Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
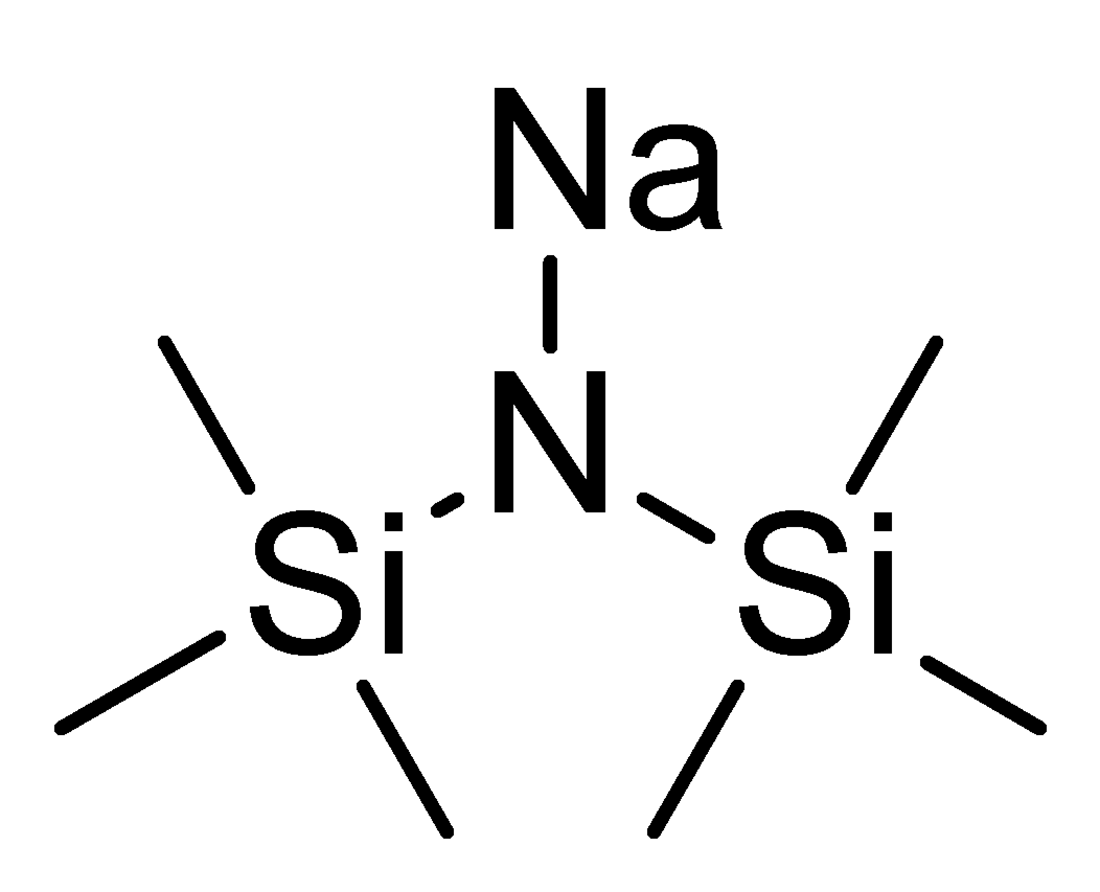
Sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide is the organosilicon compound with the formula NaN(Si(CH3)3)2. This species, usually called NaHMDS (sodium hexamethyldisilazide), is a strong base used for deprotonation reactions or base-catalyzed reactions. Its advantages are that it is commercially available as a solid and it is soluble not only in ethers, such as THF or diethyl ether, but also in aromatic solvents, like benzene and toluene by virtue of the lipophilic TMS groups.[1]
NaHMDS is quickly destroyed by water to form sodium hydroxide and bis(trimethylsilyl)amine.
Remove ads
Structure
Although the Na–N bond is polar covalent as a solid, when dissolved in nonpolar solvents this compound is trimeric, consisting of a central Na3N3 ring.[2]
Applications in synthesis
NaHMDS is used as a strong base in organic synthesis. Typical reactions:
- To deprotonate ketones and esters to generate enolate derivatives.[3]
- Generate carbenes by dehydrohalogenation of halocarbons. These carbene reagents add to alkenes to give substituted cyclopropanes and cyclopropenes.[4]
- To deprotonation of phosphonium salts, generating Wittig reagents.
NaHMDS deprotonates compounds containing weakly acidic O–H, S–H, and N–H bonds. These include cyanohydrins and thiols.[5]
NaHMDS converts alkyl halides to amines in a two step process that begins with N-alkylation followed by hydrolysis of the N–Si bonds:
- NaN(Si(CH3)3)2 + RX → RN(Si(CH3)3)2 + NaX
- RN(Si(CH3)3)2 + H2O → O(Si(CH3)3)2 + RNH2
where X is a halogen and R is an alkyl.
This method has been extended to aminomethylation via the reagent CH3OCH2N(Si(CH3)3)2, which contains a displaceable methoxy group CH3O–.
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads