
Tamil language
Dravidian language native to South India and Sri Lanka / From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Dear Wikiwand AI, let's keep it short by simply answering these key questions:
Can you list the top facts and stats about Tamil language?
Summarize this article for a 10 year old
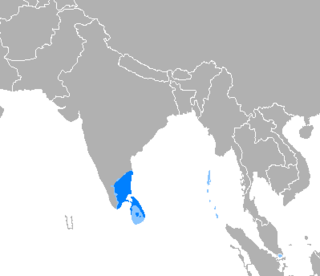
Tamil[lower-alpha 2] (தமிழ், Tamiḻ, pronounced [t̪amiɻ] ⓘ) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is an official language of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and union territory of Puducherry, and the sovereign nations of Sri Lanka and Singapore.[9][5] Tamil is also spoken by significant minorities in the four other South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is also spoken by the Tamil diaspora found in many countries, including Malaysia, Myanmar, South Africa, United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, Italy, Indonesia, and Mauritius. Tamil is also natively spoken by the Sri Lankan Moors. One of 22 scheduled languages in the Constitution of India, Tamil was the first to be classified as a classical language of India.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2024) |
| Tamil | |
|---|---|
| Tamiḻ | |
| தமிழ் | |
 The word "Tamil" in the Tamil script | |
| Pronunciation | [t̪amiɻ] ⓘ |
| Native to | India and Sri Lanka |
| Region |
|
| Ethnicity | |
Native speakers | L1: 79 million (2011–2019)[1] L2: 8 million (2011)[1] |
Early forms | |
| Dialects | |
| |
| Signed Tamil | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by | India |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | ta |
| ISO 639-2 | tam |
| ISO 639-3 | Either:tam – Modern Tamiloty – Old Tamil |
oty Old Tamil | |
| Glottolog | tami1289 Modern Tamiloldt1248 Old Tamil |
| Linguasphere | 49-EBE-a |
 | |
| This article contains IPA phonetic symbols. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols instead of Unicode characters. For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. | |
Tamil is one of the longest-surviving classical languages in the world.[10][11] A. K. Ramanujan described it as "the only language of contemporary India which is recognizably continuous with a classical past".[12] The variety and quality of classical Tamil literature has led to it being described as "one of the great classical traditions and literatures of the world".[13] Recorded Tamil literature has been documented for over 2000 years.[14] The earliest period of Tamil literature, Sangam literature, is dated from c. 300 BC until AD 300.[15][16] It has the oldest extant literature among Dravidian languages. The earliest epigraphic records found on rock edicts and 'hero stones' date from around the 3rd century BC.[17][18] About 60,000 of the approximately 100,000 inscriptions found by the Archaeological Survey of India in India are in Tamil Nadu. Of them, most are in Tamil, with only about 5 percent in other languages.[19] Tamil language inscriptions written in Brahmi script have been discovered in Sri Lanka and on trade goods in Thailand and Egypt.[20][21] The two earliest manuscripts from India,[22][23] acknowledged and registered by the UNESCO Memory of the World register in 1997 and 2005, were written in Tamil.[24]
In 1578, Portuguese Christian missionaries published a Tamil prayer book in old Tamil script named Thambiran Vanakkam, thus making Tamil the first Indian language to be printed and published.[25] The Tamil Lexicon, published by the University of Madras, was one of the earliest dictionaries published in Indian languages.[26] According to a 2001 survey, there were 1,863 newspapers published in Tamil, of which 353 were dailies.[27]