Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Formula One
Motorsport championship held worldwide From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Formula One (F1) is the highest class of worldwide racing for open-wheel, single-seater formula racing cars run by Formula One Group and sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The FIA Formula One World Championship has been one of the world's premier forms of motorsport since its inaugural running in 1950 and is often considered to be the pinnacle of motorsport. The word formula in the name refers to the set of rules all participant cars must follow. A Formula One season consists of a series of races, known as Grands Prix. Grands Prix take place in multiple countries and continents on either purpose-built circuits or closed roads.
A points scoring system is used at Grands Prix to determine two annual World Championships: one for the drivers, and one for the constructors—now synonymous with teams. Each driver must hold a valid Super Licence, the highest class of racing licence the FIA issues, and the races must be held on Grade One tracks, the highest grade rating the FIA issues for circuits.
Formula One cars are the world's fastest regulated road-course racing cars, owing to high cornering speeds achieved by generating large amounts of aerodynamic downforce, most of which is generated by front and rear wings, as well as underbody tunnels. The cars depend on electronics, aerodynamics, suspension, and tyres. Traction control, launch control, automatic shifting, and other electronic driving aids were first banned in 1994. They were briefly reintroduced in 2001 but were banned once more in 2004 and later 2008.
With the average annual cost of running a team—e.g., designing, building, and maintaining cars; staff payroll; transport—at approximately £193 million as of 2018 (though the cost cap stands at US$215 million), Formula One's financial and political battles are widely reported. The Formula One Group is owned by Liberty Media, which acquired it in 2017 for US$8 billion. The United Kingdom is the hub of Formula One racing, with six out of the ten teams based there.
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
Formula One originated from the World Manufacturers' Championship (1925–1930) and European Drivers' Championship (1931–1939). The formula is a set of rules that all participants' cars must follow. Before World War II, several Grand Prix racing organisations made suggestions for a new championship to replace the European Championship, but due to the suspension of racing during the conflict, a new International Formula for cars did not become formalised until after the war. Formula One was a formula agreed upon in 1946 to officially become effective in 1947. The first Grand Prix in accordance with the new regulations was the 1946 Turin Grand Prix, anticipating the formula's official start. The new World Championship was instituted to commence in 1950.[1][2][3]
The first world championship race, the 1950 British Grand Prix, took place at Silverstone Circuit in the United Kingdom on 13 May 1950.[4] Giuseppe Farina, competing for Alfa Romeo, won the first Drivers' World Championship, narrowly defeating his teammate Juan Manuel Fangio. Fangio won the championship in 1951, 1954, 1955, 1956, and 1957.[5] This set the record for the most World Championships won by a single driver, a record that stood for 46 years until Michael Schumacher won his sixth championship in 2003.[5]
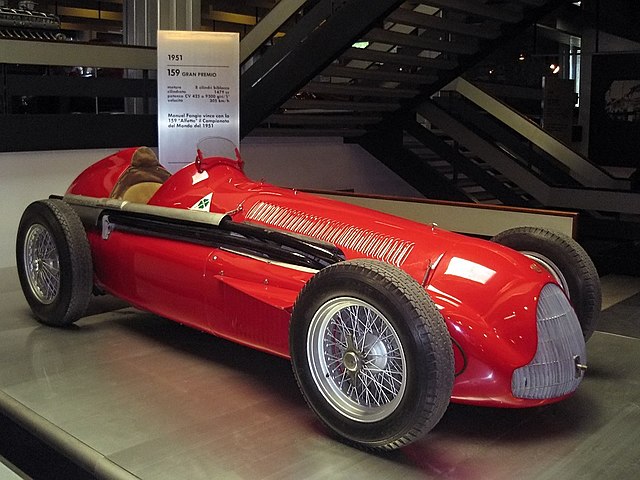

A Constructors' Championship was added in the 1958 season. Stirling Moss, despite often being regarded as one of the greatest Formula One drivers in the 1950s and 1960s, never won the Formula One championship.[6] Between 1955 and 1961, Moss finished in second in the championship four times and in third the other three times.[7][8] Fangio won 24 of the 52 races he entered—still the record for the highest Formula One winning percentage by an individual driver.[9]
Promoters also held races following Formula One regulations outside the championship for many years.[10] These events often took place on circuits that were not always suitable for the World Championship and featured local cars and drivers as well as those competing in the championship.[11] For example, South Africa's domestic Formula One championship from 1960 to 1975 used locally built or modified cars in addition to recently retired world championship cars.[12] Similarly, the British Formula One Championship utilised second-hand cars, from manufacturers such as Lotus and Fittipaldi Automotive, fitted with DFV from 1978 to 1980.[13] The increasing cost of competition, however, made such competitions less common in the 1970s. 1983 saw the last non-championship Formula One race; the 1983 Race of Champions at Brands Hatch, won by reigning World Champion Keke Rosberg in a Williams-Cosworth in a close fight with American Danny Sullivan.[11]
Technological developments

The first major technological development in the series was Bugatti's introduction of mid-engined cars. Jack Brabham, the world champion in 1959, 1960, and 1966, soon proved the mid-engine's superiority over all other engine positions. By 1961, all teams had switched to mid-engined cars. The Ferguson P99, a four-wheel drive design, was the last front-engined Formula One car to enter a world championship race. It entered the 1961 British Grand Prix, the only front-engined car to compete that year.[14]
In 1962, Lotus introduced a car with an aluminium-sheet monocoque chassis instead of the traditional space-frame design. This proved to be the greatest technological breakthrough since the introduction of mid-engined cars.[15]
In 1968, sponsorship was introduced to the sport. Team Gunston became the first team to run cigarette sponsorship on its Brabham cars, which privately entered in the orange, brown, and gold colours of Gunston cigarettes in the 1968 South African Grand Prix on 1 January 1968.[16] Five months later, Lotus, initially using British racing green, followed this example when it entered its cars painted in the red, gold, and white colours of Imperial Tobacco's Gold Leaf livery at the 1968 Spanish Grand Prix.[17]
Aerodynamic downforce slowly gained importance in car design with the appearance of aerofoils during the 1968 season. The wings were introduced by Lotus's owner, Colin Chapman, who installed modest front wings and a rear spoiler on his Lotus 49B at the 1968 Monaco Grand Prix. In the late 1970s, Lotus introduced ground-effect aerodynamics, previously used on Jim Hall's Chaparral 2J in 1970, that provided enormous downforce and greatly increased cornering speeds. The aerodynamic forces pressing the cars to the track were up to five times the car's weight. As a result, extremely stiff springs were needed to maintain a constant ride height, leaving the suspension virtually solid. This meant that the drivers depended entirely on the tyres for any small amount of cushioning of the car and driver from irregularities in the road surface.[18]
Big business
Beginning in the 1970s, Bernie Ecclestone rearranged the management of Formula One's commercial rights; he is widely credited with transforming the series into the multi-billion dollar business it now is.[19][20] When Ecclestone bought the Brabham team in 1971, he gained a seat on the Formula One Constructors' Association (FOCA), and in 1978 he became its president.[21] Previously, the circuit owners controlled the income of the teams and negotiated with each individually; Ecclestone persuaded the teams to "hunt as a pack" through FOCA.[20] He offered Formula One to circuit owners as a package they could take or leave. In return for the package, almost all that was required was to surrender trackside advertising.[19]
The formation of the Fédération Internationale du Sport Automobile (FISA) in 1979 set off the FISA–FOCA war, during which FISA and its president, Jean-Marie Balestre, argued repeatedly with FOCA over television revenues and technical regulations.[22] The Guardian said that Ecclestone and Max Mosley "used [FOCA] to wage a guerrilla war with a very long-term aim in view". FOCA threatened to establish a rival series and boycotted a Grand Prix, and FISA withdrew its sanction from races.[19] The result was the 1981 Concorde Agreement, which guaranteed technical stability, as teams were to be given reasonable notice of new regulations.[23][24] The teams signed a second Concorde Agreement in 1992 and a third in 1997.[23]
FISA imposed a ban on ground-effect aerodynamics from 1983.[25] But by then, turbocharged engines, which Renault had pioneered in 1977, were producing over 520 kW (700 bhp) and were essential to be competitive. By 1986, a BMW turbocharged engine achieved a flash reading of 5.5 bar (80 psi) of pressure, which was estimated to be over 970 kW (1,300 bhp), in qualifying for the Italian Grand Prix. The next year, power in race trim reached around 820 kW (1,100 bhp), with boost pressure limited to only 4 bar (58 psi).[26] These cars were the most powerful open-wheel circuit racing cars ever. To reduce engine power output and thus speeds, the FIA limited fuel tank capacity in 1984, and boost pressures in 1988, before banning turbocharged engines completely in 1989.[27]
The development of electronic driver aids began in the 1980s. Lotus began to develop a system of active suspension, which first appeared in 1983 on the Lotus 92.[28] By 1987, this system had been perfected and was driven to victory by Ayrton Senna in the Monaco Grand Prix that year. In the early 1990s, other teams followed suit, and semi-automatic gearboxes and traction control were a natural progression. The FIA, due to complaints that technology was determining races' outcomes more than driver skill, banned many such aids for the 1994 season. This resulted in cars that previously depended on electronic aids becoming very "twitchy" and difficult to drive. Observers felt the ban on driver aids was in name only, as they "proved difficult to police effectively".[29][30]

The rivalry between Ayrton Senna and Alain Prost became F1's central focus in 1988 and continued until Prost retired at the end of 1993.[31] Senna died at the 1994 San Marino Grand Prix after crashing into a wall on the exit of the Tamburello curve.[32] Roland Ratzenberger also died in an accident during Saturday qualifying that weekend.[33]
Since Senna's and Ratzenberger's deaths, the FIA has used safety as a reason to impose rule changes that otherwise, under the Concorde Agreement, would have had to be agreed upon by all the teams. The resultant 'narrow track' era from 1998 onwards resulted in cars with smaller rear tyres, a narrower track overall, and the introduction of grooved tyres to reduce mechanical grip. According to the FIA, the objective behind this decision was to reduce cornering speeds and produce racing similar to rainy conditions by enforcing a smaller contact patch between the tyre and the track.[34]
No driver died of injuries sustained on the track at the wheel of a Formula One car for 20 years until the 2014 Japanese Grand Prix, where Jules Bianchi collided with a recovery vehicle after aquaplaning off the circuit, dying on 17 July 2015 from his injuries.[35]
Manufacturers' return

Michael Schumacher and Ferrari won five consecutive Drivers' Championships and six consecutive Constructors' Championships. Schumacher set many new records, including those for Grand Prix wins, wins in a season, and most Drivers' Championships.[36] Schumacher's championship streak ended on 25 September 2005, when Renault driver Fernando Alonso became Formula One's youngest champion at that time (until Lewis Hamilton in 2008 and followed by Sebastian Vettel in 2010).[37] In 2006, Renault and Alonso won both titles again.[38][39] Schumacher retired at the end of 2006, after 16 years in Formula One, but came out of retirement for the 2010 season, racing for the newly formed Mercedes works team, following the rebrand of Brawn GP.[40]
During this period, FIA frequently changed the championship rules with the intention of improving the on-track action and cutting costs.[41] Team orders, legal since the championship started in 1950, were banned in 2002, after several incidents in which teams openly manipulated race results, generating negative publicity, most famously by Ferrari at the 2002 Austrian Grand Prix.[42] Other changes included the qualifying format, the point-scoring system,[43] the technical regulations,[44] and rules specifying how long engines and tyres must last.[45] A 'tyre war' between suppliers Michelin and Bridgestone saw lap times fall. At the 2005 United States Grand Prix at Indianapolis, seven out of ten teams did not race when their Michelin tyres were deemed unsafe for use, leading to Bridgestone becoming the sole tyre supplier to Formula One for the 2007 season by default.[46] On 20 December 2007, Bridgestone signed a contract that officially made it the exclusive tyre supplier for the next three seasons.[47]
Manufacturers' decline and return of the privateers
In 2008 and 2009, Honda, BMW, and Toyota all withdrew from Formula One racing within a year, blaming the economic recession. This resulted in the end of manufacturer dominance of the sport. The Honda F1 team went through a management buyout to become Brawn GP, with Ross Brawn and Nick Fry owning and running the majority of the organisation. Brawn GP laid off hundreds of employees, but won the year's world championships. BMW F1 was bought out by the founder of the team, Peter Sauber. The Lotus F1 Team[a] was another, formerly manufacturer-owned team that reverted to "privateer" ownership, together with the buy-out of the Renault team by Genii Capital investors. A link with its previous owners, however, still survived, with its car continuing to be powered by a Renault engine until 2018.[48]
McLaren also announced that it was to reacquire the shares in its team from Mercedes-Benz.[49] McLaren's partnership with Mercedes was reported to have started to sour after the former was guilty of spying on Ferrari.[50] Hence, during the 2010 season, Mercedes-Benz re-entered the series as a manufacturer after it purchased Brawn GP and split with McLaren after 15 seasons with the team.[51]
During the 2009 season, Formula One was gripped by the FIA–FOTA dispute. FIA President Max Mosley proposed numerous cost-cutting measures for the next season, including an optional budget cap for the teams;[52] teams electing to take the budget cap would be granted greater technical freedom, adjustable front and rear wings, and an engine not subject to a rev limiter.[52] The Formula One Teams Association (FOTA) believed that allowing some teams to have such technical freedom would have created a two-tier championship, and thus requested urgent talks with the FIA. Talks broke down and the FOTA teams, with the exception of Williams and Force India,[53][54] announced that "they had no choice" but to form a breakaway championship series.[54]

On 24 June, Formula One's governing body and the teams reached an agreement to prevent a breakaway series. It was agreed that teams must cut spending to the level of the early 1990s within two years, exact figures were not specified; and Max Mosley agreed he would not stand for reelection to the FIA presidency in October.[55] Following further disagreements, after Mosley suggested he would stand for reelection,[56] the FOTA made it clear that breakaway plans were still being pursued. On 8 July, the FOTA issued a press release stating it had been informed it was not entered for the 2010 season,[57] and, as an FIA press release stated, the FOTA representatives had walked out of the meeting.[58] On 1 August, it was announced that the FIA and FOTA had signed a new Concorde Agreement, bringing an end to the crisis and securing the sport's future until 2012.[59]
To compensate for the loss of manufacturer teams, four new teams were accepted into the 2010 season ahead of a much-anticipated "cost-cap". Entrants included a reborn Team Lotus—led by a Malaysian consortium including Tony Fernandes, the boss of Air Asia; Hispania Racing—the first Spanish Formula One team; and Virgin Racing—Richard Branson's entry into the series following a successful partnership with Brawn the year before. They were also joined by the US F1 Team, which planned to operate out of the United States as the only non-European-based team in the sport. Financial issues befell the teams before they even made the grid.[60] Despite the entry of these new teams, the proposed cost-cap was repealed and these teams—which did not have the budgets of the midfield and top-flight teams—ran around at the back of the field until they collapsed: HRT in 2012,[61] Caterham (formerly Lotus) in 2014,[62] and Manor (formerly Virgin, then Marussia), having survived falling into administration in 2014, at the end of 2016.[63]
Hybrid era
A major rule change in 2014 saw the 2.4-litre naturally aspirated V8 engines replaced by 1.6-litre turbocharged hybrid power units.[64] This prompted Honda to return to the series in 2015 as the championship's fourth power-unit manufacturer.[65] Mercedes emerged as the dominant force, with Lewis Hamilton winning the championship, closely followed by his main rival and teammate, Nico Rosberg, with the team winning 16 out of the 19 races that season.[66] The team continued this form in the next two seasons, again winning 16 races in 2015[67] before taking a record 19 wins in 2016,[68] with Hamilton claiming the title in the former year[69] and Rosberg winning it in the latter, by five points.[70] The 2016 season also saw a new team, Haas, join the grid,[71] while Max Verstappen became the youngest-ever race winner at age 18 in Spain.[72]

After revised aerodynamic regulations were introduced, the 2017 and 2018 seasons featured a title battle between Mercedes and Ferrari.[73][74] Mercedes ultimately won the titles with multiple races to spare and continued to dominate until 2020.[75][76][77][78] In 2021, the Honda-powered Red Bull team began to seriously challenge Mercedes, with Verstappen beating Hamilton to the Drivers' Championship after a season-long battle that saw the pair exchange the championship lead multiple times.[79]
This era has seen an increase in car manufacturers' presence in the sport. After Honda's return as an engine manufacturer in 2015, Renault came back as a team in 2016, upon buying back the Lotus F1 Team.[80] In 2018, Aston Martin and Alfa Romeo became Red Bull and Sauber's title sponsors, respectively.[81][82] Sauber was rebranded as Alfa Romeo Racing for the 2019 season.[83] Racing Point part-owner Lawrence Stroll bought a stake in Aston Martin to rebrand the Racing Point team as Aston Martin for the 2021 season.[84] In August 2020, all ten F1 teams signed a new Concorde Agreement committing them to the sport until 2025, including a $145 million budget cap for car development to support equal competition and sustainable development.[85][86]
The COVID-19 pandemic forced the series to adapt to budgetary and logistical limitations. A significant overhaul of the technical regulations intended to be introduced in the 2021 season was pushed back to 2022,[87] with constructors instead using their 2020 chassis for two seasons, and the introduction of a token system that limited which parts could be modified.[88] The start of the 2020 season was delayed by several months,[89] and both it and the 2021 seasons were subject to several postponements, cancellations, and rescheduling of races due to shifting restrictions on international travel. Many races took place behind closed doors and with only essential personnel present in order to adhere to rules regarding social distancing.[90]
In 2022, the F1 governing body announced a major rule and car design change intended to promote closer racing through the use of ground effects, new aerodynamics, larger wheels with low-profile tyres, and redesigned nose and wing regulations.[91][92] Red Bull emerged as the dominant force after the rule shakeup. The 2022 and 2023 Constructors' and Drivers' championships were won by Red Bull and Verstappen, with multiple races to spare.[93][94][95][96]
In early 2024, the Formula One landscape underwent a significant change in the sphere of team sponsorships and collaborations. Having competed for five seasons under the Alfa Romeo name, Sauber introduced a title partnership with the online casino Stake, resulting in the team's new identity as Stake F1 Team Kick Sauber. Sauber would hold Stake's sponsorship name until the end of 2025, after which it would become the Audi works team for the 2026 season onwards.[97][98] Scuderia AlphaTauri, Red Bull's junior team, dropped its name and took on sponsors from Hugo Boss and Cash App, becoming Visa Cash App RB, or VCARB for 2024.[99] Also in 2024, Formula One announced partnerships with Mattel to release Hot Wheels die-cast cars,[100] and with Lego, with the first new sets releasing in 2025.[101] In early 2025, Cadillac received final approval to join the Formula One grid as an 11th team for the 2026 season onward.[102]
Remove ads
Racing
Summarize
Perspective
A Formula One Grand Prix event spans a weekend. It typically begins with two free practice sessions on Friday and one free practice session on Saturday. Additional drivers (commonly known as third drivers) are allowed to run on Fridays, but only two cars may be used per team, requiring a race driver to give up their seat. A qualifying session is held after the last free practice session. This session determines the starting order for the race on Sunday.[103][104]
Tyre rules

Each driver is allotted four sets of intermediate tyres, three sets of wet-weather tyres and thirteen sets of dry-weather tyres for each race weekend. All unused tyres must be returned.[105]
Qualifying
For much of the sport's history, qualifying sessions differed little from practice sessions; drivers would have one or more sessions in which to set their fastest time, with the grid order determined by each driver's best single lap, with the fastest getting first place on the grid, referred to as the pole position. From 1996 to 2002, the format was a one-hour shootout. Following this, the rules were changed again because the teams were not running in the early part of the session to take advantage of better track conditions later on.[106]
The current qualifying format, known as "knock-out" qualifying, was introduced in the 2006 season. It is divided into three stages, referred to as Q1, Q2, and Q3. Drivers may complete as many laps as they choose in an attempt to progress to the next stage, with the slowest drivers being eliminated at the end of each round. Any timed lap started before the end of that period may be completed and will count toward that driver's placement. The number of cars eliminated in each session is dependent on the total number of cars entered in the championship.[107]
As of 2025[update], with 20 cars on the grid, Q1 runs for 18 minutes and eliminates the slowest five drivers. During this session, any driver whose best lap takes longer than 107% of the fastest time in Q1 will not be allowed to start the race without permission from the stewards.[108] In Q2, the 15 remaining drivers have 15 minutes to set one of the ten fastest times and proceed to the next period. Finally, Q3 lasts 12 minutes and determines the first ten grid positions.[109]
Each car is allocated one set of the softest tyres for use in Q3. The cars that qualify for Q3 must return them after the session; the cars that do not qualify for the round can use them during the race.[110] Any penalties that affect grid position are applied at the end of qualifying.[111]
Sprints
2021 saw the tryout of a "sprint qualifying" race on the Saturday of three race weekends, with the intention of testing a new approach to qualifying. The traditional qualifying would determine the starting order for the sprint, and the result of the sprint would then determine the start order for the Grand Prix.[112] From 2023, sprint races no longer impacted the start order for the main race, which would be determined by traditional qualifying. Sprints would have their own qualifying session, titled the "sprint shootout".[113] Sprint qualifying sessions are much shorter than traditional qualifying runs, and each session requires teams to fit new tyres, mediums for SQ1 and SQ2, and softs for SQ3.[114]
Race
The race begins with a formation lap to allow the drivers to check the condition of their car and the track, and to warm up their tyres to increase traction and grip [115], after which the cars assemble on the starting grid in the order they qualified.

Once all the cars have lined up on the grid, the medical car positions itself behind the pack.[116] Five red lights are then illuminated above the track at intervals of one second; before being extinguished simultaneously after an unspecified time to signal the start of the race.[117] The start procedure may be aborted in the event of a serious accident, dangerous conditions, or if a driver stalls on the grid or on the track in an unsafe position, signalled by raising their arm.[118] The race may also be started from behind the Safety Car if a racing start is considered excessively dangerous, such as in extremely heavy rainfall. There is no formation lap in such a circumstance.[119]
Throughout the race, drivers may make pit stops to change tyres and repair damage. Three dry tyre compounds, with different durability and adhesion characteristics, are available to drivers. Under wet conditions, drivers may switch to one of two specialised wet-weather tyres with additional grooves. Over the course of a race, drivers must make at least one pit stop and use two different available tyre compounds.[120][b]
The race finishes when the leader has completed the predetermined number of laps.[c] Positions for drivers on the same lap are then determined in the order that they cross the finish line. Lapped cars that have completed at least 90% of the distance are then classified according to their relative track position and number of laps completed. Races can, however, be paused or ended early if the conditions become unsafe. In the case of suspension, a ten-minute warning is given before the race is resumed behind the safety car.[122]
Race director
This race director manages the logistics of each F1 Grand Prix, enforcing FIA rules and controlling the lights at the start of each race.[123] The race director can also refer incidents to the race stewards, who may impose penalties, such as drive-through penalties (or stop-and-go penalties), demotions on a pre-race start grid, race disqualifications, and fines, should parties break regulations. As of the 2024 Las Vegas Grand Prix, the race director is Rui Marques, with Herbie Blash as a permanent advisor.[124][125]
Safety car
The Mercedes-AMG GT R (top) and Aston Martin (bottom) safety cars at the 2019 Hungarian Grand Prix and 2022 Emilia Romagna Grand Prix, respectively
In the event of an incident that risks the safety of competitors or trackside race marshals, race officials may choose to deploy the safety car. This neutralises the race, with drivers required to follow the safety car in race order at reduced speed, and overtaking is not allowed. Lapped cars may, if permitted by the race director, be allowed to unlap themselves in order to ensure a smoother restart. The safety car remains on the track until the danger is cleared. After the safety car comes off the track, the race restarts with a rolling start, with the leading car taking over its role until they reach the timing line. Pit stops under a safety car are permitted, and in many cases can offer a great advantage to teams who can pit and change tyres before the end of the safety car period.[126]
Mercedes-Benz has supplied a variety of its AMG models to Formula One to use as the safety car since 1996.[127] From 2021 onwards, Aston Martin has supplied the Vantage to share duties with Mercedes-AMGs.[128] Since 2000, the main safety car driver has been German ex-racing driver Bernd Mayländer.[129] He is usually joined by FIA technical assistant Richard Darker, who relays information between the safety car and race control.[130]
Virtual Safety Car (VSC)
In 2014, the FIA established an "accident panel" to investigate the circumstances surrounding Jules Bianchi's fatal crash at the Japanese Grand Prix.[131] They were tasked with identifying measures to reduce the risk of similar incidents, particularly in situations where deploying a safety car is not justified and yellow flags alone are inadequate.[132]
One of the recommendations was the introduction of a Virtual Safety Car period during which drivers must keep their lap times above a pre-determined minimum, also known as keeping a positive delta.[133] The system was first implemented during the 2015 Monaco Grand Prix.[134]
Flags
Flags specifications and usage are prescribed by Appendix H of the FIA's International Sporting Code.[135]
Points system
Various systems for awarding championship points have been used since 1950. The current system, in place since 2010,[d] awards the top ten cars points in the Drivers' and Constructors' Championships, with the winner receiving 25 points. Points won at each race are added up, and the driver and constructor with the most points at the end of the season are crowned World Champions.[137]
A driver must be classified to receive points. They must complete at least 90% of the race distance to receive points. Therefore, it is possible for a driver to receive points even if they retired before the end of the race.[138]
From some time between the 1977 and 1980 seasons to the end of the 2021 season, if less than 75% of the race laps were completed by the winner, then only half of the points listed in the table were awarded to drivers and constructors. The half-points rule was replaced by a distance-dependent, gradual-scale system for 2022.[139]
Remove ads
Constructors
Summarize
Perspective

A Formula One constructor is the entity credited with designing the chassis and the engine.[140] If both are designed by the same company, that company receives sole credit as the constructor (e.g., Ferrari). If they are designed by different companies, both are credited, with the name of the chassis designer being placed before that of the engine designer (e.g., McLaren-Mercedes). All constructors are scored individually, even if they share a chassis or engine with another constructor.[141] Entering a new team in the Formula One World Championship requires a $450 million up-front payment to the FIA, which is then shared equally among the existing teams.[142]
Since 1981, Formula One teams have been required to build the chassis in which they compete.[143] This requirement distinguishes Formula One from series, such as the IndyCar Series, that allows teams to purchase chassis, and "spec series", such as Formula 2, that require all cars be built to identical specifications.[144][145] Despite this rule, however, two teams used chassis built by other teams in 2007. Super Aguri started the season using a modified Honda Racing RA106 chassis, while Scuderia Toro Rosso used the same chassis used as its parent Red Bull Racing team, which was formally designed by a separate subsidiary. The exploitation of these loopholes was ended for 2010 with the publication of new technical regulations, which require each constructor to own the intellectual property rights to their chassis,[146]

Nine out of the ten teams competing in Formula One have some form of base in England, in an area centred around Oxfordshire called "Motorsport Valley".[147][148][149] Ferrari is the only team to not have an English presence and have both their chassis and engine assembly in Maranello, Italy.[150] Racing Bulls is based close to Ferrari in Faenza but also has a base in Milton Keynes,[151] whilst Sauber is based in Hinwil, Switzerland, with a "technology centre" in Bicester.[152] Haas is U.S.-based and has its primary base in Kannapolis, North Carolina, with another facility in Banbury and a design office in Maranello.[149][153][154] The Cadillac team joining the grid in 2026 is set to have bases in Fishers, Indiana, Warren, Michigan, and Silverstone.[155]
Remove ads
Drivers
Summarize
Perspective

Every team in Formula One must run two cars in every session in a Grand Prix weekend, and every team may use up to four drivers in a season.[104] A team may also run two additional drivers during Free Practice sessions,[104] which are often used to test potential new drivers for a career as a Formula One driver or allow experienced drivers to evaluate the car.[156] Most drivers are typically contracted for at least the duration of a season,[157] with driver changes taking place in-between seasons.[158] Recent years, however, have seen a move away from this trend, with teams replacing drivers such as Daniel Ricciardo,[159] Logan Sargeant,[160] and Jack Doohan mid-season.[161]
Each competitor must be in the possession of an FIA Super Licence to compete in a Grand Prix,[162] a licence that is issued to drivers who have met the criteria of success in junior motorsport categories and have achieved 300 kilometres (190 mi) of running in a Formula One car in 2 days.[163][162] Teams can also contract reserve drivers to stand in for regular drivers when necessary and develop the team's car.[164] With the reduction in testing, however, the reserve drivers' role mainly takes places on a simulator,[165] such as rFpro,[166] which is used by most of the F1 teams.[167]
Each driver chooses an unassigned number from 2 to 99 (excluding 17, which was retired following the death of Jules Bianchi)[168] upon entering Formula One and keeps that number during their time in the series. The number one is reserved for the reigning Drivers' Champion, who retains their previous number and may choose to use it instead of the number one.[169] At the onset of the championship, numbers were allocated by race organisers on an ad hoc basis from race to race.[170]
Permanent numbers were introduced for the 1974 season. Teams were allocated numbers in ascending order based on the Constructors' Championship standings at the end of the 1973 season. The teams would hold those numbers from season to season except for the team with the World Drivers' Champion, which would swap its numbers with the one and two of the previous champion's team.[171] New entrants were allocated spare numbers, except for the number 13, which has only ever been used by Divina Galica and Pastor Maldonado.[172]

As teams kept their numbers for long periods of time, car numbers became associated with a team, such as Ferrari's 27 and 28.[170] A different system was used from 1996 to 2013. During that time, at the start of each season the current Drivers' Champion was designated number one, their teammate number two, and the rest of the teams assigned ascending numbers according to the previous season's Constructors' Championship order.[171]
As of 2024[update], a total of 34 separate drivers have won the World Drivers' Championship, with Michael Schumacher and Lewis Hamilton holding the record for most championships, each with seven.[173] Jochen Rindt is the only posthumous World Champion, after his points total was not surpassed despite his fatal accident at the 1970 Italian Grand Prix, with 4 races remaining in the season.[174] Drivers from the United Kingdom have been the most successful in the sport, with 20 championships among 10 drivers and 325 wins as of 2025[update].[175]
Physical demands
Driving in Formula One is highly demanding physically, with drivers typically burning around 1,000 calories per hour and losing up to 5% of their body weight per race.[176][177] A key reason for the physical demands is the extreme g-force generated by driving at high speeds, with modern Formula One cars capable of generating forces of up to 6.5 gs when cornering (i.e. feeling a force equivalent to six and a half times their body weight), 6 gs when braking, and 2 gs when accelerating.[178][179][180] Another factor is the high temperature inside the car, as the engine is mounted directly behind the driver. The temperature in the cockpit of a Formula One car can be as high as 60 °C (140 °F), and drivers have to wear several layers of fireproof clothing.[181][182] The steering wheel and brake pedal also require considerable strength to operate. Before the introduction of power steering in the 2000s, drivers had to cope with steering forces of up to 40–50 newton-metres (30–37 lb⋅ft),[183][184] while achieving maximum braking power requires drivers to apply around 150 kg (330 lb) of force to the brake pedal.[185]
Every extra kilogram of weight noticeably reduces a drivers performance, as such, they must be light – though a minimum limit of 82 kg (181 lb) has been enforced by the FIA "in the interests of well-being".[176][186] They also need to train for cardiovascular fitness since heart rates can, on average, exceed 170 bpm during a race.[187]
Feeder series


Most F1 drivers start in kart racing competitions and then progress through traditional entry-level European single-seater series such as Formula Ford,[188] Formula Renault,[189] and Formula 4.[190] From there, drivers typically progress to higher-level regional championships at the Formula Three level, which include championships such as British F3 and European F3 historically, although similar series now hold the Formula Regional designation. In addition to this, there are also international F3 championships, including GP3 and its present-day successor, FIA F3.[191] The highest level series on the F1 ladder is the FIA Formula 2 Championship. In the past, the top level series was GP2 (2005–2016), International Formula 3000 (1985–2004 under the Formula 3000 class), and Formula Two (1948–1984).[192][193]
Drivers are not required to have competed at all levels to enter Formula One. British F3 has supplied many F1 drivers, with champions, including Nigel Mansell,[194] Ayrton Senna,[195] and Mika Häkkinen[196] having moved straight from that series to Formula One. Max Verstappen made his F1 debut following a single season in European F3.[197] More rarely, a driver may be picked from an even lower level, as was the case with 2007 World Champion Kimi Räikkönen, who went straight from Formula Renault to F1.[198]
American open-wheel car racing has also contributed to the Formula One grid. CART champions Mario Andretti and Jacques Villeneuve became F1 World Champions, while Juan Pablo Montoya won seven races in F1.[199]
Remove ads
Grands Prix
Summarize
Perspective

The number of Grands Prix held in a season has varied over the years. The inaugural 1950 World Championship season comprised only seven races,[200] alongside several non-championship Formula One events.[201] These, however, came to an end in 1983.[11] The 2024 season contained 24 races, the highest number of World Championship races in one season.[202]
Six of the original seven races took place in Europe;[200] the only non-European race that counted towards the World Championship in 1950 was the Indianapolis 500, which was held to different regulations.[203] Some of these races pre-dated the formation of the World Championship, such as the French Grand Prix.[204] Over time, the F1 championship gradually expanded to other non-European countries. Argentina hosted the first South American Grand Prix in 1953, and Morocco hosted the first African Grand Prix in 1958. Asia and Oceania followed (Japan in 1976 and Australia in 1985), and the first race in the Middle East was held in 2004.[205] The 19 races of the 2014 season were spread over every populated continent except for Africa, with 10 Grands Prix held outside Europe.[66]
The British and Italian Grands Prix are the only events to have been held every Formula One season.[206] The Monaco Grand Prix was first held in 1929 and has run continuously since 1955, except in 2020,[207] and is widely considered to be one of the most important and prestigious automobile races in the world.[208]
All Grands Prix have traditionally been run during the day, until the inaugural Singapore Grand Prix hosted the first Formula One night race in 2008,[209] which was followed by the day–night Abu Dhabi Grand Prix in 2009[210] and the Bahrain Grand Prix, which was converted to a night race in 2014.[211] Other Grands Prix in Asia have had their start times adjusted to benefit the European television audience.[212]
Contracted Grands Prix
The following twenty-four Grands Prix have contracts to be hosted at the listed circuits for the 2026 season:
One Grand Prix has a contract to be hosted at the listed circuit for the 2027 season:
Remove ads
Circuits
Summarize
Perspective

Formula One races are held on Grade A tracks, the highest grade-rating issued by the FIA for tracks.[238] Under the current regulations, circuit layouts and lap distances may vary considerably, provided that each Grand Prix covers a total race distance of 305 km (190 mi).[239][h] While most tracks are made to be run in a clockwise direction, there are a handful of tracks in the Championship that are to be run anticlockwise.[241]
A typical circuit features a stretch of straight road on which the starting grid is situated, with the pit lane normally located right next to it.[242] The pit lane is home to each team's garage, where cars are stored and serviced before a race. During a pit stop, drivers enter the pit lane to change their tyres, receive repairs or aerodynamic adjustments from their pit crew, or retire from the race (if the car is in a condition to do so). Prior to the 2010 season, pit stops also facilitated mid-race refueling of the cars.[243] Special pit roads and track markings help to make sure drivers pit and rejoin the track safely.[244]
As of 2025[update], most of the circuits are specially constructed for competition, but the calendar also features several circuits that use converted public streets to varying degrees. These tracks include Monaco, Melbourne, Singapore, Baku, Miami, Jeddah, and Las Vegas.[245] Three-time World champion Nelson Piquet famously described racing in Monaco as "like riding a bicycle around your living room".[246]
Circuit design to protect the safety of drivers is becoming increasingly sophisticated. Several of the new circuits in F1, especially those designed by Hermann Tilke, however, have also been criticised as lacking the "flow" of such classics as Spa-Francorchamps and Imola.[247] His redesign of the Hockenheim circuit in Germany, for example, while providing more capacity for grandstands and eliminating extremely long and dangerous straights, has been frowned upon by many who argue that part of the character of the Hockenheim circuit was the long and blinding straights into dark forest sections. However, it is generally agreed that these newer circuits meet the safety standards of modern Formula One better than the older ones.[248]
The Circuit of the Americas in Austin, the Sochi Autodrom in Sochi, and the Baku City Circuit in Azerbaijan have all been introduced as brand new tracks since 2012.[248] In 2020, Algarve International Circuit debuted on the F1 calendar as the venue of the Portuguese Grand Prix, with that country having last hosted a race in 1996;[249][i] Formula One announced its return to Portimão for the 2027 and 2028 seasons.[250] In 2021, Circuit Zandvoort returned to the F1 calendar as the Dutch Grand Prix, having last hosted a race in 1985.[251] The Las Vegas Grand Prix entered the series in 2023.[252]
Remove ads
Cars and technology
Summarize
Perspective

Modern Formula One cars are mid-engined, hybrid, semi-open cockpit, open-wheel, single-seaters. The chassis is made largely of carbon-fibre composites, rendering it light but extremely stiff and strong. The whole car, including the driver but not fuel, weighs only 800 kg (1,800 lb) – the minimum weight set by the regulations.[253] If the construction of the car is lighter than the minimum, ballast can be added to reach the necessary weight. The race teams take advantage of this by placing this ballast at the extreme bottom of the chassis, thereby lowering the centre of gravity as much as possible in order to improve handling and weight transfer.[254]
Aerodynamic downforce, generated by the "wings" mounted at the front and rear of Formula One cars along with ground effect created by low air pressure under the flat bottom of the car, plays a large role in determining the car's ability to be handled at high speeds.[255] A downforce of 2.5 times the car's weight can be achieved at full speed, and a lateral force with a magnitude of up to 3.5 times that of the force of gravity (3.5g) in cornering.[256]
The other major factor facilitating the cornering of the cars is the design of the tyres. From 1998 to 2008, Formula One did not use "slicks" as in most other circuit racing series. Instead, each tyre had four large circumferential grooves on its surface designed to limit the cornering speed of the cars.[257] Slick tyres were reintroduced by Formula One in the 2009 season, and are now exclusively supplied by Pirelli.[258] Formula One cars must also have four wheels made of the same metallic material, which must be one of two magnesium alloys specified by the FIA.[259] Magnesium alloy wheels made by forging are used to achieve maximum unsprung rotating weight reduction.[260] As of 2022, the wheels are covered with standardised wheel covers, the wheel diameter has increased from 13 inches to 18 inches, and small winglets have been placed over the front tyres.[261]
For most of the 21st century, Formula One cars have used double wishbone or multilink suspensions at the front and rear, with pushrod-operated springs and dampers on the chassis, though there have been some notable exceptions.[262] In 2009, the Red Bull Racing RB5 used a pullrod suspension at the rear.[263] Ferrari used a pullrod suspension at both the front and rear in their 2012 car.[264] In 2022, the McLaren MCL36 and the Red Bull Racing RB18 switched to a pullrod front suspension and push rod rear suspension.[265][266] Carbon-carbon disc brakes are used for reduced weight and increased frictional performance.[267] The carbon material enhances the brakes by maintaining an effective performance under extreme heat. To optimise this, the brakes feature 1,000 ventilation holes, ensuring cooling and thus helping maximum performance.[268]
In 2022, the technical regulations were altered considerably in order to reduce the turbulence produced by the aerodynamics of the car. This includes a redesigned front and rear wing, larger wheels with a lower tyre profile, wheel covers, small winglets, the banning of barge boards, and the reintroduction of Ground effect downforce production. These changes have been made to allow cars to follow each other at much closer distances, by helping to prevent lower downforce in the following car due to "dirty air".[91]

In 2014, the engines were changed from a 2.4-litre naturally aspirated V8 to turbocharged 1.6-litre V6 power units.[269] These run on unleaded fuel closely resembling publicly available petrol, get a significant amount of their power from electric motors, and include energy recovery technology.[270] The 2006 generation of engines spun up to 20,000 rpm and produced over 580 kW (780 bhp). Following the engine specification freeze, this was reduced to 19,000 rpm with limited development allowed in 2007 and 18,000 rpm in 2009.[271][272]
A wide variety of technologies, including active suspension, are banned under the current regulations.[273] Despite this, the current generation of cars can reach speeds in excess of 350 km/h (220 mph) at some circuits.[274] The highest straight line speed recorded during a Grand Prix was 372.6 km/h (231.5 mph), set by Juan Pablo Montoya during the 2005 Italian Grand Prix.[275] During qualifying for the 2016 European Grand Prix, Valtteri Bottas set a record top speed of 378 km/h (234.9 mph).[276]
As of 2019[update], each team may have no more than two cars available for use at any time.[277] Each driver is limited to four engines during a championship season.[278][279] They are also allowed one new gearbox for every six consecutive races and three power units per season, beyond which they incur grid penalties.[280][281]
Remove ads
Revenue and profits
Summarize
Perspective
For much of the sport's history, engine costs varied significantly between teams. In 2006, Honda, Toyota, McLaren-Mercedes, and Ferrari each spent an estimated $200 million, Renault $125 million, while Cosworth developed its V8 for just $15 million.[282] From 2007, however, the sporting regulations banned performance-related engine development.[283] The estimated cost of running a team was approximated to £193 million as of 2018.[284]
Formula One teams pay entry fees of $500,000, plus $5,000 per point scored the previous year, or $6,000 per point for the winner of the Constructors' Championship. Formula One drivers pay a FIA Super Licence fee, which in 2013 was €10,000, plus €1,000 per point.[285]
There have been controversies with the way profits are shared among the teams. The smaller teams have complained that the profits are unevenly shared, favouring established top teams. In September 2015, Force India and Sauber officially lodged a complaint with the European Union against Formula One, questioning the governance and stating that the system of dividing revenues and determining the rules is unfair and unlawful.[286]
The cost of building a brand-new permanent circuit can be hundreds of millions of dollars, while the cost of converting a public road into a temporary circuit is much less.[287] The Shanghai International Circuit cost over $300 million,[288] and the Istanbul Park circuit cost $150 million to build.[289]
In the second quarter of 2020, Formula One reported revenues of $24 million, down from the previous year's $620 million, with an operating loss of $122 million, down from a profit of $26 million the previous year. This was a result of the delay of the racing championship start due to the COVID-19 pandemic.[290]
Cost cap
When Formula 1 began in 1950, the sport's governing body did not have any regulations limiting spending by a team. Over time, this led to teams with large budgets performing significantly better than their competitors.[291] For instance, in 2019, Mercedes, the Constructors' Champion, spent $420 million, while the lowest-scoring teams, Williams and Haas, spent only $125 million and $150 million, respectively.[292][293]
To curb the growing advantage that these wealthier teams gained from extensive track time, the FIA first introduced a ban on unlimited private testing, before eventually implementing a cost cap of $175 million in 2021.[294] It was reduced to $145 million soon after, due to the economic turmoil caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. It fell further to $140 million in 2022, before settling at $135 million for the next three years.[295][296][297]
Critics have argued that the cap might not be sufficient to close the gap in competition because it excludes certain expenses such as driver salaries, compensation for the three highest-paid staff members, and marketing costs.[295] In practice, however, the cost cap seems to have helped teams maximise efficiency and foster innovation within their financial means. McLaren started the 2023 season as the slowest car on the track, with their drivers finishing outside the points. Seven months later, they were the fastest car on the grid in both qualifying and race pace, and, in 2024, they won the constructors' championship.[298]
Remove ads
Future
Summarize
Perspective

The expense of Formula One has seen the FIA and the Formula One Commission attempt to create new regulations to lower the costs for a team to compete in the sport.[299][300]
Following their purchase of the commercial rights to the series in 2017,[301][302] Liberty Media announced their vision for the future of Formula One at the 2018 Bahrain Grand Prix. Their proposal identified five key areas, including streamlining the governance of the sport, emphasising cost-effectiveness, maintaining the sport's relevance to road cars, and encouraging new manufacturers to enter the championship whilst enabling them to be competitive.[303] On 19 August 2020, it was announced that all 10 teams had signed the new Concorde Agreement.[304] This came into effect at the start of the 2021 season and changed how prize money and TV revenue are distributed.[305]
Environmental impact
Formula One has initiated a plan to become carbon neutral by 2030. By 2025, all events should have become "sustainable", including eliminating single-use plastics and ensuring all waste is reused, recycled, or composted.[306]
A report conducted by Formula One estimated that the series was responsible for 256,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions in the 2019 season, finding that 45% of emissions were from logistics and 0.7% were from emissions from the cars themselves.[307][308]
In January 2020, the FIA and Formula One signed the United Nations Sports for Climate Action framework.[309] From the 2021 season onwards, all cars increased the bio-component of their fuel, using E10 fuel, rather than the 5.75% of ethanol previously used. This percentage is expected to grow again in the future.[91] In December 2020, the FIA claimed that it had developed a fuel with 100% sustainability to be used in Formula One from either 2025 or 2026, when new engine regulations come into force.[310]
Social inequities
Before the beginning of the 2020 Formula One World Championship, F1 announced and launched the #WeRaceAsOne initiative.[311] The initiative primarily focuses on visible displays of solidarity in the fight against racism on Grand Prix weekends, as well as the creation of a Formula 1 Task Force that will "listen to people from across the paddock [...] and make conclusions on the actions required to improve the diversity and opportunity in Formula 1 at all levels".[311] The move stems from the growing questions about racism and global inequalities perpetuated by the sport.[312][313]
In addition to organization-wide measures, individual teams have also acknowledged deficiencies in the sport's cultural and political activism. During the 2020 season, the Mercedes-AMG Petronas F1 Team conducted a study of its racial composition and found that approximately 95% of its workforce was white.[314] In effort to change this, they ran a black livery to promote anti-racism messages and also launched the Accelerate 25 programme.[315] The program vows that approximately 25% of all new hires to the team will come from underrepresented minorities in the series until 2025.[316]
The 20 drivers on the grid also stood in solidarity on multiple occasions in the fight against racism, both on and off the track. Following the murder of George Floyd in the summer of 2020, all twenty drivers wore "End Racism" shirts and took part in an organised anti-racism protest during the pre-race formalities.[317] In the following season, Lewis Hamilton remained vocal through his race weekend attire, with other drivers occasionally wearing change-demanding clothing.[318]
Remove ads
Women in Formula One
Summarize
Perspective
Since the creation of Formula One in 1950, five women have competed in a Grand Prix, only one of whom finished within the points.[319] The involvement of women in the Formula One paddock has ranged from team principals, race engineers, and strategists to media and communications personnel.[320] With the release of the Netflix show, Drive to Survive, female viewership of the series has risen.[321] In 2019, 20% of the total Formula One viewership was female, and by 2022 this number had increased to 40%.[322]
Drivers
Maria Teresa de Filippis was the first woman to compete in the series at the 1958 Monaco Grand Prix. She drove in a total of five Grands Prix, racing under the Italian flag, and has been hailed as a pioneer of women in motorsport.[323]
Lella Lombardi is the only woman to place within the points at a Formula One Grand Prix. She competed in three seasons, entering seventeen races and starting twelve.[324] After finishing sixth in the 1975 Spanish Grand Prix, Lombardi became the first and only woman to score points during an official Formula One Grand Prix. Due to the race not reaching full completion, half points were awarded, and Lombardi only gained 0.5 points.[319]
Desiré Wilson is the only woman to win a Formula One race of any kind, winning the second round of the 1980 Aurora AFX F1 Championship.[325]
Giovanna Amati was the last female driver to attempt to qualify for a Formula One Grand Prix. In 1992, she was signed by Brabham and participated in three races—South Africa, Mexico, and Brazil—but failed to qualify for any of them. Amati faced significant challenges, including an underperforming car and limited testing opportunities. She was replaced by Damon Hill after Brabham struggled with financial difficulties and performance issues.[326] Her participation also marked the last time a female driver was officially listed on an F1 entry list until Susie Wolff took part in free practice sessions for Williams during her four years with the team as a development driver.[327][328]
In 2022, Formula One announced the creation of F1 Academy in an effort to "change perceptions and inspire the next generation of girls".[322][329] It is the only female single-seater racing championship.[330] Its inaugural championship was won by Marta García of Prema Racing.[331] The establishment of F1 Academy has attracted significant levels of attention to women in motorsport. Netflix premiered a docuseries in 2025 about the academy.[332] In addition to this, companies such as Tommy Hilfiger,[333] Charlotte Tilbury,[334] and Puma[335] have become sponsors due to the sport's increasing popularity.[336]
Team personnel
Austrian Monisha Kaltenborn became the sport's first-ever female team principal when she took over the role at Sauber Formula One Team in 2010.[337] English Claire Williams became the only other woman to ever manage a Formula One team when she assumed the role of Deputy Team Principal for Williams Racing in 2013.[338]
As of 2025[update], Hannah Schmitz holds the role of principal strategy engineer at Red Bull Racing. She has been with the team since 2009 and has played a strong role in its victories in 2021, 2022, and 2023.[339] Beginning in 2025, Laura Müller has served as the race engineer for Esteban Ocon at Haas, making her the first woman to serve as a race engineer on a full-time basis.[340][341]
Remove ads
Media coverage
Summarize
Perspective
Formula One is broadcast live or tape delayed in almost every country and territory, and attracts one of the largest global television audiences.[342] The cumulative television audience for the 2001 season, which was broadcast to 200 territories, was calculated to be 54 billion,[343] and has since fallen to 1.55 billion.[344]
All broadcasters are provided with an identical world feed produced by Formula One Management (FOM).[345] Previously, this footage was provided by local broadcasters who provided one feed for all, or two separate feeds – a feed for local viewers and a feed for international viewers. This approach was significantly criticised as viewers would tend to miss out on important action and incidents due to local biases.[346]
An enhanced package called F1 Digital+ was launched by FOM in 1996, which included live broadcast of all sessions as well as additional channels, including onboard and pit-lane cameras. It was initially only offered in Germany, Austria, and Switzerland, though it later became available in France, Italy, Spain, and the UK.[347] The service was never financially viable and was discontinued at the end of 2002.[348]
The official Formula One website has live timing charts that can be used during the race to follow the leaderboard in real time.[349] An official smartphone application, that has been available for the Apple App Store since 2009[350] and on Google Play since 2011,[351] shows users a real-time feed of driver positions, timing, and commentary.[352] On 26 November 2017, Formula One unveiled a new logo, which replaced the previous "flying one" in use since 1993.[353]
In March 2018, Formula One announced the launch of F1 TV, an over-the-top streaming platform that lets viewers watch multiple simultaneous video feeds and timing screens in addition to traditionally directed race footage and commentary.[354] In April 2024, FOM launched a free ad-supported streaming television channel known as the Formula 1 Channel in the United States, which plays classic Grands Prix, documentaries, and analysis from past races.[355]
Television broadcasters
In the United Kingdom, several companies have retained the right to broadcast races. In 2012, Sky launched a dedicated channel, Sky Sports F1, which covered all races live without commercial interruption as well as live practice and qualifying sessions, along with F1 programming, including interviews, archive action, and magazine shows.[356] The BBC retained similar rights until 2015, when they ended their contract three years earlier than planned.[357] The free-to-air TV rights were picked up by Channel 4 until the end of the 2018 season.[358] As of 2025, BBC Radio 5 Live, 5 Sports Extra, and BBC Sounds have rights to such coverage until 2028.[359]
In Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa, Formula One is broadcast by beIN Sports. In India, sessions are broadcast by streaming service FanCode and satellite television provider Tata Play. In China, the rights are held by Tencent, Guangdong TV, and Shanghai TV.[342]
In the United States, ESPN has held the rights since 2013, carrying the broadcast and commentary feed provided by Sky Sports UK.[360] According to The Athletic, the fee paid by ESPN is estimated at $90 million per year as of 2025, with the current deal set to expire after the 2025 season.[360] Ahead of the 2025 United States Grand Prix, it was announced that Apple Inc. had acquired the U.S. rights to Formula One under a five-year deal; most coverage will be exclusive to Apple TV subscribers, with practice sessions and selected races available for free.[361][362]
In Germany, Austria, Italy, and Switzerland, the exclusive rights are held by pay TV broadcaster Sky Sport.[342] The rights were previously shared with free-to-air channel RTL for many years, which had broadcast all Formula One qualifying and racing sessions since 1991, but lost its rights after the 2020 season due to being outbid by Sky Sport.[363] Despite no longer holding the rights themselves, RTL has broadcast selected sessions on free-to-air television and its streaming service RTL+ as part of various sublicensing agreements with Sky Sport.[364]
Remove ads
See also
Notes
- A mandatory two-pit stop rule was enforced for the 2025 Monaco Grand Prix.[121]
- From 2019 to 2024, an additional point was awarded to the car which set the fastest lap, if that car finished inside the top 10.
- De facto status of the territories is shown.
- The event will not be held in 2028 and 2030 under the rotational contract.
- The Monaco Grand Prix, run over 260 km (160 mi), is the only exception to this rule.[240]
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads





