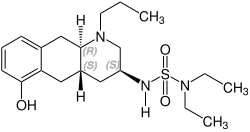Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Quinagolide
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Quinagolide (INN, BAN), sold under the brand name Norprolac, is a selective dopamine D2 receptor agonist which is used to manage hyperprolactinemia.[1] It has also been found to be effective in the treatment of breast pain.[2] It is used in the UK, but it is not available in US.
Remove ads
Chemistry
Quinagolide is a racemate composed of the following two enantiomers:[3]
Synthesis
Summarize
Perspective
Laboratory synthesis
The first synthesis of quinagolide was disclosed in patents filed by Sandoz.[4]
A sequence of nine steps is required to transform the starting material 5-methoxy-2-tetralone (1) into the octahydrobenzo[g]quinoline ring system with the correct stereochemistry required. This intermediate (11) is then converted in another five steps to the drug. Transformation of the ester (13) into the amine (15) is accomplished by a Curtius rearrangement in which an acyl hydrazide is treated with nitrosyl chloride.[4][5][6]
Manufacture
The laboratory route was not practical for the synthesis of quinagoline on a large scale. Therefore scientists at Novartis developed an improved process.[7]
The starting material is 1,6-dimethoxynaphthalene (1). This is selectively lithiated at the C-7 position and reacts with (2Z)-ethyl 2-cyano-3-ethoxyacrylate (2), to give the cyanoacrylate (3). Catalytic hydrogenation and hydrolysis produces (5). Birch reduction of (5) leads first to (6) which on acid work-up gives the imine (7), which is reduced with sodium borohydride to yield (8). Fischer esterification with methanol gives an ester that is next alkylated with 1-iodopropane to give (11). The required stereochemistry for quinagoline is set in the final steps.[7][8][9]
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads