Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
EIF1AX
Protein-coding gene in humans From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
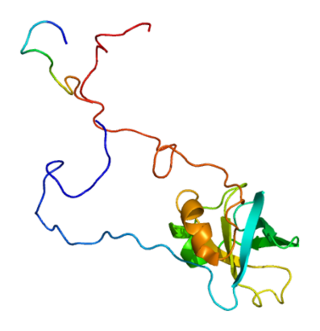
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A, X-chromosomal (eIF1A) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF1AX gene.[5][6][7] This gene encodes an essential eukaryotic translation initiation factor. The protein is a component of the 43S pre-initiation complex (PIC), which mediates the recruitment of the small 40S ribosomal subunit to the 5' cap of messenger RNAs.[7]
Remove ads
Function
eIF1A is an important part of the translation intiation mechanism. It is located at the A-site of the small ribosomal subunit. During translation initiation, the 43S pre-initiation complex scans along the mRNA in search of a start codon. eIF1A's N-terminal tail interacts with the initiator tRNA and the start codon by extending into the P-site, thereby increasing the fidelity of start codon selection.[8] After the start codon has been selected and eIF1, eIF2, and eIF5 have left the pre-initiation complex, eIF5B is recruited to continue the initiation process. Here, eIF1A interacts with eIF5B such that eIF5B is remodeled into a conformation that allows joining of the large ribosomal subunit.[9] After the joining of the subunit, it is the dissociation of eIF1A that permits eIF5B to rearrange again, placing the tRNA in its final position.[9]
Remove ads
Clinical significance
Mutations in this gene have been recurrently seen associated to cases of uveal melanoma with disomy 3.[10] eIF1A is mutated in thyroid cancers.[11]
Interactions
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads