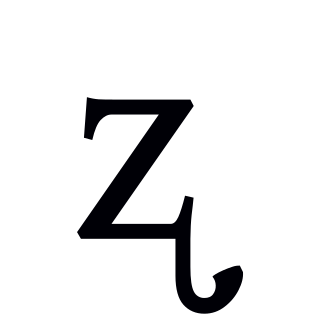Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Voiced retroflex fricative
Consonantal sound represented by ⟨ʐ⟩ in IPA From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The voiced retroflex sibilant fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʐ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is z`. Like all the retroflex consonants, the IPA symbol is formed by adding a rightward-pointing hook extending from the bottom of a z (the letter used for the corresponding alveolar consonant).
Remove ads
Features
Summarize
Perspective

Features of the voiced retroflex sibilant:
- Its manner of articulation is sibilant fricative, which means it is generally produced by channeling air flow along a groove in the back of the tongue up to the place of articulation, at which point it is focused against the sharp edge of the nearly clenched teeth, causing high-frequency turbulence.
- Its place of articulation is retroflex, which prototypically means it is articulated subapical (with the tip of the tongue curled up), but more generally, it means that it is postalveolar without being palatalized. That is, besides the prototypical subapical articulation, the tongue can be apical (pointed) or, in some fricatives, laminal (flat).
- Its phonation is voiced, which means the vocal cords vibrate during the articulation.
- It is an oral consonant, which means that air is exclusively allowed to escape through the mouth.
- It is a central consonant, which means it is produced by directing the airstream along the center of the tongue, rather than to the sides.
- Its airstream mechanism is pulmonic, which means it is articulated by pushing air solely with the intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles, as in most sounds.
Remove ads
Occurrence
Summarize
Perspective
In the following transcriptions, diacritics may be used to distinguish between apical [ʐ̺] and laminal [ʐ̻].
The commonality of [ʐ] cross-linguistically is 2% in a phonological analysis of 2155 languages.[1]
Remove ads
Voiced retroflex non-sibilant fricative
Summarize
Perspective
Features
Features of the voiced retroflex non-sibilant fricative:
- Its manner of articulation is fricative, which means it is produced by constricting air flow through a narrow channel at the place of articulation, causing turbulence.
- Its place of articulation is retroflex, which prototypically means it is articulated subapical (with the tip of the tongue curled up), but more generally, it means that it is postalveolar without being palatalized. That is, besides the prototypical subapical articulation, the tongue can be apical (pointed) or, in some fricatives, laminal (flat).
- Its phonation is voiced, which means the vocal cords vibrate during the articulation.
- It is an oral consonant, which means that air is exclusively allowed to escape through the mouth.
- It is a central consonant, which means it is produced by directing the airstream along the center of the tongue, rather than to the sides.
- Its airstream mechanism is pulmonic, which means it is articulated by pushing air solely with the intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles, as in most sounds.
Occurrence
See also
Citations
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads