Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Persian alphabet
Writing system used for the Persian language From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Persian alphabet (Persian: الفبای فارسی, romanized: Alefbâ-ye Fârsi), also known as the Perso-Arabic script, is the right-to-left alphabet used for the Persian language. This is like the Arabic script with four additional letters: پ چ ژ گ (the sounds 'g', 'zh', 'ch', and 'p', respectively), in addition to the obsolete ڤ that was used for the sound /β/. This letter is no longer used in Persian, as the [β]-sound changed to [b], e.g. archaic زڤان /zaβɑn/ > زبان /zæbɒn/ 'language'.[2][3] Although the sound /β/ (ڤ) is written as "و" nowadays in Farsi (Dari-Parsi/New Persian), it is different to the Arabic /w/ (و) sound, which uses the same letter.
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
It was the basis of many Arabic-based scripts used in Central and South Asia. It is used for both Iranian and Dari: standard varieties of Persian; and is one of two official writing systems for the Persian language, alongside the Cyrillic-based Tajik alphabet.
The script is mostly but not exclusively right-to-left; mathematical expressions, numeric dates and numbers bearing units are embedded from left to right. The script is cursive, meaning most letters in a word connect to each other; when they are typed, contemporary word processors automatically join adjacent letter forms. Persian is unusual among Arabic scripts because a zero-width non-joiner is sometimes entered in a word, causing a letter to become disconnected from others in the same word.
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
The Persian alphabet is directly derived and developed from the Arabic alphabet. The Arabic alphabet was introduced to the Persian-speaking world after the Muslim conquest of Persia and the fall of the Sasanian Empire in the 7th century. Following this, the Arabic language became the principal language of government and religious institutions in Persia, which led to the widespread usage of the Arabic script. Classical Persian literature and poetry were affected by this simultaneous usage of Arabic and Persian. A new influx of Arabic vocabulary soon entered the Persian language.[4] In the 8th century, the Tahirid dynasty and Samanid dynasty officially adopted the Arabic script for writing Persian, followed by the Saffarid dynasty in the 9th century, gradually displacing the various Pahlavi scripts used for the Persian language earlier. By the 9th-century, the Perso-Arabic alphabet became the dominant form of writing in Greater Khorasan.[4][5][6]
Under the influence of various Persian Empires, many languages in Central and South Asia that adopted the Arabic script use the Persian Alphabet as the basis of their writing systems. Today, extended versions of the Persian alphabet are used to write a wide variety of Indo-Iranian languages, including Kurdish, Balochi, Pashto, Urdu (from Classical Hindustani), Saraiki, Panjabi, Sindhi and Kashmiri. In the past the use of the Persian alphabet was common amongst Turkic languages, but today is relegated to those spoken within Iran, such as Azerbaijani, Turkmen, Qashqai, Chaharmahali and Khalaj. The Uyghur language in western China is the most notable exception to this.
During the Soviet period many languages in Central Asia, including Persian, were reformed by the government. This ultimately resulted in the Cyrillic-based alphabet used in Tajikistan today. See: Tajik alphabet § History.
Remove ads
Letters
Summarize
Perspective

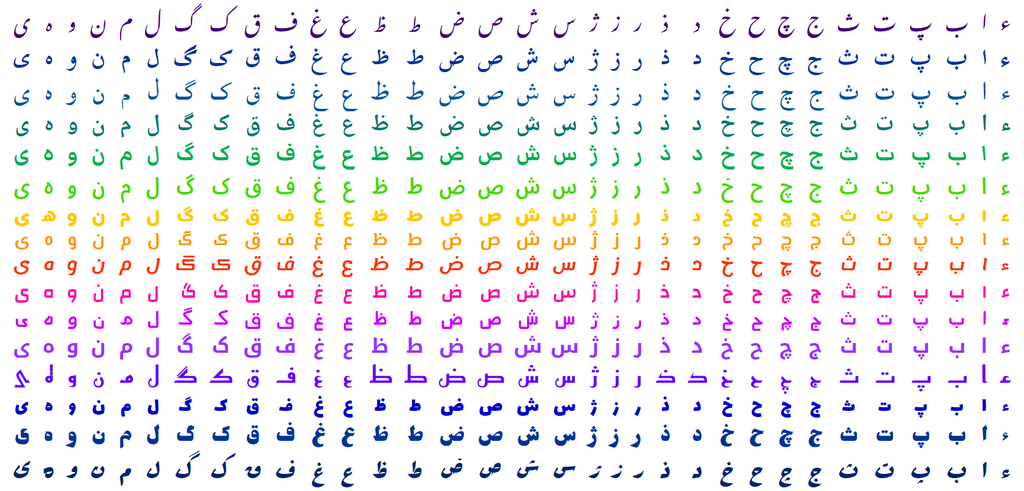
Below are the 32 letters of the modern Persian alphabet. Since the script is cursive, the appearance of a letter changes depending on its position: isolated, initial (joined on the left), medial (joined on both sides) and final (joined on the right) of a word.[7] These include 28 letters of the Arabic alphabet, in addition to 4 other letters.
The names of the letters are mostly the ones used in Arabic except for the Persian pronunciation. The only ambiguous name is he, which is used for both ح and ه. For clarification, they are often called hâ-ye jimi (literally "jim-like he" after jim, the name for the letter ج that uses the same base form) and hâ-ye do-češm (literally "two-eyed he", after the contextual middle letterform ـهـ), respectively. There are eight Persian letters that are mainly used in Arabic or foreign loanwords and not in native words: ث, ح, ذ, ص, ض, ط, ظ, ع and غ. These eight letters are also common used in proper names only. Unlike Arabic, the Persian language absolutely does not have pharyngealization at all. Although the letter غ is mainly used in Arabic loanwords, there are some native Persian words with this letter: آغاز, زغال, etc. The pronunciation of these letters in Persian can differ from their pronunciation in Arabic. For example, the letter ث is pronounced as /s/ in Persian, while it is pronounced as /θ/ in Arabic.
Overview table
Historically, in Early New Persian, there was a special letter for the sound /β/. This letter is no longer used, as the /β/-sound changed to /b/, e.g. archaic زڤان /zaβān/ > زبان /zæbɒːn/ 'language'.[9]
Another obsolete variant of the twenty-sixth letter گ /g/ is ݣ which used to appear in old manuscripts.[3]
Another obsolete variant of the twenty-fifth letter ک /k/ is ك which used to appear in old manuscripts.
The archaic letter ݿ /g/ was also used as a substitute for the twenty-sixth letter of the Persian alphabet, گ, which was used to appear in the older manuscripts of Persian in the late 18th century to the early 19th century.
Variants
| ی ه و ن م ل گ ک ق ف غ ع ظ ط ض ص ش س ژ ز ر ذ د خ ح چ ج ث ت پ ب ا ء | ||
 |
• | Noto Nastaliq Urdu |
| • | Scheherazade | |
| • | Lateef | |
| • | Noto Naskh Arabic | |
| • | Markazi Text | |
| • | Noto Sans Arabic | |
| • | Baloo Bhaijaan | |
| • | El Messiri SemiBold | |
| • | Lemonada Medium | |
| • | Changa Medium | |
| • | Mada | |
| • | Noto Kufi Arabic | |
| • | Reem Kufi | |
| • | Lalezar | |
| • | Jomhuria | |
| • | Rakkas | |
| The alphabet in 16 fonts: Noto Nastaliq Urdu, Scheherazade, Lateef, Noto Naskh Arabic, Markazi Text, Noto Sans Arabic, Baloo Bhaijaan, El Messiri SemiBold, Lemonada Medium, Changa Medium, Mada, Noto Kufi Arabic, Reem Kufi, Lalezar, Jomhuria, and Rakkas. | ||
Letter construction
^i. The i'jam diacritic characters are illustrative only; in most typesetting the combined characters in the middle of the table are used.
^ii. Persian yē has 2 dots below in the initial and middle positions only. The standard Arabic version ي يـ ـيـ ـي always has 2 dots below.
Letters that do not link to a following letter
Seven letters (و, ژ, ز, ر, ذ, د, ا) do not connect to the following letter, unlike the rest of the letters of the alphabet. The seven letters have the same form in isolated and initial position and a second form in medial and final position. For example, when the letter ا alef is at the beginning of a word such as اینجا injâ ("here"), the same form is used as in an isolated alef. In the case of امروز emruz ("today"), the letter ر re takes the final form and the letter و vâv takes the isolated form, but they are in the middle of the word, and ز also has its isolated form, but it occurs at the end of the word.
Diacritics
Persian script has adopted a subset of Arabic diacritics: zabar /æ/ (fatḥah in Arabic), zēr /e/ (kasrah in Arabic), and pēš /ou̯/ or /o/ (ḍammah in Arabic, pronounced zamme in Western Persian), tanwīne nasb /æn/ and šaddah (gemination). Other Arabic diacritics may be seen in Arabic loanwords in Persian.

Short vowels
Of the four Arabic diacritics, the Persian language has adopted the following three for short vowels. The last one, sukūn, which indicates the lack of a vowel, has not been adopted.
^a. There is no standard transliteration for Persian. The letters 'i' and 'u' are only ever used as short vowels when transliterating Dari or Tajik Persian. See Persian Phonology
^b. Diacritics differ by dialect, due to Dari having 8 distinct vowels compared to the 6 vowels of Farsi. See Persian Phonology
In Farsi, none of these short vowels may be the initial or final grapheme in an isolated word, although they may appear in the final position as an inflection, when the word is part of a noun group. In a word that starts with a vowel, the first grapheme is a silent alef which carries the short vowel, e.g. اُمید (omid, meaning "hope"). In a word that ends with a vowel, letters ع, ه and و respectively become the proxy letters for zebar, zir and piš, e.g. نو (now, meaning "new") or بسته (bast-e, meaning "package").
Tanvin (nunation)
Nunation (Persian: تنوین, tanvin) is the addition of one of three vowel diacritics to a noun or adjective to indicate that the word ends in an alveolar nasal sound without the addition of the letter nun.
Tašdid
Other characters
The following are not actual letters but different orthographical shapes for letters, a ligature in the case of the lâm alef. As to ﺀ (hamza), it has only one graphical form since it is never tied to a preceding or following letter. However, it is sometimes 'seated' on a vâv, ye or alef, and in that case, the seat behaves like an ordinary vâv, ye or alef respectively. Technically, hamza is not a letter but a diacritic.
Although at first glance, they may seem similar, there are many differences in the way the different languages use the alphabets. For example, similar words are written differently in Persian and Arabic, as they are used differently.
Unicode has accepted U+262B ☫ FARSI SYMBOL in the Miscellaneous Symbols range.[10] In Unicode 1.0 this symbol was known as SYMBOL OF IRAN.[11] It is a stylization of الله (Allah) used as the emblem of Iran. It is also a part of the flag of Iran.
The Unicode Standard has a compatibility character defined U+FDFC ﷼ RIAL SIGN that can represent ریال, the Persian name of the currency of Iran.[12]
Novel letters
The Persian alphabet has four extra letters that are not in the Arabic alphabet: /p/, /t͡ʃ/ (ch in chair), /ʒ/ (s in measure), /ɡ/. An additional fifth letter ڤ was used for /β/ (v in Spanish huevo) but it is no longer used.
Deviations from the Arabic script
Persian uses the Eastern Arabic numerals, but the shapes of the digits 'four' (۴), 'five' (۵), and 'six' (۶) are different from the shapes used in Arabic. All the digits also have different codepoints in Unicode:[13]
- Many Perso-Arabic scripts in South Asia share close similarities (use of Nastaliq, use of superscript ط to represent retroflex consonants, etc.) due to mutual contact during development. It is inaccurate to say that one Indo-Persian script directly descends from another, and instead, they are best seen as a cluster of scripts with common origin.
- However, the Arabic variant continues to be used in its traditional style in the Nile Valley, similarly as it is used in Persian and Ottoman Turkish.
Comparison of different numerals
| Western Arabic | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Eastern Arabic[a] | ٠ | ١ | ٢ | ٣ | ٤ | ٥ | ٦ | ٧ | ٨ | ٩ | ١٠ |
| Persian[b] | ۰ | ۱ | ۲ | ۳ | ۴ | ۵ | ۶ | ۷ | ۸ | ۹ | ۱۰ |
| Urdu[c] | ۰ | ۱ | ۲ | ۳ | ۴ | ۵ | ۶ | ۷ | ۸ | ۹ | ۱۰ |
| Abjad numerals | ا | ب | ج | د | ه | و | ز | ح | ط | ي |
- U+06F0 through U+06F9. The numbers 4, 5, and 6 are different from Eastern Arabic.
Remove ads
Word boundaries
Typically, words are separated from each other by a space. Certain morphemes (such as the plural ending '-hâ'), however, are written without a space. On a computer, they are separated from the word using the zero-width non-joiner.
Cyrillic Persian alphabet in Tajikistan
As part of the russification of Central Asia, the Cyrillic script was introduced in the late 1930s.[14][15][16][17] The alphabet has remained Cyrillic since then. In 1989, with the growth in Tajik nationalism, a law was enacted declaring Tajik the state language. In addition, the law officially equated Tajik with Persian, placing the word Farsi (the endonym for the Persian language) after Tajik. The law also called for a gradual reintroduction of the Perso-Arabic alphabet.[18][19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28][29][excessive citations]
The Persian alphabet was introduced into education and public life, although the banning of the Islamic Renaissance Party in 1993 slowed adoption. In 1999, the word Farsi was removed from the state-language law, reverting the name to simply Tajik. As of 2004[update] the de facto standard in use is the Tajik Cyrillic alphabet, and as of 1996[update] only a very small part of the population can read the Persian alphabet.
Remove ads
See also
- Scripts used for Persian
- Romanization of Persian
- Persian braille
- Persian phonology
- Abjad numerals
- Nastaʿlīq, the calligraphy used to write Persian before the 20th century
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads

