Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Border irregularities of Canada
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
There are multiple border irregularities in Canada. Often, they are a result of borders which do not conform to geological features such as changes in the course of a river that previously marked a border.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2025) |
Remove ads
Salients
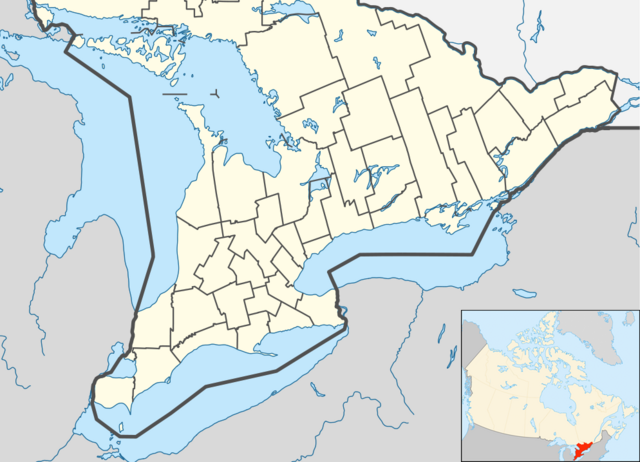
A salient, panhandle, or bootheel is an elongated protrusion of a geopolitical entity, such as a subnational entity or a sovereign state.
- Southern Ontario is a region in Ontario and is the southernmost point in Canada. It is also the most densely populated region of Canada with a population of 13.5 million people.[1] It extends south into the U.S. states of Michigan and New York, and borders Lake Huron, Erie, and Ontario.
- Tatshenshini-Alsek Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia. The park borders the U.S. state of Alaska in the West, and Yukon in the North. The park makes up of most of the salient in Northwestern British Columbia.[2]
- Madawaska County, New Brunswick is a county in Western New Brunswick. The salient borders Quebec in the Northeast and the U.S. State of Maine in the South.
Remove ads
Enclaves and Exclaves
Summarize
Perspective
An enclave is a piece of land belonging to one country (or region etc.) that is totally surrounded by another country (or region). An exclave is a piece of land that is politically attached to a larger piece but not physically contiguous with it (connected to it) because they are completely separated by a surrounding foreign territory or territories.
Enclaves
- In Montreal, the city of Westmount, the town of Mount Royal, and the communities of Côte Saint-Luc and Montréal-Est are all surrounded by Montreal.
- The city of L'Ancienne-Lorette is completely surrounded by the city of Quebec City.

Exclaves
- The Caniapiscau Regional County Municipality in Quebec is separated into multiple sections including the exclaves of Lac-Vacher and Lac-Juillet surrounded by Labrador and Nunavik.
- Greenstone, Ontario has two townsite exclaves. Nakina north of Greenstone, and Caramat south.
Semi-enclaves
- The town of Petty Harbour–Maddox Cove, in Newfoundland and Labrador, is surrounded by the city of St. John's, and the Atlantic Ocean to the East.


Pene enclaves/exclaves
- St. Regis, Quebec: Part of the Akwesasne Mohawk Nation, on the south shore of the Saint Lawrence River, has a land border with St. Regis Mohawk Reservation in New York State; road access to the rest of Canada is only available through New York State.
- Campobello Island, New Brunswick can be reached by road only by driving through the United States, across the border bridge to Maine. Connection with the rest of Canada is by ferry.
- The entrance to Aroostook Valley Country Club near Fort Fairfield, Maine, is in the U.S., but most of the club's golf course and its clubhouse are in Canada.
- The Haskell Free Library and Opera House straddles the border. The Canadian part of the building is a practical exclave of Canada, as most of the building is physically in Stanstead, Quebec, but the only public access to the building is via the front door on Caswell Avenue in Derby Line, Vermont, in the United States.
- The Salmon Glacier and Granduc Mine in Premier, British Columbia can only be reached by road through Hyder, Alaska.
- The village of Atlin, British Columbia, is only accessible by road through the Yukon Territory.[3]
- The village of Tungsten, Northwest Territories is only accessible by road through the Yukon.
- To reach the towns of Fort McPherson, Tsiigehtchic and Inuvik in the Inuvik Region by road from elsewhere in the Northwest Territories, it is necessary to drive into Yukon and take the Dempster Highway.
- Cold Lake, straddles the border between Alberta and Saskatchewan in such a way that a peninsula in Albertan territory can only be reached overland by passing through Saskatchewan's Meadow Lake Provincial Park.
- All islands in Hudson Bay, including those within James Bay, and islands in Ungava Bay and Hudson Strait, are part of the territory of Nunavut; many of those along the Ontario or Québec coasts are accessible from those provinces over frozen ice at times rather than the rest of the territory.[4]
- North Shore communities in eastern Québec are accessible by road only through Labrador, separated by a gap in Route 138.

Divided islands
- Canada and Denmark share Hans Island in Nunavut and Greenland respectively.[5]
- Canada and the U.S. divide an island in the Columbia River near the Waneta border crossing of Washington and British Columbia.
- Salt Lake in northeastern Montana, known as Alkali Lake in Saskatchewan, contains an island that is crossed by the international border at its southern tip. When the lake is not dry, the island forms pene-exclaves of each nation.
- The two nations also divide two islands on their international border in Boundary Lake, North Dakota and Manitoba.[6]
- Each nation has a pene-exclave on the 77-acre Province Island in Lake Memphremagog, Vermont and Quebec.
- The two nations divide Pine and Curry Island in Lake of the Woods on the Minnesota/Ontario border.[7]
- Killiniq Island is shared between Nunavut and the province of Newfoundland and Labrador.[8]
- Nunavut and the Northwest Territories (NWT) share four islands that are split by the 110° W meridian: Borden Island, Mackenzie King Island, Melville Island and Victoria Island. Excluding lake crossings, Melville Island contains three separate land boundaries between Nunavut and NWT due to coastal undulation, while Victoria Island contains six such land boundaries, of which one is on a small island.[9]
Remove ads
Split settlements
- Beebe Plain is an unincorporated village split by the border, with Canusa Street running down the middle. Homes on the south side are in the U.S., while those on the north side are in Canada.[10]
- Stanstead, Quebec and Derby Line, Vermont are split towns on the border with many buildings being split by the border including the Haskell Free Library and Opera House which was intentionally build on the border.[11]
- Pohenegamook, Quebec and Estcourt Station, Maine are split towns on the border. The border parallels Frontier Street and cuts through businesses and multiple homes.[12]
- Dundee, Quebec and Fort Covington, New York are split on the border with a house and the HalfWay House Freight Forwarding building split by the border.[13]
- Akwesasne, which is also a pene exclave of Quebec, is split on the border with New York, with multiple homes split on the border.[14]
- Lake Metigoshe State Park is a state park split on the border of Manitoba and North Dakota. A row of homes and docks are split by the border on the lake.[15]
- Lloydmister is a city located in Alberta and Saskatchewan and is the only city in Canada that is split by a province. [16]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads