OECD
intergovernmental economic organization From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is an international organisation of countries. Member countries of OECD all have a democratic system of government. They also accept the principle of a free economy. A country has a free economy when its government does not control the economic activities of its citizens and companies.
The OECD started 1948 as the Organisation for European Economic Co-operation (OEEC). The Second World War had just ended three years before in 1945. Some countries of Europe came together to form OEEC to help each other re-build their industry and other things destroyed in the Second World War. Later on, some non-European countries also joined this organisation. In 1960, OEEC changed its name, and it became OECD: the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
The OECD's headquarters are at the Château de la Muette in Paris.
Remove ads
Secretaries General
Remove ads
Members
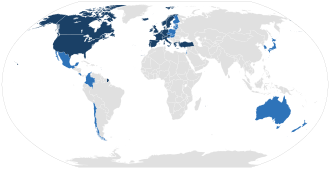
OECD has thirty-eight member countries,[7] of which 19 became members in 1961. These countries are:
- Austria
- Belgium
- Canada
- Denmark
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Luxembourg
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Portugal
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- United Kingdom
- United States
19 countries joined OECD after 1961. The names of these countries (with the year they joined in brackets), are:
Remove ads
References
Other websites
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads