home?
- Häin lähtöu huomei. = He/She leaves tomorrow.[11]
See also
Notes
Literature
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads