Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
April 1921 lunar eclipse
Partial lunar eclipse in 1921 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
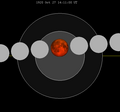
A total lunar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit on Friday, April 22, 1921,[1] with an umbral magnitude of 1.0678. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. A total lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon's near side entirely passes into the Earth's umbral shadow. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth. A total lunar eclipse can last up to nearly two hours, while a total solar eclipse lasts only a few minutes at any given place, because the Moon's shadow is smaller. Occurring only about 5.6 days after perigee (on April 16, 1921, at 16:10 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.[2]
This lunar eclipse was the third of an almost tetrad, with the others being on May 3, 1920 (total); October 27, 1920 (total); and October 16, 1921 (partial).
This was the first total lunar eclipse of Lunar Saros 130.
Remove ads
Visibility
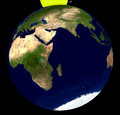
The eclipse was completely visible over much of North America and western South America, seen rising over northeast Asia and Australia and setting over eastern South America, western Europe, and west Africa.[3]
  |
Eclipse details
Shown below is a table displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. It describes various parameters pertaining to this eclipse.[4]
Remove ads
Eclipse season
This eclipse is part of an eclipse season, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight.
Related eclipses
Summarize
Perspective
Eclipses in 1921
- An annular solar eclipse on April 8.
- A total lunar eclipse on April 22.
- A total solar eclipse on October 1.
- A partial lunar eclipse on October 16.
Metonic
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of July 4, 1917
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of February 8, 1925
Tzolkinex
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of March 12, 1914
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of June 3, 1928
Half-Saros
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of April 17, 1912
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of April 28, 1930
Tritos
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of May 24, 1910
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of March 22, 1932
Lunar Saros 130
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of April 12, 1903
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of May 3, 1939
Inex
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of May 11, 1892
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of April 2, 1950
Triad
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of June 21, 1834
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of February 21, 2008
Lunar eclipses of 1919–1922
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of lunar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[5]
The penumbral lunar eclipse on March 13, 1922 occurs in the next lunar year eclipse set.
Saros 130
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 130, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 71 events. The series started with a penumbral lunar eclipse on June 10, 1416. It contains partial eclipses from September 4, 1560 through April 12, 1903; total eclipses from April 22, 1921 through September 11, 2155; and a second set of partial eclipses from September 21, 2173 through May 10, 2552. The series ends at member 71 as a penumbral eclipse on July 26, 2678.
The longest duration of totality will be produced by member 35 at 101 minutes, 53 seconds on June 26, 2029. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit.[6]
Eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
Tritos series
This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
Half-Saros cycle
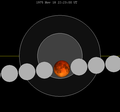
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[8] This lunar eclipse is related to two annular solar eclipses of Solar Saros 137.
| April 17, 1912 | April 28, 1930 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Remove ads
See also
Notes
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads