Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
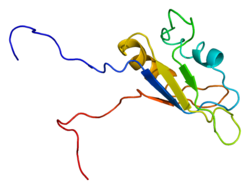
RNA-binding protein EWS
Human protein and coding gene From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
RNA-binding protein EWS is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EWSR1 gene on human chromosome 22, specifically 22q12.2.[5][6] It is one of 3 proteins in the FET protein family.[7]
Remove ads
Clinical significance
The q22.2 region of chromosome 22 encodes the N-terminal transactivation domain of the EWS protein and that region may become joined to one of several other chromosomes which encode various transcription factors; see EWS/FLI and OMIM-133450.[8] The expression of a chimeric protein with the EWS transactivation domain fused to the DNA binding region of a transcription factor generates a powerful oncogenic protein causing Ewing sarcoma and other members of the Ewing family of tumors. These translocations can occur due to chromoplexy, a burst of complex chromosomal rearrangements seen in cancer cells.[9] The normal EWS gene encodes an RNA binding protein closely related to FUS (gene) and TAF15, all of which have been associated to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.[10]
Remove ads
Interactions
The EWS protein has been shown to interact with:
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads