Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
List of Ferrari engines
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
This is a list of internal combustion engines manufactured by Ferrari.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2020) |
Straight-2
Ferrari was rare among automobile manufacturers in attempting to build a straight-2 automobile engine. The racing prototype never made it to production.[1]
Remove ads
Straight-3
During the 90s Ferrari developed an experimental straight-3 two-stroke engine.[2][3]
- Tipo F134
- 1994 1347 cc – prototype
Straight-4
Summarize
Perspective

Lampredi designed a straight-4 engine for Formula Two use. Different versions of this engine were later used in Formula One and sports car racing.
Straight-6
Lampredi also modified his four into a straight-6 for racing use.
Remove ads
V6
Summarize
Perspective
Ferrari's Dino project of the late 1956 gave birth to the company's well-known 65° V6 DOHC engines. This Vittorio Jano design formed the basis of the company's modern engines right up through the mid-2000s (decade). Another series of V6 engines was started in 1959 with a 60° V-angle and single overhead camshafts design.
- Dino 65° DOHC
- 1957 –– Dino 156 F2
- 1958–1960 –– 246 F1/246 P F1
- 1958 –– 326 MI
- 1958 –– Dino 196 S
- 1958 –– Dino 296 S
- 1959 –– 256 F1
- 1960 –– 156 F2
- 1961 –– 246 SP
- 1965 –– Dino 166 P
- 1965–1969 –– Dino 206 SP, Dino 206 S, Dino 206 GT, Fiat Dino
- 1967 –– Dino 166 F2
- 1966–1968 –– 246 F1-66, Dino 246 Tasmania
- 1969–1974 –– Dino 246 GT, Fiat Dino, Lancia Stratos (iron-block version developed by Franco Rocchi and Aurelio Lampredi)
- Dino 60° SOHC
- 1959 –– Dino 196 S
- 1959–1960 –– Dino 246 S
- 1962 –– 196 SP
- 1962 –– 286 SP
- Chiti 120°
- Turbocharged Formula One V6 engines
- Tipo 021, 031 & 032 (120° V angle) – designed by Mauro Forghieri and Nicola Materazzi
- 1980–1986 1496 cc turbocharged – Ferrari 126C, Ferrari 156/85, Ferrari F1-86
- Tipo 033 (90° V angle) – designed by Jean-Jacques His
- 1987–1988 1496 cc turbocharged – Ferrari F1-87, Ferrari F1-87/88C
- Tipo 021, 031 & 032 (120° V angle) – designed by Mauro Forghieri and Nicola Materazzi
- Turbocharged Formula One V6 turbo-hybrid engines
- Tipo 059 (90° V angle, 1600 cc turbocharged) – designed by Luca Marmorini
- 2014–2015 1598 cc –– turbocharged – Ferrari F14 T, Ferrari SF15-T, Marussia MR-03, Marussia MR-03B, Sauber C33, Sauber C34
- Tipo 060 (90° V angle, 1600 cc turbocharged)
- 2016 – Toro Rosso STR11
- Tipo 061 (90° V angle, 1600 cc turbocharged)
- 2016 – Ferrari SF16-H, Haas VF-16, Sauber C35
- 2017 – Sauber C36
- Tipo 062 (90° V angle, 1600 cc turbocharged)
- 2017 – Ferrari SF70H, Haas VF-17
- 2018 (062 EVO) – Sauber C37, Haas VF-18, Ferrari SF71H
- Tipo 064 (90° V angle, 1600 cc turbocharged)
- 2019 – Ferrari SF90, Alfa Romeo C38, Haas VF-19
- Tipo 065 (90° V angle, 1600 cc turbocharged)
- 2020 (065) – Ferrari SF1000, Alfa Romeo C39, Haas VF-20
- 2021 (065/6) – Ferrari SF21, Alfa Romeo C41, Haas VF-21
- Tipo 066 (90° V angle, 1600 cc turbocharged)
- 2022 (066/7) – Ferrari F1-75, Alfa Romeo C42, Haas VF-22
- 2023 – 2024 (066/10) – Ferrari SF-23, Alfa Romeo C43, Haas VF-23, Haas VF-24
- 2024 (066/12) – Ferrari SF-24, Kick Sauber C44
- Tipo 059 (90° V angle, 1600 cc turbocharged) – designed by Luca Marmorini
- Tipo F163 (120° V angle, turbocharged)
- 2022 2,992.4 cc – Ferrari 296 GTB
Remove ads
V8



The first Ferrari V8 engine was derived from a Lancia project, used in D50 F1 racecar. The Dino V8 family lasted from the early 1970s through 2004 when it was replaced by a new Ferrari/Maserati design.
- Lancia derived (Jano)
- Chiti
- Tipo 205/B (designed by Franco Rocchi and Angelo Bellei)
- Dino
- 1973–1983 –– 308 GT4, 308 GTB/GTS
- 1975–1981 –– 208 GT4, 208 GTB/GTS
- 1982–1989 1990 cc turbocharged –– 208 GTB/GTS Turbo, GTB/GTS Turbo
- 1984–1985 2855 cc turbocharged –– Tipo F114B – 288 GTO (designed by Nicola Materazzi)[7][8][9]
- 1980–1982 2926 cc fuel injection –– 308 GTBi/GTSi, Mondial 8
- 1982–1985 2926 cc quattrovalvole –– 308 GTB/GTS qv, Mondial qv
- 1985–1989 3185 cc –– 328 GTB/GTS, 3.2 Mondial
- 1987–1988 2936 cc turbocharged –– Tipo F120A – F40(designed by Nicola Materazzi)[7][8][9]
- 1989–1995 3405 cc –– Mondial t, 348 tb/ts, GTB/GTS, Spider
- 1994–1999 3496 cc 5-valve –– F355 GTB, GTS, Spider
- 1999–2004 3586 cc 5-valve –– 360 Modena, Spider, Challenge Stradale
- Tipo F136 Ferrari/Maserati engine
- 2001–2019 4244 cc –– Maserati Coupé, Maserati Spyder, Maserati Quattroporte V, Maserati GranTurismo
- 2004–2009 4308 cc –– F430
- 2007–2019 4691 cc –– Maserati Quattroporte V, Maserati GranTurismo, Alfa Romeo 8C Competizione
- 2008–2014 4297 cc –– California
- 2009–2015 4499 cc –– 458
- Tipo 056 (F1 engine) (designed by Gilles Simon[10])
- 2006–2013 2398 cc –– 248 F1, F2007, F2008, F60, F10, 150° Italia, F2012, F138, Force India VJM01, Red Bull RB2, Spyker F8-VII/VIIB, Toro Rosso STR2/2B, STR3, STR4, STR5, STR6, STR7, STR8, Sauber C29, C30, C31, C32
- Tipo F154 (turbocharged)
- 2013–present 3797 cc –– Maserati Quattroporte GTS/Trofeo, Maserati Levante GTS/Trofeo, Maserati Ghibli Trofeo
- 2014–present 3855 cc –– California T, GTC4Lusso T, Portofino, Roma
- 2015–present 3902 cc –– 488, F8
- 2020–present 3990 cc –– SF90 Stradale
Remove ads
V10
Ferrari used V10 engines only for F1 racecars, between 1996 and 2005.

V12
Summarize
Perspective
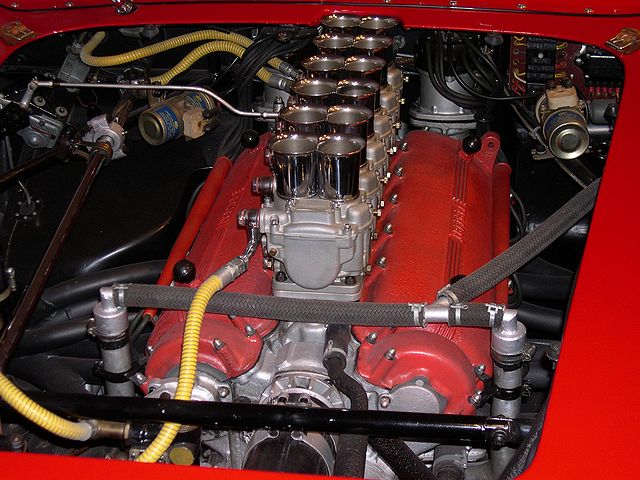



Ferrari is best known for its V12 engines.
- Colombo (60° V angle)
- 1947 1497 cc – 125 S
- 1947 1903 cc – 159 S
- 1947–1953 1995 cc – 166
- 1948–1950 1497 cc supercharged – 125 F1
- 1949–1952 1995 cc supercharged – 166 FL
- 1950–1951 2341 cc – 195
- 1950–1953 2563 cc – 212
- 1952 2714 cc – 225 S
- 1952–1954 2953 cc – 250 S, 250 MM
- 1954 2953 cc – Tipo 117/107 – 250 Monza
- 1954–1956 2953 cc – Tipo 112 – 250 Europa GT
- 1956–1963 2953 cc – Tipo 128 – 250 GT Coupé, 250 GT LWB/GTE
- 1959–1964 2953 cc – Tipo 168 – 250 GT SWB/GTO/GTL
- 1959–1964 3967 cc – Tipo 163 – 400 Superamerica, 330 TRI/LM, 330 LMB
- 1964–1966 4962 cc – Tipo 208 – 500 Superfast
- 1964–1967 3286 cc – Tipo 213 – 275 GTB/GTS
- 1966–1968 3967 cc – Tipo 209 – 330 America, 330 GTC
- 1967–1968 3286 cc – Tipo 226 – 275 GTB/4
- 1966–1976 4390 cc – 365, 365 GTC/4, Daytona
- 1969–1970 2991 cc – Ferrari 312 P
- 1976–1984 4823 cc – 400
- 1985–1989 4943 cc – 412
- Lampredi (60° V angle)
- 1950 3322 cc – 275 S, 275 F1
- 1950–1953 4101 cc – 340 F1, 340/342 America, 340 Mexico/MM
- 1950–1954 4493 cc – 375 F1/375 MM
- 1952 4382 cc – 375 Indianapolis
- 1953–1955 4522 cc – 375 America/375 MM
- 1953 2963 cc – 250 Europa
- 1954 4954 cc – 375 Plus
- 1955–1959 4962 cc – 410 S, 410 Superamerica
- Jano (60° V angle) – designed by Vittorio Jano, Vittorio Bellentani and Alberto Massimino
- 3.5L F1 engines (65° V angle)
- 1989–1994 3500 cc – Ferrari 640, Ferrari 641, Ferrari 642, Ferrari 643, Ferrari F92A, Ferrari F93A, Ferrari 412 T1
- 3.5/3.0L F1 engines (75° V angle)
- 1995 3000 cc – Ferrari 412 T2
- Tipo F116 & F133 (65° V angle)
- 1992–2001 5474 cc – 456/456 M, 550 Maranello/ 550 Barchetta Pininfarina
- 2002–2011 5748 cc – 575M Maranello/ Superamerica, 612 Scaglietti
- Ferrari iron block (Tipo F130 and F310) (65° V angle)
- Tipo F140 (65° V angle)
- 2003–2012 5998 cc – Enzo Ferrari, 599 GTB Fiorano/ 599 GTO, Maserati MC12
- 2005–present 6262 cc – FF, GTC4Lusso, F12berlinetta/F12tdf, LaFerrari
- 2017–present 6496 cc – 812, Daytona SP3, Purosangue, 12Cilindri
Remove ads
Flat-12
- Mauro Forghieri-designed racing flat-12s
- 1964–1965 1490 cc – Tipo 207 – 512 F1
- 1969 1991 cc – Tipo 232 – 212 E Montagna
- 1970–1974 2992 cc – Tipo 001 – Ferrari 312B series
- 1971–1973 2992 cc – Tipo 001 – Ferrari 312PB
- 1975–1980 2992 cc – Tipo 015 – Ferrari 312T series
- Roadgoing flat-12s, designed by Giuliano de Angelis and Angelo Bellei
- 1971–1976 4390 cc – Tipo F102A – 365 GT4 BB
- 1976–1981 4942 cc – Tipo F102B – 512 BB
- 1981–1984 – Tipo F110A – 512 BBi
- 1984–1991 – Tipo F113A/B – Testarossa
- 1991–1994 – Tipo F113D – 512 TR
- 1994–1996 – Tipo F113G – F512 M
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads