Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Outline of Canada
Overview of and topical guide to Canada From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Canada:
Flag and Arms of Canada
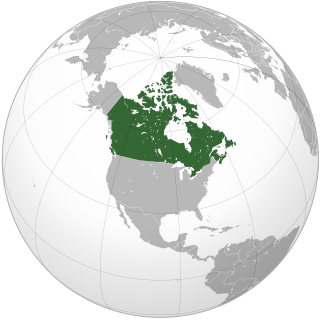
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's second-largest country by total area, with the world's longest coastline. Its border with the United States is the longest international land border. The country is characterized by a wide range of both meteorologic and geological regions. With a population of over 41 million, it has widely varying population densities, with the majority residing in urban areas and large areas of the country being sparsely populated. Canada's capital is Ottawa and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver.
A developed country, Canada has a high nominal per capita income globally and its advanced economy ranks among the largest in the world by nominal GDP, relying chiefly upon its abundant natural resources and well-developed international trade networks. Recognized as a middle power, Canada's support for multilateralism and internationalism has been closely related to its foreign relations policies of peacekeeping and aid for developing countries. Canada promotes its domestically shared values through participation in multiple international organizations and forums.
Remove ads
General reference

- Pronunciation /ˈkænədə/
- Common English country name: Canada
- Official English country name: Canada
- Common endonym: Canada
- Official endonym: Canada
- Adjectival: Canadian, Canada
- Demonym: Canadian (Fr. canadien)
- Etymology: Name of Canada
- Official languages : English, French
- ISO country codes: CA, CAN, 124
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:CA
- Internet country code top-level domain: .ca
- International rankings of Canada
Remove ads
Geography
Summarize
Perspective
- Canada is...
- Location:
- Northern Hemisphere, Western Hemisphere
- Time zones (Time in Canada):
- Newfoundland Standard Time (UTC-03:30), Newfoundland Daylight Time (UTC-02:30)
- Atlantic Standard Time (UTC-04), Atlantic Daylight Time (UTC-03)
- Eastern Standard Time (UTC-05), Eastern Daylight Time (UTC-04)
- Central Standard Time (UTC-06), Central Daylight Time (UTC-05)
- Mountain Standard Time (UTC-07), Mountain Daylight Time (UTC-06)
- Pacific Standard Time (UTC-08), Pacific Daylight Time (UTC-07)
- Extreme points of Canada
- North: Cape Columbia, Nunavut - (83°08' N, 74°13'W)
- South: Middle Island, Ontario - (41°41'N, 82°40'W)
- East: Cape Spear, Newfoundland - (47°31'N, 52°37'W)
- West: Yukon-Alaska border - (141°00'W)
- High: Mount Logan, Yukon 5,959 m (19,551 ft)
- Low: North Atlantic Ocean, Arctic Ocean, and North Pacific Ocean 0 m
- Land boundaries:
 United States 8,893 km (5,526 miles)[1]
United States 8,893 km (5,526 miles)[1] Greenland 1,280 m (4,200 feet) (on Hans Island)
Greenland 1,280 m (4,200 feet) (on Hans Island)
- Coastline: 202,080 km (125,570 miles)[2]
- Population of Canada: 36,991,981 people (2021 Census[3]) - 36th most populous country
- Area of Canada: 9,984,670 km2 (3,855,100 square miles) - 2nd most extensive country
- Atlas of Canada
Environment

- Climate of Canada
- Environmental issues in Canada
- Ecoregions in Canada
- Renewable energy in Canada
- Geology of Canada
- National parks of Canada
- Protected areas of Canada
- Wildlife of Canada
Geographic features
Regions
- Northern Canada (The North)
- Western Canada
- Eastern Canada
Other regions
- English Canada, sometimes known as the Rest of Canada (excluding Quebec) when considering topics of language
- French Canada
- Acadia
- Quebec-Windsor Corridor
Ecoregions
Provinces and territories
Provinces and territories of Canada
Provinces
Notes:
- Immediately prior to Confederation, Ontario and Quebec were part of the Province of Canada.
- Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, British Columbia, and Prince Edward Island were separate colonies at the time of joining Canada.
- Manitoba was established simultaneously with Northwest Territories.
- Saskatchewan and Alberta were created out of land that had been part of Northwest Territories.
- Prior to its entry in Confederation, Newfoundland had been a Dominion within the British Commonwealth, but due to a financial crisis during the Depression had surrendered its right to self-government and was under direct British governance.
Territories
There are currently three territories in Canada. Unlike the provinces, the territories of Canada have no inherent jurisdiction and only have those powers delegated to them by the federal government.
Note: Canada did not acquire any new land to create Yukon, Alberta, Saskatchewan, or Nunavut. All of these originally formed part of Northwest Territories.
Municipalities
Demography
Demographics by political division
Provinces
Territories
Remove ads
Government and politics
Summarize
Perspective
- Form of government: constitutional monarchy and democratic parliamentary federation
- Capital of Canada: Ottawa
- Provinces and territories of Canada
- Canadian and American politics compared
- Canadian and Australian politics compared
- Canadian Conservatism
- List of Canadian federal general elections
- Canadian Nationalism
- Elections in Canada
- Federalism in Canada
- Human rights in Canada
- Liberalism in Canada
- Political culture of Canada
- Political parties in Canada
- Political scandals of Canada
- Progressivism in Canada
- Socialism and Social Democracy in Canada
- Taxation in Canada
Branches of the government
Executive branch of the government
Legislative branch of the government
Judicial branch of the government
- Supreme Court of Canada
- Appellate Courts of the provinces and territories
- Alberta Court of Appeal
- British Columbia Court of Appeal
- Manitoba Court of Appeal
- New Brunswick Court of Appeal
- Court of Appeal of Newfoundland and Labrador
- Court of Appeal for the Northwest Territories
- Nova Scotia Court of Appeal
- Nunavut Court of Appeal
- Court of Appeal for Ontario
- Court of Appeal of Prince Edward Island
- Quebec Court of Appeal
- Saskatchewan Court of Appeal
- Court of Appeal of the Yukon Territory
- Superior-level trial courts of the provinces and territories
- Court of King's Bench of Alberta
- Supreme Court of British Columbia
- Court of King's Bench of Manitoba
- Court of King's Bench of New Brunswick
- Supreme Court of Newfoundland and Labrador
- Supreme Court of the Northwest Territories
- Supreme Court of Nova Scotia
- Nunavut Court of Justice
- Ontario Superior Court of Justice
- Supreme Court of Prince Edward Island
- Quebec Superior Court
- Court of King's Bench for Saskatchewan
- Supreme Court of the Yukon Territory
Foreign relations
International organization membership
Canada is a member of:[5]
Legal system
Military
- Command structure
- Commander-in-chief: Governor General of Canada (nominally, see also The Canadian Crown and the Canadian Forces)
- Prime Minister of Canada (de facto Commander-in-chief)
- Minister of National Defence
- Chief of the Defence Staff
- Royal Canadian Navy (RCN), command of the Navy;
- Canadian Army (CA) command of the Army;
- Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF), command of the Air Force.
- Canadian Joint Operations Command (CJOC), responsible for all operations except special forces;
- Canadian Special Operations Forces Command (CANSOFCOM), responsible for special forces operations within Canada and abroad.
- Chief of the Defence Staff
- Minister of National Defence
- Canadian Forces
- Army: Canadian Army
- Navy: Royal Canadian Navy
- Air force: Royal Canadian Air Force
- Special forces: Canadian Special Operations Forces Command
- Military reserve force: Canadian Forces reserve force
- Canadian Coast Guard
Provincial governments
Territory governments
Politics by political division
Provinces
Territories
Remove ads
History
- Former Colonies and Territories in Canada
- Constitutional history of Canada
- History of immigration to Canada
- Economic history of Canada
- Fires in Canada
- Military history of Canada
- History of monarchy in Canada
- Persons of National Historic Significance
- Territorial evolution of Canada (1867–present)
History of Canada by period
History of Canada by political division
Provinces
Territories
Remove ads
Culture
Summarize
Perspective
- Age and internet use in Canada
- Alcoholic beverages in Canada
- Architecture of Canada
- Cuisine of Canada
- Decorations and medals of Canada (in order of precedence)
- Festivals in Canada
- Humour in Canada
- Languages of Canada
- Media in Canada
- Symbols of Canada
- Canadians
- Prostitution in Canada
- Public holidays in Canada
- World Heritage Sites in Canada
Culture by political division
Provinces
Territories
- Culture of Northwest Territories
- Culture of Nunavut
- Culture of the Yukon
Art in Canada
- Art in Canada
- Cinema of Canada
- Canadian comics
- Literature of Canada
- Television in Canada
- Theatre of Canada
Music
- Canadian blues
- Canadian classical music
- Canadian hip hop
- Canadian Idol
- Canadian rock
- Caribbean music in Canada
- Music of Canadian cultures
Music by political division
Provinces
Territories
Religion in Canada
Sport in Canada
Sport in Canada Official Sports
Other sports
- Canadian football
- Canada at the Olympics
- Canada Rugby League
- Canadian Curling Association
- Canadian Figure Skating
- Association Football (Soccer) in Canada
- Cross Country Skiing
- Snowboarding in Canada
- Pickleball in Canada
Hall of Fame Museums
Remove ads
Economy and infrastructure
Summarize
Perspective
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 9th (ninth)
- Agriculture in Canada
- Banking in Canada
- Communications in Canada
- Companies of Canada
- List of convention and exhibition centres
- Currency of Canada: Dollar
- Economic history of Canada
- Energy in Canada
- Health care in Canada
- Mining in Canada
- Science and technology in Canada
- Stock exchanges:
- CNQ
- Nasdaq Canada
- Toronto Stock Exchange, S&P/TSX 60 is the main index of TSX
- TSX Venture Exchange
- Winnipeg Commodity Exchange
- Montreal Exchange
Economics by political division
Provinces
Territories
Remove ads
Education in Canada
Education by political division
Provinces
Territories
- Education in Northwest Territories
- Education in Nunavut
- Education in the Yukon
Higher Education by political division
Provinces
Territories
Remove ads
Bibliographies
Remove ads
Search
Category
- To display all subcategories below click on the ►
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads




