Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Outline of Malaysia
Country in Southeast Asia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Malaysia:

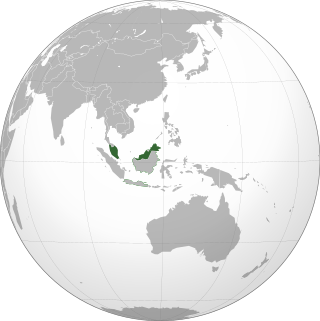
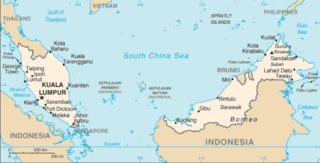
Malaysia is a sovereign country located on the Malay Peninsula and a northern portion of the Island of Borneo in Southeast Asia.[1] It comprises 13 states and three federal territories with a total land area of 329,847 square kilometres (127,355 sq mi).[2] The capital of Malaysia is Kuala Lumpur, while Putrajaya is the seat of the federal government.
The population stands at over 32 million.[1] The country is separated into two regions—Peninsular Malaysia and Malaysian Borneo—by the South China Sea.[1] Malaysia borders Thailand, Indonesia, Singapore, Brunei, the Philippines,[1] and Vietnam. The country is located near the equator and experiences a tropical climate.[1]
Malaysia is headed by the Yang di-Pertuan Agong and politically led by a Prime Minister.[3][4] The government is closely modeled after the Westminster parliamentary system.[5]
{{TO
- C limit|limit=Malaysia2}}
Remove ads
General reference
- Pronunciation: /məˈleɪʒə/ or /məˈleɪziə/
- Common English country name: Malaysia
- Official English country name: Malaysia
- Common endonym(s): Malaysia
- Official endonym(s): Malaysia
- Adjectival(s): Malaysian
- Demonym(s): Malaysians
- Etymology: Name of Malaysia
- International rankings of Malaysia
- ISO country codes: MY, MYS, 458
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:MY
- Internet country code top-level domain: .my
Remove ads
History of Malaysia
Events and treaties
Small area histories
Politics of Malaysia
Summarize
Perspective
- Form of government: Federal constitutional elective monarchy and parliamentary democracy
- Capital of Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur
- Flag of Malaysia
- Elections in Malaysia
- Political parties in Malaysia
- Political parties in Malaysia
- National Front (Barisan Nasional)
- United Malays National OrganisationN1 (UMNO)
- Malaysian Chinese Association (MCA)
- Malaysian Indian Congress (MIC)
- People's Progressive Party (PPP)
- United Traditional Bumiputera Party (PBB)
- Sarawak United People's Party (SUPP)
- Sabah Progressive Party (SAPP)
- Sabah United PartyN2 (PBS)
- Liberal Democratic Party (LDP)
- United Sabah People's Party (PBRS)
- United Pasokmomogun Kadazandusun Murut Organisation (UPKO)
- Sarawak Progressive Democratic Party (SPDP)
- Sarawak People's Party (PRS)
- Alliance of Hope (Pakatan Harapan)
- People's Justice Party (Keadilan; PKR)
- Democratic Action Party (DAP)
- National Trust Party (AMANAH)
- National Alliance (Perikatan National)
- Parti Pribumi Bersatu Malaysia (BERSATU; PBBM)
- Pan-Malaysian Islamic PartyN3 (PAS)
- Parti Gerakan Rakyat Malaysia (GERAKAN; PGRM)
- Malaysian People's Party (PRM)
- Socialist Party of Malaysia (PSM)
- Malaysian Democratic Party (MDP)
- Malaysian United Democratic Alliance (MUDA)
- National Front (Barisan Nasional)
- Yang di-Pertuan Agong (King of Malaysia)
- Civil Service in Malaysia
Branches of the government of Malaysia
Executive branch of the government of Malaysia
Legislative branch of the government of Malaysia
Judicial branch of the government of Malaysia
Foreign relations of Malaysia
International organisation membership
Malaysia is a member of:[1]
Law and order in Malaysia
Military of Malaysia
- Command
- Commander-in-chief: Supreme Commander of the Malaysian Armed Forces, Muhammad V of Kelantan
- Chief of Defence Forces: General (Jen) Tan Sri Zulkifli Zainal Abidin
- Forces
- Military history of Malaysia
Remove ads
Geography of Malaysia
Summarize
Perspective

- Malaysia is: a megadiverse country
- Location:
- Northern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere
- Eurasia (both on the mainland and offshore)
- Time zone: Malaysian Standard Time = ASEAN Common Time (UTC+08)
- Extreme points of Malaysia
- High: Gunung Kinabalu 4,095 m (13,435 ft)
- Low: South China Sea and Indian Ocean 0 m
- Land boundaries: 2,669 km
-
- Coastline: 4,675 km
- Peninsular Malaysia 2,068 km
- East Malaysia 2,607 km
- Coastline: 4,675 km
- Population of Malaysia: 27,730,000 - 43rd most populous country
- Area of Malaysia: 329,847 km2 - 66th largest country
- Atlas of Malaysia
- Malaysian Standard Time
Environment of Malaysia
- Climate of Malaysia
- Environmental issues in Malaysia
- List of ecoregions in Malaysia
- Renewable energy in Malaysia
- Protected areas of Malaysia
- Wildlife of Malaysia
Natural geographic features of Malaysia
Regions of Malaysia
- West Malaysia (Peninsula Malaysia)
- East Malaysia (Malaysian Borneo)
Ecoregions of Malaysia
Administrative divisions of Malaysia
States of Malaysia

Malaysia has 13 states:
Federal territories of Malaysia
Malaysia also has three federal territories, which are governed directly by the federal government of Malaysia:
Municipalities of Malaysia
Districts of Malaysia
Remove ads
Economy and infrastructure of Malaysia
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 38th (thirty-eighth)
- Agriculture in Malaysia
- Accounting in Malaysia
- Banking in Malaysia
- Communications in Malaysia
- Companies of Malaysia
- Energy in Malaysia
- Health care in Malaysia
- Mining in Malaysia
- Science and technology in Malaysia
- Poverty in Malaysia
- Malaysia Stock Exchange
- Telecommunications in Malaysia
- Tourism in Malaysia
- Transport in Malaysia
- Water supply and sanitation in Malaysia
Economic plans and policies
Remove ads
Demography of Malaysia
Religion
Ethnicities
Culture of Malaysia
|
|
Art in Malaysia
Sports in Malaysia
Remove ads
Education in Malaysia
- Ministry of Education
- Ministry of Higher Education
- Malaysian Qualifications Framework
- List of schools in Malaysia
- List of post-secondary institutions in Malaysia
- List of universities in Malaysia
- Issues in Malaysian Education
- Standardised examinations
- Ujian Pencapaian Sekolah Rendah (UPSR)
- Pentaksiran Tingkatan Tiga (PT3)
- Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia (SPM)
- Sijil Tinggi Persekolahan Malaysia (STPM)
Remove ads
See also
Notes
- ^ UMNO was deregistered in 1988 and the Prime Minister of Malaysia formed a new party known as United Malays National Organisation (Baru) on February 16, 1988. The term "Baru" or "New" was removed by a constitutional amendment on July of the same year.
- ^ The United Sabah Party (Parti Bersatu Sabah) was a member of Barisan Nasional from its establishment in 1985 until its withdrawal from the coalition in 1990. The party rejoined the coalition in 2002.[8]
- ^ The Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party entered a coalition with the former Alliance Party in 1972 and subsequently joined the Barisan Nasional coalition when it was founded in 1974. It withdrew from the coalition in 1977.[9]
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
