Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Turkish language
Turkic language From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Turkish (Türkçe [ˈtyɾktʃe], Türk dili, also known as Türkiye Türkçesi 'Turkish of Turkey'[17]) is the most widely spoken of the Turkic languages with around 90 million speakers. It is the national language of Turkey and one of two official languages of Cyprus. Significant smaller groups of Turkish speakers also exist in Germany, Austria, Bulgaria, North Macedonia,[18] Greece,[19] other parts of Europe, the South Caucasus, and some parts of Central Asia, Iraq, and Syria. Turkish is the 18th-most spoken language in the world.
To the west, the influence of Ottoman Turkish—the variety of the Turkish language that was used as the administrative and literary language of the Ottoman Empire—spread as the Ottoman Empire expanded. In 1928, as one of Atatürk's reforms in the early years of the Republic of Turkey, the Perso-Arabic script-based Ottoman Turkish alphabet was replaced with the Latin script-based Turkish alphabet.
Some distinctive characteristics of the Turkish language are vowel harmony and extensive agglutination. The basic word order of Turkish is subject–object–verb. Turkish has no noun classes or grammatical gender. The language makes usage of honorifics and has a strong T–V distinction which distinguishes varying levels of politeness, social distance, age, courtesy or familiarity toward the addressee. The plural second-person pronoun and verb forms can be used for referring to a single person out of respect.
Remove ads
Classification
Turkish is a member of the Oghuz group of the Turkic family. Other members include Azerbaijani, spoken in Azerbaijan and north-west Iran, Gagauz of Gagauzia, Qashqai of south Iran, and Turkmen of Turkmenistan.[20]
Historically the Turkic family was seen as a branch of the larger Altaic family, including Japanese, Korean, Mongolian and Tungusic, with various other language families proposed for inclusion by linguists.[21]
Altaic theory has fallen out of favour since the 1960s, and a majority of linguists now consider Turkic languages to be unrelated to any other language family, though the Altaic hypothesis still has a small degree of support from individual linguists.[22] The nineteenth-century Ural-Altaic theory, which grouped Turkish with Finnish, Hungarian and Altaic languages, is considered even less plausible in light of Altaic's rejection.[23] The theory was based mostly on the fact these languages share three features: agglutination, vowel harmony and lack of grammatical gender.[23]
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective

The earliest known Old Turkic inscriptions are the three monumental Orkhon inscriptions found in modern Mongolia. Erected in honour of the prince Kul Tigin and his brother Emperor Bilge Khagan, these date back to the Second Turkic Khaganate (dated 682–744 CE).[24] After the discovery and excavation of these monuments and associated stone slabs by Russian archaeologists in the wider area surrounding the Orkhon Valley between 1889 and 1893, it became established that the language on the inscriptions was the Old Turkic language written using the Old Turkic alphabet, which has also been referred to as "Turkic runes" or "runiform" due to a superficial similarity to the Germanic runic alphabets.[25]
With the Turkic expansion during Early Middle Ages (c. 6th–11th centuries), peoples speaking Turkic languages spread across Central Asia, covering a vast geographical region stretching from Siberia all the way to Europe and the Mediterranean. The Seljuqs of the Oghuz Turks, in particular, brought their language, Oghuz—the direct ancestor of today's Turkish language—into Anatolia during the 11th century.[26] Also during the 11th century, an early linguist of the Turkic languages, Mahmud al-Kashgari from the Kara-Khanid Khanate, published the first comprehensive Turkic language dictionary and map of the geographical distribution of Turkic speakers in the Dīwān Lughāt al-Turk (ديوان لغات الترك).[27]
Ottoman Turkish

Following the adoption of Islam around the year 950 by the Kara-Khanid Khanate and the Seljuq Turks, who are both regarded as the ethnic and cultural ancestors of the Ottomans, the administrative language of these states acquired a large collection of loanwords from Arabic and Persian. Turkish literature during the Ottoman period, particularly Divan poetry, was heavily influenced by Persian, including the adoption of Persian poetic meters and a great quantity of imported Persian words. The literary and official language during the Ottoman Empire period (c. 1299–1922) is termed Ottoman Turkish, which was a mixture of Turkish, Persian, and Arabic that differed considerably from today's modern Turkish and was largely unintelligible to the period's everyday Turkish. The everyday Turkish, known as kaba Türkçe or 'vulgar Turkish', spoken by the less-educated, lower and also rural members of Ottoman society, contained a higher percentage of native vocabulary and served as the basis for the modern Turkish language.[28]
While visiting the region between Adıyaman and Adana, Evliya Çelebi recorded the "Turkman language" and compared it with his own Turkish:
Language reform and modern Turkish
After the foundation of the modern state of Turkey and the script reform, the Turkish Language Association (TDK) was established in 1932 under the patronage of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, with the aim of conducting research on Turkish. One of the tasks of the newly established association was to initiate a language reform to replace loanwords of Arabic and Persian origins with Turkish equivalents.[d] By banning the usage of imported words in the press,[clarification needed] the association succeeded in removing several hundred foreign words from the language. While most of the words introduced to the language by the TDK were newly derived from Turkic roots, it also opted for reviving Old Turkish words which had not been used for centuries.[31] In 1935, the TDK published a bilingual Ottoman-Turkish/Pure Turkish dictionary that documents the results of the language reform.[32]
Owing to this sudden change in the language, older and younger people in Turkey started to differ in their vocabularies. While the generations born before the 1940s tend to use the older terms of Arabic and Persian origins, the younger generations favor new expressions. It is considered particularly ironic that Atatürk himself, in his lengthy speech to the new Parliament in 1927, used the formal style of Ottoman Turkish that had been common at the time amongst statesmen and the educated strata of society in the setting of formal speeches and documents. After the language reform, the Turkish education system discontinued the teaching of literary Ottoman Turkish, and over time the speaking and writing ability of society atrophied to the point that later generations of Turkish speakers would perceive the speech as sounding so alien that it had to be "translated" three times into modern Turkish: first in 1963, again in 1986, and most recently in 1995.[e]
The past few decades have seen the continuing work of the TDK to coin new Turkish words to express new concepts and technologies as they enter the language, mostly from English. Many of these new words, particularly information technology terms, have received widespread acceptance. However, the TDK is occasionally criticized for coining words which sound contrived and artificial. Some earlier changes—such as Turkic bölem to replace Arabic fırka, 'political party'—also failed to meet with popular approval (the Arabic loanword fırka has been replaced by the French loanword parti). Some words restored from Old Turkic have taken on specialized meanings; for example betik (originally meaning 'book') is now used to mean 'script' in computer science while the Arabic loanword kitap remains for 'book' in Turkish.[34]
Some examples of modern Turkish words and the old loanwords are:
Remove ads
Geographic distribution
Summarize
Perspective
Turkish is natively spoken by the Turkish people in Turkey and by the Turkish diaspora in some 30 other countries. The Turkish language is mutually intelligible with Azerbaijani. In particular, Turkish-speaking minorities exist in countries that formerly (in whole or part) belonged to the Ottoman Empire, such as Iraq,[36] Bulgaria, Cyprus, Greece (primarily in Western Thrace), the Republic of North Macedonia, Romania, and Serbia. More than two million Turkish speakers live in Germany; and there are significant Turkish-speaking communities in the United States, France, the Netherlands, Austria, Belgium, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom.[37] Due to the cultural assimilation of Turkish immigrants in host countries, not all ethnic members of the diaspora speak the language with native fluency.[f]

In 2005, 93% of the population of Turkey were native speakers of Turkish,[39] about 67 million at the time, with Kurdish languages making up most of the remainder.[37]
Azerbaijani language, official in Azerbaijan, is mutually intelligible with Turkish and speakers of both languages can understand them without noticeable difficulty, especially when discussion comes on ordinary, daily language. Turkey has very good relations with Azerbaijan, with a multitude of Turkish companies and authorities investing there, while the influence of Turkey in the country is very high. The rising presence of this very similar language in Azerbaijan and the fact that many children use Turkish words instead of Azerbaijani words due to satellite TV has caused concern that the distinctive features of the language will be eroded. Many bookstores sell books in Turkish language along Azerbaijani language ones, with Agalar Mahmadov, a leading intellectual, voicing his concern that Turkish language has "already started to take over the national and natural dialects of Azerbaijan". However, the presence of Turkish as foreign language is not as high as Russian.[40] In Uzbekistan, the second most populated Turkic country, a new TV channel Foreign Languages TV was established in 2022. This channel has been broadcasting Turkish lessons along with English, French, German and Russian lessons.
Official status
Turkish is the official language of Turkey and is one of the official languages of Cyprus. Turkish has official status in 38 municipalities in Kosovo, including Mamusha,[41][42], two in the Republic of North Macedonia and two in Iraq.[43][10] Cyprus has requested the European Union to add Turkish as an official language, as it is one of the two official languages of the country.[44]
In Turkey, the regulatory body for Turkish is the Turkish Language Association (Türk Dil Kurumu or TDK), which was founded in 1932 under the name Türk Dili Tetkik Cemiyeti ("Society for Research on the Turkish Language"). The Turkish Language Association was influenced by the ideology of linguistic purism: indeed one of its primary tasks was the replacement of loanwords and of foreign grammatical constructions with equivalents of Turkish origin.[g] These changes, together with the adoption of the new Turkish alphabet in 1928, shaped the modern Turkish language spoken today. The TDK became an independent body in 1951, with the lifting of the requirement that it should be presided over by the Minister of Education. This status continued until August 1983, when it was again made into a governmental body in the constitution of 1982, following the military coup d'état of 1980.[31]
Remove ads
Dialects
Summarize
Perspective
Modern Standard Turkish is based on the dialect of Istanbul.[45] This Istanbul Turkish (İstanbul Türkçesi) constitutes the model of written and spoken Turkish, as recommended by Ziya Gökalp, Ömer Seyfettin and others.[46]
Dialectal variation persists, in spite of the levelling influence of the standard used in mass media and in the Turkish education system since the 1930s.[47] Academic researchers from Turkey often refer to Turkish dialects as ağız or şive, leading to an ambiguity with the linguistic concept of accent, which is also covered with these words. Several universities, as well as a dedicated work-group of the Turkish Language Association, carry out projects investigating Turkish dialects. As of 2002[update] work continued on the compilation and publication of their research as a comprehensive dialect-atlas of the Turkish language.[48][49] Although the Ottoman alphabet, being more phonetically ambiguous than the Latin script, encoded for many of the dialectal variations between Turkish dialects, the modern Latin script fails to do this. Examples of this are the presence of the nasal velar sound [ŋ] in certain eastern dialects of Turkish which was represented by the Ottoman letter /ڭ/ but that was merged into /n/ in the Latin script. Additionally are letters such as /خ/, /ق/, /غ/ which make the sounds [ɣ], [q], and [x], respectively in certain eastern dialects but that are merged into [g], [k], and [h] in western dialects and are therefore defectively represented in the Latin alphabet for speakers of eastern dialects.
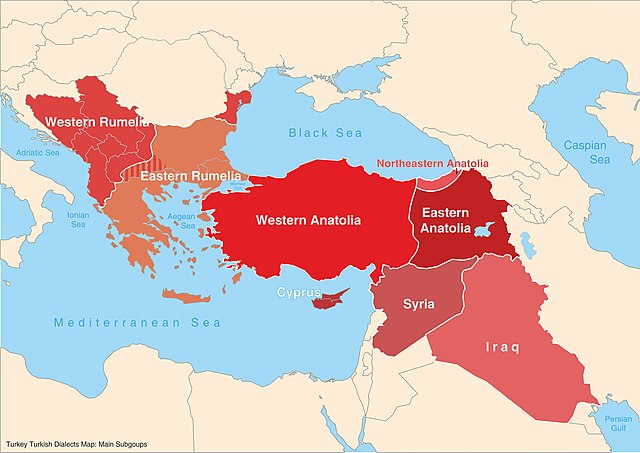
Some immigrants to Turkey from Rumelia speak Rumelian Turkish, which includes the distinct dialects of Ludogorie, Dinler, and Adakale, which show the influence of the theorized Balkan sprachbund. Kıbrıs Türkçesi is the name for Cypriot Turkish and is spoken by the Turkish Cypriots. Edirne is the dialect of Edirne. Ege is spoken in the Aegean region, with its usage extending to Antalya. The nomadic Yörüks of the Mediterranean Region of Turkey also have their own dialect of Turkish.[50] This group is not to be confused with the Yuruk nomads of Macedonia, Greece, and European Turkey, who speak Balkan Gagauz Turkish.
The Meskhetian Turks who live in Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan and Russia as well as in several Central Asian countries, also speak an Eastern Anatolian dialect of Turkish, originating in the areas of Kars, Ardahan, Artvin, Diyarbakir and Erzurum and sharing similarities with Azerbaijani, the language of Azerbaijan.[51]
The Central Anatolia Region speaks Orta Anadolu. Karadeniz, spoken in the Eastern Black Sea Region and represented primarily by the Trabzon dialect, exhibits substratum influence from Greek in phonology and syntax;[52] it is also known as Laz dialect (not to be confused with the Laz language). Kastamonu is spoken in Kastamonu and its surrounding areas. Karamanli Turkish is spoken in Greece, where it is called Kαραμανλήδικα. It is the literary standard for the Karamanlides.[53]
Remove ads
Phonology
Summarize
Perspective
Consonants
At least one source claims Turkish consonants are laryngeally-specified three-way fortis-lenis (aspirated/neutral/voiced) like Armenian, although only syllable-finally.[55]
The phoneme that is usually referred to as yumuşak g ("soft g"), written ⟨ğ⟩ in Turkish orthography, represents a vowel sequence or a rather weak bilabial approximant between rounded vowels, a weak palatal approximant between unrounded front vowels, and a vowel sequence elsewhere. It never occurs at the beginning of a word or a syllable, but always follows a vowel. When word-final or preceding another consonant, it lengthens the preceding vowel.[54]
In native Turkic words, the sounds [c], [ɟ], and [l] are mainly in complementary distribution with [k], [ɡ], and [ɫ]; the former set occurs adjacent to front vowels and the latter adjacent to back vowels. The distribution of these phonemes is often unpredictable, however, in foreign borrowings and proper nouns. In such words, [c], [ɟ], and [l] often occur with back vowels:[56]: 93–4, 6 some examples are given below. However, there are minimal pairs that distinguish between these sounds, such as kar [kɑɾ] "snow" vs kâr [cɑɾ] "profit".
Consonant devoicing
Turkish orthography reflects final-obstruent devoicing, a form of consonant mutation whereby a voiced obstruent, such as /b d dʒ ɡ/, is devoiced to [p t tʃ k] at the end of a word or before a consonant, but retains its voicing before a vowel. In loan words, the voiced equivalent of /k/ is /g/; in native words, it is /ğ/.[57][58]
This is analogous to languages such as German and Russian, but in the case of Turkish it only applies, as the above examples demonstrate, to stops and affricates, not to fricatives. The spelling is usually made to match the sound. However, in a few cases, such as ad 'name' (dative ada), the underlying form is retained in the spelling (cf. at 'horse', dative ata). Other exceptions are od 'fire' vs. ot 'herb', sac 'sheet metal', saç 'hair'. Most loanwords, such as kitap above, are spelled as pronounced, but a few such as hac 'hajj', şad 'happy', and yad 'strange' or 'stranger' also show their underlying forms.[citation needed]
Native nouns of two or more syllables that end in /k/ in dictionary form are nearly all /ğ/ in underlying form. However, most verbs and monosyllabic nouns are underlyingly /k/.[56]: 10
Vowels

The vowels of the Turkish language are, in their alphabetical order, ⟨a⟩, ⟨e⟩, ⟨ı⟩, ⟨i⟩, ⟨o⟩, ⟨ö⟩, ⟨u⟩, ⟨ü⟩.[h] The Turkish vowel system can be considered as being three-dimensional, where vowels are characterised by how and where they are articulated focusing on three key features: front and back, rounded and unrounded and vowel height.[59] Vowels are classified [±back], [±round] and [±high].[60]
The only diphthongs in the language are found in loanwords and may be categorised as falling diphthongs usually analyzed as a sequence of /j/ and a vowel.[54]
Vowel harmony

The principle of vowel harmony, which permeates Turkish word-formation and suffixation, is due to the natural human tendency towards economy of muscular effort.[61] This principle is expressed in Turkish through three rules:
- If the first vowel of a word is a back vowel, any subsequent vowel is also a back vowel; if the first is a front vowel, any subsequent vowel is also a front vowel.[61]
- If the first vowel is unrounded, so too are subsequent vowels.[61]
- If the first vowel is rounded, subsequent vowels are either rounded and close or unrounded and open.[62]
The second and third rules minimize muscular effort during speech. More specifically, they are related to the phenomenon of labial assimilation:[63] if the lips are rounded (a process that requires muscular effort) for the first vowel they may stay rounded for subsequent vowels.[62] If they are unrounded for the first vowel, the speaker does not make the additional muscular effort to round them subsequently.[61]
Grammatical affixes have "a chameleon-like quality",[64]: 21 and obey one of the following patterns of vowel harmony:
- twofold (-e/-a):[i] In his more recent works Lewis prefers to omit the superscripts, on the grounds that "there is no need for this once the principle has been grasped" (Lewis [2001]).[56]: 18 the locative case suffix, for example, is -de after front vowels and -da after back vowels. The notation -de² is a convenient shorthand for this pattern.
- fourfold (-i/-ı/-ü/-u): the genitive case suffix, for example, is -in or -ın after unrounded vowels (front or back respectively); and -ün or -un after the corresponding rounded vowels. In this case, the shorthand notation -in4 is used.
Practically, the twofold pattern (also referred to as the e-type vowel harmony) means that in the environment where the vowel in the word stem is formed in the front of the mouth, the suffix will take the e-form, while if it is formed in the back it will take the a-form. The fourfold pattern (also called the i-type) accounts for rounding as well as for front/back.[65] The following examples, based on the copula -dir4 ("[it] is"), illustrate the principles of i-type vowel harmony in practice: Türkiye'dir ("it is Turkey"),[j] kapıdır ("it is the door"), but gündür ("it is the day"), paltodur ("it is the coat").[66]
Exceptions to vowel harmony
These are four word-classes that are exceptions to the rules of vowel harmony:
- Native, non-compound words, e.g. dahi "also", ela "light brown", elma "apple", hangi "which", hani "where", inanmak "to believe", kardeş "sibling", şişman "fat", anne "mother"
- Native compound words, e.g. bugün "today", dedikodu "gossip", haydi "come on"
- Foreign words, e.g. ferman (< Farsi فرماندهی "command"), mikrop (< French microbe "microbe"), piskopos (< Greek επίσκοπος "bishop")
- Invariable suffixes: –daş (denoting common attachment to the concept expressed by the noun), –yor (denoting the present tense in the third person), –ane (turning adjectives or nouns into adverbs), –ken (meaning "while being"), –leyin (meaning "in/at/during"), –imtırak (weakening an adjective of color or taste in a way similar to the English suffix –ish as in blueish), –ki (making a pronoun or adjective out of an adverb or a noun in the locative case), –gil (meaning "the house or family of"), –gen (referring to the name of plane figures)
The road sign in the photograph above illustrates several of these features:
- a native compound which does not obey vowel harmony: Orta+köy ("middle village"—a place name)
- a loanword also violating vowel harmony: viyadük (< French viaduc "viaduct")
- the possessive suffix-i4 harmonizing with the final vowel (and softening the k by consonant alternation): viyadüğü[citation needed]
The rules of vowel harmony may vary by regional dialect. The dialect of Turkish spoken in the Trabzon region of northeastern Turkey follows the reduced vowel harmony of Old Anatolian Turkish, with the additional complication of two missing vowels (ü and ı), thus there is no palatal harmony. It is likely that elün meant "your hand" in Old Anatolian. While the 2nd person singular possessive would vary between back and front vowel, -ün or -un, as in elün for "your hand" and kitabun for "your book", the lack of ü vowel in the Trabzon dialect means -un would be used in both of these cases — elun and kitabun.[18]
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (August 2018) |
Remove ads
Word-accent
Summarize
Perspective
With the exceptions stated below, Turkish words are oxytone (accented on the last syllable).
Exceptions to word-accent rules
- Place-names are not oxytone:[61] Anádolu (Anatolia), İstánbul. Most place names are accented on their first syllable as in Páris. This holds true when place names are spelled the same way as common nouns, which are oxytone: mısír (maize), Mísır (Egypt), sirkecı̇́ (vinegar-seller), Sı̇́rkeci (district in Istanbul), bebék (doll, baby), Bébek (district in Istanbul), ordú (army), Órdu (a Turkish city on the Black Sea).
- Foreign nouns usually retain their original accentuation,[61] e.g., lokánta (< Italian locanda "restaurant"), gazéte (< Italian gazzetta "newspaper")
- Some words about family members[62] and living creatures[62] have irregular accentuation: ánne (mother), görúmce (husband's sister), çekı̇́rge (grasshopper), karínca (ant), kokárca (skunk)
- Adverbs[62] are usually accented on the first syllable, e.g., şı̇́mdi (now), sónra (after), ánsızın (suddenly), gérçekten (really), (but gerçektén (from reality)), kíşın (during winter)
- Compound words[63] are accented on the end of the first element, e.g., çırílçıplak (stark naked), bakán (minister), báşbakan (prime minister)
- Diminutives constructed by suffix –cik are accented on the first syllable, e.g., úfacık (very tiny)
- Words with enclitic suffixes, –le (meaning "with"), –ken (meaning "while"), –ce (creating an adverb), –leyin (meaning "in" or "during"), –me (negating the verbal stem), –yor (denoting the present tense)
- Enclitic words, which shift the accentuation to the previous syllable, e.g., ol- (meaning to be), mi (denoting a question), gibi (meaning similar to), için (for), ki (that), de (too)
Remove ads
Syntax
Summarize
Perspective
Sentence groups
Turkish has two groups of sentences: verbal and nominal sentences. In the case of a verbal sentence, the predicate is a finite verb, while the predicate in nominal sentence will have either no overt verb or a verb in the form of the copula ol or y (variants of "be"). Examples of both are given below:[67]
Negation
The two groups of sentences have different ways of forming negation. A nominal sentence can be negated with the addition of the word değil. For example, the sentence above would become Necla öğretmen değil ('Necla is not a teacher'). However, the verbal sentence requires the addition of a negative suffix -me to the verb (the suffix comes after the stem but before the tense): Necla okula gitmedi ('Necla did not go to school').[68]
Yes/no questions
In the case of a verbal sentence, an interrogative clitic mi is added after the verb and stands alone, for example Necla okula gitti mi? ('Did Necla go to school?'). In the case of a nominal sentence, then mi comes after the predicate but before the personal ending, so for example Necla, siz öğretmen misiniz? ('Necla, are you [formal, plural] a teacher?').[68]
Word order
Word order in simple Turkish sentences is generally subject–object–verb, as in Korean and Latin, but unlike English, for verbal sentences and subject-predicate for nominal sentences. However, as Turkish possesses a case-marking system, and most grammatical relations are shown using morphological markers, often the SOV structure has diminished relevance and may vary. The SOV structure may thus be considered a "pragmatic word order" of language, one that does not rely on word order for grammatical purposes.[69]
Immediately preverbal
Consider the following simple sentence which demonstrates that the focus in Turkish is on the element that immediately precedes the verb:[70]
Postpredicate
The postpredicate position signifies what is referred to as background information in Turkish — information that is assumed to be known to both the speaker and the listener, or information that is included in the context. Consider the following examples:[67]
Topic
There has been some debate among linguists whether Turkish is a subject-prominent (like English) or topic-prominent (like Japanese and Korean) language, with recent scholarship implying that it is indeed both subject and topic-prominent.[71] This has direct implications for word order as it is possible for the subject to be included in the verb-phrase in Turkish. There can be S/O inversion in sentences where the topic is of greater importance than the subject.
Remove ads
Grammar
Summarize
Perspective
Turkish is an agglutinative language and frequently uses affixes, and specifically suffixes, or endings.[k] One word can have many affixes and these can also be used to create new words, such as creating a verb from a noun, or a noun from a verbal root (see the section on Word formation). Most affixes indicate the grammatical function of the word.[56]: Chapter XIV The only native prefixes are alliterative intensifying syllables used with adjectives or adverbs: for example sımsıcak ("boiling hot" < sıcak) and masmavi ("bright blue" < mavi).[l]
The extensive use of affixes can give rise to long words, e.g. Çekoslovakyalılaştıramadıklarımızdanmışsınızcasına, meaning "In the manner of you being one of those that we apparently couldn't manage to convert to Czechoslovakian". While this case is contrived, long words frequently occur in normal Turkish, as in this heading of a newspaper obituary column: Bayramlaşamadıklarımız (Bayram [festival]-Recipr-Impot-Partic-Plur-PossPl1; "Those of our number with whom we cannot exchange the season's greetings").[m] Another example can be seen in the final word of this heading of the online Turkish Spelling Guide (İmlâ Kılavuzu): Dilde birlik, ulusal birliğin vazgeçilemezlerindendir ("Unity in language is among the indispensables [dispense-Pass-Impot-Plur-PossS3-Abl-Copula] of national unity ~ Linguistic unity is a sine qua non of national unity").[72]
Nouns
Gender
Turkish does not have grammatical gender and the sex of a person does not affect the forms of words. The third-person pronoun o may refer to "he", "she" or "it." Despite this lack, Turkish still has ways of indicating gender in nouns:
- Most domestic animals have male and female forms, e.g., aygır (stallion), kısrak (mare), boğa (bull), inek (cow).
- For other animals, the sex may be indicated by adding the word erkek (male) or dişi (female) before the corresponding noun, e.g., dişi kedi (female cat).
- For people, the female sex may be indicated by adding the word kız (girl) or kadın (woman), e.g., kadın kahraman (heroine) instead of kahraman (hero).
- Some foreign words of French or Arabic origin already have separate female forms, e.g., aktris (actress).
- The Serbo-Croat feminine suffix –ica is used in three borrowings: kraliçe (queen), imparatoriçe (empress) and çariçe (tsarina). This suffix was used in the neologism tanrıça (< Old Turkic tanrı "god").
Case
There is no definite article in Turkish, but definiteness of the object is implied when the accusative ending is used (see below). Turkish nouns decline by taking case endings. There are six noun cases in Turkish, with all the endings following vowel harmony (shown in the table using the shorthand superscript notation). Since the postposition ile often gets suffixed onto the noun, some analyze it as an instrumental case, although in formal speech it takes the genitive with personal pronouns, singular demonstratives, and interrogative kim. The plural marker -ler ² immediately follows the noun before any case or other affixes (e.g. köylerin "of the villages").[citation needed]
The accusative case marker is used only for definite objects; compare (bir) ağaç gördük "we saw a tree" with ağacı gördük "we saw the tree".[n] The plural marker -ler ² is generally not used when a class or category is meant: ağaç gördük can equally well mean "we saw trees [as we walked through the forest]"—as opposed to ağaçları gördük "we saw the trees [in question]".[citation needed]
The declension of ağaç illustrates two important features of Turkish phonology: consonant assimilation in suffixes (ağaçtan, ağaçta) and voicing of final consonants before vowels (ağacın, ağaca, ağacı).[citation needed]
Additionally, nouns can take suffixes that assign person: for example -imiz 4, "our". With the addition of the copula (for example -im 4, "I am") complete sentences can be formed. The interrogative particle mi 4 immediately follows the word being questioned, and also follows vowel harmony: köye mi? "[going] to the village?", ağaç mı? "[is it a] tree?".[citation needed]
Personal pronouns
The Turkish personal pronouns in the nominative case are ben (1s), sen (2s), o (3s), biz (1pl), siz (2pl, or 2h), and onlar (3pl). They are declined regularly with some exceptions: benim (1s gen.); bizim (1pl gen.); bana (1s dat.); sana (2s dat.); and the oblique forms of o use the root on. As mentioned before, all demonstrative singular and personal pronouns take the genitive when ile is affixed onto it: benimle (1s ins.), bizimle (1pl ins.); but onunla (3s ins.), onlarla (3pl ins.). All other pronouns (reflexive kendi and so on) are declined regularly.[citation needed]
Noun phrases (tamlama)
Two nouns, or groups of nouns, may be joined in either of two ways:
- definite (possessive) compound (belirtili tamlama). E.g. Türkiye'nin sesi "the voice of Turkey (radio station)": the voice belonging to Turkey. Here the relationship is shown by the genitive ending -in4 added to the first noun; the second noun has the third-person suffix of possession -(s)i4.
- indefinite (qualifying) compound (belirtisiz tamlama). E.g. Türkiye Cumhuriyeti "Turkey-Republic[o] = the Republic of Turkey": not the republic belonging to Turkey, but the Republic that is Turkey. Here the first noun has no ending; but the second noun has the ending (s)i4—the same as in definite compounds.[citation needed]
The following table illustrates these principles.[56]: 41–47 In some cases, the constituents of the compounds are themselves compounds; for clarity these subsidiary compounds are marked with [square brackets]. The suffixes involved in the linking are underlined. If the second noun group already had a possessive suffix (because it is a compound by itself), no further suffix is added.
As the last example shows, the qualifying expression may be a substantival sentence rather than a noun or noun group.[s]
There is a third way of linking the nouns where both nouns take no suffixes (takısız tamlama). However, in this case the first noun acts as an adjective,[73] e.g. Demir kapı (iron gate), elma yanak ("apple cheek", i.e. red cheek), kömür göz ("coal eye", i.e. black eye) :
Adjectives
Turkish adjectives are not declined. However most adjectives can also be used as nouns, in which case they are declined: e.g. güzel ("beautiful") → güzeller ("(the) beautiful ones / people"). Used attributively, adjectives precede the nouns they modify. The adjectives var ("existent") and yok ("non-existent") are used in many cases where English would use "there is" or "have", e.g. süt yok ("there is no milk", lit. "(the) milk (is) non-existent"); the construction "noun 1-GEN noun 2-POSS var/yok" can be translated "noun 1 has/doesn't have noun 2"; imparatorun elbisesi yok "the emperor has no clothes" ("(the) emperor-of clothes-his non-existent"); kedimin ayakkabıları yoktu ("my cat had no shoes", lit. "cat-my-of shoe-plur.-its non-existent-past tense").[citation needed]
Verbs
Turkish verbs indicate person. They can be made negative, potential ("can"), or non-potential ("cannot"). Furthermore, Turkish verbs show tense (present, past, future, and aorist), mood (conditional, imperative, inferential, necessitative, and optative), and aspect. The inferential suffix -miş4 is also glossed as a direct evidential[74] or a mirative.[75] Negation is expressed by the suffix -me²- immediately following the stem.
Verb tenses
(For the sake of simplicity the term "tense" is used here throughout, although for some forms "aspect" or "mood" might be more appropriate.) There are nine simple and 20 compound tenses in Turkish. The nine simple tenses are: simple past (di'li geçmiş), inferential past (miş'li geçmiş), present continuous, simple present (aorist), future, optative, subjunctive, necessitative ("must") and imperative.[76] There are three groups of compound forms. Story (hikaye) is the witnessed past of the above forms (except command), referral (rivayet) is the unwitnessed past of the above forms (except simple past and command), conditional (koşul) is the conditional form of the first five basic tenses.[77] In the example below, the second person singular of the verb gitmek ("go"), stem gid-/git-, is shown.
There are also so-called combined verbs, which are created by suffixing certain verb stems (like bil or ver) to the original stem of a verb. Bil is the suffix for the sufficiency mood. It is the equivalent of the English auxiliary verbs "able to", "can" or "may". Ver is the suffix for the swiftness mood, kal for the perpetuity mood and yaz for the approach ("almost") mood.[78] Thus, while gittin means "you went", gidebildin means "you could go" and gidiverdin means "you went swiftly". The tenses of the combined verbs are formed the same way as for simple verbs.
Attributive verbs (participles)
Turkish verbs have attributive forms, including present,[t] similar to the English present participle (with the ending -en2); future (-ecek2); indirect/inferential past (-miş4); and aorist (-er2 or -ir4).
The most important function of some of these attributive verbs is to form modifying phrases equivalent to the relative clauses found in most European languages. The subject of the verb in an -en2 form is (possibly implicitly) in the third person (he/she/it/they); this form, when used in a modifying phrase, does not change according to number. The other attributive forms used in these constructions are the future (-ecek2) and an older form (-dik4), which covers both present and past meanings.[u] These two forms take "personal endings," which have the same form as the possessive suffixes but indicate the person and possibly number of the subject of the attributive verb; for example, yediğim means "what I eat," yediğin means "what you eat," and so on. The use of these "personal or relative participles" is illustrated in the following table, in which the examples are presented according to the grammatical case which would be seen in the equivalent English relative clause.[v]
Remove ads
Vocabulary
Summarize
Perspective
Latest 2011 edition of Güncel Türkçe Sözlük (Current Turkish Dictionary), the official dictionary of the Turkish language published by Turkish Language Association, contains 117,000 words organized into 93,000 entries.[79][80]
Word origins
Around 86% of the Turkish vocabulary is of Turkic origin. The majority of the core vocabulary and the most commonly used words in Turkish, including those first acquired by children as they learn to speak, derive from Turkic. Nevertheless, Turkish vocabulary contains a significant number of loanwords from other languages, in which around 14% of Turkish words are of foreign origin. According to the Turkish Language Association, 6,463 of these foreign words come from Arabic, 4,974 from French, 1,374 from Persian, 632 from Italian, 538 from English, 399 from Greek, and 147 from Latin.[82]
In Turkish, there are many pairs of synonyms where one word is of foreign origin and the other of Turkic origin. These pairs are the result of the enrichment of the Turkish vocabulary with loanwords from Arabic, Persian and French, and of the Turkish language reform initiated in the early 20th century that aimed to restore foreign-origin words with Turkic equivalents.[30]
Word formation
Turkish extensively uses agglutination to form new words from nouns and verbal stems. The majority of Turkish words originate from the application of derivative suffixes to a relatively small set of core vocabulary.[83]
Turkish obeys certain principles when it comes to suffixation. Most suffixes in Turkish will have more than one form, depending on the vowels and consonants in the root- vowel harmony rules will apply; consonant-initial suffixes will follow the voiced/ voiceless character of the consonant in the final unit of the root; and in the case of vowel-initial suffixes an additional consonant may be inserted if the root ends in a vowel, or the suffix may lose its initial vowel. There is also a prescribed order of affixation of suffixes- as a rule of thumb, derivative suffixes precede inflectional suffixes which are followed by clitics, as can be seen in the example set of words derived from a substantive root below:
Another example, starting from a verbal root:
New words are also frequently formed by compounding two existing words into a new one, as in German. Compounds can be of two types- bare and (s)I. The bare compounds, both nouns and adjectives are effectively two words juxtaposed without the addition of suffixes for example the word for girlfriend kızarkadaş (kız+arkadaş) or black pepper karabiber (kara+biber). A few examples of compound words are given below:
However, the majority of compound words in Turkish are (s)I compounds, which means that the second word will be marked by the 3rd person possessive suffix. A few such examples are given in the table below (note vowel harmony):
Remove ads
Writing system
Summarize
Perspective

Turkish is written using a version of Latin script introduced in 1928 by Atatürk to replace the Ottoman Turkish alphabet, a version of Perso-Arabic script. The Ottoman alphabet marked only three different vowels—long ā, ū and ī—and included several redundant consonants, such as variants of z (which were distinguished in Arabic but not in Turkish). The omission of short vowels in the Arabic script was claimed to make it particularly unsuitable for Turkish, which has eight vowels.[54]
The reform of the script was an important step in the cultural reforms of the period. The task of preparing the new alphabet and selecting the necessary modifications for sounds specific to Turkish was entrusted to a Language Commission composed of prominent linguists, academics, and writers. The introduction of the new Turkish alphabet was supported by public education centers opened throughout the country, cooperation with publishing companies, and encouragement by Atatürk himself, who toured the country teaching the new letters to the public.[84] As a result, there was a dramatic increase in literacy from its original, pre-modern levels.[85][need quotation to verify]
The Latin alphabet was applied to the Turkish language for educational purposes even before the 20th-century reform. Instances include a 1635 Latin-Albanian dictionary by Frang Bardhi, who also incorporated several sayings in the Turkish language, as an appendix to his work (e.g. alma agatsdan irak duschamas[y]—"An apple does not fall far from its tree").
Turkish now has an alphabet suited to the sounds of the language: the spelling is largely phonemic, with one letter corresponding to each phoneme.[86] Most of the letters are used approximately as in English, the main exceptions being ⟨c⟩, which denotes [dʒ] (⟨j⟩ being used for the [ʒ] found in Persian and European loans); and the undotted ⟨ı⟩, representing [ɯ]. As in German, ⟨ö⟩ and ⟨ü⟩ represent [ø] and [y]. The letter ⟨ğ⟩, in principle, denotes [ɣ] but has the property of lengthening the preceding vowel and assimilating any subsequent vowel. The letters ⟨ş⟩ and ⟨ç⟩ represent [ʃ] and [tʃ], respectively. A circumflex is written over back vowels following ⟨k⟩ and ⟨g⟩ when these consonants represent [c] and [ɟ]—almost exclusively in Arabic and Persian loans.[z][56]: 3–7
The Turkish alphabet consists of 29 letters (q, w, x omitted and ç, ş, ğ, ı, ö, ü added); the complete list is:
- a, b, c, ç, d, e, f, g, ğ, h, ı, i, j, k, l, m, n, o, ö, p, r, s, ş, t, u, ü, v, y, and z (Capital of i is İ and lowercase I is ı.)
The specifically Turkish letters and spellings described above are illustrated in this table:
Remove ads
Sample texts
Summarize
Perspective
Dostlar Beni Hatırlasın
Dostlar Beni Hatırlasın is a Turkish folk poem by the world-renowned poet and ashik Âşık Veysel Şatıroğlu (1894–1973).
İnsan Hakları Evrensel Bildirisi
Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in Turkish:
- Bütün insanlar hür, haysiyet ve haklar bakımından eşit doğarlar. Akıl ve vicdana sahiptirler ve birbirlerine karşı kardeşlik zihniyeti ile hareket etmelidirler.
Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in English:
- All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
International Phonetic Alphabet transcription:
- [byˈt̪ʰyn̪ in̪s̪än̪ˈɫ̪äɾ̞̊ hyɾ̞̊ häjs̪iˈje̞t̪ ve̞ häk̠ˈɫ̪äɾ‿bäk̠ʰɯmɯn̪ˈd̪än̪ e̞ˈʃit̪ d̪o̞.äˈɫ̪äɾ̞̊ ‖ äˈk̠ʰɯɫ̪ ve̞ vid͡ʒd̪äˈn̪ä sä(h)ipt̪ʰiɾˈl̠ɛɾ̞̊ ve̞ biɾbiɾl̠e̞ɾiˈn̪e̞ k̠ʰäɾˈʃɯ k̠ʰäɾd̪e̞ʃˈl̠ik̟ z̪ihn̪ije̞ˈt̪ʰi‿iˈl̠e̞ häɾe̞ˈk̟ʰe̞t̪ e̞t̪me̞l̠id̪iɾˈl̠ɛɾ̞̊ ‖]
Remove ads
Turkish computer keyboard

Turkish language uses two standardised keyboard layouts, known as Turkish Q (QWERTY) and Turkish F, with Turkish Q being the most common.
See also
Notes
- Turkish language is official in Kirkuk Governorate, Saladin Governorate, and Kifri districts.[10] In addition, it is an official language in the administrative units in which they constitute density of population.
- Turkish language is currently official in Centar Zupa and Plasnica Municipality[15]
- The name TDK itself exemplifies this process. The words tetkik and cemiyet in the original name are both Arabic loanwords (the final -i of cemiyeti being a Turkish possessive suffix); kurum is a native Turkish word based on the verb kurmak, "set up, found".[citation needed]
- The vowel represented by ⟨ı⟩ is also commonly transcribed as ⟨ɨ⟩ in linguistic literature.
- In modern Turkish orthography, an apostrophe is used to separate proper names from any suffixes.
- This "splendid word" appeared at the time of Bayram, the festival marking the end of the month of fasting.[56]: 287
- Note the similarity with the French phrase un m'as-tu-vu "a have-you-seen-me?", i.e., a vain and pretentious person.
- The conventional translation of the film title Dünyayı Kurtaran Adam, The Man Who Saved the World, uses the past tense. Semantically, his saving the world takes place though in the (narrative) present.
- This more complex example from Orhan Pamuk's Kar (Snow) contains a nested structure: [which he knew [were approaching]]. Maureen Freely's more succinct and idiomatic translation is the days in prison he knew lay ahead. Pamuk uses the spelling hapisane.
- From the perspective of Turkish grammar yaklaştığını anladığı is exactly parallel to babasını gördüğüm ("whose father I saw"), and could therefore be paraphrased as "whose approaching he understood".
- In modern Turkish spelling: elma ağaçtan ırak düşmez.
- In these cases the circumflex conveys information about the preceding consonant rather than the vowel over which it is written.
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads



