Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Mazandaran province
Province of Iran From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Mazandaran Province (Persian: استان مازندران; ⓘ)[a][b] is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. Its capital is the city of Sari.[7] Located along the southern coast of the Caspian Sea and in the adjacent Central Alborz mountain range and Hyrcanian forests, it is bordered clockwise by Russia (across the sea), Golestan, Semnan, Tehran, Alborz, Qazvin, and Gilan Provinces. Mazandaran, founded in 1937, covers an area of 23,842 km2.[8][9]
The province has diverse natural resources, notably large offshore reservoirs of oil and natural gas.[10] The diverse natural habitats of the province include plains, prairies, forests and rainforest[11] stretching from the sandy beaches of the Caspian Sea to the rugged and snowcapped Alborz sierra,[12] including Mount Damavand, one of the highest peaks and volcanoes in Asia.[13]
Mazandaran is a major producer of farmed fish,[14] and aquaculture provides an important economic addition to traditional dominance of agriculture.[15] Another important contributor to the economy is the tourism industry, as people from all of Iran enjoy visiting the area.[16] Mazandaran is also a fast-growing centre for biotechnology.[10]
Remove ads
Etymology
Literally "the gate or the valley of the giants" from مازن (mâzan) + در (dar) + ـان (ân), from Avesta (Avestan: 𐬨𐬀𐬰𐬀𐬌𐬥𐬌𐬌𐬀, romanized: mazainiia, lit. 'giant'). The name has been used in Shahnameh to refer to a land inhabited by divs or (daevas) and sorcerers and is difficult to conquer.
In Mazandaran, there are places named Div Asiyab, Div Cheshmeh, Div Kela, Div Hamam, etc.
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective

Human habitation in the area dates back at least 75,000 years.[17] Recent excavations in Gohar Tape in Rostamkola provide proof that the area has been urbanized for more than 5,000 years, and the area is considered one of the most important historical sites of Iran.[18] It has played an important role in cultural and urban development of the region.[19]
Indigenous peoples of the region include the ethnic Mazanderanis,[20] who speak an Iranian language which most closely resembles Gilaki and Sangiseri language, but also has phono-typical similarities to several Caucasian languages, reflecting the history of the region and its peoples.
In the early 20th century, Reza Shah connected northern Alborz to the southern slopes by constructing seven new roads and railways, the provinces of Mazandaran and Gilan became known as Shomal by all Iranians (meaning "the North" in Persian). Mazandaran province was made part of the Region 1 upon the division of the provinces into five regions solely for coordination and development purposes on June 22, 2014.[2]


Pre-Islamic history
Before the arrival of the Iranian-speakers to Iran, native people of this area were subsistence hunters and cattle herders. Archaeological studies in caves belt and Hotu man in Behshahr in the Mazandaran date to ca. 9500 BCE.[citation needed] The Amard were a tribe living along the mountainous region bordering the Caspian Sea, including current day Amol. Tapuri[21] were a tribe in the Medes south of the Caspian Sea mentioned by Ptolemy and Arrian.[22] Ctesias refers to the land of Tapuri between the two lands of Cadusii and Hyrcania.[23]

The territory known as Mazandaran has changed hands among various dynasties from early in its history. There are several fortresses remaining from the Parthian Empire and Sasanian Empire, and many older cemeteries scattered throughout the province. During this era, Mazandaran was part of Hyrcania, which was one of the important provinces.
In 662 CE, ten years after the death of Yazdegerd III, the last Sasanian emperor, a large Muslim army under the command of Hassan ibn Ali invaded Tabarestan.
With the advent of the Sasanian Empire, the King of Mazandaran (Tabaristan and Padashkhwargar) was Gushnasp,[24] whose ancestors had reigned in the area (under the Parthian empire) since the time of Alexander the Great. In 529–536, Mazandaran was ruled by the Sasanian prince Kawus, son of Kawadh.[24] Anushirawan, the Sasanian king, defeated Zarmihr, who claimed his ancestry from the legendary blacksmith Kaveh.[24] This dynasty ruled the area till 645 AD, when Gil Gilanshah (a descendant of the Sasanian king Jamasp and a grandson of Piruz) joined Mazandaran to Gilan.[24]
In 651 the Sasanid Empire fell, and all of the Sasanid domains gradually came under Arab control, except for the Caspian region of Iran (among which Tabaristan).
Islamic history
Tabaristan maintained an existence independent of the Umayyad Caliphate which supplanted the Sasanian Empire in the early seventh century, with independent Zoroastrian houses like the Bavand and Karen fighting an effective guerilla warfare against the Ummayads. A short-lived Alid Shiite state collapsed before the subsequent take-over by the Ziyarid princes. During the post-Islamic period the local dynasties fell into three classes: local families of pre-Islamic origin; the ʿAlid sayyid; and local families of secondary importance.[24]

The Karinids claimed descent from Karin, brother of Zarmihr who was the pre-Islamic ruler under the Sasanians.[24] Their last representative Mazyar was put to death in 839.[24]
In the 9th-11th century AD, there were repetitively military raids undertaken by the Rus' between 864 and 1041 on the Caspian Sea shores of Iran, Azerbaijan, and Dagestan as part of the Caspian expeditions of the Rus'.[25] Initially, the Rus' appeared in Serkland in the 9th century traveling as merchants along the Volga trade route, selling furs, honey, and slaves. The first small-scale raids took place in the late 9th and early 10th century. The Rus' undertook the first large-scale expedition in 913; having arrived on 500 ships, they pillaged the westernmost parts of Gorgan as well as Mazandaran and Gilan, taking slaves and goods.

The Bavandids, who claimed descent from Kawus, provided three dynasties.[24] The first dynasty (665–1007) was overthrown on the conquest of Tabaristan by the Ziyarid Kabus b. Wushmgir.[24] The second dynasty reigned from 1073 to 1210, when Mazandaran was conquered by 'Ala al-Din Muhammad Khwarzamshah.[24] The third ruled from 1237 to 1349 as vassals of the Mongols.[24] The last representative of the Bavandids was killed by Afrasiyab Chulawi.[24]
The Paduspanids claimed descent from the Dabuyids of the north.[24] They came to prominence around 660 and during the rule of the ʿAlids were their vassals. Later, they were vassals of the Buyids and Bavandids, who deposed them in 1190.[24] The dynasty, restored in 1209–10, survived until the time of Timur; the branch, claiming descent from Kawus the son of Kayumarth reigned until 1567 and the other, that of Iskandar the son of Kayumarth, until 1574.[24]
In the Safavid era (1501–1736) Mazandaran was settled by very large numbers of Georgians, Circassians, Armenians, and other Peoples of the Caucasus, whose descendants still live or linger across Mazandaran. Towns, villages and neighbourhoods in Mazandaran still bear the name "Gorji" (i.e., Georgian) in them, although most of the large amounts of Georgians, Armenians, and Circassians are already assimilated into the mainstream Mazandaranis. The history of Georgian settlement is described by Iskandar Beg Munshi, the author of the 17th century Tarikh-e Alam-Ara-ye Abbasi, and both the Circassian and Georgian settlements by Pietro Della Valle, among other authors.[26]
Tabaristan remained independent until 1596, when Shah Abbas I, Mazandarani on his mother's side, incorporated Mazandaran into his Safavid empire, forcing many Armenians Circassians, Georgians, to settle in Mazandaran. Pietro della Valle (1586–1652), who visited a town near Firuzkuh in Mazandaran, noted that Mazandarani women never wore the veil and didn't hesitate to talk to foreigners. He also noted the extremely large amount of Circassians and Georgians in the region, and that he had never encountered people with as much civility as the Mazandaranis.
Today, Persia proper, Fars, Mazanderan on the Caspian Sea and many other lands of this empire are all full of Georgian and Circassian inhabitants. Most of them remain Christian to this day, but in a very crude manner, since they have neither priest nor minister to tend them.
Post-Safavid period
After the Safavid period, the Qajars began to campaign south from Mazandaran with Agha Mohammad Khan who already incorporated Mazandaran into his empire in 1782. On 21 March 1782, Agha Mohammad Shah proclaimed Sari as his imperial capital. Mazandaran was the site of local wars in those years, which led to the transfer of the capital from Sari to Tehran by Fath Ali Shah. In Modern era at Mazandaran make new house and bridge in Amol and Sari. In along the beach and in the forest built Villa and modern settlements.
Before the reign of Nader Shah, the province was briefly occupied by the Russian army in the aftermath of the Russo-Persian War (1722–23) and returned to Persia in 1735. Following the outcomes of the Russo-Persian War (1804–13) and the Russo-Persian War (1826–28) northern Iran, especially Mazandaran and Gilan, as well as, to a certain extent, Tehran, fell under a growing Russian sphere of influence.[citation needed]
In the 19th century, during the reign of Fath-Ali Shah Qajar, the verdant region of Mazandaran was paid due attention as a recreational area.
The top provincial official referred to the existence of three international airports and three major sea ports in the province and the visit of millions of Iranian and foreign tourists to Mazandaran, including health tourists.
Remove ads
Demographics
Summarize
Perspective
Language and ethnicity
The population of the province has been steadily growing during the last 50 years. The following table shows the approximate province population, excluding the Golestan province, which has separated as an independent province in 1998.
The population is overwhelmingly Mazandarani, with a minority of Gilaks, Azerbaijanis, Kurds, Georgians, Armenians, Circassians, Turkmen and others.[27][28]
Mazandarani people have a background in Tabari ethnicity and speak Mazandarni. Their origin goes back to Tapuri people. So their land was called Tapuria, the land of Tapuris. Tapuris were made to migrate to the south coast of the Caspian Sea during the Achaemenid dynasty.[22][29][30]
The native people of Sari, Amol, Qaem Shahr, Babol, Nowshahr, Chalus, and Tonekabon are Mazandarani people and speak the Mazandarani language.[31][32]
The eastern Gīlakī dialect is spoken in the entire valley of the Čālūs river, though Kurdish tribes were established in the yeylāq of Kojūr and Kalārdašt in the Qajar period.[33] Today Kurds in Mazandaran are mostly known as Khajevand Kurds and form majority of the cities of Kelardasht, Abbasabad, Nowshahr, Chalus and Kajur. Other Kurdish tribes in Mazandaran Province are Modanlu (In Sari), Jahanbeiglou (In Sari), Abdolmaleki (In Behshahr), Jalalvand (In Ramsar) and Amarlu (In Tonekabon).[27]
The Mazandarani inhabit the majority of the province. The closely related Gilak form the largest minority and are concentrated in Ramsar,[34][35] Tonekabon.[36]
In recent years the region has seen an influx of Iranians from other regions of Iran, many of them attracted by its nature and seaside.
Mazanderani or Tabari is a Northwestern Iranian language. Various Mazandarani dialects exist which are spoken in Mazandaran province and the neighboring Golestan province such as Mazanderani, and Gorgani and possibly Qadikolahi (Ghadikolahi) and Palani. Today, Mazandaranis also use Persian (Western Persian).[5] The educated can communicate and read Persian well.[37]
The people residing in Chalus speak Mazanderani language. The dialect of Kalarestaqi[38] is spoken in the west of Chalus and the dialect of Kojuri[39] in the east.
The people residing in Nowshahr speak the Kojuri-dialect of Mazanderani language.[39]
The closely related Gilaks form the largest minority in Mazandaran. They speak the Gilaki language and are concentrated in Ramsar,[34][35] and Tonekabon.[36] The native people in Ramsar are Gilaks although there are also Mazandarani people living there. They speak the Gilaki language although the style they speak has been influenced by the Mazandarani language, making it slightly different from the Gilaki spoken in Gilan. (Planhol, p. 38).[33]
Population
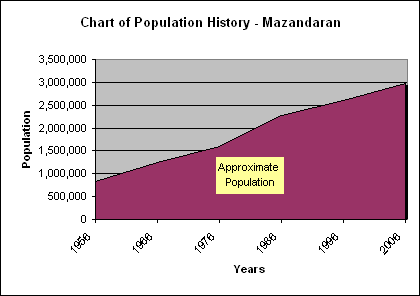
At the time of the 2006 National Census, the province's population was 2,893,087 in 783,169 households.[41] The following census in 2011 counted 3,073,943 people in 931,007 households.[42] The 2016 census measured the population of the province as 3,283,582 in 1,084,798 households.[4] Mazandaran is one of the most densely populated provinces in Iran.[43]
Administrative divisions
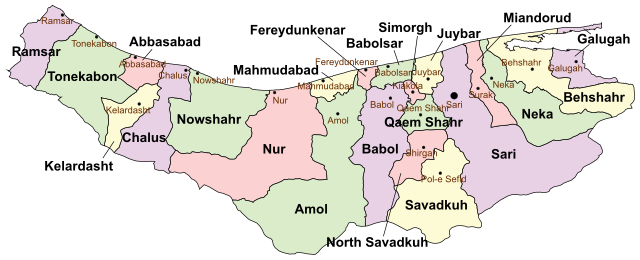 The population history and structural changes of Mazandaran province's administrative divisions over three consecutive censuses are shown in the following table.
The population history and structural changes of Mazandaran province's administrative divisions over three consecutive censuses are shown in the following table.
Cities
According to the 2016 census, 1,897,238 people (over 57% of the population of Mazandaran province) live in the following cities:[4]
Most populous cities
The following sorted table, lists the most populous cities in Mazandaran.
Remove ads
Geography
Summarize
Perspective

Mazandaran is located on the southern coast of the Caspian Sea. It is bordered clockwise by Golestan, Semnan and Tehran provinces.[50] This province also borders Qazvin and Gilan to the west.
Mazandaran province is geographically divided into two parts: the coastal plains, and the mountainous areas. The Alborz Mountain Range surrounds the coastal strip and the plains abutting the Caspian Sea like a huge wall. Due to the prevailing sea breeze and local winds of the southern and eastern coasts of the Caspian Sea, sandy hills are formed, causing the appearance of a low natural barrier between the sea and plain. There is often snowfall in the Alborz regions, which run parallel to the Caspian Sea's southern coast, dividing the province into many isolated valleys. The province enjoys a moderate, subtropical climate with an average temperature of 25 °C in summer and about 8 °C in winter. Although snow may fall heavily in the mountains in winter, it rarely falls at sea level.
- Caspian Sea coast at Nur
- Shalizar (Rice Fields)
- Pasturage
- Aseman kuh (peak in Alborz range) viewed from Kahrizak Dare (lake), Lar.
- Kafer Keli rock-cut dwellings, Larijan, Mount Damavand
- Dyvasyab Mineral springs, Dasht-e Lar, Mount Damavand
- Karaj Chalus Road
- Javarom Forest Park
- Alborz Dam Lafoor
- Forest in Mazandaran
- Arfa Kuh Summit, Mazandaran, Iran
- Ab Ask, Mazandaran Province, Iran
- Ab Ask, Mazandaran Province, Iran
- Ab Ask, Mazandaran Province, Iran
- Lar National Park
- Firoozeh, Zaman Valley
- Firoozeh, Zaman Valley
- Zaman Valley
Ecoregions:
The total wood production from these forests is estimated at 269,022 cubic metres (9,500,400 cu ft). Golestan National Park and Shastkolateh forest watershed are located in Golestan Province and Mazandaran Province (the total area of the Hyrcanian forest is estimated at 965,000 ha (2,380,000 acres). From these forests, 487,195 ha (1,203,890 acres) are used commercially, 184,000 ha (450,000 acres) are protected and the rest are regarded as forest lands or over-used forests. The total of the forest woods used in this province is estimated at 770,551 cubic metres (27,211,800 cu ft). The Kojoor, Dohezar and Sehezar forest watersheds are located in Mazandaran Province. The Elburz Range forest steppe ecoregion is an arid, mountainous 1,000-kilometer arc south of the Caspian Sea, stretching across northern Iran from the Azerbaijan border to near the Turkmenistan border. It covers 63,300 square kilometres (24,400 sq mi) and encompasses the southern and eastern slopes of the Alborz Mountains as well as their summits. The Caspian Hyrcanian mixed forests ecoregion, with its lush green mountainsides and plains that receive moisture from the Caspian Sea, forms this ecoregion's northern border. The vast Central Persian desert basin ecoregion forms its southern border. The Alborz range is composed of a granite core overlain with sedimentary rock including limestones, shales, sandstones, and tuffs. Metamorphic rocks such as schists, marbles, and amphibolite are also widely found.[51] The climate is arid with annual precipitation varying from 150 mm to 500 mm, falling mostly as winter snow.
Environment
The now-extinct Caspian tiger and the Caspian horse are two of the animals of Mazandaran province.
The 1971 Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance especially as Waterfowl Habitat was held in Mazandaran in the city of Ramsar.

Unlike the rest of Iran, Mazandaran is watered by numerous rivers, or mountain torrents, all running from the mountains to the sea. The German traveller Samuel Gottlieb Gmelin, who visited this country in 1771, says that in the space of eight miles, on the road from Resht to Amot, 250 of such streams are to be seen, many of them being so exceedingly broad and deep, that the passage across is sometimes impracticable for weeks together.
Climate

Mazandaran Province naturally comes under the influence of the geographical latitude, the Alborz mountain range, elevation from sea level, distance from the sea, and the southern barren areas of Turkmenistan, local and regional air currents, and versatile vegetation cover. These conditions result in the climatic division of the province into three types:[52]
- Moderate Caspian climate with hot, humid summers and mild, humid winters. This climate is found in the western and central plains of the province between the Caspian sea and the foothills the Alborz mountains. Rainfall is significant in this climate zone and is highest in autumn. the annual accumulation decreases from west to east. Frost occasionally occurs during winters.
- moderate mountainous climate generally in the altitude between 1,500 to 3,000 metres (4,900 to 9,800 ft) meters and is characterized by a decrease in both precipitation and monthly temperatures. winters are long, cold and freezing and summers are mild and short.
- Cold mountainous climate with long freezing winters with long periods of frost and short cool summers. There is often snowfall during most of the seasons in the latter region, which continues till mid-summer. The climate is mainly found at an altitude above 3,000 m (9,800 ft), such as the top of Mount Damavand and Alam-Kuh, where the conditions are suitable for mountain glacier
Remove ads
Governance
Mazandaran has 9 electoral fields and a total of 12 seats in the Islamic Consultative Assembly.[53]
Transportation
Summarize
Perspective

Railway
Mazandaran is served by the North Railway Dept. of the Iranian Railways. The department connects the province to Tehran to the south and Gorgan to the east. The cities of Sari, Qaemshahr, and Pol-e Sefid are major stations of the department. The Trans-Iranian Railway was a major railway building project started in 1927 and completed in 1938, under the direction of the Iranian monarch, Reza Shah, and entirely with indigenous capital. It links the capital Tehran with the Persian Gulf and Caspian Sea.
The Mazandaran train station is the city's first modern rail station and it dates from the Pahlavi dynasty.
Roads
Mazandaran is connected to Tehran by Haraz road (Amol-Rudehen), Kandovan road (Chalus-Karaj), and Firoozkooh road (Savadkuh).
Airports
Dasht-e Naz Airport, serving the capital Sari, Noshahr Airport, and Ramsar International Airport are the domestic airports that connect the province to the other parts of the country.
Remove ads
Culture
Summarize
Perspective
In literature

In the Persian epic, Shahnameh, Mazandaran is mentioned in two different sections. The first mention is implicit, when Fereydun sets its capital in a city called Tamishe near Amol:
بیاراست گیتی بسان بهشت.................... به جای گیا سرو گلبن بکشت
از آمل گذر سوی تمیشه کرد .............. نشست اندر آن نامور بیشه کرد
And when Manuchehr is returning to Fereydun's capital, Tamisheh in Mazandaran (known as Tabarestan), after his victory over Salm and Tur.[54]
In the second section, a region called Mazandaran is mentioned in the Kai Kavoos era; it is an area which is mostly inhabited by Div (demons). The legendary Iranian Shah Kaykavoos, as well as the Iranian hero Rostam, each take turn to go to Mazandaran in order to battle the demons.
In a verse from Shahnameh, Zal tells Kai Kavoos: "I heard troubling news that the king is planning to go to Mazandaran".
However, this Mazandaran is not considered identical to the modern province of Mazandaran, and is instead a land to the west of Iran. The current province was simply considered a part of Tabaristan; the name Mazandaran is a later development, perhaps based upon local terminology.[55]
In Gaston Leroux's The Phantom of the Opera, one of the characters was formerly the daroga (chief of police) of Mazanderan.
Nowruz
The Tabarian New Year, or Neowrez, occurs in the pintek days of the Tabarian Calendar. In the Mazandarani language of Iran in the Mazanderani calendar, the year is divided into 12 thirty-day months and one pentad of days, often beginning on March 21. Neowrez Khani is one of the strongest and most popular traditions of the Mazanderani people.[citation needed]
Ceremonies and events
Tirgan is a mid-summer Iranian festival, celebrated annually on Tir 13 (July 3, 4, or 5). It is performed by splashing water, dancing, reciting poetry, and serving traditional foods such as spinach soup and shole-zard. The custom of tying rainbow-colored bands on wrists, which are worn for ten days and then thrown into a stream, is also a way to rejoice for children. Other famous events like, Varf chal, traditional ceremony with almost 800 years old as one of the unique rituals of Mazandaran associated with water was held in the village of Ab Ask and Lochu Wrestling game in different time.
Music and dance
Music in this region relates to the lifestyle of the inhabitants, and the melodies revolve around issues such as the forests, cultivation or farming activities and herding. The most famous dance of this area is the Shomali dance, not forgetting the stick dance that the men perform. Popular music in the province, known as the Taleb and Zohre, Amiri Khani and Katuli.
Cuisine

The cuisine of the province is very rich in seafood due to its location by the Caspian Sea, and rice is present in virtually every meal. Mazandarani cuisine is diverse between regions; the cuisine of coastal regions is different from mountainous regions, as people in the Alborz usually use the indigenous herbs and coastal people use the dishes of fish and Caspian Mazandaran rice with vegetables.
Remove ads
Tourism
Over 15 million Iranian and some 400,000 foreign tourists visit the province annually. More than 800 registered historical and cultural sites, 338 kilometers of shorelines, mineral springs in jungles and mountains, waterfalls, and caves are among the major tourism attractions in the Mazandaran province.[56][57] Mazandaran has been picked as the tourism capital of Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO) members states in 2022.[58] Mazandaran has 65 hotels, 51 motels, 91 apartment hotels, 293 eco-lodge complexes, 4,939 guest houses, 8 recreational complexes, 123 beach facilities, and 12 camping sites, with a total capacity of 1,246,177 people per night.[59]
Historical and natural tourist attractions
Caspian Sea Coast in Mazandaran
Gorji Mahaleh Jungle
Huto and Kamarband Caves Behshahr
Haydar Amuli (Seyyed Se Tan) Tomb Tower in Amol
Lajim Tower in Savadkuh
Restek tower in Dodangeh District Sari
Babol Museum
Moalagh Bridge in Amol
Namak Abrood Tourist resort
Cheshmeh Emarat in Behshahr
Kolbadi House in Sari
Nima Yushij House in Yush Nour
Spahbed Xurshid Cave in Savadkuh
Casino Boulevard in Ramsar
- Mount Damavand
- Abbas Abad Garden, Behshahr
- Mausoleum of Mir Bozorg
- Kandolus[60]
- largan[60]
- Tomb of Haydar Amuli
- Safi Abad Palace
- Ramsar Palace
- Malek Bahman Castle
- Lajim Tower, Savadkuh
- Miankaleh peninsula
- Veresk Bridge
- Castle Poolad Baladeh
- Davazdah Cheshmeh Bridge
- Moalagh Bridge, Amol
- Shapour Bridge, Juybar
- Bathroom Vaziri, Sari
- Tomb Darvish Fakhruddin Babol
- History Museum Amol
- Museum of Babol
- Larijan Hot Spring
- Shah Neshin Castle
- Lake Valasht
- Gerdkooh ancient hill
- Gohar Tapeh
- Lar Dam
- Alam-Kuh
- Lar National Park
- Badab-e Surt
- Tomb of Imamzadeh Abbas
- Kandolus Museum Nowshahr
- Fire Temple of Amol
- Farahabad Complex
- Safi Abad Palace
- Bagh Shah, Behshahr
- Imamzadeh Ebrahim Amol
- Imamzadeh Ebrahim Babolsar
- Imamzadeh Yahya Sari
- Imamzadeh Qasem Babol
- See Sangan Jungle
- Alendan lake
- Watch Tower Babol
- Abpari Waterfall
- Cave Zangian Qaemshahr
- Alimastan Village
- Cheshmeh Kileh Bridge, Tonekabon
- Shahrak-e Namak Abrud
- Huto and Kamarband Caves
- Cemetery Sefid Chah
- Cheshmeh Kileh Bridge Tonekabon
- Resket Tower
- Shapur Place, Babol
- Waterfall Tircan
- Nassereddin Shah relief
- Jameh Mosque of Amol
- Jameh Mosque of Sari
- Elburz Range forest steppe
- Bridge Felezi of Babolsar
- Imam Hassan Askari Mosque
- Chai Khoran Palace, Chalus
- Lake Miansheh
- Forest Park Nur
- Clock tower Sari
- Haraz River
- Gerdkooh ancient hill
- Mount Takht-e Suleyman
- Waterfall Sangeno
- Heshtel Towers
- Amoloo Mineral Water Spring
- Harijan Village Chalus
- Tamishan Palace Noor
- Div Sefid Cave
- Cemetery Ispe Chah
- Alasht Village
- Cemetery Ispe Chah
- Zangian Cave
- Cheshmeh Imarat Behshar
- Mohammad Hassan Khan Bridge, Babol
- Haft Abshar Waterfall, Babol
- Hill Qlaya Ghale Kety
- Bathroom Vaziri, Sari
- House Kalbadi, Sari
- House Manouchehri, Amol
- Palace of Shapur
- Temple Kowsan
- Cave rostam Kola
- Garden Chehelsotoon
- Mansion Municipal Tonekabon
- Kangelo Castle, Savadkuh
- Tower Shervin Bavand
- Church sourkh Abad
- Watchtower of Babol
- Tomb Shah baloo zahid Amuli
- Heshtel Tower
- Mosque Jameh of Babol
- Mosque Mohadesin
- Tomb of Ibn-e Shahr Ashoob
- Imamzadeh Sayyid Ali kia Sultan
- Tomb of Seyed Mohammad Zarrin Nava
- Herijan Waterfall
- Deryouk Waterfall
- Espe-o Waterfall
- Kiasar Waterfall
- Takieh Taker
- Tower Shervin Bavand
- Lake Sahon
- Mohaddesin Mosque of Babol
- Tomb Soltan Mohammad-e Taher
- Tomb of Ibn Shahrashub
- Forest Park Chaldareh
- Forest Park Shahid Zare
- Forest Park Mirza Kuchik Khan Haraz
- Forst Park Kashpel
- Javarem Forest park
- Tamishan Palace
- Div Sefid Cave
- Marko Summit
- Forst Park Dalkhani
- Do hezar Village
- Abe ask Village
- Shahrak-e Darya Kenar
- Lavij Village
- Sheikh Musa Village
- Forest Sange no, Neka
- Amoloo mineral water Springs
- Ramsar mineral water Springs
- Pahlavi Hotel Qaem Shahr
- Band-e Borideh River
- Bazaar of Amol
- Ramsar Palace
- Ramsar Parsian Hotel
- Clock Tower of Sari
- Waterfall Sangeno
- Cellar Kafer Keli
- Imamzadeh Hashem Amol
- Shahandasht Waterfall
- Shoormast Lake, Savadkuh
- Figure King Haraz
- Kelardasht
- Ramedani Historical House, Sari
- Estakhr-e-Posht Lake
- Paband National Park
- Mal Khast Village
- Kiasar National Park
- Heyrat Village
- Sarandoon and Balandoon
Remove ads
Notable people
Summarize
Perspective
People from and/or active in Mazandaran Province or its historical region include:
Authors
- Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari (838-923), was a Tabari world historian and theologian (the most famous and widely influential person called al-Tabari).
- Espahbod Sa'ad ad-Din Varavini[61] who wrote the book called Marzuban-nama, and also a Divan of poetry in the Ṭabarí dialect, known as the Níkí-nama.
- Ibn Isfandiyar, historian, author of a history of Tabaristan (Tarikh-i Tabaristan).
- Mírzá Asadu’llah Fádil Mázandarání (1880–1957), Iranian Bahá'í scholar.
- Musa ibn Khalil Mazandarani, 19th century Mazandarani scribe and scholar.
- Zahir al-Din Mar'ashi
- Manouchehr Sotoudeh
- Parviz Natel-Khanlari
- Ali Yachkaschi
Poetry
Music
Architecture
- Omar Tiberiades (Abû Hafs 'Umar ibn al-Farrukhân al-Tabarî Amoli) (d.c. 815), Persian astrologer and architect.
- Abolhassan Sadighi
Cinema
- Shahab Hosseini
- Davoud Rashidi
- Khosrow Sinai
- Kambiz Dirbaz
- Ladan Mostofi
- Mostafa Zamani
- Mohammad Ali Sadjadi
- Anahita Hemmati
- Roya Nonahali
- Irene Zazians
- Reza Allamehzadeh
- Abbas Amiri Moghaddam
- Saba Kamali
- Mohammad Hossein Mahdavian
- Ardalan Shoja Kaveh
- Parinaz Izadyar
- Maryam Kavyani
- Leyli Rashidi
- Zinat Pirzadeh
- Hossein Rajabian
Portraiture
Scholars
History
Science
- Ali ibn Sahl Rabban al-Tabari His stature was eclipsed by his more famous pupil, Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi.
- Abul Hasan al-Tabari, a 10th-century Iranian physician.
- Abu'l Tayyeb Tabari[62] was jurisconsult, judge (qāżī), and professor of legal sciences; he was regarded by his contemporaries as one of the leading Shafeʿites of 5th/11th century Baghdad.
- Ali Yachkaschi
- Moslem Bahadori[63]
- Iraj Malekpour[64]
- Alireza Mashaghi[65]
- Pooran Farrokhzad
- Shahrokh Meskoob
- Al-Tabarani
Philosophy
- Fakhr al-Din al-Razi, theologian and philosopher
- Farhad Rachidi
Physicians and astrologers
Athletics
- Abdollah Movahed
- Imam-Ali Habibi
- Behdad Salimi
- Ghasem Rezaei
- Hassan Rangraz
- Reza Yazdani
- Hassan Yazdani
- Reza Soukhteh-Saraei
- Askari Mohammadian
- Mehdi Taghavi
- Komeil Ghasemi
- Morad Mohammadi
- Ahmad Mohammadi
- Mehdi Hajizadeh
- Masoud Esmaeilpour
- Ezzatollah Akbari
- Ali Asghar Bazri
- Bashir Babajanzadeh
- Kamran Ghasempour
- Mohammad Reza Khalatbari
- Farhad Majidi
- Rahman Rezaei
- Mehrdad Oladi
- Mohsen Bengar
- Peiman Hosseini
- Rahman Ahmadi
- Hossein Tavakkoli
- Hanif Omranzadeh
- Hadi Norouzi
- Adel Gholami
- Alireza Firouzja
- Mojtaba Mirzajanpour
- Sheys Rezaei
- Morteza Pouraliganji
- Mojtaba Abedini
- Sohrab Entezari
- Farshid Talebi
- Mousa Nabipour
- Shahab Gordan
- Noshad Alamiyan
- Sousan Hajipour
- Mahmoud Fekri
- Peyman Hosseini
- Ramin Rezaeian
- Bahador Molaei
- Maysam Baou
- Omid Ebrahimi
- Morteza Mehrzad
- Shoja Khalilzadeh
- Omid Alishah
- Hamed Kavianpour
- Abbas Hajkenari
- Kianoush Rahmati
- Ebrahim Taghipour
- Mohsen Yousefi
- Javad Asghari Moghaddam
- Manouchehr Boroumand
- Jasem Delavari
- Behnam Ehsanpour
- Mehrdad Pooladi
- Majid Torkan
- Mohsen Karimi
- Hamed Kavianpour
- Farzan Ashourzadeh
- Ahmad Mohammadi
- Ali Alipour
- Javad Manafi
- Nima Alamian
- Mohammad Reza Barari
- Ramezan Kheder
- Abbas Dabbaghi
- Reza Simkhah
- Hassan Rahnavardi
- Babak Nourzad
- Ali Asghar Bazri
- Sousan Hajipour
- Anoushiravan Nourian
- Farshid Talebi
- Allahyar Sayyadmanesh
- Ahmad Mohammadi
- Mohsen Karimi
Royalty
Military
Politics
- Ali Larijani
- Mohammad Vali Khan Tonekaboni
- Manuchehr Mottaki
- Ehsan Tabari
- Majid Rahnema
- Hossein Ghods-Nakhai
- Noureddin Kianouri
- Ali-Akbar Davar
- Esfandiar Rahim Mashaei
- Reza Salehi Amiri
- Hamid Reza Chitgar
- Sadeq Larijani
- Mohammad-Javad Larijani
- Bagher Larijani
- Ali Akbar Nategh-Nouri
- Mirza Aqa Khan Nuri
- Morteza Gholi Khan Hedayat
- Ahmad Tavakoli
- Davoud Hermidas-Bavand
- Sam Dastyari
- Reza-Qoli Khan Hedayat
- Hossein Rajabian
- Ali Kordan
- Ahmad Moshir al-Saltaneh
- Elaheh Koulaei
- Abdul Karim Hashemi Nejad
- Reza Sheykholeslam
- Shamseddin Hosseini
- Hassan Ghashghavi
- Mirza Shafi Mazandarani
- Gholam Hossein Sadighi
- Mirza Hassan Khan Esfandiary
- Davoud Hermidas-Bavand
- Haji Washington
- Hossein Dadgar
- Mirza Hassan Khan Esfandiary
- Morteza Gholi Khan Hedayat
- Mehdi Qoli Hedayat
- Abdol-samad Mirza Ezz ed-Dowleh Saloor
- Mehdi Qoli Hedayat
- Hossein Shah-Hosseini
- Fazel Larijani
- Musa Nuri Esfandiari
- Javad Saeed
Christianity
Islamic scholars
- Hassan Hassanzadeh Amoli
- Abdollah Javadi-Amoli
- Mirza Hashem Amoli
- Abd al-Qahir al-Jurjani
- Muhammad Taqi Amoli
- Haydar Amuli
- Ibn Furak
- Ali Asghar Mazandarani
- Mirza Husain Noori Tabarsi
- Mohammad Taghi Falsafi
- Ibn Shahr Ashub
- Shaykh Tabarsi
- Abul-Abbas Qassab Amoli
- Yasubedin Rastegar Jooybari
- Mulla Ali Kani
- Yasubedin Rastegar Jooybari
- Mohammad Salih al-Mazandarani
- Ibn al-Sheikh
Other religions
- Baháʼu'lláh- The founder of the Baháʼí Faith was born and grew up in Nur, Mazandaran
- Mírzá ʻAbbás Núrí – father of Baháʼu'lláh
- ʻAbdu'l-Bahá – son of Baháʼu'lláh
- Daniel al-Kumisi
- Quddús
- Subh-i-Azal
Master [clarification needed]
Medical
Remove ads
Mazandaran today
Summarize
Perspective
Mazandaran is a fast-growing centre for tourism, innovation, biotechnology, and civil engineering.
Economy

The province is one of the 5 wealthiest in Iran. Oil wealth has stimulated industries in food processing, cement, textiles, cotton, and fishing (caviar). Iran's Cultural Heritage Organization lists close to 630 sites of historical and cultural significance, many of which are tourist attractions. Rice, grain, fruits, cotton, tea, tobacco, sugarcane, Flower, Mineral water, caviar, Dairy product, Meat industry and silk are produced in the lowland strip along the Caspian shore. Oil wealth has stimulated industries in food processing, cement, textiles, cotton, and fishing (caviar). Mazandaran, with 230,000 hectares of paddies, produces about one million tonnes of rice a year, or 42 percent of the country's total.[66]
Over 70 kinds of agricultural produce are grown in Mazandaran which meets 40% of domestic demand for rice and 50% of citrus fruits. The province is also the sole domestic supplier of kiwi.[67] Mazandaran has 3,500 industrial and production units. Mazandaran is home to 460,000 hectares of farmland producing around 6 million tons of agro products annually. Over 10% of value-added in Iran's agriculture sector is generated in Mazandaran province.[68]
The textile industry included 212 large and small industrial units operating in the province in 1995. These include the Mazandaran's nassaji company, based in Qaemshahr, the Chitsazi factory of Behshahr, the Gooni bafi of Mahmudabad, and the Chukha factory of Sari.[69] Some of these industrial units are no longer active because of issues happened after being transferred to the private sector in 1990s and 2000s.[70][71][72]
Export
Germany, Russia, Iraq, France Turkey, Kazakhstan, India, Malaysia, United Arab Emirates, Afghanistan, Belarus, Italy, Bahrain, Pakistan, Switzerland Ukraine, United States, Spain, Netherlands and Central Asian countries were Mazandaran's main export destinations during the period. The province in 2017 exported close to $800 million worth of goods. In the previous year totally about 800 million dollars of non-oil goods produced in Mazandaran were exported, half of which were exported from customs outside the province.[73] In 2017 year main exports from the province consisted of dairy products (57%), food products (12%), industrial commodities (10%), pipes and profiles (8%) and cement (7%).[74]
Gas and oil
From 1951 to 1978, and particularly after the formation of National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC), the first exploration well was spudded. Up to 1970, 16 wells had been drilled near mud volcanoes. All these wells produced only natural gas and technical studies showed that continuation of these operations would be uneconomical. 10 thousand tons export oil and Uncertain amount of gas exported to Asian countries from Mazandaran.
Statistics
- 9th rank industrial units Iran
- 5th rank general industry Iran
- 4th rank tooling machines Iran
- 2nd rank coal Iran
- 1st rank livestock and agricultural products Iran
- 1st rank granite Iran
- 1st rank fluorine Iran
- 1st rank flowers and ornamental plants Iran
- 1st rank citrus exports Iran
- 1st rank food products exports Iran
Colleges and universities

Main universities of Mazandaran:
- University of Mazandaran, Babolsar
- Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari
- Babol Noshirvani University of Technology, Babol
- Babol University of Medical Sciences, Babol
- Sari Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources University, Sari
- Shomal University, Amol
- Allameh Mohaddes Nouri University, Nur
- Imam Khomeini Naval University, Nowshahr
- University of Science and Technology of Mazandaran, Behshahr
- Iran University of Science and Technology, Nur
Sports
With 7 gold, 4 silver and 4 bronze medals, Mazandaran has won 19% of Iran's medals in the Olympics, which is the largest share among Iran's medals in the Olympics. For the past several years Mazandaran has generated a consistent stream of Wrestling.[75] Football and volleyball are two other popular sports that have a lot of players in the Premier League and the national team. Weightlifting, Taekwondo, table tennis, boxing, kickboxing, kung fu, karate, rally car are other successful sports in the province. Kalleh Mazandaran VC, Shamoushak Noshahr F.C. and F.C. Nassaji Mazandaran are three famous teams in the province. Kalleh have twice won the Iranian Volleyball Super League Championship and once the AVC Championship.
Athletes in Olympics
List of Mazandaran athletes who won medals in the Olympics:
Remove ads
Gallery
- Mazandaran Coast
- Safarud Jungle and River
- Haft Abshar waterfall at Babol
- Riding a watercraft in Ramsar
- Babolsar Pleasure
- Fire Temple of Amol
- Snow in Tonekabon
- Marals at Semes Kandeh Animal Shelter
- Daryasar Plain at Tonekabon
- Didi Museum at Izadshahr
- Glacial lake in Alam Kuh Kelardasht
- Neka Railway
- Museum of Reza Shah Pahlavi at Alasht
- Davazdah Cheshmeh Bridge
- Elimalat Lake
- Coast Beach
- Badab Sort springs
- Filband Village
- Fazeli House
- Reza Shah House
- Sefid Chah Cemetery at Behshahr
- Kelardasht
- Jomeh Bazaar Bridge
Remove ads
See also
- Mazandarani people
- List of Mazanderanis
- Amardi
- Sasanian dynasty
- Tabaristan
- Dabuyid dynasty
- Pahlavi dynasty
- Alborz (Elburz) mountain range topics
![]() Media related to Mazandaran Province at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Mazandaran Province at Wikimedia Commons
Notes
- Also romanized as Ostân-e Mâzandarân; Mazanderani: مازِرون اوستان, romanized as Mâzerun Ustâne
- Based on Maz or Mazan Term: Mazanderani: مازرون Mâzerun, Persian: مازندران, Russian: Мазендеран.
Based on Tapur Term: English: Tapuria, Arabic: طبرستان Ṭabaristan, from Middle Persian Tapuristân
Mazandarani: Tapurana. (not prevalent). Ancient Greek: Hyrcania came from local name Vergana (Persian Gorgan), Caspia from local name Kaspi, See Caspian Sea - Separated from Tonekabon County after the 2006 census[44]
- Separated from Babolsar County after the 2006 census[45]
- Separated from Chalus County after the 2016 census[46]
- Separated from Sari County after the 2006 census[47]
- Separated from Savadkuh County after the 2011 census[48]
- Separated from Qaem Shahr County after the 2011 census[49]
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads



























































































































