Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Ukrainian language
East Slavic language From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Ukrainian (українська мова, ukrainska mova, IPA: [ʊkrɐˈjinʲsʲkɐ ˈmɔwɐ]) is an East Slavic language, spoken primarily in Ukraine. It is the first (native) language of a large majority of Ukrainians.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2024) |
Written Ukrainian uses the Ukrainian alphabet, a variant of the Cyrillic script. The standard language is studied by the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine and Potebnia Institute of Linguistics. Comparisons are often made between Ukrainian and Russian, another East Slavic language, yet there is more mutual intelligibility with Belarusian,[5] and a closer lexical distance to West Slavic Polish and South Slavic Bulgarian.[6]
Ukrainian is a descendant of Old East Slavic, a language spoken in the medieval state of Kievan Rusʹ. In the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the language developed into Ruthenian, where it became an official language,[7] before a process of Polonization began in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. By the 18th century, Ruthenian diverged into regional variants, and the modern Ukrainian language developed in the territory of present-day Ukraine.[8][9][10] Russification saw the Ukrainian language banned as a subject from schools and as a language of instruction in the Russian Empire, and continued in various ways in the Soviet Union.[11] Even so, the language continued to see use throughout the country, and remained particularly strong in Western Ukraine.[12][13]
Remove ads
Linguistic development
Summarize
Perspective
Theories
Specific developments that led to a gradual change of the Old East Slavic vowel system into the system found in modern Ukrainian began around the 12th/13th century (that is, still at the time of the Kievan Rusʹ) with a lengthening and raising of the Old East Slavic mid vowels e and o when followed by a consonant and a weak yer vowel that would eventually disappear completely, for example Old East Slavic котъ /kɔtə/ > Ukrainian кіт /kit/ 'cat' (via transitional stages such as /koˑtə̆/, /kuˑt(ə̆)/, /kyˑt/ or similar) or Old East Slavic печь /pʲɛtʃʲə/ > Ukrainian піч /pitʃ/ 'oven' (via transitional stages such as /pʲeˑtʃʲə̆/, /pʲiˑtʃʲ/ or similar).[14] This raising and other phonological developments of the time, such as the merger of the Old East Slavic vowel phonemes и /i/ and ы /ɨ/ into the specifically Ukrainian phoneme /ɪ ~ e/, spelled with и (in the 13th/14th centuries), and the fricativisation of the Old East Slavic consonant г /g/, probably first to /ɣ/ (in the 13th century), with /ɦ/ as a reflex in Modern Ukrainian, did not happen in Russian. Only the fricativisation of Old East Slavic г /g/ occurred in Belarusian, where the present-day reflex is /ɣ/.[citation needed]
Ahatanhel Krymsky and Aleksey Shakhmatov assumed the existence of the common spoken language of Eastern Slavs only in prehistoric times.[15] According to them the diversification of the Old East Slavic language took place in the 8th or early 9th century.[citation needed]
Russian linguist Andrey Zaliznyak stated that the Old Novgorod dialect differed significantly from that of other dialects of Kievan Rusʹ during the 11th–12th century, but started becoming more similar to them around the 13th–15th centuries. The modern Russian language hence developed from the fusion of this Novgorod dialect and the common dialect spoken by the other Kievan Rusʹ, whereas the modern Ukrainian and Belarusian languages developed from dialects which did not differ from each other in a significant way.[16]
Ukrainian linguist Stepan Smal-Stotsky denies the existence of a common Old East Slavic language at any time in the past.[17] Similar points of view were shared by Yevhen Tymchenko, Vsevolod Hantsov, Olena Kurylo, Ivan Ohienko and others. According to this theory, the dialects of East Slavic tribes evolved gradually from the common Proto-Slavic language without any intermediate stages during the 6th through 9th centuries. The Ukrainian language was formed by convergence of tribal dialects, mostly due to an intensive migration of the population within the territory of today's Ukraine in later historical periods. This point of view was also supported by George Shevelov's phonological studies,[18] which argue that specific features[which?] were already recognizable in the southern dialects of Old East Slavic (seen as ancestors to Ukrainian) as far back as these varieties can be documented.[9]
Origins and developments during medieval times
As a result of close Slavic contacts with the remnants of the Scythian and Sarmatian population north of the Black Sea, lasting into the early Middle Ages, the appearance of the voiced fricative γ/г (romanized "h"), in modern Ukrainian and some southern Russian dialects is explained by the assumption that it initially emerged in Scythian and related eastern Iranian dialects, from earlier common Proto-Indo-European *g and *gʰ.[19][20][21]
During the 13th century, when German settlers were invited to Ukraine by the princes of the Kingdom of Ruthenia, German words began to appear in the language spoken in Ukraine. Their influence would continue under[clarification needed] Poland not only through German colonists but also through the Yiddish-speaking Jews. Often such words involve trade or handicrafts. Examples of words of German or Yiddish origin spoken in Ukraine include dakh ("roof"), rura ("pipe"), rynok ("market"), kushnir ("furrier"), and majster ("master" or "craftsman").[22]
Developments under Poland and Lithuania
In the 13th century, eastern parts of Rus (including Moscow) came under Tatar rule until their unification under the Tsardom of Muscovy, whereas the south-western areas (including Kyiv) were incorporated into the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. For the following four centuries, the languages of the two regions evolved in relative isolation from each other. Direct written evidence of the existence of the Ukrainian language dates to the late 16th century.[23] By the 16th century, a peculiar official language formed: a mixture of the liturgical standardised language of Old Church Slavonic, Ruthenian and Polish. The influence of the latter gradually increased relative to the former two, as the nobility and rural large-landowning class, known as the szlachta, was largely Polish-speaking. Documents soon took on many Polish characteristics superimposed on Ruthenian phonetics.[24]
Polish–Lithuanian rule and education also involved significant exposure to Latin. Much of the influence of Poland on the development of the Ukrainian language has been attributed to this period, and is reflected in multiple words and constructions used in everyday Ukrainian speech that were taken from Polish or Latin. Examples of Polish words adopted from this period include zavzhdy (always; taken from old Polish word zawżdy) and obitsiaty (to promise; taken from Polish obiecać) and from Latin (via Polish) raptom (suddenly) and meta (aim or goal).[22]
Significant contact with Tatars and Turks resulted in many Turkic words, particularly those involving military matters and steppe industry, being adopted into the Ukrainian language. Examples include torba (bag) and tyutyun (tobacco).[22]
Because of the substantial number of loanwords from Polish, German, Czech and Latin, early modern vernacular Ukrainian (prosta mova, "simple speech") had more lexical similarity with West Slavic languages than with Russian or Church Slavonic.[25] By the mid-17th century, the linguistic divergence between the Ukrainian and Russian languages had become so significant that there was a need for translators during negotiations for the Treaty of Pereyaslav, between Bohdan Khmelnytsky, head of the Zaporozhian Host, and the Russian state.[26]
By the 18th century, Ruthenian had diverged into regional variants, developing into the modern Belarusian, Rusyn, and Ukrainian languages.[8][9][10]
Chronology
The accepted chronology of Ukrainian divides the language into Old Ukrainian, Middle Ukrainian, and Modern Ukrainian.[27] Shevelov explains that much of this is based on the character of contemporary written sources, ultimately reflecting socio-historical developments, and he further subdivides the Middle period into three phases:[28][29][30]
- Proto-Ukrainian (abbreviated PU, Ukrainian: protoukrajinsʹkyj period, until the mid-11th century), with no extant written sources by speakers in Ukraine. Corresponding to aspects of Old East Slavic.
- Old Ukrainian (OU, davnʹoukrajinsʹkyj period or davnʹoukrajinsʹka mova, mid-11th to 14th c., conventional end date 1387), elements of phonology are deduced from written texts mainly in Church Slavic. Part of broader Old East Slavic.
- Middle Ukrainian (serednʹoukrajinsʹkyj period or staroukrajinsʹka mova, 15th to 18th c.), historically called Ruthenian.
- Early Middle Ukrainian (EMU, rannʹoserednʹoukrajinsʹkyj period, 15th to mid-16th c., 1387–1575), analysis focuses on distinguishing Ukrainian and Belarusian texts.
- Middle Ukrainian (MU, serednʹoukrajinsʹkyj period, mid-16th to early 18th c., 1575–1720), represented by several vernacular language varieties as well as a version of Church Slavonic.
- Late Middle Ukrainian (LMU, piznoserednʹoukrajinsʹkyj period, rest of the 18th c., 1720–1818), found in many mixed Ukrainian–Russian and Russian–Ukrainian texts.
- Modern Ukrainian (MoU, from the very end of the 18th c., sučasnyj period or sučasna ukrajinsʹka mova, from 1818), the vernacular recognized first in literature, and subsequently all other written genres.
Ukraine marks the Day of Ukrainian Writing and Language on 9 November, the Eastern Orthodox feast day of Nestor the Chronicler.[citation needed]
Remove ads
History of the spoken language
Summarize
Perspective

Rusʹ and Kingdom of Ruthenia
The era of Kievan Rusʹ (c. 880–1240) is the subject of some linguistic controversy, as the language of much of the literature was purely or heavily Old Church Slavonic. Some theorists[which?] see an early Ukrainian stage in language development here, calling it Old Ruthenian; others[which?] term this era Old East Slavic. Russian theorists tend to amalgamate Rusʹ to the modern nation of Russia, and call this linguistic era Old Russian. However, according to Russian linguist Andrey Zaliznyak (2012), people from the Novgorod Republic did not call themselves Rusʹ until the 14th century; earlier Novgorodians reserved the term Rusʹ for the Kiev, Pereyaslavl and Chernigov principalities.[16] At the same time as evidenced by contemporary chronicles, the ruling princes and kings of Galicia–Volhynia and Kiev called themselves "people of Rusʹ" (in foreign sources called "Ruthenians"),[citation needed] and Galicia–Volhynia has alternately been called the Principality or Kingdom of Ruthenia.[31]
Also according to Andrey Zaliznyak, the Novgorodian dialect differed significantly from that of other dialects of Kievan Rus during the 11th–12th century, but started becoming more similar to them around 13th–15th centuries. The modern Russian language hence developed from the fusion of this Novgorodian dialect and the common dialect spoken by the other Kievan Rus, whereas the modern Ukrainian and Belarusian languages developed from the dialects which did not differ from each other in a significant way.[16]
In the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (c. 1349–1569)

During the 14th century, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania gradually established control over most of present-day Ukraine, except for Galicia, which would end up within the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland (since 1434 largely administered as the Ruthenian Voivodeship). Local autonomy of both rule and language was a marked feature of Lithuanian rule. In the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, administration evolved largely upon the legacy of Kievan Rus' law. Old East Slavic became the language of the chancellery, known as "Chancery Slavonic", and gradually evolved into the Ruthenian language. Ruthenian would be the prevailing language in the Lithuanian Metrica of the 15th and 16th century, and the original language of the Statutes of Lithuania (1529, 1566, and 1588), that were only later translated into Latin, and then Polish.[citation needed]
In the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland (1569–1648)
Polish rule, which came later, was accompanied by a more assimilationist policy. By the 1569 Union of Lublin that formed the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, a significant part of Ukrainian territory was moved from Lithuanian rule to Polish administration, resulting in cultural Polonization and visible attempts to colonize Ukraine by the Polish nobility.[32]
Many Ukrainian nobles learned the Polish language and converted to Catholicism during that period in order to maintain their lofty aristocratic position.[32] Lower classes were less affected because literacy was common only in the upper class and clergy. The latter were also under significant Polish pressure after the Union with the Catholic Church. Most of the educational system was gradually Polonized. In Ruthenia, the language of administrative documents gradually shifted towards Polish.[citation needed]
Polish has had heavy influences on Ukrainian, particularly in Western Ukraine. The southwestern Ukrainian dialects are transitional to Polish.[33] As the Ukrainian language developed further, some borrowings from Tatar and Turkish occurred. Ukrainian culture and language flourished in the sixteenth and first half of the 17th century, when Ukraine was part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, albeit in spite of being part of the PLC, not as a result. Among many schools established in that time, the Kyiv-Mohyla Collegium (the predecessor of the modern Kyiv-Mohyla Academy), founded by the Orthodox Metropolitan Peter Mogila, was the most important. At that time languages were associated more with religions: Catholics spoke Polish, and members of the Orthodox church spoke Ruthenian.[citation needed]
In the Cossack Hetmanate and Tsarist Russia until 1800
When the Cossack Hetmanate arose in the mid-17th century, Polish remained a language of administration in the Hetmanate, and most Cossack officers and Polish nobles (two groups which overlapped a lot) still communicated with each other using a combination of Latin, Polish and Ruthenian.[34] On the other hand, the language barrier between Cossack officers and Muscovite officials had become so great that they needed translators to understand each other during negotiations, and hetman Bohdan Khmelnytsky 'had letters in Muscovite dialect translated into Latin, so that he could read them.'[34]
The 1654 Pereiaslav Agreement between Cossack Hetmanate and Alexis of Russia divided Ukraine between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia. During the following century, both monarchies became increasingly intolerant of Ukrainian own cultural and political aspirations.[35] Ukrainians found themselves in a colonial situation.[36] The Russian centre adopted the name Little Russia for Ukraine and Little Russian for the language,[37] an expression that originated in Byzantine Greek and may originally have meant "old, original, fundamental Russia", and had been in use since the 14th century.[38] Ukrainian high culture went into a long period of steady decline. The Kyiv-Mohyla Academy was taken over by the Russian Empire. Most of the remaining Ukrainian schools also switched to Polish or Russian in the territories controlled by these respective countries, which was followed by a new wave of Polonization and Russification of the native nobility. Gradually the official language of Ukrainian provinces under Poland was changed to Polish, while the upper classes in the Russian part of Ukraine used Russian.[citation needed]
In Austrian Galicia and Lodomeria (1772–1918)
After the 1772 First Partition of Poland, when the lands annexed by the Austrian Habsburg monarchy were reorganised as the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria, the Habsburg administration was initially surprised to find out that, apart from Poles, there were a lot of other people living in it whom they began calling Ruthenen ("Ruthenians" or "Rusyny").[39] They differed from the Poles in that the vast majority of them adhered to the Greek Catholic faith (organised as the Ruthenian Uniate Church) rather than Roman Catholic, and that their liturgical language was Church Slavonic rather than Latin.[39] Most of them had not received much education; they used Ruthenian only as a spoken language, few could read or write, and those who did more often used Polish or (increasingly) German instead.[39] As Empress Maria Theresa had introduced a general compulsory education (Allgemeiner Schulzwang) in 1774, and enacted it in newly-acquired Galicia and Lodomeria in 1777, the decision was made to produce Polish and Ruthenian textbooks that were used in elementary schools for those language communities.[39]
"Language is the property of a people, and no one should forget the speech of their own folk."
