Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta, (GSK-3 beta), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GSK3B gene.[5][6] In mice, the enzyme is encoded by the Gsk3b gene.[7] Abnormal regulation and expression of GSK-3 beta is associated with an increased susceptibility towards bipolar disorder.[8]
Remove ads
Function
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a proline-directed serine-threonine kinase that was initially identified as a phosphorylating and an inactivating agent of glycogen synthase. Two isoforms, alpha (GSK3A) and beta, show a high degree of amino acid homology.[5]
GSK3B is involved in energy metabolism, neuronal cell development, and body pattern formation.[9][10] It might be a new therapeutic target for ischemic stroke.
Remove ads
Disease relevance
Homozygous disruption of the Gsk3b locus in mice results in embryonic lethality during mid-gestation.[7] This lethality phenotype could be rescued by inhibition of tumor necrosis factor.[7]
Two SNPs at this gene, rs334558 (-50T/C) and rs3755557 (-1727A/T), are associated with efficacy of lithium treatment in bipolar disorder.[11]
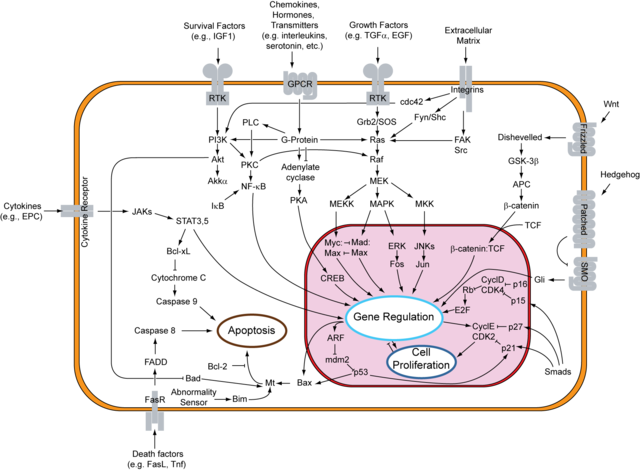
Signaling pathways
Pharmacological inhibition of ERK1/2 restores GSK-3 beta activity and protein synthesis levels in a model of tuberous sclerosis.[12]
Interactions
GSK3B has been shown to interact with:
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads







