Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Via Maris
Ancient trade route linking Egypt with Syria, Anatolia and Mesopotamia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Via Maris, or Way of Horus (Middle Egyptian: ḫꜣt Ḥr, lit. 'Khet Her') was an ancient trade route, dating from the early Bronze Age, linking Egypt with the northern empires of Syria, Anatolia and Mesopotamia – along the Mediterranean coast of modern-day Egypt, Israel, Turkey and Syria.[1] In Latin, Via Maris means "way of the sea", a translation of the Greek ὁδὸν θαλάσσης found in Isaiah 9:1 of the Septuagint, itself a translation of the Hebrew דֶּ֤רֶךְ הַיָּם֙.[2] It is a historic road that runs in part along the Israeli Mediterranean coast.[3] It was the most important route from Egypt to Syria (the Fertile Crescent) which followed the coastal plain before crossing over into the plain of Jezreel and the Jordan valley.[4] Other names are "Way of the Philistines",[5] "Great Trunk Road"[6][7] and "International Coastal Highway."[8]
This article needs additional citations for verification. (November 2013) |

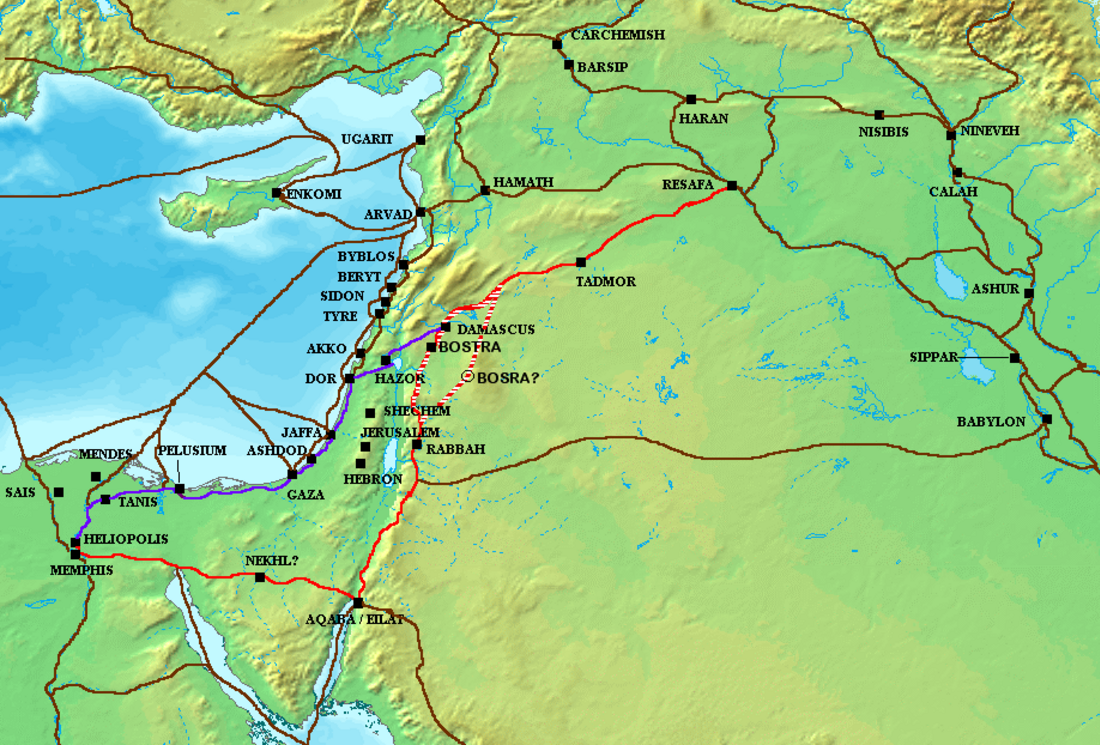
Together with the King's Highway, the Via Maris was one of the major trade routes connecting Egypt and the Levant with Anatolia and Mesopotamia. The Via Maris was crossed by other trading routes, so that one could travel from Africa to Europe or from Asia to Africa. It began in al-Qantara and went east to Pelusium, following the northern coast of Sinai through el-Arish and Rafah. From there it followed the coast of Canaan through Gaza, Ascalon, Isdud, Aphek avoiding the Yarkon River, and Dor before turning east again through Megiddo and the Jezreel Valley until it reached Tiberias on the Sea of Galilee. Again turning northward along the lake shore, the Via Maris passed through Migdal, Capernaum, and Hazor. From Hazor it crossed the northern River Jordan at what later became known as Jacob's Ford, then climbed sharply over the Golan Heights and wound its way northeast into Damascus. Here travellers could continue on the King's Highway as far as the Euphrates River or proceed northward into Anatolia.
Remove ads
Name and controversy
Summarize
Perspective
The historic name used in Ancient Egypt was "Way of Horus".[9] According to Anson Rainey (1981),[10] "Via Maris" derives from the Latin translation of Isaiah 9:1 (in the Hebrew Bible, 8:23) – "by the way of the sea".[11] The prophet was probably referring to the road from Dan to the sea at Tyre, passing through Abel-beth-maachah,[12] which marked the northern border of Israel at the time of the Assyrian conquest.
This Egypt-to-Damascus route is designated by Barry J. Beitzel as the Great Trunk Road in The New Moody Atlas of the Bible (2009), p. 85. John D. Currid and David P. Barrett use this name in the ESV Bible Atlas (2010), p. 41, as do Rainey and Notley in Carta's New Century Handbook and Atlas of the Bible (2007), p. 76. Carl G. Rasmussen in the Zondervan Atlas of the Bible (2010), p. 32, also notes the traditional misnomer and calls the Egypt–Damascus route "the International North-South Route."
Rasmussen, in agreement with Langfur and Rainey, suggests that the Via Maris was the road that connected Tyre with Damascus. Beitzel, in contrast, denotes the Via Maris as a road from Ptolemais (Acco / Acre) to Kedesh (Kedesh-naphtali) in the Galilee – also leading west to east, but slightly further south and not reaching so far inland.
Remove ads
See also
- Ancient routes
- Barid, Muslim postal network renewed during Mamluk period and connecting Cairo with Damascus
- King's Highway (ancient) – an alternative, more easterly ancient route between Egypt and Mesopotamia
- Salah al-Din Road – the main highway of the Gaza Strip, crossing the territory from north to south
- Way of the Patriarchs – the biblical north-to-south route through the mountains of Canaan
- Grand Trunk Road – one of Asia's oldest and longest major roads linking South Asia and Central Asia.
- Roman roads in Judaea – a transport network in classical antiquity
- Sites along Via Maris
- Migdal Aphek/Majdal Yaba, east of Tel Aphek
- Shimron, now Tel Shimron
- Tel Aphek/Antipatris, at the springs of the Yarkon
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads