Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
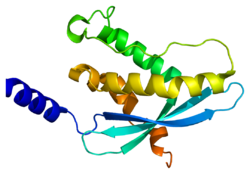
Neutrophil cytosolic factor 4
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Neutrophil cytosol factor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCF4 gene.[5][6]
Remove ads
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a cytosolic regulatory component of the superoxide-producing phagocyte NADPH-oxidase, a multicomponent enzyme system important for host defense. This protein is preferentially expressed in cells of myeloid lineage. It interacts primarily with neutrophil cytosolic factor 2 (NCF2/p67-phox) to form a complex with neutrophil cytosolic factor 1 (NCF1/p47-phox), which further interacts with the small G protein RAC1 and translocates to the membrane upon cell stimulation. This complex then activates flavocytochrome b, the membrane-integrated catalytic core of the enzyme system. The PX domain of this protein can bind phospholipid products of the PI(3) kinase, which suggests its role in PI(3) kinase-mediated signaling events. The phosphorylation of this protein was found to negatively regulate the enzyme activity. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been observed.
Remove ads
Clinical significance
GWAS studies showed that Crohn's disease patient with certain SNPs in NCF4 are more susceptible to get Crohn's disease.[7] Crohn's patient with rs4821544 variants showed a decreased reactive oxygen species after stimulation with GM-CSF which is a proinflammtory cytokine.[8]
Interactions
Neutrophil cytosolic factor 4 has been shown to interact with Ku70,[9] Neutrophil cytosolic factor 1[10][11][12] and Moesin.[13]
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads