Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Truncated tetrahexagonal tiling
Semiregular tiling of the hyperbolic plane From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
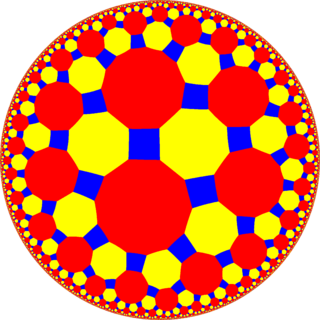
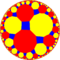
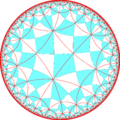
In geometry, the truncated tetrahexagonal tiling is a semiregular tiling of the hyperbolic plane. There are one square, one octagon, and one dodecagon on each vertex. It has Schläfli symbol of tr{6,4}.
| Truncated tetrahexagonal tiling | |
|---|---|
 Poincaré disk model of the hyperbolic plane | |
| Type | Hyperbolic uniform tiling |
| Vertex configuration | 4.8.12 |
| Schläfli symbol | tr{6,4} or |
| Wythoff symbol | 2 6 4 | |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | [6,4], (*642) |
| Dual | Order-4-6 kisrhombille tiling |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
Remove ads
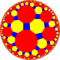
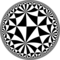
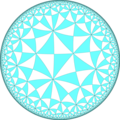
Dual tiling
 |
 |
| The dual tiling is called an order-4-6 kisrhombille tiling, made as a complete bisection of the order-4 hexagonal tiling, here with triangles shown in alternating colors. This tiling represents the fundamental triangular domains of [6,4] (*642) symmetry. | |
Related polyhedra and tilings
Summarize
Perspective
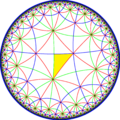
From a Wythoff construction there are fourteen hyperbolic uniform tilings that can be based from the regular order-4 hexagonal tiling.
Drawing the tiles colored as red on the original faces, yellow at the original vertices, and blue along the original edges, there are 7 forms with full [6,4] symmetry, and 7 with subsymmetry.
Remove ads
Symmetry
Summarize
Perspective







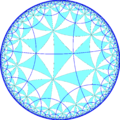
The dual of the tiling represents the fundamental domains of (*642) orbifold symmetry. From [6,4] symmetry, there are 15 small index subgroup by mirror removal and alternation operators. Mirrors can be removed if its branch orders are all even, and cuts neighboring branch orders in half. Removing two mirrors leaves a half-order gyration point where the removed mirrors met. In these images unique mirrors are colored red, green, and blue, and alternately colored triangles show the location of gyration points. The [6+,4+], (32×) subgroup has narrow lines representing glide reflections. The subgroup index-8 group, [1+,6,1+,4,1+] (3232) is the commutator subgroup of [6,4].
Larger subgroup constructed as [6,4*], removing the gyration points of [6,4+], (3*22), index 6 becomes (*3333), and [6*,4], removing the gyration points of [6+,4], (2*33), index 12 as (*222222). Finally their direct subgroups [6,4*]+, [6*,4]+, subgroup indices 12 and 24 respectively, can be given in orbifold notation as (3333) and (222222).
Remove ads
See also
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Uniform tiling 4-8-12.
References
- John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strauss, The Symmetries of Things 2008, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 (Chapter 19, The Hyperbolic Archimedean Tessellations)
- "Chapter 10: Regular honeycombs in hyperbolic space". The Beauty of Geometry: Twelve Essays. Dover Publications. 1999. ISBN 0-486-40919-8. LCCN 99035678.
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads