Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Thiazolidine
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Thiazolidine is a heterocyclic organic compound with the formula (CH2)3(NH)S. It is a 5-membered saturated ring with a thioether group and an amine group in the 1 and 3 positions. It is a sulfur analog of oxazolidine. Thiazolidine is a colorless liquid. Although the parent thiazolidine is only of academic interest, some derivatives, i.e., the thiazolidines, are important, such as the antibiotic penicillin.
Remove ads
Preparation
Thiazolidine is prepared by the condensation of cysteamine and formaldehyde.[3] Other thiazolidines may be synthesized by similar condensations. A notable derivative is 4-carboxythiazolidine (thioproline), derived from formaldehyde and cysteine. The 2-oxo-thiazolidine procysteine is produced from phosgenation of cysteine.
Derivatives
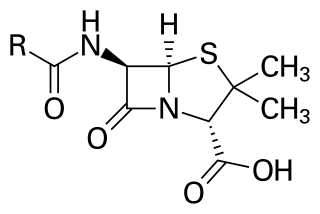
Useful thiazolidines include the drug pioglitazone, the antibiotic penicillin, and N-Methyl-2-thiazolidinethione, an accelerator for the vulcanization of chloroprene rubbers.[4]
Thiazolidines functionalized with carbonyls at the 2 and 4 positions, the thiazolidinediones, are drugs used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus type 2. Rhodanine is a related bioactive species, featuring one carbonyl and one thiocarbonyl.
Many thiazolidines are prepared from cysteine and related aminothiols.[5] p-aminocinnamaldehyde is able to differentiate between cysteine and homocysteine. With cysteine, a buffered water solution of the aldehyde changes from yellow to colorless due to a secondary ring closing reaction of the imine. Homocysteine is unable to give ring closure and the color does not change.
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads

