Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Timeline of the Qing dynasty
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
See also: Timeline of the Ming dynasty, Timeline of the Jurchens, and Timeline of Republic of China history
This is a timeline of the Qing dynasty (1644–1912).
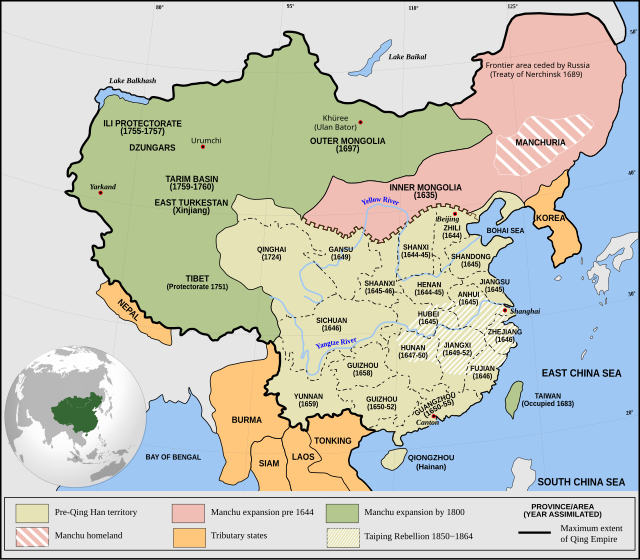
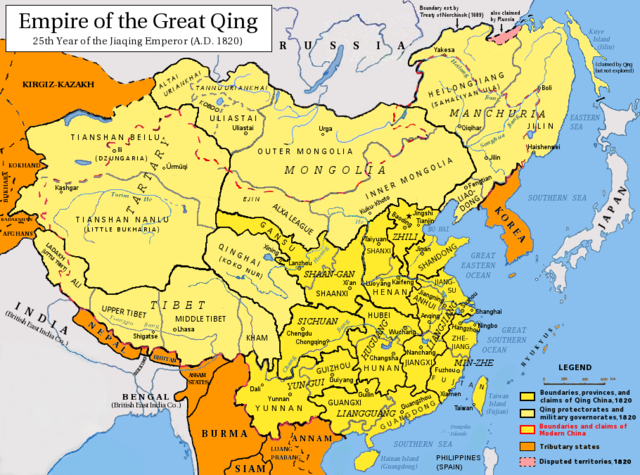
Background
16th century
1580s
1590s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1592 | Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98): Nurhaci offers to fight the Japanese but is refused; Ming reacts with alarm to the size and quality of Nurhaci's troops[3] | |
| 1593 | Nurhaci defeats the Hulun Confederation and Khorchin Mongols[4] |
Close
17th century
1600s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1600 | Nurhaci creates the Banner Army[5] | |
| 1601 | Nurhaci subjugates the Hada[6] | |
| 1603 | Nurhaci and Ming generals agree to delineate the boundary between their territories[7] | |
| Nurhaci moves his capital to Hetu Ala due to water problems at Fe Ala[8] | ||
| 1605 | Gwanghaegun of Joseon sends an expedition north of the Tumen River to destroy the Jurchen Holjaon community[6] | |
| 1607 | Nurhaci subjugates the Hoifa[6] |
Close
1610s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1611 | Nurhaci subjugates the Wild Jurchens[9] | |
| 1613 | Nurhaci incorporates the Ula into his confederation[10] | |
| 1615 | Nurhaci increases the number of banners from four to eight[10] | |
| Nurhaci sends his last tributary emissary to Beijing[11] | ||
| 1616 | Nurhaci declares the Later Jin, also known as the Amaga Aisin Gurun[12] | |
| 1618 | 9 May | Battle of Fushun: Later Jin seizes Fushun[13] |
| summer | Battle of Qinghe: Later Jin takes Qinghe[14] | |
| 1619 | 18 April | Battle of Sarhū: Ming forces are annihilated by Later Jin[15] |
| 26 July | Battle of Kaiyuan: Later Jin takes Kaiyuan[16] | |
| 3 September | Battle of Tieling: Later Jin takes Tieling[16] | |
| September | Battle of Xicheng: Later Jin annexes the Yihe Jurchens[17] | |
| Chahar-Jurchen War: Ligdan Khan attacks Guangning, a horse trading town under the protection of Nurhaci, but is defeated[18] |
Close
1620s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1621 | 4 May | Battle of Shen-Liao: Later Jin seizes Shenyang[19] |
| December | Battle of Fort Zhenjiang: Ming raids into Later Jin are repulsed[20] | |
| 1622 | 11 March | Battle of Guangning: Later Jin seizes Guangning[20] |
| 1625 | Chahar-Jurchen War: Ligdan Khan's attack is turned back by a combined Khorchin Jurchen force[21] | |
| 1626 | 10 February | Battle of Ningyuan: A Later Jin attack on Ningyuan is repulsed and Nurhaci is wounded[22] |
| 30 September | Nurhaci succumbs to his wounds and dies[23] | |
| 1627 | January - March | Later Jin invasion of Joseon: Hong Taiji is elected khan and subjugates Joseon[24] |
| spring | Battle of Ning-Jin: Later Jin forces under Hong Taiji attack Jinzhou but are repelled[25] | |
| 1629 | winter | Jisi Incident: Later Jin forces break through the Great Wall and loot the region around Beijing[26] |
Close
1630s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1630 | summer | Jisi Incident: Later Jin forces retreat[26] |
| 1631 | 21 November | Battle of Dalinghe: Later Jin seizes Dalinghe[27] |
| 1633 | April | Wuqiao Mutiny: Shandong rebels defect to Later Jin[28] |
| summer | Siege of Lüshun: Later Jin seizes Lüshun[29] | |
| 1634 | Chahar-Jurchen War: Ligdan Khan of the Chahar Mongols is overthrown and displaced by Hong Taiji[30] | |
| 1635 | Hong Taiji unites all Jurchen tribes under the name of Manchu; so ends the Jurchens[24] | |
| Hong Taiji attacks the Hurha[31] |
Close
Remove ads
17th century
1630s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1636 | April | Hong Taiji proclaims the Qing dynasty[32] |
| 9 December | Qing invasion of Joseon: Hong Taiji invades Joseon[33] | |
| 1637 | 30 January | Qing invasion of Joseon: Joseon is defeated and becomes a Qing tributary[33] |
| 1638 | Qing dynasty conquers Shandong[34] | |
| 1639 | Qing dynasty attacks the Daur and Solon people[31] |
Close
1640s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1640 | May | Qing dynasty captures the Evenk fortresses of Duochen, Asajin, Yakesa, and Duojin[31] |
| 1642 | 8 April | Battle of Song-Jin: Qing dynasty takes Jinzhou[35] |
| 1643 | Northeastern natives submit to the Qing dynasty[36] | |
| 1644 | 27 May | Battle of Shanhai Pass: Wu Sangui lets the Qing forces through the Great Wall and their forces defeat Li Zicheng in battle, after which Li retreats to Beijing[37] |
| 5 June | Qing dynasty takes Beijing and Li Zicheng flees[37] | |
| 8 November | Shunzhi Emperor is enthroned in the Forbidden City[38] | |
| 1645 | January | Qing forces capture Luoyang[39] |
| 20 May | Qing forces capture Yangzhou[39] | |
| 16 June | Qing forces capture Nanjing and the Hongguang Emperor[40] | |
| 6 July | Qing forces capture Hangzhou[40] | |
| 21 July | All nonclerical adult male citizens are ordered to adopt the Manchu queue to show their allegiance to the Qing dynasty[41] | |
| 1646 | February | Ming forces are defeated in Jiangnan[42] |
| 10 July | Qing forces defeat the Ming army at Tonglu[43] | |
| 30 September | Qing forces capture Yanping[44] | |
| 6 October | The Longwu Emperor is killed by Qing forces[44] | |
| 17 October | Qing forces take Fuzhou[44] | |
| 1647 | 2 January | Zhang Xianzhong is killed by Qing forces but his army occupies Chongqing and then occupies Sichuan under the leadership of Sun Kewang[45] |
| 20 January | Qing forces capture Guangzhou and the Shaowu Emperor[46] | |
| 5 March | Qing forces conquer Guangdong, half of Guangxi, and Hainan[46] | |
| March | Qing forces take Changsha[47] | |
| spring | Qing forces raid Anping[48] | |
| 23 September | Qing forces take Wugang[49] | |
| 1648 | 20 February | Ming loyalists rebel at Nanchang and Nanning[50] |
| 14 April | Qing forces fail to take Guilin[49] | |
| 1649 | 15 January | Ming loyalists rebel at Datong[51] |
| 1 March | Qing forces take Nanchang[52] | |
| 4 October | Ming loyalists at Datong are defeated[51] | |
| summer | Qing forces conquer southern Huguang[53] | |
| 24 November | Qing forces slaughter the population of Guangzhou[54] | |
| 27 November | Qing forces capture Guilin[54] | |
| 2 December | Qing forces capture Zhaoqing and the Yongli Emperor flees[54] |
Close
1650s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1651 | 15 October | Qing forces capture Zhoushan and Zhu Yihai flees[55] |
| 1652 | 24 March | Qing attack on Achansk is defeated[56] |
| 7 August | Rebel general Li Dingguo takes Guilin[57] | |
| winter | Sun Kewang's army is routed by Qing forces[57] | |
| 1654 | July | Battle of Hutong: Korean-Manchu army defeats a force of Russians[56] |
| Qing forces attack the Daur people[58] | ||
| 1655 | March–April | Qing forces fail to take Komar[56] |
| Li Dingguo's army is routed by Qing forces[57] | ||
| 1656 | 9 May | Qing forces try to invade Kinmen Island (Quemoy) but their fleet is destroyed in a storm[59] |
| Qing forces attack the Daur people[58] | ||
| 1657 | February | Ming forces defeat a Qing army near the Changjiang River Delta[59] |
| December | Sun Kewang surrenders to the Qing dynasty[60] | |
| 1658 | 10 June | Battle of Hutong (1658): Qing-Joseon forces defeat a Russian fleet on the Songhua River[56] |
| June | Zheng Chenggong occupies Wenzhou[61] | |
| 1659 | 7 January | Qing forces advance into Yunnan and the Yongli Emperor flees to Toungoo dynasty[62] |
| 10 March | Qing forces capture Yongchang and defeat Li Dingguo's army, securing Yunnan[62] | |
| 10 August | Zheng Chenggong takes Zhenjiang[63] | |
| 24 August | Zheng Chenggong lays siege to Nanjing[63] | |
| 9 September | Zheng Chenggong's army is annihilated and he retreats to Xiamen[64] |
Close
1660s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1660 | February | Qing forces launch an attack on Kinmen Island (Quemoy) and Xiamen but fail[64] |
| Upkeep for the Eight Banners exceeds the entire Qing dynasty's regular income[65] | ||
| 1662 | 20 January | Qing forces advance towards Inwa and force the return of the Yongli Emperor[66] |
| May | The Yongli Emperor is executed in Yunnan; so ends the Southern Ming resistance on the mainland[66] | |
| 1664 | The Qing dynasty conquers Fujian and Zheng Jing retreats to Taiwan[67] |
Close
1670s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1674 | Poverty in the Eight Banners is noted to be caused by excessive and extravagant spending[68] |
Close
1680s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1683 | July | Battle of Penghu: Qing dynasty defeats the Kingdom of Tungning and conquers the island of Taiwan, beginning the period of Taiwan under Qing rule[69] |
| 1684 | The Han Chinese banners, "Hanjun", decline to uselessness[70] | |
| 1685 | May–July | Siege of Albazin: Qing forces take Albazin[71] |
| 1686 | July–October | Siege of Albazin: The Russians return to Albazin but the Qing forces lay siege to it again until the Russians are forced to leave[71] |
| 1689 | 27 August | Treaty of Nerchinsk: The Tsardom of Russia abandons the Amur River region to the Qing in return for trading privileges[71] |
Close
1690s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1690 | 3 September | Battle of Ulan Butung: Galdan Boshugtu Khan leads 20,000 troops into battle with a Qing army 300 km north of Beijing, ending with Dzungar withdrawal[72] |
| 1691 | The Khalkha Mongols submit to the Qing dynasty[73] | |
| 1696 | Battle of Jao Modo: The Qing dynasty invades Mongolia with 100,000 troops in three columns. Galdan Boshugtu Khan suffers defeat against the Western Route Army but manages to escape.[72] The Qing dynasty takes all of Mongolia from the Dzungar Khanate[73] | |
| 1698 | Dzungar–Qing Wars: Qing dynasty occupies Hami[74] |
Close
Remove ads
18th century
1720s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1720 | Chinese expedition to Tibet (1720): The Qing dynasty expels the Dzungars from Tibet, beginning the period of Tibet under Qing rule[75] | |
| Dzungar–Qing Wars: Amin Khoja leads a rebellion in Turpan against the Dzungar Khanate and defects to the Qing dynasty[74] | ||
| Zhu Yigui rebels in Taiwan and is defeated[76] | ||
| 1723 | Plains aborigines living in Dajiaxi village along the central coastal plain of Taiwan rebel; the aborigines are defeated but Han Chinese settlers continue to rebel[77] | |
| The government starts investing in the Eight Banners' livelihoods to reduce their reliance on state subsidies[78] | ||
| 1727 | The government orders the comprehensive collection of genealogical tables for the Eight Banners[79] | |
| 1728 | 25 June | Treaty of Kyakhta (1727): The Mongolian border of the Qing dynasty and Empire of Russia is delineated[80] |
Close
1730s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1732 | Dzungar–Qing Wars: The Dzungars attack Amin Khoja, who takes his people to settle in Guazhou[74] | |
| Han Chinese rebels in Taiwan are defeated[77] | ||
| 1735 | Miao Rebellion: Qing forces defeat and massacre 28,900 Miao and Kam people in Rongjiang[81] | |
| Military upkeep reaches 32 million taels, a bit more than half of the empire's budget[82] | ||
| 1737 | Dzungar–Qing Wars: Abuse by the Dzungars cause residents of the Tarim Basin to flee to the Qing dynasty[83] |
Close
1740s
1750s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1754 | Dzungar–Qing Wars: The Dörbet and Amursana defect to the Qing dynasty[85] | |
| State investment programs for the Eight Banners end[86] | ||
| Chinese bannermen at the Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Hangzhou, and Jingkou garrisons are "let go" and "excused" from their duties[84] | ||
| 1755 | Dzungar–Qing Wars: The Qing dynasty sends 50,000 troops in two columns against the Dzungars, meeting little resistance, and complete the destruction of the khanate in just 100 days, however Amursana revolts in the aftermath[74] | |
| 1756 | All secondary status households in the Eight Banners are ordered to register as civilians[87] | |
| 1757 | Dzungar–Qing Wars: Amursana flees the Qing dynasty, dying in Tobolsk[85] | |
| Chinese bannermen in Beijing who are too old, maimed, or incompetent are let go[88] |
Close
1760s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1760 | The government spends 4 million taels buying back land from Han owners for the Eight Banners[89] | |
| 1761 | Chinese bannermen at Suiyuan are replaced by Mongols and Manchus[88] | |
| 1762 | All Chinese bannermen are given the choice of leaving the banner system[88] | |
| 1763 | Chinese bannermen at Liangzhou and Zhuanglang are let go[88] |
Close
1770s
1780s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1786 | Lin Shuangwen rebellion: Lin Shuangwen rebels in Taiwan[90] | |
| 1788 | Lin Shuangwen rebellion: Lin Shuangwen is defeated[90] |
Close
Remove ads
19th century
1820s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1820 | Poverty becomes endemic in the Eight Banners[91] |
Close
1840s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1841 | Ding Gongchen builds China's first steam engine[92] | |
| 1842 | 29 August | The Treaty of Nanking is signed between Britain and China, to come into effect on 26 June 1843. |
Close
1860s
1870s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1871 | December | Mudan incident: A Ryukyuan tributary ship crashes off the southern coast of Taiwan[94] |
| 1872 | July | Mudan incident: The survivors of the Ryukyuan shipwreck who survive a massacre by Taiwanese indigenous peoples find shelter among Han Chinese locals and are shipped home from mainland China[95] |
| 1874 | Japanese invasion of Taiwan (1874): Japanese forces invade aboriginal territory in southern Taiwan using the Mudan incident as pretext and retreat after forcing the Qing to pay an indemnity[96] |
Close
1890s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1895 | 17 April | First Sino-Japanese War: The Qing cede the Penghu islands and Taiwan to Japan in the Treaty of Shimonoseki[97] |
| 1898 | 11 June | The Guangxu Emperor begins the Hundred Days' Reform[98] |
| 5 September | Zhang Yuanji recommends ending Manchu-Han differences and dissolving the Eight Banners system[99] | |
| 21 September | Empress Dowager Cixi puts the Guangxu Emperor under house arrest[100] | |
| 22 September | Empress Dowager Cixi comes to power[101] |
Close
Remove ads
20th century
1900s
More information Year, Date ...
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1900 | June | Boxer Rebellion: Empress Dowager Cixi declares war on foreign powers[101] |
| 14 August | Boxer Rebellion: Foreign troops enter Beijing[102] | |
| 7 September | Boxer Rebellion: The Boxer Protocol is signed[103] | |
| 17 September | Boxer Rebellion: Foreign troops leave Beijing[103] | |
| 1901 | July | The Zongli Yamen is replaced with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs[104] |
| 1902 | 7 January | Empress Dowager Cixi returns to Beijing[103] |
| 1 February | Ban on intermarriage between Manchus and Han Chinese is lifted[105] | |
| 1903 | 29 December | Manchu monopoly on posts in the Eight Banners is abolished[105] |
| 1905 | 16 July | The government issues an edict proclaiming the need for leading officials to investigate new ways of government from abroad[106] |
| 24 September | Anti-Manchu proponent Wu Yue fails to assassinate the constitutional study commissioners[107] | |
| The prohibition on transfer of property from the Eight Banners to civilians is lifted[104] | ||
| 1906 | 1 September | Empress Dowager Cixi promises to form a constitutional government with no specified date[108] |
| 1907 | April | The territories of Manchuria are reorganized into provinces[104] |
| 6 July | Anhui governor Enming is assassinated by the anti-Manchu Xu Xilin[109] | |
| 20 September | Empress Dowager Cixi declares her intention to create "a bicameral deliberative body"[110] | |
| 27 September | An edict is passed to disband provincial banner garrisons over a 10-year period[111] | |
| 9 October | An edict is passed to create a set of codes which apply uniformly to Manchus and Han Chinese[110] |
Close
Remove ads
Gallery
- Major Mongol and Jurchen rulers on the eve of the Jurchen unification and conquest (early 17th century)
- Mainland East Asia in 1616
- Chahar-Jurchen War (1619-1634)
- Battle of Ningyuan in 1626
- Later Jin invasion of Joseon in 1627
- Qing invasion of Joseon in 1636
- Battle of Shanhai Pass in 1644
- Southern Ming in November 1644
- Russian-Qing border conflicts (1652-1686)
- Dzungar Khanate (1634–1758) and Khoshut Khanate (1642–1717)
- Revolt of the Three Feudatories (1673–1681)
- Taiwan in the 17th century prior to the Qing conquest in 1683
- Mainland East Asia in 1688
- Dzungar–Qing Wars (1687–1757)
- Mainland East Asia in 1757
- Changes in Russian-Chinese borders from the Treaty of Nerchinsk in 1689 to the Convention of Peking in 1860
- First Opium War (1839–1842)
- Taiping Rebellion (1850– 1864)
- Nian Rebellion (1851–1868)
- Yellow River course change in 1855
- Sino-French War (1884–1885)
- Boxer Rebellion (1900-1901)
Remove ads
References
Bibliography
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
Remove ads
























