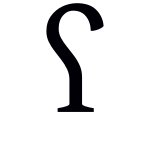Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Voiced pharyngeal fricative
Consonantal sound represented by ⟨ʕ⟩ in IPA From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
A voiced pharyngeal fricative or approximant is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʕ⟩.
Although the official classification of manner for this sound in the IPA is a fricative, spectrographic and acoustic studies have found that it is most often realized as an approximant.[1] The IPA symbol itself is ambiguous, as no language is known to make a phonemic distinction between voiced pharyngeal fricatives and approximants. For clarity, the approximant may be distinguished with the IPA diacritic for lowering, such as ⟨ʕ̞⟩.[2] Additionally, laryngoscopic studies by John Esling have shown the vowel ⟨ɑ⟩ to have distinct pharyngeal constriction and resonance in its articulation,[3] making ⟨ʕ̞⟩ the analogous semivowel of ⟨ɑ⟩. Esling furthers this notion in his expanded notation of the IPA chart; alongside merging pharyngeal and epiglottal consonants into a single column, he suggests that if it were spatially possible to align the vowel chart with the consonant chart, so that the relations between vowels and their semivowel counterparts are maintained (such as ⟨i⟩ below ⟨j⟩ and ⟨u⟩ below ⟨w⟩), then the vowels ⟨ɑ⟩ and ⟨ɒ⟩ should be placed under the combined pharyngeal/epiglottal column.[2]
The IPA letter ⟨ʕ⟩ is caseless. Capital ⟨⟩ and lower-case ⟨⟩ were added to Unicode in September, 2025 with version 17.0.[4]
Remove ads
Features
Features of a voiced pharyngeal approximant fricative:
- Its manner of articulation varies between approximant and fricative, which means it is produced by narrowing the vocal tract at the place of articulation, but generally not enough to produce much turbulence in the airstream. Languages do not distinguish voiced fricatives from approximants produced in the throat.
- Its place of articulation is pharyngeal, which means it is articulated with the tongue root against the back of the throat (the pharynx).
- Its phonation is voiced, which means the vocal cords vibrate during the articulation.
- It is an oral consonant, which means that air is not allowed to escape through the nose.
- It is a central consonant, which means it is produced by directing the airstream along the center of the tongue, rather than to the sides.
- Its airstream mechanism is pulmonic, which means it is articulated by pushing air only with the intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles, as in most sounds.
Remove ads
Occurrence
Summarize
Perspective
Pharyngeal consonants are not widespread. Sometimes, a pharyngeal approximant develops from a uvular approximant. Many languages that have been described as having pharyngeal fricatives or approximants turn out on closer inspection to have epiglottal consonants instead. For example, the candidate /ʕ/ sound in Arabic and standard Hebrew (not modern Hebrew – Israelis generally pronounce this as a glottal stop) has been variously described as a voiced epiglottal fricative [ʢ], an epiglottal approximant [ʕ̞],[5] or a pharyngealized glottal stop [ʔˤ].[6]
Remove ads
See also
Citations
General references
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads