Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Tourism in Germany
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Germany is the seventh-most-visited country in the world,[1][2] with a total of 407.26 million overnights during 2012.[3] This number includes 68.83 million nights by foreign visitors, the majority of foreign tourists in 2009 coming from the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and Switzerland (see table). Additionally, more than 30% of Germans spend their holiday in their own country. According to Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Reports, Germany is ranked 3 out of 136 countries in the 2017 report, and is rated as one of the safest travel destinations worldwide.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2025) |
This article contains too many images for its overall length. (August 2025) |

In 2012, over 30.4 million international tourists arrived in Germany, bringing over US$38 billion in international tourism receipts to the country.[4] Domestic and international travel and tourism combined directly contribute over EUR43.2 billion to the German GDP. Including indirect and induced impacts, the industry contributes 4.5% of German GDP and supports 2 million jobs (4.8% of total employment).[5] The ITB Berlin is the world's leading tourism trade fair.[6]
According to surveys,[citation needed] the top three reasons for tourists to come to Germany are the German culture, outdoor activities, German holidays and festivities, the countryside and rural areas, and the German cities.[clarification needed]
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
The history of tourism in Germany goes back to cities and landscapes being visited for education and recreation. From the late 18th century onwards, cities like Dresden, Munich, Weimar and Berlin were major stops on a European Grand tour.
Spas and Seaside resorts on the North and Baltic Sea (e.g. Rugia and Usedom islands, Heiligendamm, the islands Norderney and Sylt) particularly developed during the 19th and early 20th century, when major train routes were built to connect the seaside spas to urban centers. An extensive bathing and recreation industry materialized in Germany around 1900. At rivers and close to natural landscapes (along the Middle Rhine valley and in Saxon Switzerland for example) many health spas, hotels and recreational facilities were established since the 19th century.
Since the end of World War II tourism has expanded greatly, as many tourists visit Germany to experience a sense of European history and the diverse German landscape. The country features 14 national parks, including the Jasmund National Park, the Vorpommern Lagoon Area National Park, the Müritz National Park, the Wadden Sea National Parks, the Harz National Park, the Hainich National Park, the Saxon Switzerland National Park, the Bavarian Forest National Park and the Berchtesgaden National Park. In addition, there are 14 Biosphere Reserves, as well as 98 nature parks.
The countryside has a pastoral aura, while the bigger cities exhibit both a modern and classical feel. Small and medium-sized cities often preserved their historical appearance and have old towns with remarkable architectural heritage – these are called Altstadt in German.
Remove ads
Statistics
Summarize
Perspective

 |




The table below shows the distribution of national and international visitor nights spent in each of the sixteen states of Germany in 2017.
Germany overall had 459 million visitor nights in 2017, of which 83 million were of foreign guests. With 94.3 million nights spent in hotels, hostels or clinics, Bavaria has the most visitors. With 18.4 nights per inhabitant, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern has the highest density of tourists per population (German average: 5.5 nights per inhabitant).[10]
Most visitors arriving to Germany on short-term basis are from the following countries of nationality:[11][12]
Surveys
The official body for tourism in Germany is the German National Tourist Board (GNTB), represented worldwide by National Tourist Offices in 29 countries. Surveys by the GNTB include perceptions and reasons for holidaying in Germany, which are as follows: culture (75%), outdoors/countryside (59%), cities (59%), cleanliness (47%), security (41%), modernity (36%), good hotels (35%), good gastronomy/cuisine (34%), good accessibility (30%), cosmopolitanism/hospitality (27%), good shopping opportunities (21%), exciting nightlife (17%) and good price/performance ratio (10%) (multiple answers were possible).
Remove ads
Countryside
Summarize
Perspective
Health
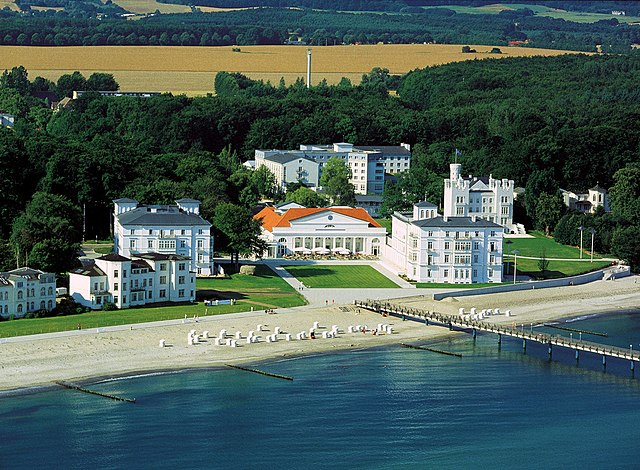

About 242 million nights, or two-thirds of all nights spent in hotels in Germany, are spent in spa towns.[13] Germany is well known for health tourism, with many of the numerous spa towns having been established at a hot spring, offering convalescence (German: Kur) or preventive care by means of mineral water and/or other spa treatment. Spa towns and seaside resorts carry official designations such as Mineral and mud spas (Mineral- und Moorbäder), Healthy climate resorts (Heilklimatische Kurorte), Kneipp cure resorts (Kneippkurorte = water therapy resorts), Seaside resorts (Seebäder), Climatic resorts (Luftkurorte), and Recreation resorts (Erholungsorte). The largest and most well known resorts also have casinos, most notably at Bad Wiessee, Baden-Baden (Kurhaus), Wiesbaden (Kurhaus), Aachen, Travemünde and Westerland (Kurhaus).
Regions


The most visited tourist regions in Germany are the East Frisian and North Frisian Islands, the Baltic Sea coasts of Holstein, Mecklenburg and Vorpommern, the Rhine Valley, the Bavarian and Black Forest, and the Bavarian Alps.
The table below shows the five most visited rural districts in 2008:[14]
Other popular regions include
- in the north: Usedom, Holstein Switzerland, the Lüneburg Heath, Harz and Mecklenburg Lake District
- in the west: Teutoburg Forest, Sauerland, Eifel and the Moselle Valley
- in the east: Saxon Switzerland, Thuringian Forest, Ore Mountains and the Elbe Valley
- in the south: Taunus, Spessart, Rhön, Odenwald and Allgäu.
Theme routes

Since the 1930s, local and regional governments have set up various theme routes, to help visitors get to know a specific region and its cultural or scenic qualities. The table below shows some of the most prominent theme routes. Other popular German theme routes include parts of the European Route of Brick Gothic and European Route of Industrial Heritage, the Harz-Heide Road, Bertha Benz Memorial Route and Bergstrasse.
Winter sport

The main winter sport regions in Germany are the Bavarian Alps and Northern Limestone Alps, as well as the Ore Mountains, Harz Mountains, Fichtel Mountains and Bavarian Forest within the Central Uplands. First class winter sport infrastructure is available for alpine skiing and snowboarding, bobsledding and cross-country skiing.
In most regions, winter sports are limited to the winter months November to February. During the Advent season, many German towns and cities host Christmas markets.
Remove ads
Cities
Summarize
Perspective
In terms of numbers of overnight stays, travel to the twelve largest cities in Germany more than doubled between 1995 and 2005, the largest increase of any travel destination.[15][citation needed] This increase mainly arises from growth of cultural tourism, often in conjunction with educational or business travel. Consequently, the provision and supply of more and higher standards of cultural, entertainment, hospitality, gastronomic, and retail services also attract more international guests.
The table below shows the ten most visited cities in Germany in 2012. Other cities and towns with over 1 million nights per year are Rostock, Hannover, Bremen, Cuxhaven, Bonn, Freiburg, Münster, Lübeck, Wiesbaden, Essen and Regensburg.
Berlin

Berlin has a yearly total of about 135 million day visitors, which puts it in third place among the most-visited city destinations in the European Union. Berlin had 781 hotels with over 125,000 beds in June 2012.[17] The city recorded 20.8 million overnight hotel stays and 9.1 million hotel guests in 2010.[18] In the first half of 2012, there was an increase of over 10% compared to the same period the year before.[17]
Munich
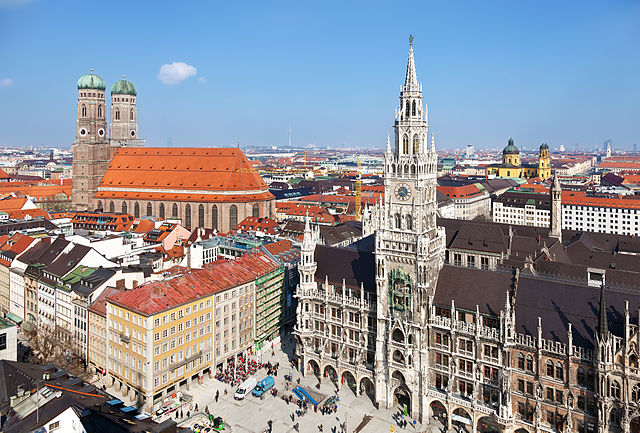

Munich, the capital of Bavaria, is one of Germany’s most popular tourist destinations, known for its rich history, vibrant culture, and architectural beauty. At the heart of the city lies Marienplatz, the central square featuring the Neues Rathaus with its famous Glockenspiel, which draws crowds daily for its animated show.
A short walk away is Frauenkirche, Munich’s iconic cathedral with its twin domes and panoramic city views. The Munich Residenz, once the royal palace of Bavarian monarchs, now houses a museum complex showcasing centuries of art, furniture, and jewels.
For art lovers, the Kunstareal features world-class museums like the Alte Pinakothek, Neue Pinakothek, and Pinakothek der Moderne, each covering different periods of European art. Families often enjoy the Deutsches Museum, one of the largest science and technology museums in the world.
Munich also offers green escapes, such as the expansive Englischer Garten, larger than New York’s Central Park, complete with beer gardens and even river surfing. Nymphenburg Palace, with its baroque architecture and gardens, offers a glimpse into royal life.
The city’s mix of tradition and innovation makes it a must-visit destination in Germany.
Hamburg

In 2007, more than 3,985,105 visitors with 7,402,423 overnight stays visited Hamburg.[19] The tourism sector employs more than 175,000 people full-time and brings in revenue of €9.3 billion, making the tourism industry a major economic force in the Hamburg Metropolitan Region. Hamburg has one of the fastest-growing tourism industries in Germany. From 2001 to 2007, the overnight stays in the city increased by 55.2% (Berlin +52.7%, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania +33%).[20]
A typical Hamburg visit includes a tour of the city hall and the grand church St. Michaelis (called the Michel), and visiting the old warehouse district (Speicherstadt) and the harbour promenade (Landungsbrücken). Sightseeing buses connect these points of interest. As Hamburg is one of the world's largest harbours many visitors take one of the harbour and/or canal boat tours (Große Hafenrundfahrt, Fleetfahrt) which start from the Landungsbrücken. Major destinations also include museums.
The area of Reeperbahn in the quarter St. Pauli is Europe's largest red light district and home of strip clubs, brothels, bars and nightclubs. The Beatles had stints on the Reeperbahn early in their careers. Others prefer the laid-back neighbourhood Schanze with its street cafés, or a barbecue on one of the beaches along the river Elbe. Hamburg's famous zoo, the Tierpark Hagenbeck, was founded in 1907 by Carl Hagenbeck as the first zoo with moated, barless enclosures.[21]
Gallery
- The Brandenburg Gate at night. Berlin is Germany's largest and most visited city.
- View over Hamburg Binnenalster
- Heidelberg with its famous Castle ruins
- The Semperoper in Dresden is the most famous building of an opera house in Germany.
- View over Nuremberg's Old Town from the Nuremberg Castle
- View over Leipzig old town, Germany's Boomtown
- View over Quedlinburg
- The small town of Rothenburg ob der Tauber is a destination for tourists from around the world.
- The Kongresshalle (Congress Hall) on the Nazi party rally grounds in Nuremberg
- View over Munich's Old Town
- The Aula Palatina of Trier, a basilica constructed during the reign of the Roman emperor Constantine I (r. 306–337 AD)
- The Palatine Chapel, Aachen, built during the reign of the Carolingian emperor Charlemagne (r. 800-814 AD)
Events
The table below shows some of the largest annually recurring events in Germany:
Note: This list only includes the largest, annually recurring events in selected categories. This list may be incomplete.
Trade fairs


Germany is home to several of the world's largest trade fairgrounds, and many of the international exhibitions are considered trend-setters or industry leaders. Thousands of national and international trade fairs, conventions and congresses are held in Germany annually. In 2008, 10.3 million people visited the 150 largest trade fairs alone. More than half of these visitors come from abroad, more than one third from countries outside Europe. The table below shows some of the most visited trade fairs.
Note: This list only includes trade fairs with 250,000 visitors per year or more. This list may be incomplete.
Remove ads
Most visited
Summarize
Perspective
Protected areas
The table below shows the most visited protected areas in Germany.
- View from Mt. Lusen in the Bavarian Forest over the Alpine Foreland
- Wilseder Berg in the Lüneburg Heath
Note: This list only includes protected areas with 1 million or more visitors per year. This list may be incomplete.
Landmarks
The German Tourism Association (Deutscher Tourismusverband) irregularly publishes statistics on the most visited landmarks. With an average of over 6 million visitors entering Cologne Cathedral per year, the cathedral is Germany's most visited landmark. Second and third places go to the Reichstag building in Berlin and the Hofbräuhaus in Munich. Other much visited architectural landmarks include the Drosselgasse in Rüdesheim (3.0m), the medieval old towns of Rothenburg ob der Tauber (2.5m), Regensburg (2.0m), Frauenkirche in Dresden (2.5m), Bad Münstereifel (2m), the Brandenburg Gate in Berlin and the Holsten Gate in Lübeck 1.
Note: This list only includes physical landmarks with 1.0 million visitors per year or more. This list may be incomplete.
Theme parks
The table below shows some of the most visited theme parks or related facilities in Germany.

Note: This list only includes the largest theme parks/facilities in selected categories. This list may be incomplete.
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads