Kuiper-toà
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Kuiper-toà (Kuiper belt) sī Thài-iông-hē lāi-té ùi Hái-ông-chheⁿ (Ji̍t-thaû sǹg--koè-lâi 30 AU) kaù 50 AU hit tah, kap n̂g-tō (ecliptic) kāng 1 ê pêⁿ-bīn.
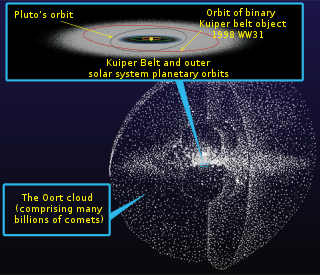
Kok-chè Thian-bûn Liân-bêng (International Astronomical Union, IAU) kā Kuiper-toà ê chheⁿ-thé hō-chò Hái-ông-chheⁿ goā chheⁿ-thé (trans-Neptunian object), sǹg sī 1 chióng sè lia̍p he̍k-chheⁿ (minor planet). Mā ū lâng kā kiò chò sió-he̍k-chheⁿ (asteroid).
Kuiper-toà ê chīn-pōng m̄ sī chhìn-chhái tēng--ê, hia ū 1 ê hō-chò "Kuiper-phāng" (Kuiper gap) iah "Kuiper-khàm" (Kuiper cliff) ê toā phoà-khiah. Sī án-choáⁿ ē án-ni-siⁿ? Ū 1 chióng lí-lūn kóng ū 1 lia̍p chhan-chhiūⁿ Tē-kiû iah Hoé-chheⁿ hiah toā lia̍p ê chheⁿ-thé kā hia ê iù-sap-á lóng saù kah lī-lī-lī.
Remove ads
Goā-pō͘ liân-kiat
- Dave Jewitt's page @ University of Hawaii
- The Kuiper Belt Electronic Newsletter Archived 2010-01-19 at the Wayback Machine.
- Wm. Robert Johnston's TNO page
- Minor Planet Center: Plot of the Outer Solar System, illustrating Kuiper gap
| Pún bûn-chiuⁿ sī chi̍t phiⁿ phí-á-kiáⁿ. Lí thang tàu khok-chhiong lâi pang-chō͘ Wikipedia. |
Remove ads
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