– Ivan Mohylnytsky, Information on the Ruthenian Language (1829)[40]: 56
Although some Ruthenian parish schools were established in some villages, and some printed primers and catechisms in Ruthenian were distributed there, the effects of Ruthenian-language education achieved very little until 1815.[39] That year, Ivan Mohylnytsky, a Przemyśl eparchy canon who contributed to the establishment of a strong network of Ruthenian parish schools and a teacher training school, published a catechism at the Royal University of Buda entitled Christian Learning in the Case of the Common Catechism for Parish Children.[41] He followed this up in 1823 by a Grammar of the Slovene–Ruthenian language (never published), and in 1829 by his treatise Information on the Ruthenian Language (published both in Polish as Rozprawa o ięzyku ruskim and in Ruthenian as "Відомість о руском языці"), which represents the first scholarly study arguing that Ruthenian was a language in its own right, separate from Polish, Russian, and Church Slavonic.[41] On the other hand, new educational regulations in 1818 determined that schools that were exclusively attended by children of Greek Catholic parents were to receive instruction in Ruthenian, whereas schools attended by children of both Roman Catholic and Greek Catholic parents had Polish as the medium of instruction.[42] Nevertheless, pupils at Ruthenian-instruction schools had to learn Polish as a second language as well.[42]
In higher education, Ruthenian was not valued as an equal language, and students were expected to learn and use Latin and Polish instead.[42] Students training to become Greek Catholic priests at the University of Lviv did receive instruction in Ruthenian in the so-called "Studium ruthenum" according to Austrian regulations between 1787 and 1809, but it was not a fully-fledged course; instead, it was regarded as a temporary measure for students who did not yet know Latin.[42] Both its professors and alumni received only half the salary of their counterparts from the "Studium latinum", the number of students steadily decreased over the decades, and in 1809 the Ruthenians themselves requested the "Studium ruthenum" to be abandoned.[42]
In the first few decades of the Austrian period in Galicia, there was also confusion amongst both the Habsburg administration and educated Ruthenians about which variety of written Ruthenian to use: late Church Slavonic, literary Russian, traditional written Ruthenian, or something close to how Ruthenian was actually spoken in Galicia at that time.[43] The Habsburg Imperial censor for Slavic publications, Jernej Kopitar (himself from Slovenia), encouraged Ruthenian authors to base their written language on the Ruthenian vernacular, and from December 1833 onwards, to write Ruthenian in a Latin alphabet rather than Cyrillic.[44] This initiated a discussion on Ruthenian identity, later called the "First Alphabet War" or "Blizzard".[44] Although most Ruthenian intellectuals did respond by increasingly basing their writings on spoken Ruthenian, the majority of them defended the use Cyrillic over concerns of Polonisation.[44] Nevertheless, they could not agree on various standardisation issues; three different Ruthenian grammars were published between 1834 and 1848, and none of them was widely adopted.[44] Before 1848, no Ruthenian dictionaries were produced, no Ruthenian-language periodical press existed within Habsburg Galicia, and Ruthenian played no role as language of administration.[44]

The Revolutions of 1848 in the Austrian Empire changed everything: the native languages of most populations in the Empire, including Ruthenian, were accorded official status, and all laws in the Danubian monarchy would be published in these languages from 1 October 1849 onwards.[45] Ruthenian would henceforth be used in local administration in the Landesgesetzblätter.[46] From 1849 onwards, various official periodicals were established in Ruthenian, and the Interior Ministry stipulated in July 1849 that street signs in Lviv had to include Ruthenian versions.[47] In October 1852, the Ministry of Justice also decreed that Ruthenian could be used by parties involved in legal issues in their communication with the courts of law, although it would take until 1861 to allow these letters to employ skoropys Cyrillic rather than Latin script (or the Muscovite graždanka variety of Cyrillic).[47] In the post-1848 era, there were some contradictory developments, some of which countered Polonisation in the sphere of education, while others stimulated further Polonisation in the sphere of administration.[48] Similarly, Galician Russophilia or Moscophilia strived towards ever greater assimilation of Ruthenian towards the so-called "Great Russian" language as used in Moscow, which still heavily leaned on Church Slavonic. Both the Habsburg administration and Greek Catholic Church raised concerns that these were "barely comprehensible" to the common people of Galicia and hampered the "development of the Ruthenian language", adding that Orthodox Imperial Russia was a threat to the overwhelmingly Catholic Habsburg realm.[49]
Matters once again came to a head in May 1859, when the Polish governor of Galicia Gołuchowski recommended Czech linguist Josef Jireček's proposal for a Ruthenian Latin alphabet, leading to the "Second Alphabet War" or "Blizzard".[50] Ruthenian intellectuals almost unanimously rejected the proposal for fear of Polonisation, leading the government to overreact by banning the "Russian script" (meaning the Muscovite graždanka) in July 1859, which Ruthenian writers generally ignored.[50] By March 1861, the Habsburg State Ministry essentially conceded defeat by stating that the Ruthenians themselves were responsible for developing their own language, and that it was not up to the government.[48] Around the same time, however, Ruthenian intellectuals became acquainted with the writings of Ukrainian intellectuals from "Little Russia" in the Russian Empire, such as poet Taras Shevchenko (died 1861), who was fiercely anti-Russian and Ukrainophile, leading many Galician Ruthenians to abandon their earlier Russophilia.[51] In between the pro-Polish and pro-Russian tendencies, the Ruthenian language in Galicia would gradually develop into an independent literary and intellectual written language in the second half of the 19th century, when it was increasingly called "Ukrainian".[52]
In the Russian Empire
During the 19th century, a revival of Ukrainian self-identification manifested in the literary classes of both Russian-Empire Dnieper Ukraine and Austrian Galicia. The Brotherhood of Sts Cyril and Methodius in Kyiv applied an old word for the Cossack motherland, Ukrajina, as a self-appellation for the nation of Ukrainians, and Ukrajinsʹka mova for the language. Many writers published works in the Romantic tradition of Europe demonstrating that Ukrainian was not merely a language of the village but suitable for literary pursuits.[citation needed]
However, in the Russian Empire expressions of Ukrainian culture and especially language were repeatedly persecuted for fear that a self-aware Ukrainian nation would threaten the unity of the empire. In 1804 Ukrainian as a subject and language of instruction was banned from schools.[11] In 1811, by order of the Russian government, the Kyiv-Mohyla Academy was closed.[citation needed]
In 1847 the Brotherhood of St Cyril and Methodius was terminated. The same year Taras Shevchenko was arrested, exiled for ten years, and banned for political reasons from writing and painting. In 1862 Pavlo Chubynsky was exiled for seven years to Arkhangelsk. The Ukrainian magazine Osnova was discontinued. In 1863, the tsarist interior minister Pyotr Valuyev proclaimed in his decree that "there never has been, is not, and never can be a separate Little Russian language".[53][54]
Although the name of Ukraine is known since 1187, it was not applied to the language until the mid-19th century.[55] The linguonym Ukrainian language appears in Yakub Holovatsky's book from 1849,[56] listed there as a variant name of the Little Russian language. In a private letter from 1854, Taras Shevchenko lauds "our splendid Ukrainian language".[57] Valuyev's decree from 1863 derides the "Little Russian" language throughout, but also mentions "the so-called Ukrainian language" once.[53] In Galicia, the earliest applications of the term Ukrainian to the language were in the hyphenated names Ukrainian-Ruthenian (1866, by Paulin Święcicki) or Ruthenian-Ukrainian (1871, by Panteleimon Kulish and Ivan Puluj), with non-hyphenated Ukrainian language appearing shortly thereafter (in 1878, by Mykhailo Drahomanov).[58][59]
A following ban on Ukrainian books led to Alexander II's secret Ems Ukaz, which prohibited publication and importation of most Ukrainian-language books, public performances and lectures, and even banned the printing of Ukrainian texts accompanying musical scores.[60] A period of leniency after 1905 was followed by another strict ban in 1914, which also affected Russian-occupied Galicia.[61]
For much of the 19th century the Austrian authorities demonstrated some preference for Polish culture, but the Ukrainians were relatively free to partake in their own cultural pursuits in Halychyna and Bukovina, where Ukrainian was widely used in education and official documents.[62] The suppression by Russia hampered the literary development of the Ukrainian language in Dnipro Ukraine, but there was a constant exchange with Halychyna, and many works were published under Austria and smuggled to the east.[citation needed]
By the time of the Russian Revolution of 1917 and the collapse of Austro-Hungary in 1918, Ukrainians were ready to openly develop a body of national literature, institute a Ukrainian-language educational system, and form an independent state (the Ukrainian People's Republic, shortly joined by the West Ukrainian People's Republic). During this brief independent statehood the stature and use of Ukrainian greatly improved.[13]
Speakers in the Russian Empire

In the Russian Empire Census of 1897 the following picture emerged, with Ukrainian being the second most spoken language of the Russian Empire. According to the Imperial census's terminology, the Russian language (Русскій) was subdivided into Ukrainian (Малорусскій, 'Little Russian'), what is known as Russian today (Великорусскій, 'Great Russian'), and Belarusian (Бѣлорусскій, 'White Russian').[citation needed]
The following table shows the distribution of settlement by native language ("по родному языку") in 1897 in Russian Empire governorates (guberniyas) that had more than 100,000 Ukrainian speakers.[63]
Although in the rural regions of the Ukrainian provinces, 80% of the inhabitants said that Ukrainian was their native language in the Census of 1897 (for which the results are given above), in the urban regions only 32.5% of the population claimed Ukrainian as their native language. For example, in Odesa (then part of the Russian Empire), at the time the largest city in the territory of current Ukraine, only 5.6% of the population said Ukrainian was their native language.[64]
Until the 1920s the urban population in Ukraine grew faster than the number of Ukrainian speakers. This implies that there was a (relative) decline in the use of Ukrainian language. For example, in Kyiv, the number of people stating that Ukrainian was their native language declined from 30.3% in 1874 to 16.6% in 1917.[64]
Soviet era

During the seven-decade-long Soviet era, the Ukrainian language held the formal position of the principal local language in the Ukrainian SSR.[65] However, practice was often a different story:[65] Ukrainian always had to compete with Russian, and the attitudes of the Soviet leadership towards Ukrainian varied from encouragement and tolerance to de facto banishment.[citation needed]
Officially, there was no state language in the Soviet Union until the very end when it was proclaimed in 1990 that Russian language was the all-Union state language and that the constituent republics had rights to declare additional state languages within their jurisdictions.[66] Still it was implicitly understood in the hopes of minority nations that Ukrainian would be used in the Ukrainian SSR, Uzbek would be used in the Uzbek SSR, and so on.[citation needed] However, Russian was used as the lingua franca in all parts of the Soviet Union and a special term, "a language of inter-ethnic communication", was coined to denote its status.[citation needed]
Stalin
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to itadding to it or making an edit request. (October 2023) |
Khrushchev thaw

After the death of Stalin (1953), a general policy of relaxing the language policies of the past was implemented (1958 to 1963). The Khrushchev era which followed saw a policy of relatively lenient concessions to development of the languages at the local and republic level, though its results in Ukraine did not go nearly as far as those of the Soviet policy of Ukrainianization in the 1920s. Journals and encyclopedic publications advanced in the Ukrainian language during the Khrushchev era, as well as transfer of Crimea under Ukrainian SSR jurisdiction.[citation needed]
Yet, the 1958 school reform that allowed parents to choose the language of primary instruction for their children, unpopular among the circles of the national intelligentsia in parts of the USSR, meant that non-Russian languages would slowly give way to Russian in light of the pressures of survival and advancement. The gains of the past, already largely reversed by the Stalin era, were offset by the liberal attitude towards the requirement to study the local languages (the requirement to study Russian remained).[citation needed]
Parents were usually free to choose the language of study of their children (except in few areas where attending the Ukrainian school might have required a long daily commute) and they often chose Russian, which reinforced the resulting Russification. In this sense, some analysts argue that it was not the "oppression" or "persecution", but rather the lack of protection against the expansion of Russian language that contributed to the relative decline of Ukrainian in the 1970s and 1980s. According to this view, it was inevitable that successful careers required a good command of Russian, while knowledge of Ukrainian was not vital, so it was common for Ukrainian parents to send their children to Russian-language schools, even though Ukrainian-language schools were usually available.[citation needed]
The number of students in Russian-language in Ukraine schools was constantly increasing, from 14 percent in 1939 to more than 30 percent in 1962.[67]
Shelest period
The Communist Party leader from 1963 to 1972, Petro Shelest, pursued a policy of defending Ukraine's interests within the Soviet Union. He proudly promoted the beauty of the Ukrainian language and developed plans to expand the role of Ukrainian in higher education. He was removed, however, after only a brief tenure, for being too lenient on Ukrainian nationalism.[citation needed]
Shcherbytsky period
The new party boss from 1972 to 1989, Volodymyr Shcherbytsky, purged the local party, was fierce in suppressing dissent, and insisted Russian be spoken at all official functions, even at local levels. His policy of Russification was lessened only slightly after 1985.[citation needed]
Gorbachev and perebudova

The management of dissent by the local Ukrainian Communist Party was more fierce and thorough than in other parts of the Soviet Union. As a result, at the start of the Mikhail Gorbachev reforms perebudova and hlasnist’ (Ukrainian for perestroika and glasnost), Ukraine under Shcherbytsky was slower to liberalize than Russia itself.[citation needed]
Although Ukrainian still remained the native language for the majority in the nation on the eve of Ukrainian independence, a significant share of ethnic Ukrainians were russified. In Donetsk there were no Ukrainian language schools and in Kyiv only a quarter of children went to Ukrainian language schools.[68]
The Russian language was the dominant vehicle, not just of government function, but of the media, commerce, and modernity itself. This was substantially less the case for western Ukraine, which escaped the artificial famine, Great Purge, and most of Stalinism. And this region became the center of a hearty, if only partial, renaissance of the Ukrainian language during independence.[citation needed]
Independence in the modern era
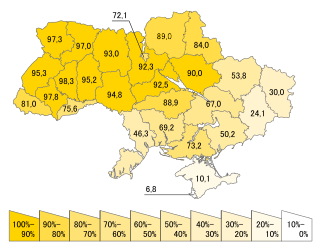

Since 1991, Ukrainian has been the official state language in Ukraine, and the state administration implemented government policies to broaden the use of Ukrainian. The educational system in Ukraine has been transformed over the first decade of independence from a system that is partly Ukrainian to one that is overwhelmingly so. The government has also mandated a progressively increased role for Ukrainian in the media and commerce.[citation needed]
In the 2001 census, 67.5% of the country's population named Ukrainian as their native language (a 2.8% increase from 1989), while 29.6% named Russian (a 3.2% decrease).[69] For many Ukrainians (of various ethnic origins), the term native language may not necessarily associate with the language they use more frequently. The overwhelming majority of ethnic Ukrainians consider the Ukrainian language native, including those who often speak Russian.[70]
According to the official 2001 census data, 92.3% of Kyiv region population responded "Ukrainian" to the native language (ridna mova) census question, compared with 88.4% in 1989, and 7.2% responded "Russian".[70]
In 2019, the law of Ukraine "On protecting the functioning of the Ukrainian language as the state language" was approved by the parliament, formalizing rules governing the usage of the language and introducing penalties for violations.[71]
Remove ads
Literature and literary language
Summarize
Perspective
The literary Ukrainian language, which was preceded by Old East Slavic literature, may be subdivided into two stages: during the 12th to 18th centuries what in Ukraine is referred to as "Old Ukrainian", but elsewhere, and in contemporary sources, is known as the Ruthenian language, and from the end of the 18th century to the present what in Ukraine is known as "Modern Ukrainian", but elsewhere is known as just Ukrainian.[citation needed]
Influential literary figures in the development of modern Ukrainian literature include the philosopher Hryhorii Skovoroda, Ivan Kotlyarevsky, Mykola Kostomarov, Mykhailo Kotsiubynsky, Shevchenko, Ivan Franko, and Lesia Ukrainka. The earliest literary work in the Ukrainian language was recorded in 1798 when Kotlyarevsky, a playwright from Poltava in southeastern Ukraine, published his epic poem, Eneyida, a burlesque in Ukrainian, based on Virgil's Aeneid. His book was published in vernacular Ukrainian in a satirical way to avoid being censored, and is the earliest known Ukrainian published book to survive through Imperial and, later, Soviet policies on the Ukrainian language.[citation needed]
Kotlyarevsky's work and that of another early writer using the Ukrainian vernacular language, Petro Artemovsky, used the southeastern dialect spoken in the Poltava, Kharkiv and southern Kyiv regions of the Russian Empire. This dialect would serve as the basis of the Ukrainian literary language when it was developed by Shevchenko and Kulish in the mid 19th century. In order to raise its status from that of a dialect to that of a language, various elements from folklore and traditional styles were added to it.[72]
The Ukrainian literary language developed further when the Russian state banned the use of the Ukrainian language, prompting many of its writers to move to the western Ukrainian region of Galicia which was under more liberal Austrian rule; after the 1860s the majority of Ukrainian literary works were published in Austrian Galicia. During this period Galician influences were adopted in the Ukrainian literary language, particularly with respect to vocabulary involving law, government, technology, science, and administration.[72]
Remove ads
Current usage
Summarize
Perspective

The use of the Ukrainian language is increasing after a long period of decline. Although there are almost fifty million ethnic Ukrainians worldwide, including 37.5 million in Ukraine in 2001 (77.8% of the total population at the time), the Ukrainian language is prevalent mainly in western and central Ukraine. In Kyiv, both Ukrainian and Russian are spoken, a notable shift from the recent past when the city was primarily Russian-speaking.[73]
The shift is believed to be caused mainly by an influx of migrants from western regions of Ukraine but also by some Kyivans opting to use the language they speak at home more widely in public settings. Public signs and announcements in Kyiv are displayed in Ukrainian. In southern and eastern Ukraine, Russian is the prevalent language in most large and some small cities. According to the Ukrainian Census of 2001, 87.8% of people living in Ukraine were fluent in Ukrainian.[73]
In August 2022, a survey in Ukraine by Rating Group found that 85% said they speak Ukrainian or Ukrainian and Russian at home, 51% only Ukrainian, an increase from 61% and 44% in February 2014.[74][75] In the same survey, 76% considered Ukrainian their native language (ridna mova), up from 57% in July 2012, including 30% of Russian speakers.[74][75]
Popular culture
Music
Ukrainian has become popular in other countries through movies and songs performed in the Ukrainian language. The most popular Ukrainian rock bands, such as Okean Elzy, Vopli Vidopliassova, and BoomBox perform regularly in tours across Europe, Israel, North America and especially Russia. In countries with significant Ukrainian populations, bands singing in the Ukrainian language sometimes reach top places on the charts, such as Enej (a band from Poland). Other notable Ukrainian-language bands are The Ukrainians from the United Kingdom, Klooch from Canada, Ukrainian Village Band from the United States, and the Kuban Cossack Choir from the Kuban region in Russia.[citation needed]
Cinema
This section needs to be updated. (April 2017) |
The 2010s saw a revival of Ukrainian cinema.[76] The top Ukrainian-language films (by IMDb rating) are:[77][better source needed]
Argots
Oleksa Horbach's 1951 study of argots analyzed historical primary sources (argots of professionals, thugs, prisoners, homeless, school children, etc.) paying special attention to etymological features of argots, word formation and borrowing patterns depending on the source-language (Church Slavonic, Russian, Czech, Polish, Romani, Greek, Romanian, Hungarian, German).[78]
Dialects

Northern group
South-eastern group
South-western group
Several modern dialects of Ukrainian exist.[79][80]
- Northern (Polissian) dialects:[81]
- (3) Eastern Polissian is spoken in Chernihiv (excluding the southeastern districts), in the northern part of Sumy, and in the southeastern portion of the Kyiv Oblast as well as in the adjacent areas of Russia, which include the southwestern part of the Bryansk Oblast (the area around Starodub), as well as in some places in the Kursk, Voronezh and Belgorod Oblasts.[82] No linguistic border can be defined. The vocabulary approaches Russian as the language approaches the Russian Federation. Both Ukrainian and Russian grammar sets can be applied to this dialect.[83]
- (2) Central Polissian is spoken in the northwestern part of the Kyiv Oblast, in the northern part of Zhytomyr and the northeastern part of the Rivne Oblast.[84]
- (1) West Polissian is spoken in the northern part of the Volyn Oblast, the northwestern part of the Rivne Oblast, and in the adjacent districts of the Brest Region in Belarus. The dialect spoken in Belarus uses Belarusian grammar and thus is considered by some to be a dialect of Belarusian.[85]
- Southeastern dialects:[86]
- (4) Middle Dnieprian is the basis of the Standard Literary Ukrainian. It is spoken in the central part of Ukraine, primarily in the southern and eastern part of the Kyiv Oblast. In addition, the dialects spoken in Cherkasy, Poltava, and Kyiv regions are considered to be close to "standard" Ukrainian.
- (5) Slobodan is spoken in Kharkiv, Sumy, Luhansk, and the northern part of Donetsk, as well as in the Voronezh and Belgorod regions of Russia.[87] This dialect is formed from a gradual mixture of Russian and Ukrainian, with progressively more Russian in the northern and eastern parts of the region. Thus, there is no linguistic border between Russian and Ukrainian, and, thus, both grammar sets can be applied.[83]
- A (6) Steppe dialect is spoken in southern and southeastern Ukraine. This dialect was originally the main language of the Zaporozhian Cossacks.[88]
- A Kuban dialect related to or based on the Steppe dialect is often referred to as Balachka and is spoken by the Kuban Cossacks in the Kuban region in Russia by the descendants of the Zaporozhian Cossacks, who settled in that area in the late 18th century. It was formed from a gradual mixture of Russian into Ukrainian. This dialect features the use of some Russian vocabulary along with some Russian grammar.[89] There are three main variants, which have been grouped together according to location.[90]
- Southwestern dialects:[91]
- (13) Boyko is spoken by the Boyko people on the northern side of the Carpathian Mountains in the Lviv and Ivano-Frankivsk Oblasts. It can also be heard across the border in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship of Poland.
- (12) Hutsul is spoken by the Hutsul people on the northern slopes of the Carpathian Mountains, in the extreme southern parts of the Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast, and in parts of the Chernivtsi and Transcarpathian Oblasts.
- Lemko is spoken by the Lemko people, whose homeland rests outside the borders of Ukraine in the Prešov Region of Slovakia along the southern side of the Carpathian Mountains, and in the southeast of modern Poland, along the northern sides of the Carpathians.
- (8) Podillian is spoken in the southern parts of the Vinnytsia and Khmelnytskyi Oblasts, in the northern part of the Odesa Oblast, and in the adjacent districts of the Cherkasy Oblast, the Kirovohrad Oblast, and the Mykolaiv Oblast.[92]
- (7) Volynian is spoken in Rivne and Volyn, as well as in parts of Zhytomyr and Ternopil. It is also used in Chełm, Poland.
- (11) Pokuttia (Bukovinian) is spoken in the Chernivtsi Oblast of Ukraine. This dialect has some distinct vocabulary borrowed from Romanian.
- (9) Upper Dniestrian (Kresy) is considered to be the main Galician dialect, spoken in the Lviv, Ternopil, and Ivano-Frankivsk Oblasts. Its distinguishing characteristics are the influence of Polish and the German vocabulary, which is reminiscent of the Austro-Hungarian rule. Some of the distinct words used in this dialect can be found here.[93]
- (10) Upper Sannian is spoken in the border area between Ukraine and Poland in the San river valley.
- The Rusyn language is considered by Ukrainian linguists to be a dialect of Ukrainian as well:[94]
- Dolinian Rusyn or Subcarpathian Rusyn is spoken in the Transcarpathian Oblast.[citation needed]
- Pannonian or Bačka Rusyn is spoken in northwestern Serbia and eastern Croatia. Rusin language of the Bačka dialect is one of the official languages of the Serbian Autonomous Province of Vojvodina.[citation needed]
- Pryashiv Rusyn is the Rusyn spoken in the Prešov (in Ukrainian: Pryashiv) region of Slovakia, as well as by some émigré communities, primarily in the United States of America.[citation needed]
Neighbouring countries

All the countries neighbouring Ukraine (except for Hungary) historically have regions with a sizable Ukrainian population and therefore Ukrainian language speakers. Ukrainian is an official minority language in Belarus, Romania, and Moldova.[citation needed]
Ukrainian diaspora
Ukrainian is also spoken by a large émigrée population, particularly in Canada, the United States, and several countries of South America like Brazil, Argentina, and Paraguay.[citation needed] The founders of this population primarily emigrated from Galicia, which used to be part of Austro-Hungary before World War I, and belonged to Poland between the World Wars. The language spoken by most of them is the Galician dialect of Ukrainian from the first half of the 20th century. Compared with modern Ukrainian, the vocabulary of Ukrainians outside Ukraine reflects less influence of Russian, but often contains many loanwords from the local language.[citation needed]
Most of the countries where it is spoken are ex-USSR, where many Ukrainians have migrated. Canada and the United States are also home to a large Ukrainian population. Broken up by country (to the nearest thousand):[1]
- Russia 1,129,838 (according to the 2010 census);[95]
- Canada 200,525[96] (67,665 spoken at home[97] in 2001, 148,000 spoken as "mother tongue" in 2001)[98]
Ukrainian is declaratively proclaimed as one of three official languages of the breakaway Moldovan region of Transnistria.[99]
Ukrainian is widely spoken within the 400,000-strong (in 1994) Ukrainian community in Brazil.[100] It is the official language in Prudentópolis alongside Portuguese.[101][102][103]
Remove ads
Language structure
Summarize
Perspective
- Cyrillic letters in this article are romanized using scientific transliteration.
Grammar
Ukrainian is a fusional, nominative–accusative, satellite-framed language. It exhibits T–V distinction, and is null-subject. The canonical word order of Ukrainian is SVO.[104] Other word orders are common due to the free word order enabled by Ukrainian's inflectional system.[citation needed]
Nouns have one of 3 genders: masculine, feminine, neuter; nouns decline for:[citation needed]
- 7 cases: nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, instrumental, locative, vocative;
- 2 numbers: singular, plural.
Adjectives agree with nouns in gender, case, and number.[citation needed]
Verbs conjugate for:[citation needed]
- 4 tenses: past, pluperfect, present, future;
- 2 voices: active, mediopassive;
- 3 persons: first, second, third;
- 2 numbers: singular, plural.
Ukrainian verbs come in aspect pairs: perfective, and imperfective. Pairs are usually formed by a prepositional prefix and occasionally a root change. The past tense agrees with its subject in number and gender (but not person), having developed from the perfect participle.[citation needed]
The Old East Slavic and Russian o in syllables ending in a consonant, often correspond to a Ukrainian i, as in pod → pid (під, 'under'). Thus, in the declension of nouns, the o can re-appear when it is no longer located in a closed syllable, such as rik (рік, 'year') (nom): rotsi (loc) (році). Similarly, some words can have і in some cases when most of the cases have o, for example слово (nominative singular), слова (nominative plural) but слiв (genitive plural).[citation needed]
Ukrainian case endings are somewhat different from Old East Slavic, and the vocabulary includes a large overlay of Polish terminology. Russian na pervom etaže 'on the first floor' is in the locative (prepositional) case. The Ukrainian corresponding expression is na peršomu poversi (на першому поверсі). -omu is the standard locative (prepositional) ending, but variants in -im are common in dialect and poetry, and allowed by the standards bodies. The kh of Ukrainian poverkh (поверх) has mutated into s under the influence of the soft vowel i (k is similarly mutable into c in final positions).[citation needed]
Phonology
The Ukrainian language has six vowels, /i/, /u/, /ɪ/, /ɛ/, /ɔ/, /a/.[citation needed]
A number of the consonants come in three forms: hard, soft (palatalized) and long, for example, /l/, /lʲ/, and /lː/ or /n/, /nʲ/, and /nː/.[citation needed]
The letter ⟨г⟩ represents the voiced glottal fricative /ɦ/, often transliterated as Latin h. It is the voiced equivalent of English /h/. Russian speakers from Ukraine often use the soft Ukrainian /ɦ/ in place of Russian /ɡ/, which comes from northern dialects of Old East Slavic. The Ukrainian alphabet has the additional letter ⟨ґ⟩ for /ɡ/, which appears in a few native words such as ґринджоли gryndžoly 'sleigh' and ґудзик gudzyk 'button'. However, /ɡ/ appears almost exclusively in loan words, and is usually simply written ⟨г⟩. For example, loanwords from English on public signs usually use ⟨г⟩ for both English g and h.[citation needed]
Another phonetic divergence between the Ukrainian and Russian languages is the pronunciation of Cyrillic ⟨в⟩ v/w. While in standard Russian it represents /v/, in many Ukrainian dialects it denotes /w/ (following a vowel and preceding a consonant (cluster), either within a word or at a word boundary, it denotes the allophone [u̯], and like the off-glide in the English words "flow" and "cow", it forms a diphthong with the preceding vowel). Native Russian speakers will pronounce the Ukrainian ⟨в⟩ as [v], which is one way to tell the two groups apart. As with ⟨г⟩ above, Ukrainians use ⟨в⟩ to render both English v and w; Russians occasionally use ⟨у⟩ for w instead.[citation needed]
Unlike Russian and most other modern Slavic languages, Ukrainian does not have final devoicing.[citation needed]
Alphabet
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Ґ ґ | Д д | Е е | Є є | Ж ж | З з | И и |
| І і | Ї ї | Й й | К к | Л л | М м | Н н | О о | П п | Р р | С с |
| Т т | У у | Ф ф | Х х | Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ь ь | Ю ю | Я я |
Ukrainian is written in a version of Cyrillic, consisting of 33 letters, representing 38 phonemes; an apostrophe is also used. Ukrainian orthography is based on the phonemic principle, with one letter generally corresponding to one phoneme, although there are a number of exceptions. The orthography also has cases where the semantic, historical, and morphological principles are applied.[citation needed]
The modern Ukrainian alphabet is the result of a number of proposed alphabetic reforms from the 19th and early 20th centuries, in Ukraine under the Russian Empire, in Austrian Galicia, and later in Soviet Ukraine. A unified Ukrainian alphabet (the Skrypnykivka, after Mykola Skrypnyk) was officially established at a 1927 international Orthographic Conference in Kharkiv, during the period of Ukrainization in Soviet Ukraine. But the policy was reversed in the 1930s, and the Soviet Ukrainian orthography diverged from that used by the diaspora. The Ukrainian letter ge ґ was banned in the Soviet Union from 1933 until the period of Glasnost in 1990.[105]
The letter щ represents two consonants [ʃt͡ʃ]. The combination of [j] with some of the vowels is also represented by a single letter ([ja] = я, [je] = є, [ji] or [jı̽] = ї, [ju] = ю), while [jɔ] = йо and the rare regional [jɨ] = йи are written using two letters. These iotated vowel letters and a special soft sign change a preceding consonant from hard to soft. An apostrophe is used to indicate the hardness of the sound in the cases when normally the vowel would change the consonant to soft; in other words, it functions like the yer in the Russian alphabet.[citation needed]
A consonant letter is doubled to indicate that the sound is doubled, or long.[citation needed]
The phonemes [d͡z] and [d͡ʒ] do not have dedicated letters in the alphabet and are rendered with the digraphs дз and дж, respectively. [d͡z] is equivalent to English ds in pods, [d͡ʒ] is equivalent to j in jump.[citation needed]
As in Russian, the acute accent may be used to denote vowel stress.[citation needed]
Transliteration
Orthography
Spelling search,[clarification needed] which began in the late 18th century with the emergence of modern literary language, led to the emergence of several spelling options. In particular, there was the spelling system of Oleksii Pavlovskyi, the spelling version of "Mermaid of the Dniester" (1837), Kulishivka (P. Kulish's spelling system), Drahomanivka (produced in Kyiv in the 1870s by a group of cultural figures led by linguist P. Zhytetskyi, which included and M. Drahomanov), Zhelekhivka (system of Yevhen Zhelekhovskyi (1886), enshrined in the Ruthenian Grammar by Smal-Stotskyi and Theodore Gartner 1893).[citation needed]
Borys Hrinchenko used some corrections in the fundamental four-volume Dictionary of the Ukrainian Language (1907–1909). Most of the spelling rules (practically based on phonetics – "write as you hear") used in Hrinchenko's dictionary are still valid. Hrinchenko's work became an informal spelling and model for Ukrainian writers and publications from 1907 until the creation of the first official Ukrainian spelling in 1918.[citation needed]
On 17 January 1918, the Central Rada of Ukraine issued the "Main Rules of Ukrainian orthography", which, however, did not cover the entire scope of the language. On 17 May 1919, the Ukrainian Academy of Sciences approved the "Main Rules of Ukrainian Orthography", which became the basis for all subsequent revisions and amendments.[citation needed]
On 23 July 1925, the Council of People's Commissars of the USSR decided to organize a State Commission for the Organization of Ukrainian Spelling (State Spelling Commission). It included more than 20 academics from the USSR, who also expressed a desire to invite representatives of Western Ukraine: Smal-Stotskyi, Volodymyr Hnatiuk and Vasyl Simovych.[citation needed]
After almost a year of work in April 1926, the "Project of Ukrainian Spelling" was published to acquaint the general public with the new system. After several months of discussion and consideration of the project at the All-Ukrainian Spelling Conference (26 May – 6 June 1927), the Ukrainian orthography of 1928 was adopted in accordance with the RNC resolution of 6 September 1928. It went down in history as "Kharkiv" or "Skrypnik orthography" – from the place of creation, or from the surname of Skrypnyk.[citation needed]
In 1929, Hryhorii Holoskevych published the Ukrainian Spelling Dictionary (about 40,000 words), agreed with the full spelling produced by the State Spelling Commission and approved by the People's Commissar for Education (6 September 1928).[106]
In 1933, a spelling commission headed by Andrii Khvylia branded the Ukrainian orthography of 1928 as "nationalist", immediately stopped publishing any dictionaries, and without any discussion, in a very short time (five months), created a new spelling that unified as never before the Ukrainian and Russian languages. The letter ґ was removed from the alphabet, and Ukrainian scientific terminology was revised and harmonized with Russian-Ukrainian dictionaries (the Institute of Ukrainian Scientific Language was abolished in 1930). This version of the spelling was approved by the resolution of the People's Commissar of Education of the USSR of 5 September 1933.[citation needed]
Some minor changes were made in the spelling of 1946 and 1959 (published the following year). It was connected with the document "The rules of Russian spelling and punctuation", published in 1956. From 1960 until 1990, the 1960 edition was the official standard.[citation needed]
After the beginning of "perestroika", the issue of improving Ukrainian spelling became relevant again: the editing of the spelling code was started by the Orthographic Commission at the LMM of the USSR Academy of Sciences. The project was also discussed in the newly established Ukrainian Language Society. T. Shevchenko (headed by Dmytro Pavlychko). The new version was approved on 14 November 1989, and published in 1990. The main achievements were the restoration of the letter ґ and the accusative case (in Soviet times it was optional and was called the accusative form).[citation needed]
Today, despite the existence of the official spelling of the Ukrainian language, it is not the only spelling standard in use. Even in Ukraine itself, many publishers and publications use other versions of the spelling, which either tend to "skrypnykivka", or else differ from the official rules of transmission of words of foreign origin.[citation needed]
On 22 May 2019, the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine approved a new version of the orthography prepared by the Ukrainian National Commission on Spelling. The new edition brought to life some features of orthography in 1928, which were part of the Ukrainian orthographic tradition. At the same time, the commission was guided by the understanding that the language practice of Ukrainians in the second half of the 20th to the beginning of the 21st century has already become part of the Ukrainian orthographic tradition.[107]
Vocabulary
The Dictionary of the Ukrainian Language, in 11 volumes, contains 253,000 entries.[108] Lexical card catalog of the Ukrainian Institute of Language Studies has six million cards.[109] As mentioned at the top of the article, Ukrainian is most closely related lexically to Belarusian, and is also closer to Polish than to Russian (for example, можливість, mozhlyvistʹ, "possibility", and Polish możliwość, but Russian возможность, vozmozhnostʹ).[citation needed]
False cognates with Russian
The standard Ukrainian language which is based on the Kyiv–Poltava dialect has a plethora of false friends with the standard Russian language which is based on the dialect of Moscow. Many people intentionally do or do not use them, causing their language shift into what is known as Surzhyk, where the meaning of some words mimicking Russian could be understood out of context rather than their literal meaning in Ukrainian.[citation needed]
Remove ads
Classification
Summarize
Perspective

Ukrainian has varying degrees of mutual intelligibility with other Slavic languages. It is closely related to other East Slavic languages with high levels of mutual intelligibility.[5] Ukrainian is considered to be most closely related to Belarusian.[110]
The separation of the East Slavic languages is considered to be relatively recent.[5] In the 19th century, the question of whether the Ukrainian, Belarusian and Russian languages were dialects of a single language or three separate languages was actively discussed, with the debate affected by linguistic and political factors.[5] The political situation (Ukraine and Belarus being mainly part of the Russian Empire at the time) and the historical existence of the medieval state of Kievan Rusʹ, which occupied large parts of these three nations, led to the creation of the common classification known later as the East Slavic languages. The underlying theory of the grouping is their descent from a common ancestor. In modern times, Ukrainian, Russian, and Belarusian are usually listed by linguists as separate languages.[111][112][1]
The Ukrainians were predominantly peasants and petits bourgeois. In 1897, 93% of Ukrainians were peasants.[12] As a result, the Ukrainian language was mostly vernacular and few earlier literary works from the period can be found. In the cities, Ukrainian coexisted with Church Slavonic—a literary language of religion that evolved from Old Church Slavonic—and later Polish and Russian, both languages which were more often used in formal writing and communication during that time.[citation needed]
Differences from other Slavic languages
The Ukrainian language has the following similarities with and differences from other Slavic languages:
- Like all Slavic languages with the exception of Russian, Belarusian, standard written Slovak[c] and Slovene, the Ukrainian language has preserved the Common Slavic vocative case. When addressing one's sister (sestra) she is referred to as sestro. In the Russian language the vocative case has been almost entirely replaced by the nominative (except for a handful of vestigial forms, e.g. Bozhe "God!" and Gospodi "Lord!").[113]
- The Ukrainian language, in common with all Slavic languages other than Russian, Slovak and Slovene, has retained the Common Slavic second palatalization of the velars *k, *g and *x in front of the secondary vowel *ě of the dative and locative ending in the female declension, resulting in the final sequences -cě, -zě, and -sě. For example, ruka (hand) becomes ruci in Ukrainian. In Russian, the dative and locative of ruka is ruke.
- The Ukrainian language, in common with Serbo-Croatian and Slovene, has developed the ending -mo for first-person plurals in verbs (khodymo for "we walk").[113] In all cases, it resulted from lengthening of the Common Slavic -mŭ.[citation needed][dubious – discuss]
- The Ukrainian language, along with Russian and Belarusian, has changed the Common Slavic word-initial ye- into o, such as in the words ozero (lake) and odyn (one).[113]
- The Ukrainian language, in common with Czech, Slovak, Upper Sorbian, Belarusian and southern Russian dialects, has changed the Common Slavic "g" into an "h" sound (for example, noha – leg).[113]
- The Ukrainian language, in common with some northern Russian and Croatian dialects, has transformed the Common Slavic yě into i (for example, lis – forest).[113]
- The Ukrainian language, in common with Russian, Belarusian, Bulgarian, Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian, and Slovene, has simplified the Common Slavic tl and dl into l (for example, mela – she swept").[113]
- The Ukrainian language, in common with the most of Slavic ones, is a stress-timed language, in which syllables may last different amounts of time, but there is perceived to be a fairly constant amount of time (on average) between consecutive stressed syllables.[114]
- The Ukrainian language, in common with all modern Slavic languages other than Bulgarian and Macedonian, does not use articles.
- Other Slavic o in closed syllables, i.e., syllables ending in a consonant, in many cases corresponds to a Ukrainian i, as in pod → pid (під, 'under'). This also includes place names such as Lviv (Львів in Ukrainian), Lwów in Polish, and Львов (Lvov) in Russian.[citation needed]
Unlike all other Slavic languages, Ukrainian has a synthetic future (also termed inflectional future) tense which developed through the erosion and cliticization of the verb "to have" (or possibly "to take"): pysat-ymu (infinitive-future-1st sg.) I will write.[115] Although the inflectional future (based on the verb 'to have') is characteristic of Romance languages, Ukrainian linguist A. Danylenko argues that Ukrainian differs from Romance in the choice of auxiliary, which should be interpreted as 'to take' and not 'to have.' He states that Late Common Slavic (LCS) had three verbs with the same Proto-Indo-European root *h₁em-:
- a determined imperfective LCS *jęti: *jĭmǫ 'to take' (later superseded by numerous prefixed perfectives)
- an indetermined imperfective LCS *jĭmati: jemljǫ 'to take' (which would not take any prefixes)
- an imperfective LCS *jĭměti: *jĭmamĭ 'to hold, own, have'
The three verbs became conflated in East Slavic due to morphological overlap, in particular of *iměti "to have" and *jati "to take" as exemplified in the Middle Ukrainian homonymic imut’ from both iměti (< *jĭměti) and jati (< *jęti). Analogous grammaticalization of the type take ("to take", "to seize") > future is found in Chinese and Hungarian.[116]
Remove ads
Sample text
Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in Ukrainian:
Всі люди народжуються вільними і рівними у своїй гідності та правах. Вони наділені розумом і совістю і повинні діяти у відношенні один до одного в дусі братерства.[117]
The romanization of the text into Latin alphabet:
Vsi lyudy narodzhuyutʹsya vilʹnymy i rivnymy u svoyiy hidnosti ta pravakh. Vony nadileni rozumom i sovistyu i povynni diyaty u vidnoshenni odyn do odnoho v dusi braterstva.
Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in English:[118]
All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
Remove ads
See also
Notes
References
Sources
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads