Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Arabic alphabet
Writing system of the Arabic language From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Arabic alphabet,[a] or the Arabic abjad, is the Arabic script as specifically codified for writing the Arabic language. It is a unicameral script written from right-to-left in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters,[b] of which most have contextual forms. Unlike the modern Latin alphabet, the script has no concept of letter case. The Arabic alphabet is an abjad, with only consonants required to be written (though the long vowels – ā ī ū – are also written, with letters used for consonants); due to its optional use of diacritics to notate vowels, it is considered an impure abjad.[2]
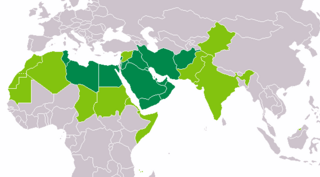
as the sole official script
a co-official script
Remove ads
Letters
Summarize
Perspective
This section needs additional citations for verification. (July 2024) |
The basic Arabic alphabet contains 28 letters. Forms using the Arabic script to write other languages added and removed letters: for example ⟨پ⟩ is often used to represent /p/ in adaptations of the Arabic script. Unlike Greek-derived alphabets, Arabic has no distinct upper and lower case letterforms.
Many letters look similar but are distinguished from one another by dots (ʾiʿjām) above or below their central part (rasm). These dots are an integral part of a letter, since they distinguish between letters that represent different sounds. For example, the Arabic letters ب b, ت t, and ث th have the same basic shape, but with one dot added below, two dots added above, and three dots added above respectively. The letter ن n also has the same form in initial and medial forms, with one dot added above, though it is somewhat different in its isolated and final forms. Historically, they were often omitted, in a writing style called rasm.
Both printed and written Arabic are cursive, with most letters within a word directly joined to adjacent letters.
Alphabetical order
There are two main collating sequences ('alphabetical orderings') for the Arabic alphabet: Hija'i, and Abjadi.
The Hija'i order (هِجَائِيّ Hijāʾiyy /hid͡ʒaːʔijj/) is the more common order and it is used when sorting lists of words and names, such as in phonebooks, classroom lists, and dictionaries.
The original Abjadi order (أَبْجَدِيّ ʾabjadiyy /ʔabd͡ʒadijj/) derives from that used by the Phoenician alphabet and therefore resembles the sequence of letters in Hebrew and Greek. Letters are also assigned numerical values (abjad numerals) for purposes of numerology, as is done in Hebrew gematria and Greek isopsephy. Letters in the Hija'i order are not considered to have numerical values.
Hijaʼi
Modern dictionaries and reference books use the hijāʾī alphabetical order instead of the Abjadi alphabetical order, in which letters are arranged mainly by similarity of shape. The hijaʼi order is never used for numerals.
| ا | ب | ت | ث | ج | ح | خ | د | ذ | ر | ز | س | ش | ص | ض | ط | ظ | ع | غ | ف | ق | ك | ل | م | ن | ه | و | ي |
| ʾ | b | t | th | j | ḥ | kh | d | dh | r | z | s | sh | ṣ | ḍ | ṭ | ẓ | ʻ | gh | f | q | k | l | m | n | h | w | y |
A different hijaʼi order was used in the Maghreb but is now considered obsolete. The sequence is:[3]
| ا | ب | ت | ث | ج | ح | خ | د | ذ | ر | ز | ط | ظ | ك | ل | م | ن | ص | ض | ع | غ | ف | ق | س | ش | ه | و | ي |
| ʾ | b | t | th | j | ḥ | kh | d | dh | r | z | ṭ | ẓ | k | l | m | n | ṣ | ḍ | ʻ | gh | f | q | s | sh | h | w | y |
| The colors indicate which letters have different positions from the previous table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The al-iklīl order, now obsolete, also arranged letters mainly by shape. It was first used in the 10th-century work Kitāb al-Iklīl. The sequence is:[4]
| ا | ب | ت | ث | ج | ح | خ | د | ذ | ك | ل | م | و | ن | ص | ض | ع | غ | ط | ظ | ف | ق | ر | ز | ه | س | ش | ي |
| ʾ | b | t | th | j | ḥ | kh | d | dh | k | l | m | w | n | ṣ | ḍ | ʻ | gh | ṭ | ẓ | f | q | r | z | h | s | sh | y |
| The colors indicate which letters have different positions from the previous table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Abjadi
The abjadi order is the usual Arabic order in dictionaries and reference books of the late 1st millennium to the early 2nd millennium. However, this Arabic adjadi order is not a simple correspondence with the earlier north Semitic alphabetic order, as the latter has a position corresponding to the Aramaic letter samek 𐡎, which has no cognate letter in the Arabic alphabet historically because Proto-Semitic fricatives *š (represented by šin 𐡔 in Aramaic[note 1]) and *s (represented by samek 𐡎 in Aramaic[note 2]) had merged into Arabic s س,[5][6] while Proto-Semitic *ś became Arabic š ش.
The loss of sameḵ was compensated for:
- In the Mashriqi abjad sequence, by splitting the letter šīn 𐡔 into two independent Arabic letters: ش shīn[note 3] and س sīn[note 4], with the latter taking the place of sameḵ 𐡎;
- And in the Maghrebi abjad sequence, by splitting the letter ṣāḏē 𐡑 into two independent Arabic letters: ض ḍad[note 5] and ص ṣad[note 6], with the latter taking the place of sameḵ 𐡎.
The six other letters that do not correspond to any north Semitic letter are placed at the end.
| ا | ب | ج | د | ه | و | ز | ح | ط | ي | ك | ل | م | ن | س | ع | ف | ص | ق | ر | ش | ت | ث | خ | ذ | ض | ظ | غ |
| ʾ | b | j | d | h | w | z | ḥ | ṭ | y | k | l | m | n | s | ʻ | f | ṣ | q | r | sh | t | th | kh | dh | ḍ | ẓ | gh |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 | 1000 |
This is commonly vocalized as follows:
- ʾabjad hawwaz ḥuṭṭī kalaman saʿfaṣ qarashat thakhadh ḍaẓagh.
Another vocalization is:
- ʾabujadin hawazin ḥuṭiya kalman saʿfaṣ qurishat thakhudh ḍaẓugh[citation needed]
| ا | ب | ج | د | ه | و | ز | ح | ط | ي | ك | ل | م | ن | ص | ع | ف | ض | ق | ر | س | ت | ث | خ | ذ | ظ | غ | ش |
| ʾ | b | j | d | h | w | z | ḥ | ṭ | y | k | l | m | n | ṣ | ʻ | f | ḍ | q | r | s | t | th | kh | dh | ẓ | gh | sh |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 | 1000 |
| The colors indicate which letters have different positions from the previous table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This can be vocalized as:
- ʾabujadin hawazin ḥuṭiya kalman ṣaʿfaḍ qurisat thakhudh ẓaghush
Notes:
Letter forms
The Arabic alphabet is always cursive and letters vary in shape depending on their position within a word. Letters can exhibit up to four distinct forms corresponding to an initial, medial (middle), final, or isolated position (IMFI). While some letters show considerable variations, others remain almost identical across all four positions. Generally, letters in the same word are linked together on both sides by short horizontal lines, but six letters (و ,ز ,ر ,ذ ,د ,ا) can only be linked to their preceding letter. In addition, some letter combinations are written as ligatures (special shapes), notably lām-alif لا,[8] which is the only mandatory ligature (the unligated combination لا is considered difficult to read).
Table of basic letters
Notes
- Arabic: الْأَبْجَدِيَّة الْعَرَبِيَّة al-ʾabjadiyyah l-ʿarabiyyah [alʔabd͡ʒaˈdijːa‿lʕaraˈbijːa]
- Alif can represent different phonemes; initially: a/i/u /a, i, u/ or sometimes silent in the definite article ال (a)l-. Medially and finally it represents a long vowel ā /aː/. It is also used in some hamzah /ʔ/ forms, check #Hamzah forms
- When speaking Modern Standard Arabic (الفصحى al-Fuṣḥā) the ج pronunciation varies regionally, most prominently [d͡ʒ] in most of the Arabian Peninsula, parts of the Levant, parts of Egypt (especially the countryside and upper Egypt), Iraq, and northern-central Algeria, it is also considered as the predominant pronunciation of Literary Arabic when reciting the Quran and in Arabic studies outside the Arab world, [ʒ] in most of Northwest Africa and parts of the Levant (especially urban centers) and parts of the Arabian Peninsula, while [ɡ] is the standard pronunciation only in Egypt, ([ɡ] appears as a dialectal pronunciation in coastal Yemen, and coastal Oman), as well as [ɟ] in Sudan.
- In certain contexts such as serial numbers and license plates the initial form is used to prevent confusion with the western number zero or Eastern Arabic Numeral for 5(٥). It's also worth mentioning that the initial form هـ is usually used when writing the letter separately, rather than using the isolated form ه.
- See the article Romanization of Arabic for details on various transliteration schemes. Arabic language speakers may usually not follow a standardized scheme when transcribing words or names. Some Arabic letters which do not have an equivalent in English (such as ط) are often spelled as numbers when Romanized. Also names are regularly transcribed as pronounced locally, not as pronounced in Literary Arabic (if they were of Arabic origin).
- Regarding pronunciation, the phonemic values given are those of Modern Standard Arabic, which is taught in schools and universities. In practice, pronunciation may vary considerably from region to region. For more details concerning the pronunciation of Arabic, consult the articles Arabic phonology and varieties of Arabic.
- The names of the Arabic letters can be thought of as abstractions of an older version where they were meaningful words in the Proto-Semitic language.
- Six letters (و ز ر ذ د ا) do not have a distinct medial form and have to be written with their final form without being connected to the next letter. Their initial form matches the isolated form. The following letter is written in its initial form, or isolated form if it is the final letter in the word.
- The letter alif originated in the Phoenician alphabet as a consonant-sign indicating a glottal stop. Today it has lost its function as a consonant, and, together with ya’ and wāw, is a mater lectionis, a consonant sign standing in for a long vowel (see below), or as support for certain diacritics (maddah and hamzah).
- Arabic currently uses a punctuation mark called the hamzah (ء) to denote the glottal stop [ʔ], written alone or with a carrier:
- alone: ء
- with a carrier: إ أ (above or under an alif), ؤ (above a wāw), ئ (above a dotless yā’ or yā’ hamzah).
- In academic work, the hamza is transliterated with the modifier letter right half ring (ʾ) or (ʔ) on Wiktionary, while the modifier letter left half ring (ʿ) or (ʕ) on Wiktionary, transliterates the letter ‘ayn (ع), which represents a different sound, not found in English.
- The hamza has a single form, since it is never linked to a preceding or following letter. However, it is sometimes combined with a wāw, yā’, or alif, and in that case the carrier behaves like an ordinary wāw, yā’, or alif, check the table below:
Hamza forms
The Hamza /ʔ/ (glottal stop) can be written either alone, as if it were a letter, or with a carrier, when it becomes a diacritic.[9] Hamzat al-madd (آ) indicates a long /ʔ/ + /aː/ sound as in آسف ʾāsif /ʔaː.sif/ "sorry", while the other Hamzas indicate the glottal stop /ʔ/ in different positions of the word as in مسؤول masʾūl /mas.ʔuːl/ and سائل sāʾil /saː.ʔil/, the writing of the Hamza is based on a set of rules, For the writing rule of each form, see Hamza § Arabic "seat" rules.
Modified letters
The following are not individual letters, but rather different contextual variants of some of the Arabic letters.
Long vowels
In the fully vocalized Arabic text found in texts such as the Quran, a long ā following a consonant other than a hamzah is written with a short a sign (fatḥah) on the consonant plus an ʾalif after it; long ī is written as a sign for short i (kasrah) plus a yāʾ; and long ū as a sign for short u (ḍammah) plus a wāw. Briefly, ᵃa = ā; ⁱy = ī; and ᵘw = ū. Long ā following a hamzah may be represented by an ʾalif maddah or by a free hamzah followed by an ʾalif (two consecutive ʾalifs are never allowed in Arabic).
The table below shows vowels placed above or below a dotted circle replacing a primary consonant letter or a shaddah sign. For clarity in the table, the primary letters on the left used to mark these long vowels are shown only in their isolated form. Most consonants do connect to the left with ʾalif, wāw and yāʾ written then with their medial or final form. Additionally, the letter yāʾ in the last row may connect to the letter on its left, and then will use a medial or initial form. Use the table of primary letters to look at their actual glyph and joining types.
In unvocalized text (one in which the short vowels are not marked), the long vowels are represented by the vowel in question: ʾalif mamdūdah/maqṣūrah, wāw, or yāʾ. Long vowels written in the middle of a word of unvocalized text are treated like consonants with a sukūn (see below) in a text that has full diacritics. Here also, the table shows long vowel letters only in isolated form for clarity.
Combinations وا and يا are always pronounced wā and yā respectively. The exception is the suffix ـوا۟ in verb endings where ʾalif is silent, resulting in ū or aw. In addition, when transliterating names and loanwords, Arabic language speakers write out most or all the vowels as long (ā with ا ʾalif, ē and ī with ي yaʾ, and ō and ū with و wāw), meaning it approaches a true alphabet.
Diphthongs
The diphthongs حروف اللين ḥurūfu l-līn /aj/ and /aw/ are represented in vocalized text as follows:
A final yaʾ is usually written at the end of words for nisba (اَلنِّسْبَة nisbah) which is a common suffix to form adjectives of relation or pertinence. The suffix is ـِيّ -iyy for masculine (ـِيَّة -iyya(t)- for feminine); for example اِشْتِرَاكِيّ ištirākiyy "socialist", it is also used for a singulative ending that applies to human or other sentient beings as in جندي jundiyy "a soldier". However nowadays this final yaʾ is mostly pronounced with a long yaʾ (yāʾ mamdūdah) -ī as in اِشْتِرَاكِي ištirākī /iʃtiraːkiː/ instead of اِشْتِرَاكِيّ ištirākiyy /iʃtiraːkijj/. A similar mistake happens at the end of some third person plural verbs as in جَرَوْا jaraw "they ran" which is pronounced nowadays as جَرُوا jarū /d͡ʒaruː/.
Ligatures

1. alif
2. hamzat waṣl (ْهَمْزَة وَصْل)
3. lām
4. lām
5. shadda (شَدَّة)
6. dagger alif (أَلِفْ خَنْجَریَّة)
7. hāʾ
The use of ligature in Arabic is common. There is one compulsory ligature, that for lām ل + alif ا, which exists in two forms. All other ligatures, of which there are many,[10] are optional.
A more complex ligature that combines as many as seven distinct components is commonly used to represent the word Allāh الله. The only ligature within the primary range of Arabic script in Unicode (U+06xx) is lām + alif. This is the only one compulsory for fonts and word-processing. Other ranges are for compatibility to older standards and contain other ligatures, which are optional.
Note: Unicode also has in its Presentation Form B FExx range a code for this ligature. If your browser and font are configured correctly for Arabic, the ligature displayed above should be identical to this one, U+FEFB
Remove ads
Diacritics
Summarize
Perspective
Users of Arabic usually write long vowels but omit short ones, so readers must utilize their knowledge of the language in order to supply the missing vowels. However, in the education system and particularly in classes on Arabic grammar these vowels are used since they are crucial to the grammar. An Arabic sentence can have a completely different meaning by a subtle change of the vowels. This is why in an important text such as the Qur’ān the three basic vowel signs are mandated, like the Arabic diacritics and other types of marks, like the cantillation signs.
Short vowels
In the Arabic handwriting of everyday use, in general publications, and on street signs, short vowels are typically not written. On the other hand, copies of the Qur’ān cannot be endorsed by the religious institutes that review them unless the diacritics are included. Children's books, elementary school texts, and Arabic-language grammars in general will include diacritics to some degree. These are known as "vocalized" texts.
Short vowels may be written with diacritics placed above or below the consonant that precedes them in the syllable, called ḥarakāt. All Arabic vowels, long and short, follow a consonant; in Arabic, words like "Ali" or "alif", for example, start with a consonant: ‘Aliyy, alif.
Nunation
Nunation (Arabic: تنوين tanwīn) is the addition of a final -n to a noun or adjective. The vowel before it indicates grammatical case. In written Arabic, nunation is indicated by doubling the vowel diacritic at the end of the word, e.g. شُكْرًا šukran [ʃukran] 'thank you'.
Gemination
Gemination is the doubling of a consonant. Instead of writing the letter twice, Arabic places a W-shaped sign called shaddah above it.
Vowel omission
An Arabic syllable can be open (ending with a vowel) or closed (ending with a consonant):
- open: CV [consonant-vowel] (long or short vowel)
- closed: CVC (short vowel only)
A normal text is composed only of a series of consonants plus vowel-lengthening letters; thus, the word qalb, "heart", is written qlb, and the word qalaba "he turned around", is also written qlb. To write qalaba without this ambiguity, we could indicate that the l is followed by a short a by writing a fatḥah above it.
To write qalb, we would instead indicate that the l is followed by no vowel by marking it with a diacritic called sukūn ( ْ), like this: قلْب. This is one step down from full vocalization, where the vowel after the q would also be indicated by a fatḥah: قَلْب.
The Qurʾān is traditionally written in full vocalization.
The long i sound in some editions of the Qur’ān is written with a kasrah followed by a diacritic-less y, and long u by a ḍammah followed by a bare w. In others, these y and w carry a sukūn. Outside of the Qur’ān, the latter convention is extremely rare, to the point that y with sukūn will be unambiguously read as the diphthong /aj/, and w with sukūn will be read /aw/.
For example, the letters m-y-l can be read like English meel or mail, or (theoretically) also like mayyal or mayil. But if a sukūn is added on the y then the m cannot have a sukūn (because two letters in a row cannot be sukūnated), cannot have a ḍammah (because there is never an uy sound in Arabic unless there is another vowel after the y), and cannot have a kasrah (because kasrah before sukūnated y is never found outside the Qur’ān), so it must have a fatḥah and the only possible pronunciation is /majl/ (meaning mile, or even e-mail). By the same token, m-y-t with a sukūn over the y can be mayt but not mayyit or meet, and m-w-t with a sukūn on the w can only be mawt, not moot (iw is impossible when the w closes the syllable).
Vowel marks are always written as if the i‘rāb vowels were in fact pronounced, even when they must be skipped in actual pronunciation. So, when writing the name Aḥmad, it is optional to place a sukūn on the ḥ, but a sukūn is forbidden on the d, because it would carry a ḍammah if any other word followed, as in Aḥmadu zawjī "Ahmad is my husband".
Another example: the sentence that in correct literary Arabic must be pronounced Aḥmadu zawjun shirrīr "Ahmad is a wicked husband", is usually pronounced (due to influence from vernacular Arabic varieties) as Aḥmad zawj shirrīr. Yet, for the purposes of Arabic grammar and orthography, is treated as if it were not mispronounced and as if yet another word followed it, i.e., if adding any vowel marks, they must be added as if the pronunciation were Aḥmadu zawjun sharrīrun with a tanwīn 'un' at the end. So, it is correct to add an un tanwīn sign on the final r, but actually pronouncing it would be a hypercorrection. Also, it is never correct to write a sukūn on that r, even though in actual pronunciation it is (and in correct Arabic MUST be) sukūned.
Of course, if the correct i‘rāb is a sukūn, it may be optionally written.
The sukūn is also used for transliterating words into the Arabic script. The English name "Mark" is written مارك, for example, might be written with a sukūn above the ر to signify that there is no vowel sound between that letter and the ك.
Additional diacritics
These diacritics are uncommon in modern publications but are often used in Quran and some manuscripts.
ٰThe alif khanjariyyah (أَلِف خَنْجَرِيَّة, 'dagger ’alif') is written as short vertical stroke on top of a letter. It indicates a long /aː/ sound for which alif is normally not written. For example: ⟨هَٰذَا⟩ (hādhā) or ⟨رَحْمَٰن⟩ (raḥmān).
The Wasla or hamzat al-waṣl (هَمْزَةُ ٱلْوَصْلِ, 'hamza of connection') is a variant of the letter hamza (ء) resembling part of the letter ṣād (ص) that is rarely placed over the letter ʾalif (أَلِف الْوَصْلِ ʾalif al-waṣl (ا)) to form (ٱ) at the beginning of the word (ٱ). It indicates that the ʾalif is not pronounced as a glottal stop (written as the hamza), but that the word is connected to the previous word (like liaison in French). Outside of vocalised liturgical texts, the waṣla is usually not written.[11][12] e.g. Abdullah عَبْدُ ٱلله can be written with hamzat al-wasl on the first letter of the word ٱلله but it is mostly written without it عَبْدُ الله.
Remove ads
Additional letters
Summarize
Perspective
Regional variations
Some letters take a traditionally different form in specific regions:
Non-standard letters
Some modified letters are used to represent non-native sounds to Modern Standard Arabic. These letters are used as an optional alternative in transliterated names, loanwords and dialectal words. The usage of these letters depends on the writer and their country of origin and their usage is not mandatory.
The phoneme /ɡ/ (considered a standard pronunciation of ج in Egypt, Oman, and coastal Yemen) has the highest number of variations when writing loanwords or foreign proper nouns in Literary Arabic, and it can be written with either the standard letters ج, غ, ق, and ك or with the non-standard letters ڨ (used only in Tunisia and Algeria), ڭ (used only in Morocco), and گ (used mainly in Iraq) for example "Golf" pronounced /ɡoːlf/ can be written جولف, غولف, قولف, كولف, ڨولف, ڭولف or گولف depending on the writer and their country of origin. On the other hand, /ɡ/ is considered a native phoneme in most Arabic dialects, either as a reflex of ج as in lower Egypt, parts of Oman and parts of Yemen (e.g. جمل [gamal]) or as a reflex of ق as in most of the Arabian peninsula, Iraq, Sudan, and parts of Egypt, Levant and North Africa (e.g. قال [gaːl]).
Note: The sounds /p/ and /v/ are non-native to most Arabic dialects (excl. Anatolian Arabic where ذِئْب "Wolf" is pronounced vīp [viːp][14] instead of Standard Arabic [ðɪʔb]), while /g/, /t͡ʃ/ and /ʒ/ appear as a native phoneme or allophone in many dialects.
Used in languages other than Arabic
Remove ads
Numerals
There are two main kinds of numerals used along with Arabic text; Western Arabic numerals and Eastern Arabic numerals. In most of present-day North Africa, the usual Western Arabic numerals are used. Like Western Arabic numerals, in Eastern Arabic numerals, the units are always right-most, and the highest value left-most. Eastern Arabic numbers are written from left to right.
Letters as numerals
In addition, the Arabic alphabet can be used to represent numbers (Abjad numerals). This usage is based on the ʾabjadī order of the alphabet. أ ʾalif is 1, ب bāʾ is 2, ج jīm is 3, and so on until ي yāʾ = 10, ك kāf = 20, ل lām = 30, ..., ر rāʾ = 200, ..., غ ghayn = 1000. This is sometimes used to produce chronograms.
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective

The Arabic alphabet can be traced back to the Nabataean script used to write Nabataean Aramaic. A transitional phase, between the Nabataean Aramaic script and a subsequent, recognizably Arabic script, is known as Nabataean Arabic. The pre-Islamic phase of the script as it existed in the fifth and sixth centuries, once it had become recognizably similar to the script as it came to be known in the Islamic era, is known as Paleo-Arabic.[18]
The first known text in the Arabic alphabet is a late fourth-century inscription from Jabal Ram 50 km east of ‘Aqabah in Jordan, but the Zabad trilingual inscription is the earliest dated Arabic text from 512, and was discovered in Syria.[19] Nevertheless, the epigraphic record is extremely sparse. Later, dots were added above and below the letters to differentiate them. (The Aramaic language had fewer phonemes than the Arabic, and some originally distinct Aramaic letters had become indistinguishable in shape.
The first surviving document that definitely uses these dots is also the first surviving Arabic papyrus (PERF 558), dated April 643, although they did not become obligatory until much later. Important texts were and still are frequently memorized, especially in Qurʾan memorization.
Later still, vowel marks and the hamza were introduced, beginning some time in the latter half of the 7th century, preceding the first invention of Syriac and Tiberian vocalizations. Initially, this was done by a system of red dots, said to have been commissioned in the Umayyad era by Abu al-Aswad al-Du'ali, a dot above = a, a dot below = i, a dot on the line = u, and doubled dots indicated nunation. However, this was cumbersome and easily confusable with the letter-distinguishing dots, so about 100 years later, the modern system was adopted. The system was finalized around 786 by al-Khalil ibn Ahmad al-Farahidi.
Other tributes and alphabets written in Arabic dialects
Arabic dialects were written in different alphabets before the spread of the Arabic alphabet currently in use. The most important of these alphabets and inscriptions are the Safaitic inscriptions, amounting to 30,000 inscriptions discovered in the Levant desert.[20]
There are about 3,700 inscriptions in Hismaic in central Jordan and northwest of the Arabian Peninsula, and Nabataean inscriptions, the most important of which are the Umm al-Jimal I inscription and the Numara inscription.[21]

Arabic printing
Medieval Arabic blockprinting flourished from the 10th century until the 14th. It was devoted to tiny texts, which were usually used in amulets.
In 1514, following Johannes Gutenberg's invention of the printing press in 1450, Gregorio de Gregorii, a Venetian, published an entire book of hours in Arabic script; it was entitled Kitab Salat al-Sawa'i and was intended for eastern Christian communities.[22] Between 1580 and 1586, type designer Robert Granjon designed Arabic typefaces for Cardinal Ferdinando de' Medici, and the Medici Oriental Press published many Christian prayer and scholarly Arabic texts in the late 16th century.[23]

Maronite monks at Monastery of Qozhaya on Mount Lebanon published the first Arabic books to use movable type in the Middle East. The monks employed Garshuni, the practice of writing Arabic using the Syriac script, usually by Christians.
Although Napoleon generally receives credit for introducing the printing press to Egypt during his invasion of the country in 1798, and though he did indeed bring printing presses and Arabic presses to print the French occupation's official newspaper Al-Tanbiyyah "The Courier," printing in the Arabic language had started several centuries earlier. A goldsmith (like Gutenberg) designed and implemented an Arabic script movable type printing press in the Middle East. The Lebanese Melkite monk Abdallah Zakher set up an Arabic printing press using movable type at the monastery of Saint John at the town of Dhour El Shuwayr in Mount Lebanon, the first homemade press in Lebanon using Arabic script. He cut the type molds and founded the typeface. The first book came off his press in 1734; this press continued in use until 1899.[24]
Remove ads
Computers
Summarize
Perspective
The Arabic alphabet can be encoded using several character sets, including ISO-8859-6, Windows-1256 and Unicode, the latter of which contains the "Arabic segment", entries U+0600 to U+06FF. However, none of the sets indicates the form that each character should take in context. It is left to the rendering engine to select the proper glyph to display for each character.
Each letter has a position-independent encoding in Unicode, and the rendering software can infer the correct glyph form (initial, medial, final or isolated) from its joining context. That is the current recommendation. However, for compatibility with previous standards, the initial, medial, final and isolated forms can also be encoded separately.
Unicode
As of Unicode 16.0, the Arabic script is contained in the following blocks:[25]
- Arabic (0600–06FF, 256 characters)
- Arabic Supplement (0750–077F, 48 characters)
- Arabic Extended-A (08A0–08FF, 96 characters)
- Arabic Extended-B (0870–089F, 42 characters)
- Arabic Extended-C (10EC0–10EFF, 7 characters)
- Arabic Presentation Forms-A (FB50–FDFF, 631 characters)
- Arabic Presentation Forms-B (FE70–FEFF, 141 characters)
- Rumi Numeral Symbols (10E60–10E7F, 31 characters)
- Indic Siyaq Numbers (1EC70–1ECBF, 68 characters)
- Ottoman Siyaq Numbers (1ED00–1ED4F, 61 characters)
- Arabic Mathematical Alphabetic Symbols (1EE00—1EEFF, 143 characters)
The basic Arabic range encodes the standard letters and diacritics but does not encode contextual forms (U+0621-U+0652 being directly based on ISO 8859-6). It also includes the most common diacritics and Arabic-Indic digits. U+06D6 to U+06ED encode Qur'anic annotation signs such as "end of ayah" ۖ and "start of rub el hizb" ۞. The Arabic supplement range encodes letter variants mostly used for writing African (non-Arabic) languages. The Arabic Extended-A range encodes additional Qur'anic annotations and letter variants used for various non-Arabic languages.
The Arabic Presentation Forms-A range encodes contextual forms and ligatures of letter variants needed for Persian, Urdu, Sindhi and Central Asian languages. The Arabic Presentation Forms-B range encodes spacing forms of Arabic diacritics, and more contextual letter forms. The Arabic Mathematical Alphabetical Symbols block encodes characters used in Arabic mathematical expressions.
See also the notes of the section on modified letters.
Keyboards



Keyboards designed for different nations have different layouts, so proficiency in one style of keyboard, such as Iraq's, does not transfer to proficiency in another, such as Saudi Arabia's. Differences can include the location of non-alphabetic characters.
All Arabic keyboards allow typing Roman characters, e.g., for the URL in a web browser. Thus, each Arabic keyboard has both Arabic and Roman characters marked on the keys. Usually, the Roman characters of an Arabic keyboard conform to the QWERTY layout, but in North Africa, where French is the most common language typed using the Roman characters, the Arabic keyboards are AZERTY.
To encode a particular written form of a character, there are extra code points provided in Unicode which can be used to express the exact written form desired. The range Arabic presentation forms A (U+FB50 to U+FDFF) contain ligatures while the range Arabic presentation forms B (U+FE70 to U+FEFF) contains the positional variants. These effects are better achieved in Unicode by using the zero-width joiner and zero-width non-joiner, as these presentation forms are deprecated in Unicode and should generally only be used within the internals of text-rendering software; when using Unicode as an intermediate form for conversion between character encodings; or for backwards compatibility with implementations that rely on the hard-coding of glyph forms.
Finally, the Unicode encoding of Arabic is in logical order, that is, the characters are entered, and stored in computer memory, in the order that they are written and pronounced without worrying about the direction in which they will be displayed on paper or on the screen. Again, it is left to the rendering engine to present the characters in the correct direction, using Unicode's bi-directional text features. In this regard, if the Arabic words on this page are written left to right, it is an indication that the Unicode rendering engine used to display them is out of date.[26][27]
There are competing online tools, e.g. Yamli editor, which allow entry of Arabic letters without having Arabic support installed on a PC, and without knowledge of the layout of the Arabic keyboard.[28]
Variations
| ي و ه ن م ل ك ق ف غ ع ظ ط ض ص ش س ز ر ذ د خ ح ج ث ت ب ا | Hijā’ī sequence | |
 |
• | Noto Nastaliq |
| • | Scheherazade New | |
| • | Lateef | |
| • | Noto Naskh Arabic | |
| • | Markazi Text | |
| • | Noto Sans Arabic | |
| • | El Messiri | |
| • | Lemonada | |
| • | Changa | |
| • | Mada | |
| • | Noto Kufi Arabic | |
| • | Reem Kufi | |
| • | Lalezar | |
| • | Jomhuria | |
| • | Rakkas | |
Remove ads
See also
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Arabic alphabet.
Notes
- See the section on regional variations in letter form.
References
Sources
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads


