Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Protactinium(V) fluoride
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Protactinium(V) fluoride is a fluoride of protactinium with the chemical formula PaF5.
Remove ads
Preparation
Protactinium(V) fluoride can be obtained by reacting protactinium(V) oxide with bromine trifluoride or bromine pentafluoride at 600 °C:[1]
- 6 Pa2O5 + 20 BrF3 → 12 PaF5 + 10 Br2 + 15 O2
- 6 Pa2O5 + 12 BrF5 → 12 PaF5 + 6 Br2 + 15 O2
It can also be obtained by reacting protactinium(V) chloride or protactinium(IV) fluoride with fluorine gas at 700 °C:[1]
- 2 PaF4 + F2 → 2 PaF5
The hydrate form of protactinium(V) fluoride can be formed by the reaction of protactinium(V) oxide and hydrofluoric acid in an aqueous solution:[1]
- Pa2O5 + 10 HF → 2 PaF5·2H2O + 6 H2O
It can also be decomposed from fluorine-containing protactinium complexes.[2]
Remove ads
Properties
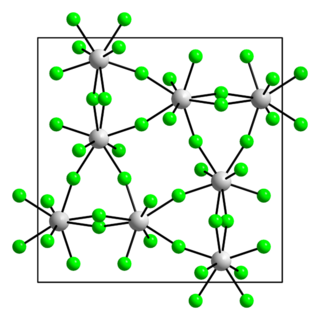
Protactinium(V) fluoride is a white, volatile, extremely hygroscopic solid that is partially soluble in water and soluble in hydrofluoric acid. It has a tetragonal crystal structure of the β-uranium pentafluoride type with the space group I42d (space group no. 122) with the lattice parameters a = 1153 pm, c = 510 pm. Quartz and Pyrex are attacked by the compound at higher temperatures. As a dihydrate, it is a colourless, hygroscopic, crystalline solid that is waxy in nature. It is soluble in water and hydrofluoric acid.[1] It reacts with phosphorus trifluoride to form protactinium(IV) fluoride.[3] The dihydrate cannot be converted into the anhydrous form in air, hydrogen fluoride or fluorine at low temperatures. Instead, diprotactinium(V) oxide octafluoride (Pa2OF8) is formed. At higher temperatures around 325 °C, a mixture of the diprotactinium(V) oxide octafluoride and protactinium(V) fluoride is formed.[2]
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads