Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
ICAM2
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Intercellular adhesion molecule 2 (ICAM2), also known as CD102 (Cluster of Differentiation 102), is a human gene, and the protein resulting from it.
Remove ads
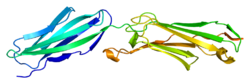
Protein structure
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) family. All ICAM proteins are type I transmembrane glycoproteins, contain 2–9 immunoglobulin-like C2-type domains, and bind to the leukocyte adhesion LFA-1 protein.
Protein functions
ICAM-2 molecules regulate spermatid adhesion on Sertoli cell on the apical side of the blood-testis barrier (towards the lumen), thus playing a major role in spermatogenesis.[5]
This protein may also play a role in lymphocyte recirculation by blocking LFA-1-dependent cell adhesion. It mediates adhesive interactions important for antigen-specific immune response, NK-cell mediated clearance, lymphocyte recirculation, and other cellular interactions important for immune response and surveillance.[6]
Remove ads
Interactions
ICAM2 has been shown to interact with EZR.[7] It has also been shown to bind to P9 (Uniprot: B2UM07), a secreted protein from Akkermansia muciniphila.[8]
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads