Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Canaan
Region in the ancient Near East From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Canaan[i][1][2] was an ancient Semitic-speaking civilization and region of the Southern Levant during the late 2nd millennium BC. Canaan had significant geopolitical importance in the Late Bronze Age Amarna Period (14th century BC) as the area where the spheres of interest of the Egyptian, Hittite, Mitanni, and Assyrian Empires converged or overlapped. Much of present-day knowledge about Canaan stems from archaeological excavation in this area at sites such as Tel Hazor, Tel Megiddo, En Esur, and Gezer.
The name "Canaan" appears throughout the Bible as a geography associated with the "Promised Land". The demonym "Canaanites" serves as an ethnic catch-all term covering various indigenous populations—both settled and nomadic-pastoral groups—throughout the regions of the southern Levant.[3] It is by far the most frequently used ethnic term in the Bible.[4] Biblical scholar Mark Smith, citing archaeological findings, suggests "that the Israelite culture largely overlapped with and derived from Canaanite culture ... In short, Israelite culture was largely Canaanite in nature."[5]: 13–14 [6]
The name "Canaanites" is attested, many centuries later, as the endonym of the people later known to the Ancient Greeks from c. 500 BC as Phoenicians,[7] and after the emigration of Phoenicians and Canaanite-speakers to Carthage (founded in the 9th century BC), was also used as a self-designation by the Punics (as "Chanani") of North Africa during Late Antiquity.
Remove ads
Etymology
Summarize
Perspective
Canaan
The English term "Canaan" (pronounced /ˈkeɪnən/ since c. 1500, due to the Great Vowel Shift) comes from the Hebrew כנען (Kənaʿan), via the Koine Greek Χανααν Khanaan and the Latin Canaan. It appears as Kinâḫna (Akkadian: 𒆳𒆠𒈾𒄴𒈾, KURki-na-aḫ-na) in the Amarna letters (14th century BC) and several other ancient Egyptian texts.[8] In Greek, it first occurs in the writings of Hecataeus (c. 550–476 BC) as "Khna" (Χνᾶ).[9] It is attested in Phoenician on coins from Berytus dated to the 2nd century BC.[10]
The etymology is uncertain. An early explanation derives the term from the Semitic root knʿ, "to be low, humble, subjugated".[11] Some scholars have suggested that this implies an original meaning of "lowlands", in contrast with Aram, which would then mean "highlands",[12] whereas others have suggested it meant "the subjugated" as the name of Egypt's province in the Levant, and evolved into the proper name in a similar fashion to Provincia Nostra (the first Roman colony north of the Alps, which became Provence).[13]
An alternative suggestion, put forward by Ephraim Avigdor Speiser in 1936, derives the term from Hurrian Kinaḫḫu, purportedly referring to the colour purple, so that "Canaan" and "Phoenicia" would be synonyms ("Land of Purple"). Tablets found in the Hurrian city of Nuzi in the early 20th century appear to use the term "Kinaḫnu" as a synonym for red or purple dye, laboriously produced by the Kassite rulers of Babylon from murex molluscs as early as 1600 BC, and on the Mediterranean coast by the Phoenicians from a byproduct of glassmaking. Purple cloth became a renowned Canaanite export commodity which is mentioned in Exodus. The dyes may have been named after their place of origin. The name 'Phoenicia' is connected with the Greek word for "purple", apparently referring to the same product, but it is difficult to state with certainty whether the Greek word came from the name, or vice versa. The purple cloth of Tyre in Phoenicia was well known far and wide and was associated by the Romans with nobility and royalty. However, according to Robert Drews, Speiser's proposal has generally been abandoned.[14][15]
Djahy
Retjenu (Anglicised 'Retenu') was the usual ancient Egyptian name for Canaan and Syria, covering the region from Gaza in the south, to Tartous in the north. Its borders shifted with time, but it generally consisted of three regions.[citation needed] The region between Ascalon and the Lebanon, stretching inland to the Sea of Galilee, was named Djahy,[16] which was approximately synonymous with Canaan.[citation needed]
Remove ads
History and archaeology
Summarize
Perspective
Overview
There are several periodization systems for Canaan.[clarification needed] One of them is the following.[citation needed]
- Prior to 4500 BC (prehistory – Stone Age): hunter-gatherer societies slowly giving way to farming and herding societies
- 4500–3500 BC (Chalcolithic): early metal-working and farming
- 3500–2000 BC (Early Bronze): prior to written records in the area[dubious – discuss]
- 2000–1550 BC (Middle Bronze): city-states[17][18]
- 1550–1200 BC (Late Bronze): Egyptian hegemony
- 1200–various dates by region (Iron Age)
After the Iron Age the periods are named after the various empires that ruled the region: Assyrian, Babylonian, Persian, Hellenistic (related to Greece) and Roman.[19]
Canaanite culture developed in situ from multiple waves of migration merging with the earlier Circum-Arabian Nomadic Pastoral Complex, which in turn developed from a fusion of their ancestral Natufian and Harifian cultures with Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) farming cultures, practicing animal domestication, during the 6200 BC climatic crisis which led to the Neolithic Revolution/First Agricultural Revolution in the Levant.[20] The majority of Canaan is covered by the Eastern Mediterranean conifer–sclerophyllous–broadleaf forests ecoregion.[citation needed]
Chalcolithic (4500–3500 BC)


The first wave of migration, called Ghassulian culture, entered Canaan circa 4500 BC.[21] This is the start of the Chalcolithic in Canaan. From their unknown homeland, they brought an already complete craft tradition of metalwork. They were expert coppersmiths and their work is similar to artifacts from the later Maykop culture, leading some scholars to believe they represent two branches of an original metalworking tradition. Their main copper mine was at Wadi Feynan. The copper was mined from the Cambrian Burj Dolomite Shale Unit in the form of the mineral malachite. All of the copper was smelted at sites in Beersheba culture.
Genetic analysis has shown that the Ghassulians belonged to the West Asian haplogroup T-M184.[22]
The end of the Chalcolithic period saw the rise of the urban settlement of 'En Esur on the southern Mediterranean coast.[23]
Early Bronze Age (3500–2000 BC)

By the Early Bronze Age other sites had developed, such as Ebla (where an East Semitic language, Eblaite, was spoken), which by c. 2300 BC was incorporated into the Mesopotamia-based Akkadian Empire of Sargon the Great and Naram-Sin of Akkad (biblical Accad). Sumerian references to the Mar.tu ("tent dwellers", later Amurru, i.e. Amorite) country west of the Euphrates River date from even earlier than Sargon, at least to the reign of the Sumerian king, Enshakushanna of Uruk, and one tablet credits the early Sumerian king Lugal-Anne-Mundu with holding sway in the region, although this tablet is considered less credible because it was produced centuries later.[citation needed]
Amorites at Hazor, Kadesh (Qadesh-on-the-Orontes), and elsewhere in Amurru (Syria) bordered Canaan in the north and northeast. (Ugarit may be included among these Amoritic entities.)[25] The collapse of the Akkadian Empire in 2154 BC saw the arrival of peoples using Khirbet Kerak ware (pottery),[26] coming originally from the Zagros Mountains (in modern Iran) east of the Tigris. In addition, DNA analysis revealed that between 2500 and 1000 BC, populations from the Chalcolithic Zagros and Bronze Age Caucasus migrated to the Southern Levant.[27]
The first cities in the southern Levant arose during this period. The major sites were 'En Esur and Meggido. These "proto-Canaanites" were in regular contact with the other peoples to their south such as Egypt, and to the north Asia Minor (Hurrians, Hattians, Hittites, Luwians) and Mesopotamia (Sumer, Akkad, Assyria), a trend that continued through the Iron Age. The end of the period is marked by the abandonment of the cities and a return to lifestyles based on farming villages and semi-nomadic herding, although specialised craft production continued and trade routes remained open.[28] Archaeologically, the Late Bronze Age state of Ugarit (at Ras Shamra in Syria) is considered quintessentially Canaanite,[5] even though its Ugaritic language does not belong to the Canaanite language group proper.[29][30][31]
A disputed reference to a "Lord of ga-na-na" in the Semitic Ebla tablets (dated 2350 BC) from the archive of Tell Mardikh has been interpreted by some scholars to mention the deity Dagon by the title "Lord of Canaan"[32] If correct, this would suggest that Eblaites were conscious of Canaan as an entity by 2500 BC.[33] Jonathan Tubb states that the term ga-na-na "may provide a third-millennium reference to Canaanite", while at the same time stating that the first certain reference is in the 18th century BC.[5]: 15 See Ebla-Biblical controversy for further details.
Middle Bronze Age (2000–1550 BC)

Urbanism returned and the region was divided among small city-states, the most important of which seems to have been Hazor.[34] Many aspects of Canaanite material culture now reflected a Mesopotamian influence, and the entire region became more tightly integrated into a vast international trading network.[34]
As early as Naram-Sin of Akkad's reign (c. 2240 BC), Amurru was called one of the "four quarters" surrounding Akkad, along with Subartu/Assyria, Sumer, and Elam.[citation needed] Amorite dynasties also came to dominate in much of Mesopotamia, including in Larsa, Isin and founding the state of Babylon in 1894 BC. Later on, Amurru became the Assyrian/Akkadian term for the interior of south as well as for northerly Canaan. At this time the Canaanite area seemed divided between two confederacies, one centred upon Megiddo in the Jezreel Valley, the second on the more northerly city of Kadesh on the Orontes River.[citation needed] An Amorite chieftain named Sumu-abum founded Babylon as an independent city-state in 1894 BC. One Amorite king of Babylonia, Hammurabi (1792–1750 BC), founded the First Babylonian Empire, which lasted only as long as his lifetime. Upon his death the Amorites were driven from Assyria but remained masters of Babylonia until 1595 BC, when they were ejected by the Hittites.[citation needed]
The semi-fictional Story of Sinuhe describes an Egyptian officer, Sinuhe, conducting military activities in the area of "Upper Retjenu" and "Fenekhu" during the reign of Senusret I (c. 1950 BC). The earliest bona fide Egyptian report of a campaign to "Mentu", "Retjenu" and "Sekmem" (Shechem) is the Sebek-khu Stele, dated to the reign of Senusret III (c. 1862 BC).[citation needed]
A letter from Mut-bisir to Shamshi-Adad I (c. 1809–1776 BC) of the Old Assyrian Empire (2025–1750 BC) has been translated: "It is in Rahisum that the brigands (habbatum) and the Canaanites (Kinahnum) are situated". It was found in 1973 in the ruins of Mari, an Assyrian outpost at that time in Syria.[5][35] Additional unpublished references to Kinahnum in the Mari letters refer to the same episode.[36] Whether the term Kinahnum refers to people from a specific region or rather people of "foreign origin" has been disputed,[37][38] such that Robert Drews states that the "first certain cuneiform reference" to Canaan is found on the Alalakh statue of King Idrimi (below).[39]
A reference to Ammiya being "in the land of Canaan" is found on the Statue of Idrimi (16th century BC) from Alalakh in modern Syria. After a popular uprising against his rule, Idrimi was forced into exile with his mother's relatives to seek refuge in "the land of Canaan", where he prepared for an eventual attack to recover his city. The other references in the Alalakh texts are:[36]
West Asian visitors to Egypt (c. 1900 BC)
A group of West Asian foreigners, possibly Canaanites, labelled as Aamu (ꜥꜣmw), with the leader labelled as a Hyksos, visiting the Egyptian official Khnumhotep II c. 1900 BC. Tomb of 12th dynasty official Khnumhotep II, at Beni Hasan.[40][41][42][43]
- AT 154 (unpublished)
- AT 181: A list of 'Apiru people with their origins. All are towns, except for Canaan
- AT 188: A list of Muskenu people with their origins. All are towns, except for three lands including Canaan
- AT 48: A contract with a Canaanite hunter.
Around 1650 BC, Canaanites invaded the eastern Nile delta, where, known as the Hyksos, they became the dominant power.[44] In Egyptian inscriptions, Amar and Amurru (Amorites) are applied strictly to the more northerly mountain region east of Phoenicia, extending to the Orontes.

Archaeological excavations of a number of sites, later identified as Canaanite, show that prosperity of the region reached its apogee during this Middle Bronze Age period, under the leadership of the city of Hazor, at least nominally tributary to Egypt for much of the period. In the north, the cities of Yamkhad and Qatna were hegemons of important confederacies, and it would appear that biblical Hazor was the chief city of another important coalition in the south.[citation needed]
Late Bronze Age (1550–1200 BC)
In the early Late Bronze Age, Canaanite confederacies centered on Megiddo and Kadesh, before being fully brought into the Egyptian Empire and Hittite Empire. Later still, the Neo-Assyrian Empire assimilated the region.[citation needed]
According to the Bible, the migrant ancient Semitic-speaking peoples who appear to have settled in the region included (among others) the Amorites, who had earlier controlled Babylonia. The Hebrew Bible mentions the Amorites in the Table of Peoples (Book of Genesis 10:16–18a). Evidently, the Amorites played a significant role in the early history of Canaan. In Book of Genesis 14:7 f., Book of Joshua 10:5 f., Book of Deuteronomy 1:19 f., 27, 44, we find them located in the southern mountain country, while verses such as Book of Numbers 21:13, Book of Joshua 9:10, 24:8, 12, etc., tell of two great Amorite kings residing at Heshbon and Ashteroth, east of the Jordan. Other passages, including Book of Genesis 15:16, 48:22, Book of Joshua 24:15, Book of Judges 1:34, regard the name Amorite as synonymous with "Canaanite". The name Amorite is, however, never used for the population on the coast.[45]

In the centuries preceding the appearance of the biblical Hebrews, parts of Canaan and southwestern Syria became tributary to the Egyptian pharaohs, although domination by the Egyptians remained sporadic, and not strong enough to prevent frequent local rebellions and inter-city struggles. Other areas such as northern Canaan and northern Syria came to be ruled by the Assyrians during this period.[citation needed]
Under Thutmose III (1479–1426 BC) and Amenhotep II (1427–1400 BC), the regular presence of the strong hand of the Egyptian ruler and his armies kept the Amorites and Canaanites sufficiently loyal. Nevertheless, Thutmose III reported a new and troubling element in the population. Habiru or (in Egyptian) 'Apiru, are reported for the first time. These seem to have been mercenaries, brigands, or outlaws, who may have at one time led a settled life, but with bad luck or due to the force of circumstances, contributed a rootless element to the population, prepared to hire themselves to whichever local mayor, king, or princeling would pay for their support.[citation needed]
Although Habiru SA-GAZ (a Sumerian ideogram glossed as "brigand" in Akkadian), and sometimes Habiri (an Akkadian word) had been reported in Mesopotamia from the reign of the Sumerian king, Shulgi of Ur III, their appearance in Canaan appears to have been due to the arrival of a new state based in Asia Minor to the north of Assyria and based upon a Maryannu aristocracy of horse-drawn charioteers, associated with the Indo-Aryan rulers of the Hurrians, known as Mitanni.[citation needed]

The Habiru seem to have been more a social class than an ethnic group.[citation needed] One analysis shows that the majority were Hurrian, although there were a number of Semites and even some Kassite and Luwian adventurers amongst their number.[citation needed] The reign of Amenhotep III, as a result, was not quite so tranquil for the Asiatic province, as Habiru/'Apiru contributed to greater political instability. It is believed[by whom?] that turbulent chiefs began to seek their opportunities, although as a rule they could not find them without the help of a neighbouring king. The boldest of the disaffected nobles was Aziru, son of Abdi-Ashirta, who endeavoured to extend his power into the plain of Damascus. Akizzi, governor of Katna (Qatna?) (near Hamath), reported this to Amenhotep III, who seems to have sought to frustrate Aziru's attempts.[citation needed] In the reign of the next pharaoh, Akhenaten (reigned c. 1352 to c. 1335 BC) both father and son caused infinite trouble to loyal servants of Egypt like Rib-Hadda, governor of Gubla (Gebal),[45] by transferring their loyalty from the Egyptian crown to the Hittite Empire under Suppiluliuma I (reigned c. 1344–1322 BC).[48]
Egyptian power in Canaan thus suffered a major setback when the Hittites (or Hatti) advanced into Syria in the reign of Amenhotep III, and when they became even more threatening in that of his successor, displacing the Amorites and prompting a resumption of Semitic migration. Abdi-Ashirta and his son Aziru, at first afraid of the Hittites, afterwards made a treaty with their king, and joining with the Hittites, attacked and conquered the districts remaining loyal to Egypt. In vain did Rib-Hadda send touching appeals for aid to the distant Pharaoh, who was far too engaged in his religious innovations to attend to such messages.[45]
The Amarna letters tell of the Habiri in northern Syria. Etakkama wrote thus to the Pharaoh:
Behold, Namyawaza has surrendered all the cities of the king, my lord to the SA-GAZ in the land of Kadesh and in Ubi. But I will go, and if thy gods and thy sun go before me, I will bring back the cities to the king, my lord, from the Habiri, to show myself subject to him; and I will expel the SA-GAZ.

Similarly, Zimrida, king of Sidon (named 'Siduna'), declared, "All my cities which the king has given into my hand, have come into the hand of the Habiri." The king of Jerusalem, Abdi-Heba, reported to the Pharaoh:
If (Egyptian) troops come this year, lands and princes will remain to the king, my lord; but if troops come not, these lands and princes will not remain to the king, my lord.
Abdi-heba's principal trouble arose from persons called Iilkili and the sons of Labaya, who are said to have entered into a treasonable league with the Habiri. Apparently this restless warrior found his death at the siege of Gina. All these princes, however, maligned each other in their letters to the Pharaoh, and protested their own innocence of traitorous intentions. Namyawaza, for instance, whom Etakkama (see above) accused of disloyalty, wrote thus to the Pharaoh,[45]
Behold, I and my warriors and my chariots, together with my brethren and my SA-GAZ, and my Suti ?9 are at the disposal of the (royal) troops to go whithersoever the king, my lord, commands."[49]

Around the beginning of the New Kingdom period, Egypt exerted rule over much of the Levant. Rule remained strong during the Eighteenth Dynasty, but Egypt's rule became precarious during the Nineteenth and Twentieth Dynasties. Ramses II was able to maintain control over it in the stalemated battle against the Hittites at Kadesh in 1275 BC, but soon thereafter, the Hittites successfully took over the northern Levant (Syria and Amurru). Ramses II, obsessed with his own building projects while neglecting Asiatic contacts, allowed control over the region to continue dwindling. During the reign of his successor Merneptah, the Merneptah Stele was issued which claimed to have destroyed various sites in the southern Levant, including a people known as "Israel". Egypt's withdrawal from the southern Levant was a protracted process lasting some one hundred years beginning in the late 13th century BC and ending close to the end of the 12th century BC. The reason for the Egypt's withdrawal was most likely political turmoil in Egypt proper rather than the invasion by the Sea Peoples, as there is little evidence that the Sea Peoples caused much destruction ca. 1200 BC. Many Egyptian garrisons or sites with an "Egyptian governor's residence" in the southern Levant were abandoned without destruction including Deir al-Balah, Ascalon, Tel Mor, Tell el-Far'ah (South), Tel Gerisa, Tell Jemmeh, Tel Masos, and Qubur el-Walaydah.[50] Not all Egyptian sites in the southern Levant were abandoned without destruction. The Egyptian garrison at Aphek was destroyed, likely in an act of warfare at the end of the 13th century.[51] The Egyptian gate complex uncovered at Jaffa was destroyed at the end of the 12th century between 1134–1115 based on C14 dates,[52] while Beth-Shean was partially though not completely destroyed, possibly by an earthquake, in the mid-12th century.[50]
Amarna letters

References to Canaanites are also found throughout the Amarna letters of Pharaoh Akhenaten c. 1350 BC. In these letters, some of which were sent by governors and princes of Canaan to their Egyptian overlord Akhenaten (Amenhotep IV) in the 14th century BC, are found, beside Amar and Amurru (Amorites), the two forms Kinahhi and Kinahni, corresponding to Kena and Kena'an respectively, and including Syria in its widest extent, as Eduard Meyer has shown. The letters are written in the official and diplomatic East Semitic Akkadian language of Assyria and Babylonia, though "Canaanitish" words and idioms are also in evidence.[53] The known references are:[36]
- EA 8: Letter from Burna-Buriash II to Akhenaten, explaining that his merchants "were detained in Canaan for business matters", robbed and killed "in Hinnatuna of the land of Canaan" by the rulers of Acre and Shamhuna, and asks for compensation because "Canaan is your country"
- EA 9: Letter from Burna-Buriash II to Tutankhamun, "all the Canaanites wrote to Kurigalzu saying 'come to the border of the country so we can revolt and be allied with you'"
- EA 30: Letter from Tushratta: "To the kings of Canaan... Provide [my messenger] with safe entry into Egypt"
- EA 109: Letter of Rib-Hadda: "Previously, on seeing a man from Egypt, the kings of Canaan fled before him, but now the sons of Abdi-Ashirta make men from Egypt prowl about like dogs"
- EA 110: Letter of Rib-Hadda: "No ship of the army is to leave Canaan"
- EA 131: Letter of Rib-Hadda: "If he does not send archers, they will take [Byblos] and all the other cities and the lands of Canaan will not belong to the king. May the king ask Yanhamu about these matters."
- EA 137: Letter of Rib-Hadda: "If the king neglects Byblos, of all the cities of Canaan, not one will be his"
- EA 367: "Hani son (of) Mairēya, "chief of the stable" of the king in Canaan"
- EA 162: Letter to Aziru: "You yourself know that the king does not want to go against all of Canaan when he rages"
- EA 148: Letter from Abimilku to the Pharaoh: "[The king] has taken over the land of the king for the 'Apiru. May the king ask his commissioner, who is familiar with Canaan"
- EA 151: Letter from Abimilku to the Pharaoh: "The king, my lord wrote to me: 'write to me what you have heard from Canaan'." Abimilku describes in response what has happened in eastern Cilicia (Danuna), the northern coast of Syria (Ugarit), in Syria (Qadesh, Amurru, and Damascus) as well as in Sidon.
Other Late Bronze Age mentions
Text RS 20.182 from Ugarit is a copy of a letter of the king of Ugarit to Ramesses II concerning money paid by "the sons of the land of Ugarit" to the "foreman of the sons of the land of Canaan (*kn'ny)" According to Jonathan Tubb, this suggests that the people of Ugarit, contrary to much modern opinion, considered themselves to be non-Canaanite.[5]: 16 The other Ugarit reference, KTU 4.96, shows a list of traders assigned to royal estates, one of the estates having three Ugaritans, an Ashdadite, an Egyptian and a Canaanite.[36]
Ashur tablets
A Middle Assyrian letter during the reign of Shalmaneser I includes a reference to the "travel to Canaan" of an Assyrian official.[36]
Hattusa letters
Four references are known from Hattusa:[36]
- An evocation to the Cedar Gods: Includes reference to Canaan alongside Sidon, Tyre and possibly Amurru
- KBo XXVIII 1: Ramesses II letter to Hattusili III, in which Ramesses suggested he would meet "his brother" in Canaan and bring him to Egypt
- KUB III 57 (also KUB III 37 + KBo I 17): Broken text which may refer to Canaan as an Egyptian sub-district
- KBo I 15+19: Ramesses II letter to Hattusili III, describing Ramesses' visit to the "land of Canaan on his way to Kinza and Harita
Bronze Age collapse

Ann Killebrew has shown that cities such as Jerusalem were large and important walled settlements in the pre-Israelite Middle Bronze IIB and the Israelite Iron Age IIC period (c. 1800–1550 and c. 720–586 BC), but that during the intervening Late Bronze (LB) and Iron Age I and IIA/B Ages sites like Jerusalem were small and relatively insignificant and unfortified towns.[54]
Just after the Amarna period, a new problem arose which was to trouble the Egyptian control of southern Canaan (the rest of the region then being under Assyrian control). Pharaoh Horemhab campaigned against Shasu (Egyptian = "wanderers"),[citation needed] nomadic pastoralist tribes who had moved across the Jordan River to threaten Egyptian trade through Galilee and Jezreel. Seti I (c. 1290 BC) is said to have conquered these Shasu, Semitic-speaking nomads living just south and east of the Dead Sea, from the fortress of Taru (Shtir?) to "Ka-n-'-na". After the near collapse of the Battle of Kadesh, Rameses II had to campaign vigorously in Canaan to maintain Egyptian power. Egyptian forces penetrated into Moab and Ammon, where a permanent fortress garrison (called simply "Rameses") was established.
Some believe the "Habiru" signified generally all the nomadic tribes known as "Hebrews", and particularly the early Israelites of the period of the "judges", who sought to appropriate the fertile region for themselves.[55] However, the term was rarely used to describe the Shasu. Whether the term may also include other related ancient Semitic-speaking peoples such as the Moabites, Ammonites and Edomites is uncertain.[56]
There is little evidence that any major city or settlement in the southern Levant was destroyed around 1200 BC.[57] At Lachish, The Fosse Temple III was ritually terminated while a house in Area S appears to have burned in a house fire as the most severe evidence of burning was next to two ovens while no other part of the city had evidence of burning. After this though the city was rebuilt in a grander fashion than before.[58] For Megiddo, most parts of the city did not have any signs of damage and it is only possible that the palace in Area AA might have been destroyed though this is not certain.[57] While the monumental structures at Hazor were indeed destroyed, this destruction was in the mid-13th century BC long before the end of the Late Bronze Age began.[59] However, many sites were not burned to the ground around 1200 BC including: Asqaluna, Ashdod (ancient city), Tell es-Safi, Tel Batash, Tel Burna, Tel Dor, Tel Gerisa, Tell Jemmeh, Khirbet Rabud, Tel Zeror, and Tell Abu Hawam among others.[50][51][57]
Despite many theories which claim that trade relations broke down after 1200 BC in the southern Levant, there is ample evidence that trade with other regions continued after the end of the Late Bronze Age in the Southern Levant.[60][61] Archaeologist Jesse Millek has shown that while the common assumption is that trade in Cypriot and Mycenaean pottery ended around 1200 BC, trade in Cypriot pottery actually largely came to an end at 1300, while for Mycenaean pottery, this trade ended at 1250 BC, and destruction around 1200 BC could not have affected either pattern of international trade since it ended before the end of the Late Bronze Age.[62] He has also demonstrated that trade with Egypt continued after 1200 BC.[63] Archaeometallurgical studies performed by various teams have also shown that trade in tin, a non-local metal necessary to make bronze, did not stop or decrease after 1200 BC, even though the closest sources of the metal were modern Afghanistan, Kazakhstan, or perhaps even Cornwall, England.[64][65] Lead from Sardinia was still being imported to the southern Levant after 1200 BC during the early Iron Age.[66]
Iron Age
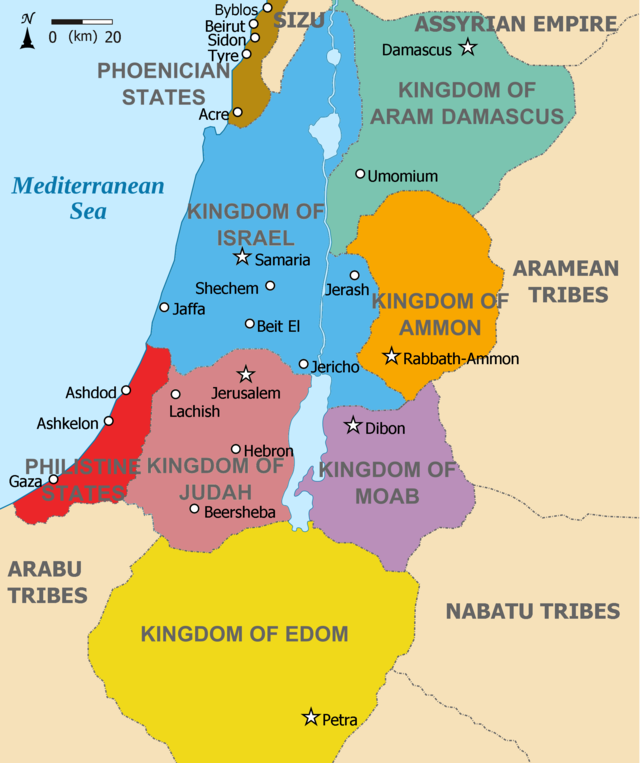
By the Early Iron Age, the southern Levant came to be dominated by the kingdoms of Israel and Judah, besides the Philistine city-states on the Mediterranean coast, and the kingdoms of Moab, Ammon, and Aram-Damascus east of the Jordan River, and Edom to the south. The northern Levant was divided into various petty kingdoms, the so-called Syro-Hittite states and the Phoenician city-states.[citation needed]
The entire region (including all Phoenician/Canaanite and Aramean states, together with Israel, Philistia, and Samaria) was conquered by the Neo-Assyrian Empire during the 10th and 9th centuries BC, and would remain so for three hundred years until the end of the 7th century BC.[citation needed] Emperor-kings such as Ashurnasirpal, Adad-nirari II, Sargon II, Tiglath-Pileser III, Esarhaddon, Sennacherib and Ashurbanipal came to dominate Canaanite affairs. During the Twenty-fifth Dynasty the Egyptians made a failed attempt to regain a foothold in the region but were vanquished by the Neo-Assyrian Empire, leading to an Assyrian conquest of Egypt.
Between 616 and 605 BC the Neo-Assyrian Empire collapsed due to a series of bitter civil wars, followed by an attack by an alliance of Babylonians, Medes, and Persians and the Scythians. The Neo-Babylonian Empire inherited the western part of the empire, including all the lands in Canaan and Syria.[citation needed] They successfully defeated the Egyptians and remained in the region in an attempt to regain a foothold in the Near East.
The Neo-Babylonian Empire itself collapsed in 539 BC, and the region became a part of the Achaemenid Empire. It remained so until in 332 BC it was conquered by the Greeks under Alexander the Great, later to fall to the Roman Empire in the late 2nd century BC, and then Byzantium, until the Arab conquest in the 7th century AD.[67]
Egyptian hieroglyphic and hieratic (1500–1000 BC)

During the 2nd millennium BC, Ancient Egyptian texts use the term "Canaan" to refer to an Egyptian-ruled colony, whose boundaries generally corroborate the definition of Canaan found in the Hebrew Bible, bounded to the west by the Mediterranean Sea, to the north in the vicinity of Hamath in Syria, to the east by the Jordan Valley, and to the south by a line extended from the Dead Sea to around Gaza. Nevertheless, the Egyptian and Hebrew uses of the term are not identical: the Egyptian texts also identify the coastal city of Qadesh in northwest Syria near Turkey as part of the "Land of Canaan", so that the Egyptian usage seems to refer to the entire Levantine coast of the Mediterranean Sea, making it a synonym of another Egyptian term for this coastland, Retjenu.[citation needed]
Lebanon, in northern Canaan, bordered by the Litani river to the watershed of the Orontes River, was known by the Egyptians as upper Retjenu.[68] In Egyptian campaign accounts, the term Djahi was used to refer to the watershed of the Jordan river. Many earlier Egyptian sources also mention numerous military campaigns conducted in Ka-na-na, just inside Asia.[69]

Archaeological attestation of the name "Canaan" in Ancient Near Eastern sources relates almost exclusively to the period in which the region operated as a colony of the New Kingdom of Egypt (16th–11th centuries BC), with usage of the name almost disappearing following the Late Bronze Age collapse (c. 1206–1150 BC).[70] The references suggest that during this period the term was familiar to the region's neighbors on all sides, although scholars have disputed to what extent such references provide a coherent description of its location and boundaries, and regarding whether the inhabitants used the term to describe themselves.[71]
16 references are known in Egyptian sources, from the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt onwards.[36]
- Amenhotep II inscriptions: Canaanites are included in a list of prisoners of war
- Three topographical lists
- Papyrus Anastasi I 27,1" refers to the route from Sile to Gaza "the [foreign countries] of the end of the land of Canaan"
- Merneptah Stele
- Papyrus Anastasi IIIA 5–6 and Papyrus Anastasi IV 16,4 refer to "Canaanite slaves from Hurru"
- Papyrus Harris[72] After the collapse of the Levant under the so-called "Peoples of the Sea" Ramesses III (c. 1194 BC) is said to have built a temple to the god Amen to receive tribute from the southern Levant. This was described as being built in Pa-Canaan, a geographical reference whose meaning is disputed, with suggestions that it may refer to the city of Gaza or to the entire Egyptian-occupied territory in the southwest corner of the Near East.[73]
Greco-Roman historiography
The Greek term Phoenicia is first attested in the first two works of Western literature, Homer's Iliad and Odyssey. It does not occur in the Hebrew Bible, but occurs three times in the New Testament in the Book of Acts.[74] In the 6th century BC, Hecataeus of Miletus affirms that Phoenicia was formerly called χνα, a name that Philo of Byblos subsequently adopted into his mythology as his eponym for the Phoenicians: "Khna who was afterwards called Phoinix". Quoting fragments attributed to Sanchuniathon, he relates that Byblos, Berytus and Tyre were among the first cities ever built, under the rule of the mythical Cronus, and credits the inhabitants with developing fishing, hunting, agriculture, shipbuilding and writing.
Coins of the city of Beirut / Laodicea bear the legend, "Of Laodicea, a metropolis in Canaan"; these coins are dated to the reign of Antiochus IV (175–164 BC) and his successors until 123 BC.[75]

Saint Augustine also mentions that one of the terms the seafaring Phoenicians called their homeland was "Canaan". Augustine also records that the rustic people of Hippo in North Africa retained the Punic self-designation Chanani.[76][77] Since 'punic' in Latin also meant 'non-Roman', some scholars, however, argue that the language referred to as Punic in Augustine may have been Libyan.[78]
The Greeks also popularized the term Palestine, named after the Philistines or the Aegean Pelasgians, for roughly the region of Canaan, excluding Phoenicia, with Herodotus' first recorded use of Palaistinê, c. 480 BC. From 110 BC, the Hasmoneans extended their authority over much of the region, creating a Judean-Samaritan-Idumaean-Ituraean-Galilean alliance. The Judean (Jewish, see Ioudaioi) control over the wider area resulted in it also becoming known as Judaea, a term that had previously only referred to the smaller region of the Judean Mountains, the allotment of the Tribe of Judah and heartland of the former Kingdom of Judah.[79][80] Between 73 and 63 BC, the Roman Republic extended its influence into the region in the Third Mithridatic War, conquering Judea in 63 BC, and splitting the former Hasmonean Kingdom into five districts. Around 130–135 AD, as a result of the suppression of the Bar Kochba revolt, the province of Iudaea was joined with Galilee to form a new province of Syria Palaestina. There is circumstantial evidence linking Hadrian with the name change,[81] although the precise date is not certain,[81] and the interpretation of some scholars that the name change may have been intended "to complete the dissociation with Judaea"[82][83] is disputed.[84]
Later sources
Padiiset's Statue is the last known Egyptian reference to Canaan, a small statuette labelled "Envoy of the Canaan and of Peleset, Pa-di-Eset, the son of Apy". The inscription is dated to 900–850 BC, more than 300 years after the preceding known inscription.[85]
During the period c. 900–330 BC, the dominant Neo-Assyrian and Achaemenid Empire make no mention of Canaan.[86]
Remove ads
Canaanites
Summarize
Perspective
The Canaanites were the inhabitants of ancient Canaan, a region that roughly corresponds to present-day Israel and Palestine, western Jordan, southern and coastal Syria, Lebanon, and continued up to the southern border of Turkey. They are believed to have been one of the oldest civilizations in human history.[87]
History
The Levant was inhabited by people who referred to the land as ka-na-na-um as early as the mid-third millennium BC.[88] The Akkadian word "kinahhu" referred to the purple-coloured wool, dyed from the Murex molluscs of the coast—which was a key export of the region. When the ancient Greeks later traded with the Canaanites, this meaning of the word seems to have predominated, as they referred to the Canaanites as Phoenikes (Φοίνικες; Phoenicians), which may derive from the Greek-language word "phoenix" (φοίνιξ; transl. "crimson" or "purple"), and also described the cloth for which the Greeks traded. The word "phoenix" was transcribed by the Romans to "poenus"; the descendants of the Canaanite settlers in Carthage were likewise referred to as Punic.[citation needed]
Thus, while "Phoenician" and "Canaanite" refer to the same culture, archaeologists and historians commonly refer to the Bronze Age pre-1200 BC Levantine peoples as Canaanites, while their Iron Age descendants, particularly those living on the coast, are referred to as Phoenicians. More recently, the term "Canaanite" has been used for the secondary Iron Age states of the Levantine interior that were not ruled by Aramean peoples, that is, that were ruled by a separate and closely related ethnic group which included the Philistines and the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah.[89]
Culture

According to archaeologist Jonathan N. Tubb, "Ammonites, Moabites, Israelites, and Phoenicians undoubtedly achieved their own cultural identities, and yet ethnically they were all Canaanites", "the same people who settled in farming villages in the region in the 8th millennium BC."[5]: 13–14
There is uncertainty about whether the name "Canaan" refers to a specific Semitic-speaking ethnic group wherever they live, the homeland of this ethnic group, a region under the control of this ethnic group, or perhaps any combination of the three.
Canaanite civilization was a response to long periods of stable climate interrupted by short periods of climate change. During these periods, Canaanites profited from their intermediary position between the ancient civilizations of the Middle East—Ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia (Sumer, Akkad, Assyria, Babylonia), the Hittites, and Minoan Crete—to become city-states of merchant princes along the coast, with small kingdoms specializing in agricultural products in the interior. This polarity, between coastal towns and agrarian hinterland, was illustrated in Canaanite mythology by the struggle between the storm god, variously called Teshub (Hurrian) or Ba'al Hadad (Semitic Amorite/Aramean) and Ya'a, Yaw, or Yam, god of the sea and rivers. Early Canaanite civilization was characterized by small walled market towns, surrounded by peasant farmers growing a range of local horticultural products, along with commercial growing of olives, grapes for wine, and pistachios, surrounded by extensive grain cropping, predominantly wheat and barley. Harvest in early summer was a season when transhumance nomadism was practised—shepherds staying with their flocks during the wet season and returning to graze them on the harvested stubble, closer to water supplies in the summer. Evidence of this cycle of agriculture is found in the Gezer calendar and in the biblical cycle of the year.
Periods of rapid climate change generally saw a collapse of this mixed Mediterranean farming system; commercial production was replaced with subsistence agricultural foodstuffs; and transhumance pastoralism became a year-round nomadic pastoral activity, whilst tribal groups wandered in a circular pattern north to the Euphrates, or south to the Egyptian delta with their flocks. Occasionally, tribal chieftains would emerge, raiding enemy settlements and rewarding loyal followers from the spoils or by tariffs levied on merchants. Should the cities band together and retaliate, a neighbouring state intervenes or should the chieftain suffer a reversal of fortune, allies would fall away or intertribal feuding would return. It has been suggested that the Patriarchal tales of the Bible reflect such social forms.[90]
Since 3100 BC, most Canaanites, particularly those that lived on the land that is now Israel/Palestine, lived in walled settlements in the plains and coastal regions. These settlements were surrounded by mud-brick fortifications and agricultural hamlets, which the inhabitants relied on for food.[91][ii] In the 2nd millennium BC, urban Canaanite elites ruled over rural and pastoral areas. The material culture of the city-states was relatively uniform.[92] New burial customs were implicitly influenced by a belief in the afterlife.[91][93]
During the periods of the collapse of Akkadian Empire in Mesopotamia and the First Intermediate Period of Egypt, the Hyksos invasions and the end of the Middle Bronze Age in Assyria and Babylonia, and the Late Bronze Age collapse, trade through the Canaanite area would dwindle, as Egypt, Babylonia, and to a lesser degree Assyria, withdrew into their isolation. When the climates stabilized, trade would resume firstly along the coast in the area of the Philistine and Phoenician cities. As markets redeveloped, new trade routes that would avoid the heavy tariffs of the coast would develop from Kadesh Barnea, through Hebron, Lachish, Jerusalem, Bethel, Samaria, Shechem, Shiloh through Galilee to Jezreel, Hazor, and Megiddo. Secondary Canaanite cities would develop in this region. Further economic development would see the creation of a third trade route from Eilath, Timna, Edom (Seir), Moab, Ammon, and thence to the Aramean states of Damascus and Palmyra. Earlier states (for example the Philistines and Tyrians in the case of Judah and Samaria, for the second route, and Judah and Israel for the third route) tried generally unsuccessfully to control the interior trade.[94]
Eventually, the prosperity of this trade would attract more powerful regional neighbours, such as Ancient Egypt, Assyria, the Babylonians, Persians, Ancient Greeks, and Romans, who would control the Canaanites politically, levying tribute, taxes, and tariffs. Often in such periods, thorough overgrazing would result in a climatic collapse and a repeat of the cycle (e.g., PPNB, Ghassulian, Uruk, and the Bronze Age cycles already mentioned). The fall of later Canaanite civilization occurred with the incorporation of the area into the Greco-Roman world (as Iudaea province), and after Byzantine times, into the Umayyad Caliphate. Western Aramaic, one of the two lingua francas of Canaanite civilization, is still spoken in a number of small Syrian villages, whilst Phoenician Canaanite disappeared as a spoken language in about 100 CE. A separate Akkadian-infused Eastern Aramaic is still spoken by the existing Assyrians of Iraq, Iran, northeast Syria, and southeast Turkey.
Tel Kabri contains the remains of a Canaanite city from the Middle Bronze Age (2000–1550 BC). The city, the most important of the cities in the Western Galilee during that period, had a palace at its center. Tel Kabri is the only Canaanite city that can be excavated in its entirety because after the city was abandoned, no other city was built over its remains. It is notable because the predominant extra-Canaanite cultural influence is Minoan; Minoan-style frescoes decorate the palace.[95]
Significant figures
Figures mentioned in historiography or known through archaeology
- Rulers of Ugarit
- Ammittamru I of Ugarit (Amarna letters)
- Niqmaddu II of Ugarit (Amarna letters) (1349–1315 BC)
- Arhalba of Ugarit (1315–1313 BC)
- Niqmepa of Ugarit (1313–1260 BC)
- Ammittamru II of Ugarit (1260–1235 BC)
- Ibiranu of Ugarit (1235–1220 BC)
- Ammurapi of Ugarit (1215–1185 BC)
- Rulers of Tyre
- Abibaal 990–978 BC
- Hiram I 978–944 BC
- Baal-Eser I (Balbazer I) 944–927 BC
- Abdastartus 927–918 BC
- Astarymus 906–897 BC
- Phelles 897–896 BC
- Ithobaal I 896–863 BC
- Baal-Eser II (Balbazer II) 863–829 BC
- Mattan I 829–820 BC
- Pygmalion 820–774 BC
- Ithobaal II 750–739 BC
- Hiram II 739–730 BC
- Luli 729 694 BC
- Baal I 680–660 BC
- Abbar 563–562 BC
- Abdemon c. 420–411 BC
- Others
- Aziru, ruler of Amurru (Amarna letters)
- Labaya, lord of Shechem (Amarna letters)
- Abdi-Heba, local chieftain of pre-Israelite Jerusalem (Jebus) (Amarna letters)
- Šuwardata, king of the Canaanite city of Gath or 'mayor' of Qiltu (Amarna letters)
- Cronos (Ilus), founder of Byblos according to Sanchuniathon
Genetic studies
A 2017 study of five Canaanite skeletons found that approximately half of the skeletons' genes originated from agricultural settlers in the Levant around 10,000 years ago. The other half was from a population tied to Iran, which researchers estimate arrived in the Levant approximately 5,000 years ago.[96]
Hajjej (2018) revealed that when using HLA genes, Levantine Arabs, such as Palestinians, Syrians, Lebanese and Jordanians, were closely related populations with common Canaanite ancestry. They shared a common geographic territory, which was later disrupted by 19th-century British and French colonization. Their Canaanite ancestors came from North Africa or the Arabian peninsula via Egypt in 3300 BC and settled in the Levant lowlands after the Ghassulian collapse in 3800-3350 BC. The Levantine Arabs were also related to East Mediterranean populations, such as Turks, Greeks and Cretans, Egyptians and Iranians, which can be explained by the high migratory flow between Levantine sub-regions. However, Levantine Arabs were genetically distant from Arabian Peninsula populations such as Saudis, Kuwaitis and Yeminis before the 7th century Islamic conquests.[97]
Agranat-Tamir et al. (2020) stated that Canaanites from the Intermediate Bronze Age (c. 2500–2000 BC) to late Iron Age I (c. 1000 BC) were genetically similar to each other. They lived in modern Israel, Jordan and Lebanon and could be modeled as "a mixture of local earlier Neolithic populations and populations from the northeastern part of the Near East (i.e. Zagros Mountains, Caucasians/Armenians and possibly, Hurrians)". Exceptions include the 2nd millennium BC inhabitants of Sidon, Abel Beth Maacah and Ashkelon, who were relatively heterogenous due to inflow from the eastern Mediterranean basin. The inhabitants of Ba'qah in Jordan also have probable admixture from "eastern desert groups". Following the Bronze Age, there was an addition of European-related and East African-related components, which were represented by Late Neolithic and Bronze Age Europeans and Somalis, from a north-south and south-north gradient respectively. The majority of modern Jewish and Levantine Arabic-speaking groups have 50% or more ancestry from peoples who were related to Bronze Age Levantines and Chalcolithic Zagros groups. This does not mean that any of these present-day groups bear direct ancestry from people who lived in the Middle to Late Bronze Age Levant or in Chalcolithic Zagros; rather, it indicates that they have ancestries from populations whose ancient proxy can be related to the Middle East.[98]
Almarri et al. (2021) stated that Levantines and Arabians diverged from each other before the Neolithic period, with Levantines adopting a sedentary agricultural lifestyle. In the Bronze Age, immigrants with ancient Iranian-related ancestry replaced about 50% of the local Levantine ancestry. They were believed to introduce haplogroup J1, which was not found in earlier Levantines. After the Bronze Age, Eastern Hunter Gatherer (EHG) ancestry was introduced, along with southeast European and Anatolian ancestry. Anatolian ancestry is significantly higher in modern Levantines than Arabians.[99]
Lazaridis et al. (2022) clarified that ancient Levantines and their descendants exhibit a decrease of ~8% local Neolithic ancestry, which is mostly Natufian, every millennium, starting from the Pre-Pottery Neolithic to the Medieval period. It was largely replaced by Caucasus-related and Anatolian-related ancestries, from the north and west respectively. However, despite the decline in the Natufian component, this key ancestry source made an important contribution to peoples of later periods, continuing until the present.[100]

Remove ads
In Jewish and Christian scriptures
Summarize
Perspective
Hebrew Bible
Canaan and the Canaanites are mentioned some 160 times in the Hebrew Bible, mostly in the Torah and the books of Joshua and Judges.[101]
They descended from Canaan, who was the son of Ham and the grandson of Noah. Canaan was cursed with perpetual slavery because his father Ham had "looked upon" the drunk and naked Noah. The expression "look upon" at times has sexual overtones in the Bible, as in Leviticus 20:11, "The man who lies with his father's wife has uncovered his father's nakedness..." As a result, interpreters have proposed a variety of possibilities as to what kind of transgression has been committed by Ham, including the possibility of castrating or raping his father or maternal incest.[102][103] However, some believe that Canaan was the perpetrator of the crime, based on the surrounding verses.[104]
According to the Table of Nations, Canaan was also the ancestor of other nations, which were collectively considered to be Canaanite:
Canaan is the father of Sidon, his firstborn; and of the Hittites, Jebusites, Amorites, Girgashites, Hivites, Arkites, Sinites, Arvadites, Zemarites, and Hamathites. Later the Canaanite clans scattered, and the borders of Canaan reached [across the Mediterranean coast] from Sidon toward Gerar as far as Gaza, and then [inland around the Jordan Valley ] toward Sodom, Gomorrah, Admah and Zeboiim, as far as Lasha.
Other passages in the Bible offer different lists of the exact names of the Canaanite tribes. For example, Genesis 15:19–21 lists the Kenites, Kenizzites, Kadmonites, Hittites, Perizzites, Rephaim, Amorites, Canaanites, Girgashites, and Jebusites. In contrast, Exodus 3:8 only lists the Canaanite, the Hittite, the Amorite, the Perizzite, the Hivite, and the Jebusite. How those other Biblical lists of Canaanite tribes agree with the genealogical listing of Canaan's sons has been subject to much discussion. It has further been argued that the Biblical term Canaanite is actually synecdoche, referring to both the broader Canaanite nation and to a specific Canaanite tribe within that nation.[105]
Ann E. Killebrew states that the biblical ethnogenesis of Canaan is problematic, because there is archaeological and linguistic evidence that suggests that the ancient Israelites were largely Canaanites themselves.[101] In particular, they were a subset of Canaanite culture.[5][6] Alternatively, other scholars have suggested that the Israelites originated from the Shasu and other seminomadic peoples from the desert regions south of the Levant, only later settling in the highlands of Canaan.[106][107][108] It has been also suggested that the Hamitic origin myth could be a reference to Canaan's colonization by the Egyptians in the Late Bronze Age, who were Hamites according to the Hebrew Bible.[69]: 45
Volkmar Fritz argues that there are also dissimilarities in the material culture of the early Israelites and Canaanites, suggesting that the new settlers were unrelated to the former inhabitants of the Canaanite cities. While Fritz agrees that there are some similarities between the two cultures, he argues that this resulted from close contact between them over a long period. In his view, cultural similarities developed when nomadic Israelites entered the land and gradually formed close economic relationships with Canaanites. The Israelites eventually became self-sufficient in the highlands but retained aspects of the shared Canaanite material culture.[109]
Biblical scholar David Frankel argues that a narrative in the Books of Chronicles tenuously indicates the historical reality of Israel's ethnogenesis. In his view, the text makes reference to an established Israelite presence in Canaan before Joshua's conquest, which primarily consisted of Ephraimites.[110]
According to the Hebrew Bible, Canaan was located to the west of the Jordan River. The Canaanites were described as living "by the sea, and along by the side of the Jordan" (Book of Numbers 13:29)[111] and "around Jordan" (Book of Joshua 22:9).[112] More specifically, they inhabited the Mediterranean coastlands (Joshua 5:1), including Lebanon corresponding to Phoenicia (Isaiah 23:11) and the Gaza Strip corresponding to Philistia (Zephaniah 2:5) and the Jordan Valley (Joshua 11:3, Numbers 13:29, Genesis 13:12). Numbers 34:3–12 provide even more specific boundaries, which covered territory that was considered to be "small" by ancient standards.[113][114]
John N. Oswalt observes that "Canaan consists of the land west of the Jordan and is distinguished from the area east of the Jordan." Oswalt then goes on to say that in Scripture, Canaan "takes on a theological character" as "the land which is God's gift" and "the place of abundance".[115]
Whilst the inhabitants of Canaan are called Canaanites, they are also called Amorites, similar to the citizens of the multi-ethnic Soviet Union being called Russian, and Hethites/Hittites.[116] Abraham, the ancestor of the Israelites, was most likely an Amorite-Aramean, according to some early theories.[117]
Conquest of Canaan
Yahweh promises the land of Canaan to Abraham in the Book of Genesis and eventually delivers it to descendants of Abraham, the Israelites. The Hebrew Bible describes the Israelite conquest of Canaan in the "Former Prophets" (Nevi'im Rishonim, נביאים ראשונים), viz. the books of Joshua, Judges, Samuel, and Kings. These books give the narrative of the Israelites after the death of Moses and their entry into Canaan under the leadership of Joshua.[118] The renaming of the Land of Canaan as the Land of Israel marks the Israelite conquest of the Promised Land.[119]
The Canaanites (Hebrew: כנענים, Modern: Kna'anim, Tiberian: Kənaʻănîm) are said to have been one of seven "nations" driven out by the Israelites following the Exodus. The other nations were the Hittites, the Girgashites, the Amorites, the Perizzites, the Hivites, and the Jebusites (Deuteronomy 7:1). One of the 613 commandments prescribes that no inhabitants of the cities of six Canaanite nations, the same as mentioned in 7:1, minus the Girgashites, were to be left alive. (Deuteronomy 20:16).
Kingdom of Israel and Judah
After the Israelite conquest of Canaan, Canaan existed as a kritarchy and later, a monarchy.[120][121] Under the Israelite monarchy, the Israelite tribes were united as one kingdom. However, it split into the Kingdom of Israel and the Kingdom of Judah.[122]
In 738 BC, the Neo-Assyrian empire conquered the Kingdom of Israel. In 586 BC, the Kingdom of Judah was annexed into the Neo-Babylonian Empire. The city of Jerusalem fell after a siege which lasted either eighteen or thirty months.[123] By 586 BC, much of Judah was devastated, and the former kingdom suffered a steep decline of both economy and population.[124]
Significant figures
- Characters in the Hebrew Bible
- Canaan, son of Ham (Gen. 10:6)
- Sidon, firstborn son of Canaan (Gen. 10:15)
- Heth, son of Canaan (Gen. 10:15)
- Sihon, king of Amorites (Deut 1:4)
- Og, king of Bashan (Deut 1:4)
- Adonizedek, king of Jerusalem (Josh. 10:1)
- Debir, king of Eglon (Josh. 10:3)
- Jabin, name of two kings of Hazor (Josh. 11:1; Judges 5:6)
New Testament
"Canaan" (Ancient Greek: Χανάαν, romanized: Khanáan)[2] is used only twice in the New Testament: both times in Acts of the Apostles when paraphrasing Old Testament stories.[125] Additionally, the derivative "Khananaia" (Χαναναία, "Canaanite woman") is used in Matthew's version of the exorcism of the Syrophoenician woman's daughter, while the Gospel of Mark uses the term "Syrophoenician" (Συροφοινίκισσα). It is implied that the New Testament authors considered all non-Jewish inhabitants in the northern coastlines of Canaan to be Canaanite.[126]
In the King James Version of the Bible one of the disciples is known as Simon the Canaanite.[127]
Uses of the name
By the Second Temple period (530 BC – 70 AD), "Canaanite" in the Hebrew language had come to be not an ethnic designation, so much as a general synonym for "merchant", as it is interpreted in, for example, Book of Job 40:30, or Book of Proverbs 31:24.[128]
The name "Canaanites" is attested as the endonym of the people later known to the Ancient Greeks from c. 500 BC as Phoenicians,[7] and following the emigration of Canaanite-speakers to Carthage (founded in the 9th century BC), was also used as a self-designation by the Punics (chanani) of North Africa during Late Antiquity.
The Septuagint (3rd and 2nd century BC) mostly renders Canaan as Χαναάν (Khanaan), but on two occasions as "Phoenicia" (Exod 16:35 and Josh 5:12).[129]
Remove ads
Legacy
Summarize
Perspective
"Canaan" is used as a synonym of the Promised Land; for instance, it is used in this sense in the hymn "Canaan's Happy Shore", with the lines: "Oh, brothers, will you meet me, (3x)/On Canaan's happy shore," a hymn set to the tune later used in The Battle Hymn of the Republic.[130]
In the 1930s and 1940s, some Revisionist Zionist intellectuals in Mandatory Palestine founded the ideology of Canaanism, which sought to create a unique Hebrew identity, rooted in ancient Canaanite culture, rather than a Jewish one.[131]
Israeli Prime Minister David Ben-Gurion observed the contradictions between the secular and biblical records of Jewish indigeneity to Canaan, which was nonetheless affirmed in the Declaration of Independence. Whilst he used secular arguments to justify Jewish indigeneity, he argued that the biblical narrative of Abraham migrating to Canaan was a "reunion with indigenous Hebrews who shared his theological belief". He also argued that not all Hebrews joined Jacob's family when they migrated to Egypt and later, birthed the generation of the Hebrews that endured the Exodus.[132] Some professors find this view tenable, based on 1 Chronicles 7:20–24, which preserved heterodox traditions of Jewish indigeneity.[110][132]
Remove ads
See also
Notes
- /ˈkeɪnən/; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – KNʿN; Hebrew: כְּנַעַן – Kənáʿan, in pausa כְּנָעַן – Kənāʿan; Biblical Greek: Χαναάν – Khanaán; Arabic: كَنْعَانُ – Kan'ān
- The independent Canaanite city-states of the early Bronze Age (3000–2200 BC) were situated mostly in plains or coastal regions, surrounded by defensive walls built of mud brick and guarded by watchtowers. Most of the cities were surrounded by agricultural hamlets, which supplied their food needs (Shahin 2005, p. 4).
Remove ads
Citations
Sources
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads



