Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Merrill Field
Airport in Anchorage, Alaska From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Merrill Field (IATA: MRI, ICAO: PAMR, FAA LID: MRI)[2] is a public-use general aviation airport located one mile (1.6 km) east of downtown Anchorage in the U.S. state of Alaska. The airport is owned by Municipality of Anchorage.[1] It opened in 1930 as Anchorage Aviation Field and was renamed in honor of Alaska aviation pioneer Russel Merrill.
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective

Merrill Field, located on the east end of 5th Avenue in Anchorage, was the first official airport in the city when it opened in 1930. It was Anchorage's only airport until 1951, when Ted Stevens Anchorage International Airport opened, along with the introduction of ever larger and faster commercial aircraft required that an airfield with longer and heavier runways be built.
Construction of the original 35-acre (14 ha) site one mile east of the city was completed on 22 Aug. 1929. Originally named Anchorage Aviation Field, it was later renamed Anchorage Municipal Airport. The airport is now named for Russel Merrill, an Alaskan aviation pioneer. An aerodrome beacon was located at Merrill Field and dedicated on 25 September 1932 in Merrill's honor.[3]
The airfield remains in use today as the primary field for private wheel-equipped aircraft in the warmer months, and for ski-equipped aircraft in the winter. A section of the property used to be a municipal landfill.
Remove ads
Facilities and aircraft
Summarize
Perspective
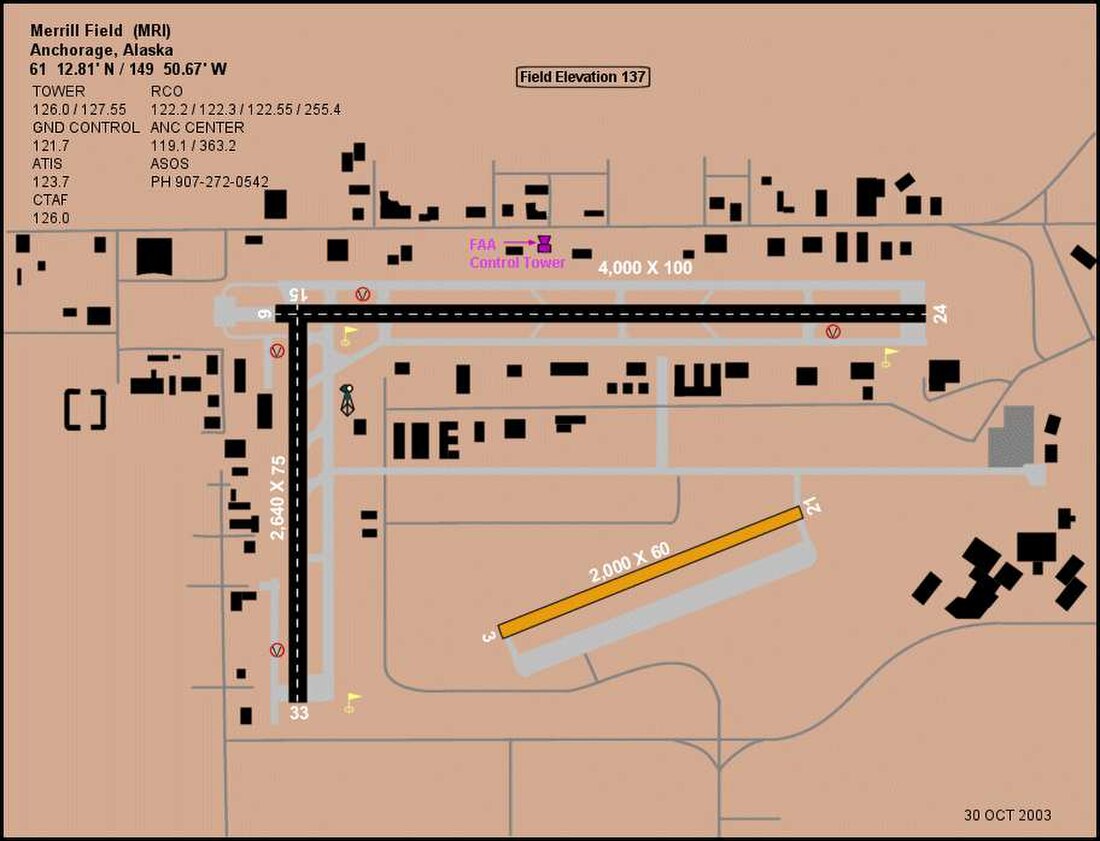
Merrill Field is a towered airport, with the tower's normal hours of operation from 7 AM-10 PM. Aircraft are still permitted to operate at the airport outside of these hours by using the airport's common traffic advisory frequency (CTAF). During its hours of operation, Merrill Tower routinely provides an ATIS broadcast every hour. This is broadcast on the frequency 124.25 MHz. The weather information on this broadcast is obtained from the airfield's ASOS, which is accessible on 124.25 MHz outside of tower hours, or on the phone number (907) 271-5277. [4]
Merrill Field covers 436 acres (176 ha, 1.76 km2) and has three runways:[1]
- Runway 5/23: 2,000 x 60 ft (610 x 18 m), surface: gravel/dirt
- Runway 8/26: 4,000 x 100 ft (1,219 x 30 m), surface: asphalt
- Runway 16/34: 2,640 x 75 ft (805 x 23 m), surface: asphalt
For the 12-month period ending September 30, 2013, the airport had 126,234 aircraft operations, all of which were general aviation. There are 844 aircraft based at this airport: 786 single engine, 41 multi-engine, 16 helicopters and one glider.[1]
There are no based jets,[1] although one retired Boeing 727 donated by FedEx is used as a training aid by the University of Alaska Anchorage's Aviation Technology Division,[5][6] which is based at the airfield. It is not airworthy.
When it landed in February 2013, the Boeing 727 was the largest aircraft ever to have landed at Merrill Field.[7] The landing required special permission from the city,[5][7] and preparatory surveys of the runway and airfield infrastructure to ensure the aircraft could be landed safely;[6] the captain practiced the landing in a flight simulator beforehand.[8]
The airfield hosts five flight schools, air taxi services, and fixed-base operators. Both 100LL and Jet A fuel is available 24/7.[9] An extension of the Q Taxiway connects the airport to Alaska Regional Hospital for MEDEVAC operations. These airfield facilities include, but are not limited to:[9]
- Alyeska Helicopters (flight school)
- Angel Aviation Alaska (flight school)
- Land and Sea Aviation (flight school)
- Birch Creek Aviation (flight school)
- UAA Aviation Technology Center (flight school)
- Crowley Fuels (FBO)
- Spernak Airways (FBO)
Merrill field also has a VOR test facility (VOT), accessible on the VHF frequency 111.0 MHz. The VOT is operational 24 hours a day. [4] A section of the airport is built over the closed Merrill Field Land Fill. This section requires slightly more maintenance due to settling and emissions.
From June 1 - August 31, 2025, Merrill field underwent airfield construction for the first time in 20 years. This project included replacing the airport beacon, installing new airfield lighting, and replacing runway 7/25 with runway 8/26. [10] As of November 2025, the construction is complete, however the runway 8/26 REILs and PAPIs are not yet operational. [11]
Remove ads
Airport Procedures
Summarize
Perspective
Merrill field is a Class D airport, with its airspace extending up to 2,500 feet above mean sea level. Outside of the tower's hours of operation, the airfield reverts to Class E airspace, and the tower frequency is used as a CTAF. [12] Merrill field has two traffic patterns, one for runways 8/26 and one for runways 16/34. The patterns are left traffic for runways 26 & 34, and right traffic for runways 8 & 16. The traffic pattern altitude is 900 feet MSL for aircraft traveling below 105 knots, and 1200 feet MSL for aircraft traveling above 105 knots. [12]
Merrill field has several departure and arrival procedures, along with common traffic pattern entries, listed in the notices section of the Alaska chart supplement. [12] This section of the chart supplement also contains information regarding Merrill Field's part 93 special airspace. This special airspace is designed to help facilitate safe flow of air traffic in the heavily congested Anchorage Bowl. [13] There are special airspace segments outlined for Ted Stevens Anchorage International Airport, Elmendorf Air Force Base, Lake Hood Seaplane Base, Bryant Army Airfield, and Merrill Field, governing speed and altitude restrictions of aircraft in these segments in order to ensure sufficient separation of aircraft arriving and departing from these airports. [12] Deviations from these restrictions are available upon request via Anchorage TRACON, however they may not always be granted. [13]
Merrill Field has 4 GPS instrument approach procedures, as well as 1 standard instrument departure and an obstacle departure procedure. [14] These can be found in the Alaska Terminal Procedures Publication.
Airline and destinations
Passenger
Statistics
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads