Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Tourniquet test
Test for fragility of blood vessels From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
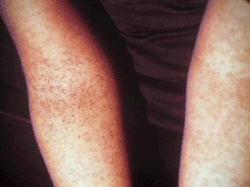
A tourniquet test (also known as a Hess test, Rumpel-Leede test, Rumpel-Leede capillary-fragility test or simply a capillary fragility test) determines capillary fragility.[1] It is a clinical diagnostic method to determine a patient's haemorrhagic tendency. It assesses fragility of capillary walls and is used to identify thrombocytopenia (a reduced platelet count) and is associated with low vitamin C or scurvy.
A blood pressure cuff is applied and inflated to the midpoint between the systolic and diastolic blood pressures for five minutes. The test is positive if there are more than 10 to 20 petechiae per square inch.[2][3] Normally less than 15 petechiae are seen in a 5 cm diameter circle of the area under pressure.[4]
The test was once part of the World Health Organization (WHO) algorithm for diagnosis of dengue fever,[5] however it is no longer used in the latest WHO guidance.[6] Studies have shown that the tourniquet test has low predictive value for dengue fever and should be used in conjunction with other tests for a reliable diagnosis.[7][8][9][10]
More broadly, a positive response occurs due to poor platelet function, bleeding diathesis or thrombocytopenia, and can be seen in cases of scurvy,[11] and dengue fever.
Remove ads
Etymology
The Hess test is named after Alfred Fabian Hess.
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads