Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
January–March 2023 in science
Overview of the events of 2023 in science From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
This article lists a number of significant events in science that have occurred in the first quarter of 2023.
Events
January
- 3 January – Researchers report molecular mechanisms that appear to underlie some of the reported health benefits of periods of intermittent fasting: changes to gene expression or rhythmicity of ~80% of young male mouse genes in at least one tissue.[1][2]
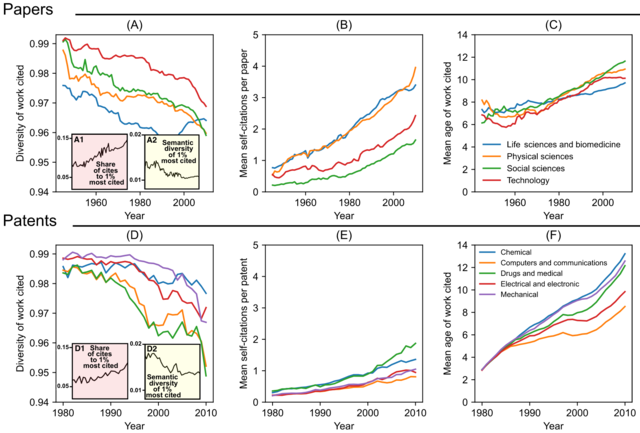
- 4 January – Metascientists introduce the 'CD index' intended to characterize "how papers and patents change networks of citations in science and technology" and report that it has declined, which they interpret as "slowing rates of disruption". They propose linking this to changes to three "use of previous knowledge"-indicators ("the diversity of work cited, mean number of self-citations and mean age of work cited") which they interpret as "contemporary discovery and invention" being informed by "a narrower scope of existing knowledge". The overall number of papers has risen while the total of "highly disruptive" papers hasn't. The 1998 discovery of the accelerating expansion of the universe has a CD index of 0. Their results also suggest scientists and inventors "may be struggling to keep up with the pace of knowledge expansion".[3][4]
- 5 January
- Scientists report the discovery of an unknown thin membrane meningeal layer in brain anatomy, the SLYM, that likely plays a role in CSF functions and is both a protective barrier and host of immune cells. It appears to be substantially involved in major brain diseases and brain aging that monitor the brain for infection and neuroinflammation.[5][6]
- Archaeologists report that notational signs from ~37,000 years ago in caves, apparently conveying calendaric meaning about the behaviour of animal species drawn next to them, are the first known (proto-)writing in history.[7][8]
- Progress in climate change mitigation implementation research:
- A meta-analysis reports "required technology-level investment shifts for climate-relevant infrastructure until 2035" within the EU, which it finds to be "most drastic for power plants, electricity grids and rail infrastructure", ~€87 billion above the planned budgets and in need of sustainable finance policies.[9][10]
- A study (12 Jan) suggests that applying the principle of extended producer responsibility to fossil fuels could deconflict energy security and climate policy at an affordable cost, in particular authors suggest the responsibility could be used to establish the financing of CO2 storage and nature-based solutions.[11][12]
- A study (30 Jan) outlines challenges of aviation decarbonization by 2050 whose identified factors mainly are future demand, continuous efficiency improvements, new short-haul engines, higher SAF (biofuel) production, CO2 removal to compensate for non-CO2 forcing, and related policy-options. With constant air transport demand and aircraft efficiency, decarbonizing aviation would require nearly five times the 2019 worldwide biofuel production, competing with other hard-to-decarbonize sectors and land-use (or food security).[13]

- 6 January
- An international collaboration shows that hidden marine heatwaves, associated with ocean eddies that modulate undersea internal waves, threaten coastal ecosystems by driving unexpected sub-surface heating and severe coral bleaching and mortality across depths.[14][additional citation(s) needed]
- News outlets report on a brief meta-analysis (21 Dec 2022) that confirms gas stoves are a major risk factor for asthma and updates effect-size estimates, finding around one in eight cases in the U.S. could be attributed to these.[15][16]
- 9 January
- A study suggests logged and structurally degraded (South Asian) tropical forests are carbon sources for at least a decade – even when recovering[clarification needed] – due to larger carbon losses from soil organic matter and deadwood, indicating the tropical forest carbon sink "may be much smaller than previously estimated".[17][18]
- Researchers demonstrate an open-brain surgery-free brain implant, Stentrode, that can record brain activity from a nearby blood vessel, showing it can be used to operate a computer.[19][20]
- 10 January
- A second potentially Earth-like planet in the TOI 700 system is reported using data from NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS).[21]
- The long-term impact of biodiversity loss in Madagascar is modelled, suggesting that recovery from extinctions could take as long as 23 million years.[22][23]
- Cyclic sighing is found to be effective in reducing anxiety, negative mood and stress, and more so than mindfulness meditation.[24][25]
- 11 January
- NASA scientists report the discovery of LHS 475 b, an Earth-like exoplanet – and the first exoplanet observed by the James Webb Space Telescope.[26]
- NASA publishes images of a debris disk surrounding the red dwarf AU Mic, taken by the James Webb Space Telescope, capturing details as close to the star as 5 astronomical units (~750 million km) – the equivalent of Jupiter's orbit in the Solar System.[27]
- Teleportation of energy is demonstrated for the first time by researchers using an IBM quantum computer.[28][29]
- Cellular bioengineers report the development of nonreplicating bacterial 'cyborg cells' (similar to artificial cells) using a novel approach, assembling a synthetic hydrogel polymer network as an artificial cytoskeleton inside the bacteria. The cells can resist stressors that would kill natural cells and e.g. invade cancer cells or potentially act as biosensors.[30][31]
- The White House and federal agencies in the U.S. (a major source region of scientific work globally) declare the Year of Open Science, listing several actions towards open science.[32] The science policy "Framework for Federal Scientific Integrity Policy and Practice" issued by the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy a day later is criticized as a "gag order" on scientists by PEER in an open letter (30 Jan).[33][34]

- 12 January
- Progress in life extension research:
- A team led by David Sinclair shows how DNA breaks are a major driver of epigenetic change, and how the loss of epigenetic information is a cause of aging in mammals. Using a treatment based on Yamanaka factors, they demonstrate an ability to drive aging in both the forward and reverse directions in mice.[35][36][37]
- In a review, the authors of a heavily cited paper on the hallmarks of aging update the set of proposed hallmarks after a decade (3 Jan).[38][39] On the same day, a review with overlapping authors merge or link various hallmarks of cancer with those of aging.[40][additional citation(s) needed]
- A study reports the development of deep learning software using anatomic magnetic resonance images to estimate brain age with the highest accuracy for AI so far, including detecting early signs of Alzheimer's disease and varying neuroanatomical patterns of neurological aging (3 Jan).[41][42]
- In a preprint, another team of researchers reports the use of reprogramming to modestly extend the lifespan in elderly mice. However, if it was also applicable to humans, risks reportedly may include the formation of cancer (5 Jan).[36][43][44]
- A study concludes that retroviruses in the human genomes (endogenous) can become awakened from dormant states and contribute to aging which can be blocked by neutralizing antibodies (6 Jan).[45][46]
- A study reports large reductions of snow cover in the Alps, emphasizing climate change adaptation needs due to their impacts on the climate and socio-economic activities.[47][48]
- Progress in life extension research:
- 13 January – A study of ancient DNA supports or confirms[49] that recent human evolution to resist infection of pathogens also increased inflammatory disease risk in post-Neolithic Europeans over the last 10,000 years, estimating nature, strength, and time of onset of selections.[50][additional citation(s) needed]
- 16 January
- NASA announces preliminary considerations of several future space telescope programs, including the Great Observatory Technology Maturation Program (GOMAP), Habitable Worlds Observatory and New Great Observatories.[51][52]
- Researchers for the first time demonstrate redirection of lightning with lasers.[53][54]
- 17 January
- Promising results of therapeutic candidates are reported:
a third phase 3-trialed RSV vaccine candidate,[55] a prebiotic fibre formula against type 2 diabetes (3 Jan),[56][57] a bifunctional therapeutic and vaccine against brain cancer (4 Jan),[58][59] a phase 2-trialed probiotic against S. aureus infection (13 Jan),[60][61] the mice gene therapy-tested LAV-BPIFB4 protein (or this gene in gene therapy) against heart aging (13 Jan),[62] mice-tested in-use anakinra (or blockade of its target IL-1β) against haematopoietic blood aging (17 Jan),[63][64] mice-tested phase 2-scheduled IkT-148009 against Parkinson's disease (18 Jan),[65][66] C. elegans-tested in-use rilmenidine as a CRM against aging (20 Jan).[67][68]
- Promising results of therapeutic candidates are reported:
- 18 January
- News outlets report on an investigation and a set of recent studies that indicate that carbon emission reductions from projects launched to earn carbon-offset credits have been vastly overstated to the extent that ~90% of rainforest offset credits of the Verified Carbon Standard are called likely to be "phantom credits".[69]
- A metagenomic analysis provides data and insights into microbial sharing between individuals, finding substantial strain sharing among cohabiting individuals, with median strain-sharing rates for the gut and oral microbiomes being 12% (34% for mothers and their 0–3-years-old offspring) and 32% (38% for partners) in the used data. Time since cohabitation was the largest factor and bacterial strain sharing "recapitulated host population structures better[clarification needed] than species-level profiles did".[70][71]
- 19 January
- A study using electronic health records shows 45 (with 22 of these being replicated with the UK Biobank) viral exposures can significantly elevate risks of neurodegenerative disease, including up to 15 years after infection.[72][73]
- Progress in healthy/sustainable food system research: a review outlines benefits (such as high protein production per acre), recent advancements and challenges of developing algae as a large-scale food source,[74][75] a study identifies "11 key measures" that can reduce nitrogen chemicals pollution of air (NH3, NOx and N2O) and water from croplands (4 Jan),[76][77] a first review indicates vegan diets, which are more sustainable, would not have adverse impacts on the health of both pet dogs and cats (12 Jan),[78][additional citation(s) needed] researchers outline large environmental benefits of using insects for animal feed (12 Jan),[79][80] Chinese scientists report the cloning of multiple "supercows" with a substantial milk productivity increase (31 Jan).[81]
- Researchers from Scripps Institution of Oceanography discovered the Pyrolycus jaco. It was first detailed in a paper published in the journal Zootaxa on January 19, 2023.[82]
- ~20 January
- Progress in AI software and applications:
- News outlets report on a preprint (26 Dec 2022) that describes the development of a large language model software that can answer medical questions with a 67.6% accuracy on US Medical License Exam questions and nearly matched human clinician performance when answering open-ended medical questions, Med-PaLM. The AI makes use of comprehension-, recall of knowledge-, and medical reasoning-algorithms but remains inferior to clinicians.[83][84][85] As of 2023, humans often – if not most often – conduct query-based web searches, read websites and/or conduct physical doctor's visits to inquire health information, despite various difficulties,[86][87][88][89] partly as they typically did not undergo any formal training in media literacy,[90] digital literacy[91][92] or health literacy,[93] as such is not part of schools curricula in most education systems as of 2023.[93][90][91]
- A novel potentially significantly more efficient text-to-image approach, as implemented in MUSE, is reported (2 Jan).[94][95]
- A first successful autonomous long-duration operation (Dec 21 and/or Dec 22), including simulated combat, of a modified F-16 fighter jet, X-62A, by two AI software is reported (4 Jan).[96][97][98]
- A text-to-speech synthesizer, VALL-E, that can be trained to mimic anybody's voice with just three seconds of voice data and may produce the most natural-sounding results to date is reported in a preprint (5 Jan).[99][100]
- A use of world models for a wide range of domains that makes decisions using e.g. different 3D worlds and reward frequencies and outperforms previous approaches, DreamerV3, is reported as a step towards general artificial intelligence in a preprint (10 Jan).[101][102]
- A large language model, ProGen, that can generate functional protein sequences with a predictable function, with the input including tags specifying protein properties, is reported (26 Jan).[103][104]
- A deep-learning model, ZFDesign, for zinc finger design for any genomic target for gene- and epigenetic-editing is reported (26 Jan).[105][106]
- Software for generating 3D dynamic scenes (text-to-4D), Make-A-Video3D, is reported (26 Jan).[107][108]
- A study reports the development of deep learning algorithms to identify technosignature candidates, finding 8 potential alien signals not detected earlier (30 Jan).[109][110]
- Chatbot and text-generating AI, ChatGPT (released on 30 Nov 2022), a large language model, becomes highly popular, with some considering the large public's attention as unwarranted hype as potential applications are limited, similar software such as Cleverbot existed for many years, and the software is, on the fundamental level, not structured toward accuracy – e.g. providing seemingly credible but incorrect answers to queries and operating "without a contextual understanding of the language" – but only toward essentially the authenticity of mimicked human language (~Jan).[111][112][113][114][115] It was estimated that only two months after its launch, it had 100 million active users.[116] Applications may include solving or supporting school writing assignments,[117] malicious social bots (e.g. for misinformation, propaganda, and scams),[118][119] and providing inspiration (e.g. for artistic writing or in design or ideation in general).[120][121]
- Progress in AI software and applications:
- 23 January
- The most affordable carbon capture and conversion system to date, bringing the cost down to just $39 per metric ton, is revealed. The process takes flue gas from power plants, uses a solvent to strip out the CO2, then converts it to industrially-useful methanol.[122][123]
- In two studies (20 & 23 Jan), researchers report that substitution of PET adhesive tapes could prevent nearly all self-discharge in the widely used lithium-ion batteries, extending battery life.[124][125][126]
- A geophysical study reports that the spin of the Earth's inner core has stopped spinning faster than the planet's surface and likely is now rotating slower than it. This is not thought to have major effects and one cycle of the oscillation is about seven decades, coinciding with several other geophysical periodicities ("especially the length of day and magnetic field").[127][128]
- 25 January
- Engineers report the design of millimetre-sized robots able to rapidly shift between liquid and solid states. The devices could be used to fix electronics or remove objects from the body.[129][130]
- Researchers report the development of a viable wearable continuous heart ultrasound imager.[131][132]
- Progress in disease screening or diagnosis: researchers demonstrate the use of ants as biosensors to detect cancer via urine,[133][134] in two separate studies (11 & 27 Jan) Alzheimer's disease is detected early via blood biomarkers,[135][136][137][138] a non-invasive alternative to difficult rarely-used catheter testing for a common cause of high blood pressure is reported (16 Jan).[139][140]
- The US NIH begins "requiring most of the 300,000 researchers and 2,500 institutions it funds annually to include a data-management plan in their grant applications — and to eventually make their data publicly available". Advantages of such requirements may include making science more accessible, increasing public trust in science and increasing efficiency and reproducibility.[141]
- 27 January
- A study finds that the world has enough rare earths and other raw materials to switch from fossil fuels to renewable energy.[142][143]
- ESA reports the successful demonstration of a braking sail-based satellite deorbiter, Drag Augmentation Deorbiting System, which could be used by space debris mitigation measures.[144][145]
- 30 January
- Climate scientists predict, using artificial intelligence, that global warming will exceed 1.5 °C in the next decade (scenario SSP2-4.5), and a nearly 70% chance of 2 °C between 2044 and 2065 (~2054) – a substantial probability of exceeding the 2 °C threshold – even if emissions rapidly decline (scenario SSP1-2.6).[146][147]
- In two studies (4 & 30 Jan) separate teams of researchers report substantial improvements to green hydrogen production methods, enabling higher efficiencies and durable use of untreated seawater.[148][149][150][151]
- 31 January – A news outlet reports on a study (9 Nov 2022) that concludes that a "visual flicker paradigm to entrain individuals at their own brain rhythm (i.e. peak alpha frequency)" results in faster ("at least three times faster than control groups") perceptual visual learning, maintained the day following training.[152][153]
February

- 1 February
- C/2022 E3 (ZTF), a green-coloured comet from the Oort cloud, is observed in the night sky making its closest approach to Earth.[154]
- An article examines Leonardo da Vinci's experiments on gravity in the Codex Arundel and presents a solution using Newtonian mechanics to confirm Leonardo's "equivalence principle".[155]
- 3 February – Researchers show how pre-installed apps on Android smartphones in China are used for mass surveillance in China. They show the apps have been granted dangerous privileges, transmit to many third-party domains privacy-sensitive information such as geolocation, user profile and social relationships, etc all "without consent or even notification".[156][157]
- 6 February
- Astronomers announce the discovery of an additional 12 moons of Jupiter.[158]
- A previously unknown cell mechanism involved in aging is discovered, which explains how cells 'remember' their identity when they divide – the cells' so-called epigenetic memory.[159][additional citation(s) needed]
- A study integrates policy as an aspect into an integrated assessment model, showing that Powering Past Coal Alliance-based (from COP23) coal phase-out is highly unlikely (<5%) with current policies where both coal-use would substantially only shift from power to other industries (steel, cement, and chemicals) and China now potentially "dangerously delay[ing]" the phase-out.[160][161]
- 7 February
- A study quantifies and maps threats of glacial lake outburst floods caused by climate change, finding ~15 million people to be at risk. More than half of the exposed population are in India, Pakistan, Peru, and China.[162][163]
- A UN report projects there could be 10 million annual deaths from antimicrobial-resistant (AMR) superbugs by 2050 if steps aren't taken and highlights driving factors like climate change and economic sectors' activities, suggesting a One Health-type approach.[164][165] An analysis of global antibiotics use in livestock – which is one of the known drivers of AMR in livestock and wildlife/environment and also impacts human health[166][167][168] – shows that it has declined in Europe and China (plateaued) due to new policy but increased globally (1 Feb).[169][170] Around 1 February, news report on 'super pigs' – invasive hybrids resulting from cross-breeding domestic pigs with wild boars, that are relatively intelligent, adaptable and resilient and by that time cause major economic- and environmental damage across North America as well as human health risks[171][172] – previously described as the "most prolific invasive mammals on Earth".[173]
- News outlets report on a study (21 Nov 2022) demonstrating locust antennae implanted as biosensors into (bio-hybrid) robots for AI-interpreted machine olfaction.[174][175]



- 8 February
- The minor planet Quaoar is found to have a ring system, following observations by the CHEOPS space telescope.[176][177]
- Scientists in the U.S. propose mining the lunar soil and launching it towards the Sun to form a shield (space sunshade) against global warming.[178][179]
- The first direct transfer of qubits between quantum computer microchips is demonstrated, with a 99.999993% accuracy rate and connection speed of 2424/s. The research team suggests their work has "the potential to scale-up by connecting hundreds or even thousands of quantum computing microchips."[180][181]
- Two studies show how the microbiome can drive and interact with chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS).[182][183][184]
- 3D printing-like additive 3D assembly of matter using holographic sound fields is demonstrated, with early fields of applications including rapid biofabrication/TE, having several advantages over a similar method using light reported in 2017.[185][186]
- 9 February
- Scientists review safety-by-design technology- and policy-based approaches to ensure biosafety and biosecurity to prevent engineered pathogen pandemics, such as sequence screening and biocontainment systems, some of which already implemented and part of regulations to some degree.[187][additional citation(s) needed]
- A study reports results of the first longevity caloric restriction (CR) trial, CALERIE, finding that two years of CR slowed the pace of aging as measured by one of three aging clocks (modest DunedinPACE effects). A continuous 25% CR diet which already yielded the 2y DunedinPACE effects within one year.[188][189]
- Researchers demonstrate a magnetic medical microbot, I-RAMAN, for cleaning clogged arteries which could (among other things) replace endovascular surgery with pigs and with a vascular model that has a pseudo blood clot. The separable and recombinable magnetic robots (SRMR) can be steered, separate, tunnel, deliver drugs, and recombine.[190][191]
- 13 February – Public health knowledge becomes more robust: a study demonstrates that school meal programs (the HHFKA) can substantially improve the health of youths as measured by BMI.[192][193] Scientists show associations between ultra-processed foods (such as breakfast cereals) consumption and cancer-related mortality in ~200,000 UK Biobank participants (31 Jan).[194][195] An umbrella review confirms that physical activity is highly beneficial (as in ~1.5 times more effective than counseling) for improving symptoms of depression, anxiety and distress in adults and should be one "mainstay approach" (1 Feb).[196] A separate review comes to similar conclusions for depressive symptoms, also giving broad recommendations for the selection of exercise type(s), i.a. reporting AE and RE types showed large effects whereas mixing both did not (1 Feb).[197] Scientists, using data of ~9 million U.S. citizens, report worldwide-prevalent air pollution is a potential risk factor for late-onset depression (10 Feb).[198][199] A study expands on the evidence of air pollution-related bone damage (14 Feb).[200]
- 14 February
- A new record low Antarctic sea ice extent is reported by the National Snow and Ice Data Center in the US, beating the previous record set a year earlier.[201][202]
- Researchers report a potential first pharmacological acute contraception for men, 100% effective in tests with mice.[203][204]
- 15 February
- Two joint studies by the British Antarctic Survey and the US Antarctic programme find that glaciers on the icy continent may be more sensitive to changes in sea temperature than previously thought. Researchers used sensors and an underwater robot beneath the Thwaites glacier to study melting.[205][206][207]
- Scientists report that the possible sounds that ankylosaur dinosaurs may have made were bird-like vocalizations based on a finding of a fossilized larynx from the ankylosaur Pinacosaurus grangeri.[208][209]
- The engineering of metastructures that allow the electrical fields inside the device to be controlled at the sub-wavelength scale is shown to be a viable approach for developing ultra-fast electronics in 6G communications.[210][211]
- Researchers report the development of Erodium-inspired self-burying seed carriers for aerial seeding of a large range of seed sizes in agriculture and reforestation.[212][213]
- Two studies (15 & 2 Feb) report observational evidence and calculations that indicate "stellar remnant black holes are the astrophysical origin of dark energy", as closer supermassive black holes appear to be much larger than distant ones (from the past) which suggests that their growth is driven by the expansion of the Universe, with them contributing "an effectively constant cosmological energy density", so "that black holes contribute cosmologically as vacuum energy", giving the ΩΛ as measured by Planck. Their explanation depends on black holes containing dark energy and, if validated with more observations and studies of Einstein's theory of relativity, would solve one of the top key known questions of cosmology and would also avoid black hole singularities.[214][215][216] A preprint (7 Feb) outlines, via draft theoretical modelling using an EoS partly motivated by loop quantum cosmology[clarification needed] and FLRW, how dark energy could also enable a Big Bounce in the ultimate future – cyclical Big Bangs – by being nonlinear as in evolving between a high energy effective cosmological constant (ECC) and a low energy ECC "close to the observed dark energy density today", "sometimes growing the cosmos, sometimes shrinking it down until the conditions are right for a new Big Bang to occur".[217][218]
- A study strengthens the invalidation of the common argument for high medication costs that research and development (R&D) investments are reflected in and necessitate the treatment costs, finding that during recent decades, the largest biopharmaceutical companies spent more on selling, general and administrative activities (SG&A such as marketing and advertising) than on R&D, with the same largely also applying to share buybacks. It also mentions past public investments, suggests valuable innovation could get accelerated and concludes that high prices in specific as well as higher new medication price medians – both burdens to consumers and healthcare systems – are not justified.[219][220]
- 16 February
- An effective new method for carbon dioxide removal from the ocean is described. It could be implemented by ships that would process seawater as they travel, at offshore drilling platforms or aquaculture fish farms.[221]
- An international norms and arms control proposal for artificial intelligence in the military (such as LAWs and weapons decision-making), the Political Declaration on Responsible Military Use of Artificial Intelligence and Autonomy, is published by the U.S. government.[222][223][224] The first international summit on military AI led to a joint unbinding statement by the U.S., China and other nations, with some external calls for starting negotiations on an internationally binding law or an enforcement-mechanisms-driven law.[225]
- A study models the burden of the global energy price crisis on household spending caused by the Russo-Ukrainian War, projecting economic mechanisms and fossil fuel dependency will potentially push an additional 78–141 million people into extreme poverty, "offering a basis for targeted support measures".[226][227]
- A study shows how many psychedelics promote neural plasticity as psychoplastogens: by getting inside nerve cells and activating 5-HT2A receptors inside, rather than (only) on the surface, of cells, which can e.g. lead to antidepressant-like effects.[228][229]
- 18 February – Researchers report the development of a biocomposite 3D printing ink, BactoInk, containing calcium carbonate-producing microorganisms which could be used for restoration, artificial reefs and potentially bone-repair.[230][231]
- 19 February – A study reports that rationing has been neglected as a policy option for mitigating climate change, and, partly based on historical data and economic analysis, concludes that such personal carbon allowances (PCAs) for few or many products could help states reduce emissions rapidly and fairly. It suggests built-in fair shares mechanisms would be a key part of two-currency PCA economics and that carbon taxes-only economics would not have effects that are as quick and equitable, with their fairness issues potentially including disproportionate impacts on low-income populations (or intensified economic inequality in general). There could be 'carbon cards' for all-encompassing CAs (e.g. using life-cycle assessment for supermarket items ) or per-capita rationing of (scientifically) selected goods such as meat, flights, and/or fossil fuels to adapt to the scarce (physically limited) carbon budget available to meet goals. PCAs could also help address other issues such as the energy crisis and viably accelerate sustainability transitions of domains ranging from lifestyles to investments but may require smaller initial steps than an entire-population-national rationing implementation.[232][233]
- 20 February – Progress in sex-, reproduction-, and gender studies: a researcher reports "sexual loneliness" is increasing, is a neglected substantial public health problem (of men's health), and that the distribution of the number of lifetime sex partners is as unequal as the distribution of wealth among the most unequal countries and concentrating further – with the number of lifetime sex partners of the top 5% of American men rising substantially within a decade, accounting for more sex acts than the bottom 50% by 2012 – and that while "women can get attention from thousands of men online [with dating apps] in just a few hours, men are lucky if anyone is interested in them", which may be one aspect of gender equality and other issues or topics.[234][235] News reports on a study (23 Jan) that investigates a subset of the well-being effects of dating app use.[236][237] A study reviews data on polygyny as a potential way for increasing fertility in developed countries (6 Feb).[238] A review shows that investigated gender differences in basic skills are larger in more gender-equal countries, the gender-equality paradox (16 Feb).[239] News reports on a study (19 Jan) that shows that "women are [now] 3 to 15 times more likely to be selected as members of the AAAS and NAS than men with similar publication and citation records".[240][241]

- 21 February
- Scientists report the findings of a "dark microbiome" of microorganisms in the Atacama Desert in Chile, a Mars-like region on Earth.[242][243]
- Neuroethicists propose a framework that differentiates consciousness into multiple (ten) dimensions, relevant to consciousness studies and questions about non-human consciousness, with nuanced cognitive capacity levels in each that via indicators could form comparable consciousness profiles.[244] On 23 February, a study reports first brain recordings of freely moving octopuses, which are among the most intelligent animals of Earth, also enabling novel intelligence studies and finding both human-like and never-before-seen brain waves.[245][246]
- A study shows DNA methylation aging clocks could be useful indicators of health while social factors – such as health behaviors and poverty – are at least as good predictors and e.g. can better predict cognitive functioning.[247] Around February, Bryan Johnson's Project Blueprint for one of the first comprehensive, possibly largely public,[248] (self-)experimentations of a comprehensive combination therapy informed by the large scientific corpus on the topic and organ measurements to maximally reverse biological age and (epigenetic) aging markers achieves substantial media attention,[249][250][251] with such activities previously largely reserved to biohackers without resources and means to evaluate effects.
- 22 February
- Soft, 3D-printed heart replicas that can be personalised for individual patients are demonstrated by engineers for applications in device development, procedural planning, and outcome prediction.[252][253]
- Concerns about and research of avian influenza (bird flu) H5N1 rise as increasing spillovers to and between mammals are reported,[needs update][262] with the incoming WHO chief scientist warning governments should invest in H5N1 vaccines for all flu strains,[263] and prepare for a potential outbreak among humans (pandemic preparedness),[255] which, if there is a significant risk, could possibly also be prevented.[264]
- Archaeologists report the earliest evidence of bow and arrow use outside Africa – ~54,000 years ago in France, showing the earliest known H. sapiens to migrate into Neandertal territories used these technologies.[265][266]
- 23 February
- The world's first COVID-19 drug designed by generative AI is approved for human use, with clinical trials expected to begin in China. The new drug, ISM3312, is developed by Insilico Medicine.[267]
- The growing of electrodes in the living tissue of zebrafish (including in the brain) and medicinal leeches is demonstrated, using an injectable gel and the animals' own endogenous molecules to trigger the formation. The researchers claim their breakthrough enables "a new paradigm in bioelectronics."[268][269]
- After the EU's ECHA published a restriction policy proposal for all PFAS on 7 February which would largely ban the use of these harmful 'forever chemicals',[270][271][272] scientific journalists of "The Forever Pollution Project" release the first comprehensive map of PFAS contamination for Europe.[273][274] While the map only shows contamination of surface- and groundwater but not bottled and tap water, consumers could protect their health using specific types of faucet water filters.[275][276] A map released on 22 February by EWG integrates scientific data about prevalent PFAS contamination of wildlife.[277]
- 27 February
- The channelling of ions into defined pathways in perovskite materials is shown to improve the stability and operational performance of perovskite solar cells. A research team claims this could boost their efficiency from 25 to 40%.[278][279]
- A study links the common artificial sweetener erythritol to substantially increased major cardiovascular event risk, also elucidating causal mechanics via in vivo data. One author explains that if "your blood level of erythritol was in the top 25% compared to the bottom 25%, there was about a two-fold higher risk for heart attack and stroke. It's on par with the strongest of cardiac risk factors, like diabetes".[280][281][282]
- 28 February
- Scientists coalesce recent developments using human brain organoids into a new field they term organoid intelligence (OI), seeking to harness OI for computing – as a novel type of AI – in an ethically responsible way. Networks of such miniature tissues could become functional using stimulus-response training or organoid-computer interfaces – to potentially become "more powerful than silicon-based computing" for a range of tasks – and could also be used for research of various pathophysiologies, brain development, human learning, memory and intelligence, and new therapeutic approaches against brain diseases.[283][284]
- Promising results of therapeutic candidates are reported: a phase 3 trialed pegylated interferon lambda against COVID-19 (and other viruses) (9 Feb), a monkey-tested potential first Marburg virus vaccine (10 Feb),[285][286] in human neurons and in mice tested in-use lamotrigine for recovering MYT1L-caused autism (14 Feb),[287] phase 3 trial results (~94% efficacy against severe disease) for one of the three late-stage and near-FDA-approval RSV vaccines in elderly (16 Feb),[288][289][290] one of two phase 2 trialed RSV vaccines (16 Feb),[288][291] a trialed electrical stimulation of cervical spinal circuits against post-stroke hemiparesis (20 Feb),[292][293] a phase 3 trialed MPC[clarification needed] stem cell therapy against cardiac events in people with HFrEF heart failure (27 Feb).[294][295]
- Progress in screening or diagnosis: a news-reported possibly inexpensive high-throughput static droplet microfluidic device against cancer that isolates and metabolomically analyzes circulating tumor cells in blood (16 Dec 2022),[296][297] retinal eye screening and monitoring biomarkers against Alzheimer's disease (AD) (9 Feb),[298][299] autoantibody biomarkers in blood for inexpensively detecting AD (21 Feb).[300]
March


- 1 March
- Biological organoid intelligence , 'Brainoware', is demonstrated to solve computational tasks (non-linear equations) in a preprint, with implications for bioethics and potential bottlenecks and limits of nonbio-AI.[301][302]
- A new record for the closest and oldest ultracool dwarf binary pair is reported. The newly discovered stars, in a system named LP 413-53AB, orbit each other in just 17 hours and are believed to be billions of years old.[303][304]
- An ICIJ-led investigation 'Deforestation Inc.' shows or reaffirms how an unregulated greenwashing industry overlooks deforestation and human rights (HR) violations when granting environmental certifications that are used to claim compliance to environmental standards, labor laws and HR.[305][306]
- A U.S. DNI report concludes that the 'anomalous health incidents' (AHIs) termed 'Havana syndrome' are "very unlikely" to get induced by a foreign adversary.[307] A previous report declassified on 28 March considered directed energy as in directed energy weapons as a plausible cause.[308][309]
- Bioengineers show bodily system changes can induce anxiety, in specific altered heart rate by itself in risky contexts,[310][311] after earlier studies also implicated immune system elements.[312][313]
- An "adversarial collaboration" study shows larger financial incomes increase mental wellbeing beyond a previously believed flattening threshold, except for a ceiled "unhappy" minority.[314][315]
- A study about global spatiotemporal PM2.5 fine particle air pollution suggests that in 2019, only "0.001% of the global population had an annual exposure to PM2.5 at concentrations lower than 5 μg/m3 [WHO annual limit]".[316][317] On 14 March, the annual IQAir World Air Quality Report that uses a sensor network suggests of the countries assessed,[quantify] six countries (Australia, Estonia, Finland, Grenada, Iceland and New Zealand) may have met[contradictory] the WHO guideline specific to this type of air pollution.[318] Air pollution is one of the largest causes (in terms of number of cases, not potential years of life lost DALYs) of early deaths.
- The largest study of ancient Europeans' DNA (356 UP–Neolithic hunter-gatherers) is published, with implications for the history of ancestry changes during the last Ice Age.[319][320] On 23 March, geneticists report on immune function (MHC) and pigmentation (SLC24A5) as targets of adaptation in Neolithic admixture, with farmers inheriting many immunity genes.[321][322]
- Science results of the first test of asteroidal planetary defense, DART , are published.[323][331]
- 2 March
- A study reports boreal fires, "typically accounting for 10% of global fire carbon dioxide emissions, contributed 23% [...] in 2021".[332][333]
- After a study (27 Feb) indicated pathological changes to subcortical motor and cognitive hubs in (fatigued) long COVID cases,[334] a small comparative study shows differences in volumes of brainstem regions are similar for ME/CFS and long COVID patients, being larger than in 10 healthy subjects.[335][336]
- 6 March – The highest-granularity study on food GHGs reports that global food consumption alone would lead to ("add nearly 1 °C to warming by 2100") failed climate goals with constant patterns, with ~75% of the projected warming due to ruminant meat, dairy and rice, albeit consumption currently shifts towards higher emissions overall as economic development is expected to facilitate acquisitions of undifferentiated goods like beef.[337][338]

- 8 March
- A new way of capturing carbon, which transforms the gas into bicarbonate of soda and stores it safely in seawater, is shown to be three times more efficient than existing methods.[339][340]
- A bacterial hydrogenase enzyme, Huc, for biohydrogen energy from the air is reported.[341][342]
- The first global precise global time series of ocean surface plastic pollution is released. The study finds that "Today's global abundance is estimated at approximately 82–358 trillion plastic particles weighing 1.1–4.9 million tonnes." There was "no clear detectable trend until 1990, a fluctuating but stagnant trend from then until 2005, and a rapid increase until the present." It concludes "urgent international policy interventions" are needed.[343][344]
- 9 March – Researchers report the development of a fuel cell implant powered by blood glucose. It can also release insulin at certain levels and have enough energy to allow smartphone implant control.[345][346]
- 10 March
- The entire brain of a fruit fly larva is mapped in complete detail for the first time, showing all 3,016 neurons and 548,000 synapses.[347][348]
- News outlets report on a study (27 Feb), alongside related reports, that concludes "Russia's role as a major player in the global nuclear power sector has remained largely below the [Russian invasion of Ukraine related] sanctions radar".[349][350] On 7 March, news reports of a study (28 Feb) that uses ICIJ data to investigate offshore networks of oligarchs, suggesting sanctioning of professional intermediary wealth managers.[351][352]

- 13 March
- A study affirms total intensity of extreme weather events is strongly correlated with global mean temperature during 2002–2021, not using mainly models but historical data.[353][354]
- An analysis concludes there is large potential (~9,400 TWh/yr) for floating solar photovoltaics on reservoirs,[355][356] at the upper range of the prior 2020 study.
- The first comprehensive assessment of 'bottom marine heat waves' is published.[357][358]
- An analysis concludes there is large potential for mycoforestry incorporation for carbon sequestration, ecosystem support, and food production.[359][360]
- 14 March
- Progress in healthy sustainable food research:
- Medical researchers report a 24% reduction of heart disease risk in women on a Mediterranean-type diet.[361][362]
- A study (1 Mar) reports average carbon footprints of average diets in a US cohort. Pescatarian diets were the healthiest, followed by the two other plant-based diets.[363][364] There may also be substantial variation within diets.
- Vegan: ~0.69 CO2-eq/1000 kcal (less than 0.5 oz (14 g) total of meat, poultry, seafood, eggs; less than 0.25 cup (~60 mL) equivalent of dairy)
- Vegetarian: ~1.16 — less than 0.5 oz (14 g) of meat, poultry, and seafood
- Pescatarian: ~1.66 — less than 0.5 oz (14 g) of meat and poultry, consumed seafood
- Omnivore: ~2.23 — anything else
- Paleo: ~2.62 — less than 0.5 oz (14 g) total grains and legumes, less than 0.25 cup (~60 mL) of dairy
- Keto: ~2.91 — ≤50 g of net carbohydrates (total carbohydrates minus total fiber)
- A study (7 Mar) using data of 0.5 M participants strengthens the association between ultra-processed foods and cancer risks.[365][366]
- A post-mortem study (8 Mar) finds green leafy vegetable intake inversely correlates with Alzheimer's disease pathology.[367][368]
- Scientists report (22 Mar) fMRI results showing daily consumption of a high-fat/high-sugar snack alters, similar to drug addiction and likely directly, brain reward circuits, altering food preferences.[369][370]
- Progress relating to AI research:
- The LLM GPT-4 is launched by OpenAI.[371][372] It and ChatGPT based on it continue to receive major global media attention.
- Researchers suggest that growing influence of industry in AI research means that "public interest alternatives for important AI tools may become increasingly scarce" (2 Mar).[373]
- Google reveals PaLM-E, an embodied multimodal language model with 562 billion parameters (7 Mar).[374][375]
- Google releases chatbot Bard due to effects of the ChatGPT release,[376] with potential for integration into its Web search and, like ChatGPT software, also as a software development helper tool[377] (21 Mar). DuckDuckGo releases the DuckAssist feature integrated into its search engine that summarizes information from Wikipedia to answer search queries that are questions (8 Mar). The experimental feature is shut down without explanation on 12 April.[378][379][380] A broader alternative approach to the software's Q&A applications and use of text generation for assignments may be the improvement of media literacy and Web search skills in education systems.
- A method for editing NeRF scenes, a novel media technique from 2020,[381] with natural language commands is demonstrated by Nvidia (22 Mar).[382][383]
- An open letter "Pause Giant AI Experiments" by the Future of Life Institute calls for "AI labs to immediately pause for at least 6 months the training of AI systems more powerful than GPT-4" due to "profound risks to society and humanity".[384][385] It received substantial media attention and also contributed to speculations about perceived large LLM potential (22 Mar). At the time there is extensive media coverage of views that regard ChatGPT as a potential step towards AGI or sentient machines, also extending to some academic works (e.g. a popular 22 Mar preprint by a company).[386] The coverage focused on such views may not represent the majority expert views and, for example, some researchers note that e.g. the ability to generate coherent text and imitations are not the same as understanding language.[387] A set of techniques under development include self-refining code or text.[388]
- The first clear evidence of active volcanism on Venus is presented, based on a reanalysis of old images from the Magellan spacecraft.[389][390][391] On 24 March, a second study finds that Venus hosts far more volcanoes than previously mapped, creating a new catalog.[392][393]
- A news outlet reports on a two/multi-robot and beacons mesh communication paradigm (11 Feb) for exploration by robotic probes, drones, spacecraft, disaster recovery rovers or underwater robots.[394][395]
- Progress in healthy sustainable food research:
- 15 March
- The structure of olfactory receptor protein OR51E2 is found, the first elucidation of the structure of any human olfactory receptor to date.[396][397]
- A technique for offspring from two male mice via skin cells (differentiated to oocytes) and many (7 out of 630 successful) embryo transfers is demonstrated.[398][399]
- 16 March – The first Global Biolabs Report documents a rapid rise of high-risk pathogen labs around the world, many of which in urban areas or with particularly weak biorisk management, with BSL-4 labs doubling within a decade. Its results raise concerns about contemporary pandemic prevention measures for which the report makes broad key recommendations to prevent reckless, accidental – for which there are track-records[400][401][402][403] – or malicious releases.[404][405]
- 17 March – A study suggests in developed countries (Sweden) wealth (lottery winning) increases marriage formation and fertility (likely via desirability) for males, with the only discernible effect on female winners being increased short-run (but not long-run) divorce risk.[406][407]
- 19 March – A news outlet reports on a systematic study of major issues in popular currently available commercial VPNs for Internet privacy and security.[408][409] On 3 March, researchers report on their paper about 'digital resignation', calling for regulations and education reform.[410]
- 20 March
- The final synthesis of the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report is published. It summarises the state of knowledge relating to climate change with assessed levels of confidence. Conclusions in the summary for contemporary policy-makers include that the extent to which both current and future generations will be impacted depends on choices now and in the near-term, with "high confidence" that policies implemented by the end of 2020 are "projected to result in higher global GHG emissions in 2030 than emissions implied by NDCs" and would fail to meet global climate goals.[411]
- The CDC reports of rising concerns over the accelerating (95% increase in 2021) spread of antimicrobial-resistant C. auris fungus in U.S. healthcare facilities.[412][413][414] On 13 March, a study reports the first case of C. purpureum causing disease in a human – a mycologist, highlighting cross-kingdom human pathogen potential.[415][416]
- A consciousness- and psychedelics science study shows the most comprehensive view of the acute brain action of psychedelics during trips with the first EEG-fMRI neuroimaging results about DMT effects on the brain.[417][418]
- 21 March
- Analysis of samples from the near-Earth asteroid Ryugu reveals the presence of uracil, one of the four nucleobases in RNA needed for life.[419][420]
- A university reports on a study (23 Feb) that concludes that "the public has more-positive attitudes towards [fossil fuel] subsidy removal if optimal use of the saved fiscal revenues is specified".[421]
- 22 March – Astronomers report that ʻOumuamua, an interstellar object discovered in 2017 passing through the Solar System, was a comet after all, "originating as a planetesimal relic"; the observed acceleration was "due to the release of entrapped molecular hydrogen that formed through energetic processing of an H2O-rich icy body".[422][423]
- 23 March
- Progress in health literacy and communication:
- A review about mitochondria and health is published, suggesting that "a normalization of a lack of physical activity in our modern society has led to the perception that exercise is an 'intervention'" instead of part of a modus vivendi engrained in human bodies and that lessons learned from elite athlete research (healthy subjects) could be translated to the betterment of populations' health.[424]
- On 2 March, a report projects more than half of the global population will be obese within 12 years, assessing the situations in 187 countries, including their obesity prevention policies commitment.[425][426]
- On 21 March, a psychologist reports on a study (10 Feb) that hypothesizes mental health awareness efforts (in current forms) or glamorised and romanticised mental disorders on social media (e.g. quotes about depression on aesthetically appealing backgrounds shared widely on certain social media[which?]) may contribute to the recent rise in reported mental health problems – by intensifying and over-diagnosing of such – beyond e.g. increased reporting of previously under-recognised symptoms or mental health-related issues.[427][428]
- A study, as part of a series[429] and alongside a WHO fact sheet[image needed] (21 Mar),[430][431] robustifies the recent[432] concept of "commercial determinants of health" suggesting "transnational corporations", facilitated by economic and governance systems[433] and a "shift towards market fundamentalism", are responsible for escalating rates of avoidable ill health, planetary damage, and social and health inequity", with just four industry sectors ("tobacco, ultra-processed food, fossil fuel, and alcohol") "already account[ing] for [or being involved in] at least a third of global deaths". It concludes that while policy-related capacities "have been impoverished and disempowered or captured by commercial interests", "many policy solutions [to some degree of adoptability] are available [but are] not being implemented".[434][435] On 22 March, a news outlet reports on a paper (25 Jan) that contributes to an understanding of already-existing law that suggests that fossil fuel companies may be chargeable with homicide due to climate change effects and e.g. partly their deception of the public and proactive prevention of regulations. The paper is focused on corporate actors and does not address e.g. politicians' and policymakers' responsibilities, media people or issues, economic pressures or incentives, and responsibilities for facilitations of solutions to these underlying economic conditions.[436][437]
- The first (9) multi-organ-based human virome, of (31) post-mortem healthy individuals, is published, including a dark virome from body sites previously considered to be sterile. Positive and negative long-term consequences of such resident DNA viruses, including reactivation factors and issues, are largely unknown.[438][additional citation(s) needed]
- Progress in health literacy and communication:
- 28 March – A new viable lithium-ion battery recycling method is reported.[439][440] On 21 March, a university and one news outlet report on a study (21 Feb) suggesting incentives and regulations are needed for producers to design solar panels that can be more easily recycled.[441][442]
- 29 March
- A study of ~90,000 adults finds that increased physical activity levels can reduce the mortality risks associated with short or long sleep duration.[443][444]
- Astronomers identify an "ultramassive" black hole, one of the largest ever discovered, and the first to be confirmed through gravitational lensing, at the centre of the galaxy Abell 1201 BCG.[445]
- News outlets report on a study (19 Feb) that indicates the language connectome is shaped by factors that include native language characteristics.[446][447]
- A study reports a bacterial new PVC injection system-based way of protein delivery, one of the biggest unsolved problems[needs update] of gene editing.[448][449]
- 30 March
- A study of the deep ocean currents around Antarctica finds they could slow by 40% by 2050, with significant implications for the global climate.[450][451] On 27 March, a study attempts to provide estimations of the tipping point(s) of the Greenland ice sheet. It found that "critical ice volumes are crossed for cumulative emissions of 1,000 and 2,500 GtC, which would cause long-term sea level rise by 1.8 and 6.9 m respectively", suggesting a "tipping of the GIS within the range of the temperature limits of the Paris agreement".[452][453]
- Botanists report plants emit ultrasonic sounds under stress which can be interpreted, relevant to agriculture.[454][455]
- A news outlet reports on a DVGW report that suggests gas pipeline infrastructures (in Germany) are suitable to be repurposed to transport hydrogen, showing limited corrosion.[456][457]
- 31 March
- Parts of Twitter's recommender algorithms become open source, welcomed and requested by many albeit with several issues related to code exclusion and verifiability.[458][459][460] Around that time, the free version of its API, which was also used for research, is shut down[461] – followed shortly thereafter by Reddit's[462] – proprietary verification checkmarks cause controversy,[463] parts of its source code are leaked,[464] and applications of a "state-affiliated media" label – which purportedly uses "publicly funded broadcasters" data which, like the label, does not differentiate and list the shares of funding sources – cause controversy.[465][466]
- A university reports on a study (14 Jan) demonstrating functional integration of a magnetically steered microbot containing neurons, 'Mag-Neurobot', in a mouse "organotypic hippocampal slice" (OHS) as physical (semi-)artificial neurons.[467][468]
- Promising innovations relating to global challenges are demonstrated:[image needed] a low-cost open source air pollution sensor (Flatburn) (1 Mar),[469][470] a second biotech company commercializes sustainable MS mycelium protein after Quorn in 1983 (Meati Foods) (6 Mar),[471] another agrivoltaic greenhouse which outperforms a conventional glass-roof greenhouse (6 Mar),[472][473] first kWh by a TLP floating airborne wind turbine system (X30) possibly as part of a "new wave of startups" in this area[474] (7 Mar),[475] WHO recommendations on two new types of insecticide-treated nets for Malaria prevention (14 Mar),[476] a biodegradable and biorecyclable glass (17 Mar),[477][478] a COTS demining drone (~21 Mar),[479][480] nonalcoholic first powdered beer (Dryest Beer) (23 Mar),[481] a reforestation drone (AirSeed) (24 Mar),[482] a phase-change materials embedded in wood-based energy-saving building material (27 Mar),[483][484] cultivated meat from extinct mammoths as demonstration of potential (28 Mar),[485] media reports on a study (17 Jul 2022) demonstrating a CNC radiative cooling film (29 Mar).[486][487]
- Promising results of therapeutic candidates are reported: mice-tested CMD (cysteine and methionine deprivation) diet with RSL3 against cancer (2 Mar),[488] a phase 1 trialed tuberculosis vaccine (6 Mar),[489] trialed pulsed field ablation (PFA) against atrial fibrillation (6 Mar),[490] mice-tested FGF21 (also activated by β-klotho) for alcohol intoxication recovery (7 Mar),[491][492] a mice-tested mRNA vaccine against potential antibiotic-resistant plague which may also be useful for other antibacterial vaccines (8 Mar),[493][494] a study (28 Feb) indicates Naloxone access does not promote high-risk opioid use behaviors (9 Mar),[495] rat-tested mitochondrial transplantation (MTx) for cardiac arrest recovery (16 Mar),[496][497] an EEG BCI headgear (16 Mar),[498][499] mice-tested menin target against aging (16 Mar),[500][501] a mice-tested novel-type CRISPR gene editing system PESpRY against RP vision loss (17 Mar),[502] a mice-tested wearable patch for accelerated cutaneous chronic wound healing (24 Mar),[503] phase 3 trialed pembrolizumab addition against recurrent endometrial cancer (27 Mar),[504] a phase 3 trialed percutaneous approach against chronic limb threatening ischemia without amputation (30 Mar),[505] a mice-tested self-charging battery ROS-emitting implant against cancer (31 Mar).[506]
Remove ads
Deaths
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads