Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Solar eclipse of April 19, 1958
20th-century annular solar eclipse From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
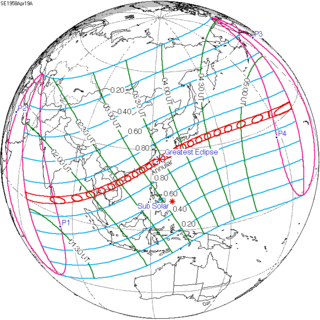
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Saturday, April 19, 1958,[1] with a magnitude of 0.9408. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 2.2 days after apogee (on April 16, 1958, at 22:40 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller.[2]
Annularity was visible in the Maldives, Nicobar Islands, Burma, Thailand including the capital city Bangkok, Cambodia, Laos, North Vietnam and South Vietnam (now belonging to Vietnam), China, British Hong Kong, Taiwan, Ryukyu Islands and Japan. Places east of International Date line witnessed the eclipse on April 18 (Friday). A partial eclipse was visible for most of Asia.
This was the last of four central solar eclipses visible from Bangkok from 1948 to 1958, where it is extremely rare for a large city to witness four central solar eclipses within 10 years.
Remove ads
Observation
Summarize
Perspective
Compared with a total solar eclipse, the chromosphere, corona and solar prominence are invisible during an annular eclipse. However, observations of millimeter-wave solar radio can provide data for lower- and mid-layer structure of the chromosphere, which is more valuable during an annular solar eclipse.[3]
China
A joint observation team formed by the Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union (predecessor of today's Russian Academy of Sciences) and the Chinese Academy of Sciences conducted 8-millimeter radio observation in Sanya, Hainan Island, China using the equatorial parabolic radio telescope manufactured by the Lebedev Physical Institute and the dual-channel radiometer as a receiver.[3][4] Radio astronomy started to develop from then in China.[5] Due to the Sino-Soviet split soon after this eclipse, the two countries did not conduct any joint observations of the total solar eclipse of September 22, 1968. On January 23, 1969, the People's Daily published an article reporting the observation of the eclipse in 1968, where it also criticized that the Soviet Union "plundered data of the annular solar eclipse" in 1958, only left China a "worn radio telescope antenna", and later even asked for it back.[6]
Japan
Observation ships were sent to Hachijō-jima, Izu Islands, Japan.[7] Pictures were also taken in Tanegashima, Osumi Islands, and luminosity, air pressure, temperature, humidity, water temperature of the storage tank, ground temperature, wind direction, wind speed and other data were recorded every 10 minutes.[8]
Remove ads
Eclipse details
Summarize
Perspective
Shown below are two tables displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. The first table outlines times at which the moon's penumbra or umbra attains the specific parameter, and the second table describes various other parameters pertaining to this eclipse.[9]
Remove ads
Eclipse season
This eclipse is part of an eclipse season, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight. The first and last eclipse in this sequence is separated by one synodic month.
Related eclipses
Eclipses in 1958
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on April 4.
- An annular solar eclipse on April 19.
- A partial lunar eclipse on May 3.
- A total solar eclipse on October 12.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on October 27.
Metonic
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of June 30, 1954
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of February 5, 1962
Tzolkinex
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of March 7, 1951
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of May 30, 1965
Half-Saros
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of April 13, 1949
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of April 24, 1967
Tritos
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of May 20, 1947
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of March 18, 1969
Solar Saros 128
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of April 7, 1940
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of April 29, 1976
Inex
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of May 9, 1929
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of March 29, 1987
Triad
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of June 18, 1871
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of February 16, 2045
Solar eclipses of 1957–1960
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[10]
Saros 128
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 128, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 73 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on August 29, 984 AD. It contains total eclipses from May 16, 1417 through June 18, 1471; hybrid eclipses from June 28, 1489 through July 31, 1543; and annular eclipses from August 11, 1561 through July 25, 2120. The series ends at member 73 as a partial eclipse on November 1, 2282. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of totality was produced by member 27 at 1 minutes, 45 seconds on June 7, 1453, and the longest duration of annularity was produced by member 48 at 8 minutes, 35 seconds on February 1, 1832. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s descending node of orbit.[11]
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
Tritos series
This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
Remove ads
Notes
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads