Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Snub polyhedron
Polyhedron resulting from the snub operation From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
In geometry, a snub polyhedron is a polyhedron obtained by performing a snub operation: alternating a corresponding omnitruncated or truncated polyhedron, depending on the definition. Some, but not all, authors include antiprisms as snub polyhedra, as they are obtained by this construction from a degenerate "polyhedron" with only two faces (a dihedron).
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (March 2025) |
Chiral snub polyhedra do not always have reflection symmetry and hence sometimes have two enantiomorphous (left- and right-handed) forms which are reflections of each other. Their symmetry groups are all point groups.
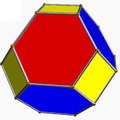
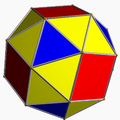
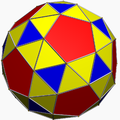
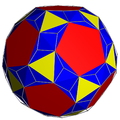
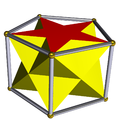
For example, the snub cube:
 |
 |
Snub polyhedra have Wythoff symbol | p q r and by extension, vertex configuration 3.p.3.q.3.r. Retrosnub polyhedra (a subset of the snub polyhedron, containing the great icosahedron, small retrosnub icosicosidodecahedron, and great retrosnub icosidodecahedron) still have this form of Wythoff symbol, but their vertex configurations are instead
Remove ads
List of snub polyhedra
Summarize
Perspective
Uniform
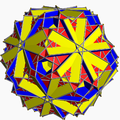
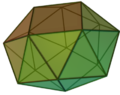
There are 12 uniform snub polyhedra, not including the antiprisms, the icosahedron as a snub tetrahedron, the great icosahedron as a retrosnub tetrahedron and the great disnub dirhombidodecahedron, also known as Skilling's figure.
When the Schwarz triangle of the snub polyhedron is isosceles, the snub polyhedron is not chiral. This is the case for the antiprisms, the icosahedron, the great icosahedron, the small snub icosicosidodecahedron, and the small retrosnub icosicosidodecahedron.
In the pictures of the snub derivation (showing a distorted snub polyhedron, topologically identical to the uniform version, arrived at from geometrically alternating the parent uniform omnitruncated polyhedron) where green is not present, the faces derived from alternation are coloured red and yellow, while the snub triangles are blue. Where green is present (only for the snub icosidodecadodecahedron and great snub dodecicosidodecahedron), the faces derived from alternation are red, yellow, and blue, while the snub triangles are green.
Notes:
- The icosahedron, snub cube and snub dodecahedron are the only three convex ones. They are obtained by snubification of the truncated octahedron, truncated cuboctahedron and the truncated icosidodecahedron - the three convex truncated quasiregular polyhedra.
- The only snub polyhedron with the chiral octahedral group of symmetries is the snub cube.
- Only the icosahedron and the great icosahedron are also regular polyhedra. They are also deltahedra.
- Only the icosahedron, great icosahedron, small snub icosicosidodecahedron, small retrosnub icosicosidodecahedron, great dirhombicosidodecahedron, and great disnub dirhombidodecahedron also have reflective symmetries.
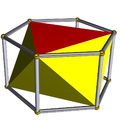
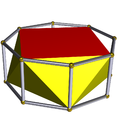
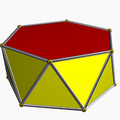
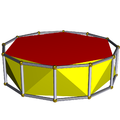
There is also the infinite set of antiprisms. They are formed from prisms, which are truncated hosohedra, degenerate regular polyhedra. Those up to hexagonal are listed below. In the pictures showing the snub derivation, the faces derived from alternation (of the prism bases) are coloured red, and the snub triangles are coloured yellow. The exception is the tetrahedron, for which all the faces are derived as red snub triangles, as alternating the square bases of the cube results in degenerate digons as faces.
Notes:
- Two of these polyhedra may be constructed from the first two snub polyhedra in the list starting with the icosahedron: the pentagonal antiprism is a parabidiminished icosahedron and a pentagrammic crossed-antiprism is a parabidiminished great icosahedron, also known as a parabireplenished great icosahedron.
Non-uniform
Two Johnson solids are snub polyhedra: the snub disphenoid and the snub square antiprism. Neither is chiral.
Remove ads
Bibliography
- Coxeter, Harold Scott MacDonald; Longuet-Higgins, M. S.; Miller, J. C. P. (1954), "Uniform polyhedra", Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 246 (916): 401–450, Bibcode:1954RSPTA.246..401C, doi:10.1098/rsta.1954.0003, ISSN 0080-4614, JSTOR 91532, MR 0062446, S2CID 202575183
- Wenninger, Magnus (1974). Polyhedron Models. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-09859-9.
- Skilling, J. (1975), "The complete set of uniform polyhedra", Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 278 (1278): 111–135, Bibcode:1975RSPTA.278..111S, doi:10.1098/rsta.1975.0022, ISSN 0080-4614, JSTOR 74475, MR 0365333, S2CID 122634260
- Mäder, R. E. Uniform Polyhedra. Mathematica J. 3, 48-57, 1993.
Remove ads
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads