Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
SRD5A1
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
3-Oxo-5α-steroid 4-dehydrogenase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SRD5A1 gene.[5] It is one of three forms of steroid 5α-reductase.
Steroid 5α-reductase (EC 1.3.99.5) catalyzes, among other reactions, the conversion of testosterone into the more potent androgen, 5α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT). The SRD5A1, SRD5A2, and SRD5A3 genes in humans all encode 5α-reductase isozymes.[6]
Remove ads
Function
The 3-oxo-5α-steroid 4-dehydrogenase 1 enzyme is involved in bile acid biosynthesis, androgen and estrogen metabolism. For instance, the enzyme catalyzes the conversion of testosterone into the more potent androgen, 5α-dihydrotestosterone. It can also catalyze the conversion of progesterone, corticosterone or other steroids, to its corresponding 5α-3-oxo-steroids. This chemical reaction is called 5α-reduction, i.e. the reduction of the Δ5-4 double bond in steroids by catalyzing direct hydride transfer from NADPH to the carbon 5 position of the steroid substrate.[7][8][9]
Remove ads
Regulation
The SRD5A1 gene is particularly susceptible to epigenetic regulation, and responsive to environmental stressors at key stages during postnatal development. This regulation leads to increased DNA methylation at the gene's intronic enhancer, and its reduced expression, which have lasting effects on reproductive function.[10][11]
ETV4 family members bind to ETS DNA-binding sites and both regulate their own expression and the transcription of a subset of genes that are dependent upon testicular luminal fluid factors, including Ggt_pr4, SRD5A1, and Gpx5.[12]
Six-month dietary vitamin E deficiency in rats resulted in a twofold increase in the mRNA level of SRD5A1 gene and a twofold decrease in the mRNA level of GCLM gene but is not directly mediated by changes in promoter DNA methylation.[13]
Insulin increases the expression of 5α-reductase type 1 mRNA via Akt signalling suggest that elevated levels of 5α-reduced androgens seen in hyperinsulinemic conditions might be explained on the basis of a stimulatory effect of insulin on 5α-reductase in granulosa cells leading to impaired follicle growth and ovulation.[14]
Remove ads
Clinical significance
Hyperinsulinemia acutely enhances ACTH effects on both the androgen and glucocorticoid pathways leading to changes in steroid metabolites molar ratios that suggest insulin stimulation of 5α-reductase activity.[15]
PCOS is associated with enhanced androgen and cortisol metabolite excretion and increased 5α-reductase activity that cannot be explained by obesity alone. Increased adrenal corticosteroid production represents an important pathogenic pathway in PCOS.[16]
Progression to castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) is accompanied by increased expression of SRD5A1 over SRD5A2, which is otherwise the dominant isoenzyme expressed in the prostate. The dominant route of DHT synthesis in human CRPC bypasses testosterone, and instead requires 5α-reduction of androstenedione by SRD5A1 to 5α-androstanedione, which is then converted to DHT fuelling cancer growth.[17]
Expression

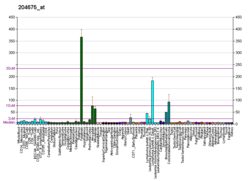
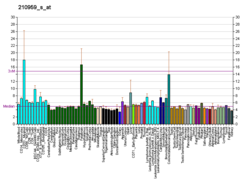
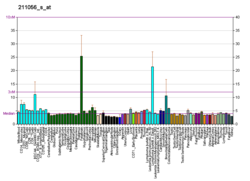
In humans, the protein isozyme encoded by the SRD5A1 gene is expressed in esophagus, liver, skin and 24 other tissues.[20][19]
See also
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads