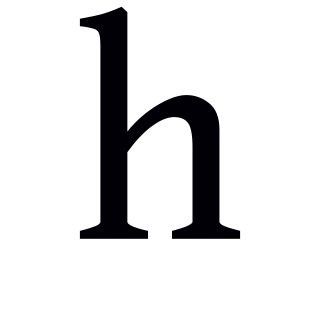Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Voiceless glottal fricative
Consonantal sound represented by ⟨h⟩ in IPA From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The voiceless glottal fricative, sometimes called voiceless glottal transition or the aspirate,[1][2] is a type of sound used in some spoken languages that patterns like a fricative or approximant consonant phonologically, but often lacks the usual phonetic characteristics of a consonant. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨h⟩. However, [h] has been described as a voiceless phonation because in many languages, it lacks the place and manner of articulation of a prototypical consonant, as well as the height and backness of a prototypical vowel:
[h and ɦ] have been described as voiceless or breathy voiced counterparts of the vowels that follow them [but] the shape of the vocal tract [...] is often simply that of the surrounding sounds. [...] Accordingly, in such cases it is more appropriate to regard h and ɦ as segments that have only a laryngeal specification, and are unmarked for all other features. There are other languages [such as Hebrew and Arabic] which show a more definite displacement of the formant frequencies for h, suggesting it has a [glottal] constriction associated with its production.[3]
An effort undertaken at the Kiel Convention in 1989 attempted to move glottal fricatives, both voiceless and voiced, to approximants.[4][5] The fricative may be represented with the extIPA diacritic for strong articulation, ⟨h͈⟩.
The Shanghainese language, among others, contrasts voiced and voiceless glottal fricatives.[6]
Remove ads
Features
Summarize
Perspective
Features of the "voiceless glottal fricative":
- In some languages, it has the constricted manner of articulation of a fricative. However, in many if not most it is a transitional state of the glottis or an approximant, with no manner of articulation other than its phonation type. Because there is no other constriction to produce friction in the vocal tract in the languages they are familiar with, many phoneticians[who?] no longer consider [h] to be a fricative. However, the term "fricative" is generally retained for historical reasons.
- It may have a glottal place of articulation. However, it may have no fricative articulation, in which case the term 'glottal' only refers to the nature of its phonation, and does not describe the location of the stricture nor the turbulence. All consonants except for the glottals, and all vowels, have an individual place of articulation in addition to the state of the glottis. As with all other consonants, surrounding vowels influence the pronunciation [h], and [h] has sometimes been presented as a voiceless vowel, having the place of articulation of these surrounding vowels.
- Its phonation is voiceless, which means it is produced without vibrations of the vocal cords. In some languages the vocal cords are actively separated, so it is always voiceless; in others the cords are lax, so that it may take on the voicing of adjacent sounds.
- It is an oral consonant, which means that air is exclusively allowed to escape through the mouth.
- Because the sound is not produced with airflow over the tongue, the central–lateral dichotomy does not apply.
- Its airstream mechanism is pulmonic, which means it is articulated by pushing air solely with the intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles, as in most sounds.
Remove ads
Occurrence
Summarize
Perspective
Fricative or transition
Remove ads
See also
Notes
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads