Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Ibogalog
Class of chemical compounds From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
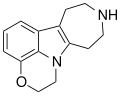
An ibogalog, or simplified ibogaine analogue, also known as a substituted 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydroazepino[4,5-b]indole (or simply substituted hexahydroazepinoindole), is a derivative of noribogaminalog and a simplified analogue of iboga alkaloids and related compounds such as ibogaine.[1][2][3][4] They are tricyclic cyclized tryptamines and are closely related to the β-carbolines or harmala alkaloids.[1][2][4] However, ibogalogs have a mostly-hydrogenated 7-membered azepine ring instead of the variably-saturated 6-membered pyridine ring present in β-carbolines.[1][2] Relative to the iboga alkaloids, ibogalogs retain the indole and hydrogenated azepine rings, but the isoquinuclidine (2-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octane) ring system has been removed, simplifying the chemical structure.[1][4]

Remove ads
Use and effects
Ibogalogs have been limitedly tested in humans, but anecdotal reports concerning tabernanthalog exist.[5][6][7]
Interactions
Pharmacology
Summarize
Perspective
Pharmacodynamics
Ibogalogs are known to act as potent serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor agonists, as well as acting as agonists of other serotonin receptors.[2][4][8] This is in contrast to iboga alkaloids like ibogaine and noribogaine, which are inactive as serotonin receptor agonists.[1] Ibogalogs also possess other actions, such as serotonin 5-HT2B receptor antagonism or partial agonism,[2] monoamine reuptake inhibition,[2] and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor inhibition.[9][10] Unlike iboga alkaloids like noribogaine, they show no opioid receptor agonism, for instance of the κ-opioid receptor.[1] In addition, the compounds have dramatically reduced potency at the hERG antitarget compared to ibogaine, which confers much less cardiotoxicity.[1][4]
Ibogalogs have been reported to produce psychoplastogenic,[2][1] antidepressant-like,[2][1] anxiolytic-like,[11] sedative-like,[11][12] antiaddictive-like,[1][13] and analgesic effects in animals.[14][15] Based on the rodent head-twitch response, a behavioral proxy of serotonergic psychedelic activity, ibogainalog may produce psychedelic effects in humans, while other assessed ibogainalogs, including tabernanthalog, ibogaminalog, noribogainalog, and catharanthalog, appear to be non-psychedelic.[1][11][15][4] In addition, PNU-22394 was non-hallucinogenic in clinical studies.[8]
History
Ibogalogs, such as PNU-22394, were first developed and described in the 1960s.[12][16] In the early 2000s, ibogalogs like PNU-22394 were studied and described further as potential appetite suppressants and weight loss drugs.[17][8][18] Subsequently, ibogalogs were studied and described in the early 2020s and thereafter, including by David E. Olson and colleagues at the University of California, Davis and Delix Therapeutics, as potential treatments of central nervous system disorders.[19][1][2] Relatedly, tabernanthalog (TBG; DLX-007) is under development for potential medical use.[1][20][21]
Remove ads
List of ibogalogs
Remove ads
Related compounds
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads