Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
RTL6
Human protein From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Retrotransposon Gag Like 6 is a protein encoded by the RTL6 gene in humans.[5] RTL6 is a member of the Mart family of genes, which are related to Sushi-like retrotransposons and were derived from fish and amphibians.[6] The RTL6 protein is localized to the nucleus and has a predicted leucine zipper motif that is known to bind nucleic acids in similar proteins, such as LDOC1.
Remove ads
Gene
Locus

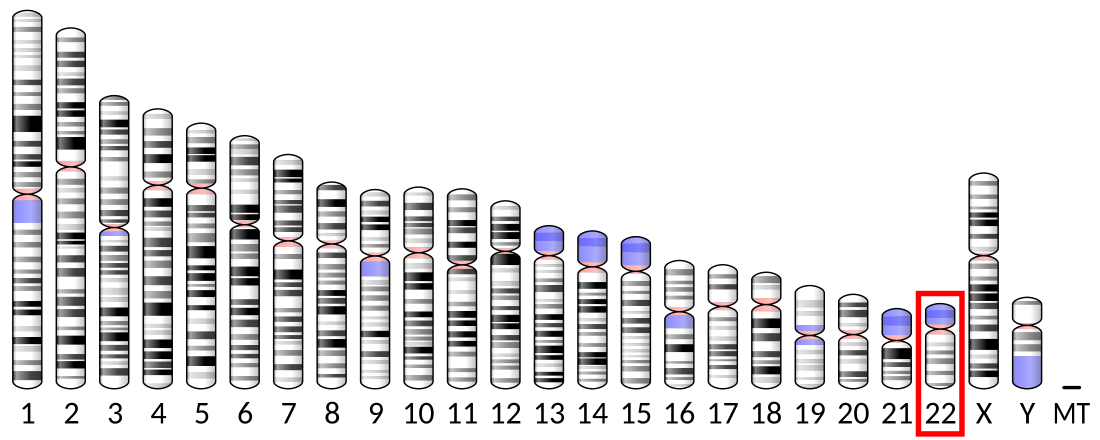
The gene is on Chromosome 22 (human) at 22q13.31 on the minus strand from 44492570 to 44498125 nt on the GRCh38.p7 assembly of the human genome. Aliases for the gene include LDOC1L, MAR6, MART6, and SIRH3. RTL6 is made up of 2 exons and is encoded by 5556 base pairs of DNA .[7]
Origin
RTL6 is a retrotransposon GAG related gene. It is one of eleven MART (Mammalian Retrotransposon Derived) genes in humans related to Sushi-like retrotransposons with long terminal repeats from fish and amphibians.[6] Between 170 and 310 MYA, MART genes lost their ability to retrotranspose and concomitantly gained new, beneficial function for its host organism.[8]
Remove ads
mRNA
RTL6 has an alternate start of transcription 140 base pairs upstream of the normal transcribed region. The lengths of the primary mRNA and that with the upstream start of transcription are 5355 and 5495 base pairs respectively.[7]
Protein
Summarize
Perspective
Primary information
The primary amino acid sequence for RTL6 is made up of 239 residues.[5] There are no known alternative splice variants of the protein. The molecular weight of the protein is 26.2 kDa and the isoelectric point is 11.58.[9] RTL6 is a proline and arginine rich protein.[9]


Domains and motifs
RTL6 contains a predicted leucine zipper motif known to participate in nucleic acid binding in other proteins.[9] RTL6 also contains a domain of unknown function from amino acid residues 98-177 . RTL6 is one of a number of genes belonging to the DUF4939 (domain of unknown function) superfamily.[14]
Secondary structure
The secondary structure of RTL6 is made up of largely alpha helices.[15] One region of RTL6 is also predicted to participate in a coiled-coil structure from amino acid residues 29–63.[14]
Post-translational modifications
There are also two predicted phosphorylation sites for Protein Kinase C with high confidence scores at amino acid residues 6 and 45.[16][17] There is also a predicted ubiquitination site with medium-confidence at amino acid residue 8.[18]

Cellular sublocation
RTL6 is expected to be localized to the nucleus and cytosol based on the presence of a leucine zipper domain, the absence of signals indicating secretion or transmembrane domains, and immunohistochemical staining.[19][20][21]
Expression
RTL6 has been shown to be expressed at high levels during all stages of development and in a wide variety of tissues.[22][23][13]
RTL6 expression has been shown to fall in HeLa cervical cancer cells upon treatment with chemotherapeutic Casiopeinas and in A549 lung cancer cells upon treatment with Actinomycin D.[24][25]
Interacting proteins
RTL6 has been shown to interact with the following proteins:
| DDIT3 | DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 protein [26] |
| NXF1 | Nuclear RNA export factor 1 [27] |
| STX18 | Syntaxin 18 [28] |
| MAFF | MAF bZIP transcription factor F [28] |
| GOPC | Golgi-associated PDZ and coiled-coil motif-containing protein [28] |
| BATF3 | Basic leucine zipper transcriptional factor ATF-like 3 [28] |
| TERF2 | Telomeric repeat-binding factor 2 [29] |
| UXAC | Uronate isomerase (Yersinia pestis) [30] |
Remove ads
Clinical significance
The RTL6 protein has been shown to interact with the UXAC protein from Yersinia pestis, the gram-negative bacterium responsible for the bubonic plague.[30]
Homology/evolution
Summarize
Perspective
Paralogs
Eleven paralogs were identified for RTL6 in humans. The paralogs have diverse functions and expression patterns, although many are known to have zinc finger domains and bind nucleic acids:
Orthologs
RTL6 is highly conserved across mammals, including the leucine zipper motif and DUF4939. The gene is also conserved in marsupials such as the opossum but not in birds such as the chicken, suggesting the gene was likely formed after the divergence of mammals and birds but before the divergence of marsupials and mammals (170-310 MYA:[6]
The most distantly detectable organisms with homology in the gene are bony fishes including salmon and the common carp, but similarity to the human protein sequence is markedly less than that of mammals. No traces of the gene can be seen in intermediates between mammals and bony fishes such as reptiles or amphibians:
Remove ads
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads