Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
2021 in science
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
This is a list of several significant scientific events that occurred or were scheduled to occur in 2021.

Events
January
February
March
April
May
June
July
- 1 July
- Construction begins on the Square Kilometre Array, with first light planned for 2027.[311]
- In the debate about the cognitive impacts of smartphones and digital technology a group reports that, contrary to widespread belief, scientific evidence doesn't show that these technologies harm biological cognitive abilities and that they instead only change predominant ways of cognition – such as a reduced need to remember facts or conduct mathematical calculations by pen and paper outside contemporary schools. However, some activities – like reading novels – that require long attention spans and don't feature ongoing rewarding stimulation may become more challenging in general.[312][313]
- A study finds that ~9.4% of global deaths between 2000 and 2019 – ~5 million annually – can be attributed to extreme temperature with cold-related ones making up the larger share and decreasing and heat-related ones making up ~0.91 % and increasing.[314][315]
- 2 July
- The first scientific review in the professional academic literature about global plastic pollution in general finds that the rational response to the "global threat" would be "reductions in consumption of virgin plastic materials, along with internationally coordinated strategies for waste management" – such as banning export of plastic waste unless it leads to better recycling – and describes the state of knowledge about "poorly reversible" impacts.[316][317]
- Researchers report that a mix of microorganisms from cow stomachs could break down three types of plastics.[318][319]
- Scientists identify GPR75 variants as alleles protective against obesity in ~640,000 sequenced exomes.[320][321]
- 5 July
- Scientists report the discovery of a bone carving, one of the world's oldest works of art, made by Neanderthals about 51,000 years ago.[322][323]
- A scientific review summarizes evidence from nutrition research for diets for atherosclerosis prevention.[324][325]
- 7 July
- A preprint finds the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant to cause a ~108 % increased – or more than twice as large – risk for hospitalization, a ~234 % increase for ICU admission and 132% for death compared to non-VOC variants.[326][327]
- Researchers present a programmable quantum simulator that can operate with 256 qubits.[328][329]
- 8 July – Scientists report that in the past – with little relevance to future evolution – lower temperatures were associated with larger Homo body sizes and that long-term variability in precipitation was correlated with brain size.[330][331]

- 10 July – Scientists report in a preprint the discovery of long extrachromosomal DNA structures, they call borgs, which appear to incorporate genes from organisms they encounter. These structures, which could turn out to be an unknown form of giant viruses or "giant linear plasmids",[333][332] co-occur with a species of archaeon which may host them, shares many of their genes, whose main chromosome is only three times larger and whose capacity for anaerobic oxidation of methane as well as other biological functions – such as production of proteins – the borgs may augment.[334][335][332]
- 12 July – Scientists report in a preprint that the viral load in the first positive test of infections with the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant was on average ~1000 times higher than with compared infections during 2020.[336][337]
- 14 July
- Researchers report finding the earliest known fossil life on Earth, in the form of "putative filamentous microfossils", possibly of methanogens and/or methanotrophs, that lived about 3.42-billion-year-old in "a paleo-subseafloor hydrothermal vein system of the Barberton greenstone belt in South Africa."[338][339]
- Astronomers report the detection, for the first time, of an isotope in the atmosphere of an exoplanet. In specific, the isotope Carbon-13 (13C) was found in the atmosphere of a gas giant exoplanet named TYC 8998-760-1 b.[340][341]
- Researchers used a brain-computer interface to enable a man who was paralyzed since 2003 to produce comprehensible words and sentences by decoding signals from electrodes in the speech areas of his brain.[342][343]
- Researchers describe effects of deforestation and climate change in a transformation of Amazonia from carbon sink to carbon source .[344][345]
- 15 July – Scientists report that the Chicxulub impactor likely was an outer main-belt asteroid, a carbonaceous chondrite C-type asteroid.[346][347]
- 16 July
- Recently thought subglacial lakes under the Southern Polar cap of Mars based on a 2018 MARSIS measurement could also be clay minerals and frozen brine.[348][349]
- Japan achieves a new world record Internet speed over ~3.000 km: 319 Tbit/s, beating a previous record of 178 Tbit/s.[350][351]
- A study concludes only 1.5-7 % of "regions"[clarification needed] of the modern human genome to be specific to modern humans. These regions have neither been altered by archaic hominin DNA due to admixture nor are shared with Neanderthals or Denisovans according to their used genomic datasets. They also found two bursts of changes specific to modern human genomes which involve genes related to brain development and function.[352][353]
- A study using whole-genome resequencing indicates that Cannabis sativa was first domesticated about 12,000 years ago in the early Neolithic period in East Asia, with the results being consistent with a single domestication origin.[354][355]
- 18 July – Journalists and researchers report the discovery of spyware, called "Pegasus", developed and distributed by a private company which can and has widely been used to infect iOS and Android smartphones often – partly based on 0-day exploits – without the need for any user-interaction or significant clues to the user and then be used to exfiltrate data, track user locations, capture film through its camera, and activate the microphone at any time.[356]

- 19 July
- Researchers review 217 analyses of on-the-market products and services as well as existing alternatives to mainstream food, holidays, and furnishings, and conclude that total greenhouse gas emissions by Swedes could be lowered by to date up to 36–38 % if consumers – without a decrease in total estimated expenditure or considerations of self-interest rationale – instead were to obtain those they could assess to be more sustainable.[358]
- Researchers report that higher exposure to woodland urban green spaces is associated with improved cognitive development and risks of mental problems for urban 15-16 years old adolescents.[359][360]
- Scientists report that wild pigs are causing soil disturbance that, among other problems, globally results in annual carbon dioxide emissions equivalent to that of ~1.1 million passenger vehicles, implying that wild pig meat – unlike other meat products – has beneficial effects on the environment.[361][362]

- 20 July
- Researchers conclude that a previously rejected abiotic origin of phosphine concentrations on Venus reported in September 2020 – high rates of active plume volcanism – could be plausible.[364][365]
- A scientific review concludes that, except for poultry, at 50 g/day unprocessed red (~9 % increase) and processed meat (~18 %) appear to be risk factors for ischemic heart disease.[366][367]
- Scientists report that worldwide adolescent loneliness and depression increased substantially after 2012 and that loneliness in contemporary schools appears to be associated with smartphone access and Internet use.[368][369]

- 22 July
- Astronomers using the Atacama Large Millimetre/submillimeter Array (ALMA) report the first clear detection of a moon-forming disc around an exoplanet; in this case, the Jupiter-like planet PDS 70c.[371][372]
- DeepMind announces that its AlphaFold AI has predicted the structures of over 350,000 proteins, including 98.5% of the ~20,000 proteins in the human body. The 3D data along with their degrees of confidence for accuracy is made freely available with a new database, doubling the previous number of protein structures in the public domain.[357]
- 26 July
- The Galileo Project, headed by Avi Loeb, is launched. The project seeks to gather and report scientific evidence of extraterrestrials or extraterrestrial technology – such as of UFOs/UAP with alien origins – on or near Earth via telescope technology.[373][374][375]
- Scientists report to have created the first complete neuron-level-resolution 3D map of a monkey brain which they scanned within 100 hours.[376][377]
- A study finds that the increasing probability of record week-long heat extremes occurrence depends on warming rate, rather than global warming level and provides projections.[378][379]
- A scientific review summarizes studies about long COVID.[380][381]
- 28 July
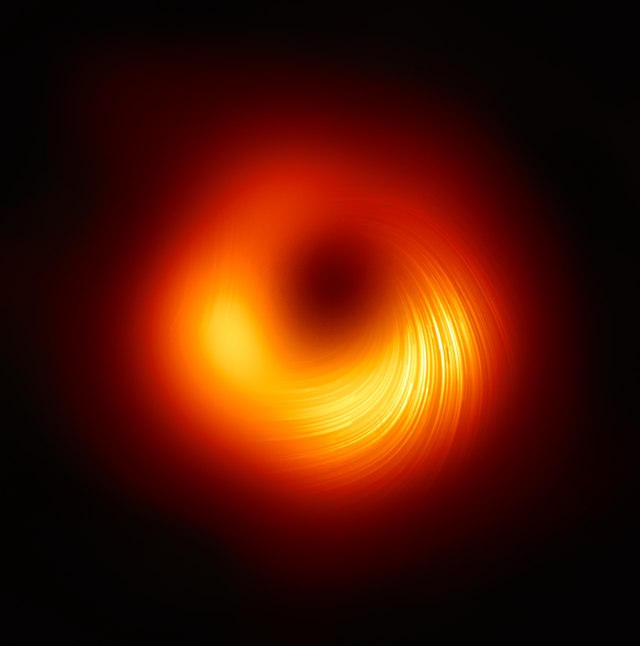
- The first direct observation of light from behind a black hole is reported, further confirming Einstein's theory of general relativity.[363][382][383]
- Metallic water is prepared for the first time in an ordinary Earth lab.[384][385]
- In an update to the World Scientists' Warning to Humanity, scientists report that evidence of nearing or crossed tipping points of critical elements of the Earth system is accumulating, that 18 of 31 planetary vital signs have reached record values, that 1990 jurisdictions have formally recognized a state of climate emergency, that frequent and accessible updates on the emergency are needed, that COVID-19 "green recovery" has been insufficient and that root-cause system changes above politics are required.[386][370]
- 29 July – A study indicates gut microbiomes with large amounts of microbes capable of generating unique secondary bile acids are a key element of centenarians' longevity.[387][388]
- 31 July – A kitchen robot – one of the first of its kind – for autonomous preparation of school meal program or delivery-service level amounts of discrete meals is demonstrated.[389]
August

- 2 August – Engineers report the development of a prototype wave energy converter that is twice as efficient as similar existing experimental technologies, which could be a major step towards practical viability of tapping into the sustainable energy source.[390][391]
- 4 August
- Scientists identify genetic determinants of ovarian ageing and possible effects of extending fertility in women.[392][393]
- Scientists describe the molecular mechanisms by which insect olfactory systems are sensitive enough to recognize and discriminate a vast number of molecules with very few smell receptors.[394][395]
- 5 August
- New observations of the M-type star L 98-59 and its surrounding system reveal three new bodies: a planet in the habitable zone, an ocean world, and a planet with half the mass of Venus, making it the lightest exoplanet ever to be measured using the radial velocity method.[396][397]
- A study introduces an early-warning indicator for critical transitions of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) and finds early-warning signals in eight independent AMOC indices. A, possibly abrupt,[398] likely irreversible collapse from the current strong to a weak mode is thought to have severe impacts on Earth system components and global climate.[399][400] The Sixth IPCC report assesses a 'medium confidence' that such a collapse won't happen by 2100.[401]
- 8 August – The National Ignition Facility achieves a 70% yield, compared to the laser energy required to sustain fusion, from inertial confinement fusion energy, an 8X improvement over previous experiments in spring 2021 and a 25X increase over the yields achieved in 2018.[402]
- 9 August
- The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) releases the first part of its Sixth Assessment Report, which summarizes the state of physical science on climate change based on over 14,000 papers and concludes that effects of human-caused climate change are now "widespread, rapid, and intensifying".[403][404][405]
- Neuroscientists show that transplantation of fecal microbiota from young donor mice into aged recipient mice substantially rejuvenates the brains of the latter,[406][407] complementing similar results of a 2020 study.[408]
- A scientific review assesses the long-term effects of COVID-19, including in prevalent cases of long COVID.[409][410]
- A researcher reports that solar superstorms would cause global months-long Internet outages. She describes potential mitigation measures and exceptions – such as user-powered mesh networks, related peer-to-peer applications and new protocols – and the robustness of the current Internet infrastructure.[411][412][413]
- 10 August
- A study based on OSIRIS-REx data concludes there to be a 1:1750 chance of an impact of asteroid (101955) Bennu by 2300, with the highest chance of impact being in 2182.[414][415]
- A small-scale study suggests that persistent blood clotting is a cause of long COVID.[416][417]
- 11 August – Researchers report promising results of ongoing testing and development of an engineered monoclonal antibodies based female contraception.[418][419]
- 12 August – Scientists report that the Ayta Magbukun people in the Philippines have the highest level of Denisovan ancestry in the world and describe the related genetic history in the region.[420][421]
- 13 August – Researchers demonstrate that probiotics can help coral reefs mitigate heat stress, indicating that such could make them more resilient to climate change and mitigate coral bleaching.[422][423]
- 16 August
- Scientists conclude that personal carbon allowances could be a component of climate change mitigation. They find that the economic recovery from COVID-19 and novel digital technology capacities open a window of opportunity for first implementations of such monetary/credit feedback and decreasing default levels of emissions concessions.[424][425][426]
- Researchers assess regionally-differentiated drivers and risks associated with worldwide pollinator decline, informing globally-relevant policy responses.[427][428]
- 17 August – Scientists report of human brain organoids that could intrinsically develop eye-type sensory structures.[429][430]
- 18 August – A study suggests that the global policy Montreal Protocol intended to control the production of ozone-depleting substances has also substantially mitigated climate change.[431][432]
- 20 August – Medical scientists confirm that hormone irisin confers neurobiological effects of physical exercise and, when its circulating levels are increased, can be an exercise mimetic in mice which may be useful for interventions to improve cognitive function or alleviate Alzheimer's disease.[433][434][435]
- 22 August – Astronomers conclude in a preprint that – controversially due to there being only few data points – there is high confidence "Planet 9" exists, that it likely has a mass of ~6.2 Earths and is closer than thought previously and report its likely orbit.[436][437]

- 24 August
- Cerebras announces a new hardware and software platform that can support AI models of 120 trillion parameters, enabling neural networks greater than the equivalent number of human brain synapses.[438]
- Researchers present a bioprinting method to produce steak-like cultured meat, composed of three types of bovine cell fibers.[439][440]
- 26 August – Astronomers report a new class of habitable exoplanets, named hycean planets (from hydrogen and ocean), which are described as hot, water-covered planets with a hydrogen-rich atmosphere that are possibly capable of harboring life.[441][442]
- 27 August – Scientists report about vaccine effectiveness, pandemic severity impacts and regional prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant overall and its newly subdivided subvariants named from AY.1 onwards,[443] the first two of which were differentiated like so – also termed "Delta Plus" – in June.[444] On 10 August a preprint reports a case of asymptomatic transmissions associated with high viral load among vaccinated patients infected by AY.3.[445]
- 28 August – The world's northernmost island, a small patch of land measuring 60 x 30 metres, is reported by scientists off the coast of Greenland. The name Qeqertaq Avannarleq is proposed, which means "the northernmost island" in Greenlandic.[446]
- 30 August
- The comprehensive 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention is published.[447][448] On 27 August the 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure is published.[449][450]
- A preprint study of nationwide data of Israel's vaccination programme finds a strong effect of waning immunity from the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine after 6 months.[451][452]
- 31 August – Scientists report that the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum ~56 million years ago was directly preceded by volcanism and that data about the event supports the existence of substantial climate-shifting tipping points in the Earth system.[453][454]
September
- 1 September
- NASA reports the successful sampling of a rock on Mars, named "Rochette", after a less successful first attempt.[455][456][457]
- Scientists report the development of a new solar-energy passive off-grid chemically stored on-demand cooling system for houses and/or refrigeration without electrical components which may be useful for climate change mitigation and adaptation.[458][459][460]

- 2 September
- Observation of a new class of supernova triggered by a black hole or neutron star crashing into the core of a companion star is reported by astronomers, based on studies of an extremely luminous source of radio waves called VT 1210+4956.[461][462][463]
- Astronomers report the detection of peculiar radio waves from near the galactic center whose unidentified source could represent a new class of astronomical objects.[464][465][466]
- A study finds that outdoor air pollution is associated with substantially increased mortality "even at low pollution levels below the current European and North American standards and WHO guideline values".[467][468] On 22 September, for the first time since 2005, the World Health Organization (WHO), after a systematic review of the accumulated evidence, adjusted their air quality guidelines whose adherence could save millions of lives, protect against future diseases and help meet climate goals.[469][470]
- 3 September
- Bioengineers report the development of a viable CRISPR-Cas gene-editing system, "CasMINI", that is about twice as compact as the commonly used Cas9 and Cas12a.[471][472]
- Researchers report that autoantibodies against one's own ACE2 enzymes (the major entry point receptors for COVID-19),[473][474] autoimmune disease, may be a (main) cause of long COVID.[475][476][477] Earlier studies suggested this may explain unusual pattern of organ damage by COVID-19.[478]
- Scientists report that the accelerated, higher-variability warming of the Arctic can cause (more frequent) extremely cold winter weather across parts of Asia and North America – including the February 2021 North American cold wave – via a, observed and modeled, stratospheric polar vortex disruption.[479][480]
- 6 September – Experts report that one-third of all chondrichthyes fish species are threatened with extinction, mainly caused by overfishing.[481][482]
- 8 September
- Cysteamine, an antioxidant drug already approved for human use, is shown to reverse atherosclerosis, the process responsible for heart attacks and strokes, in mice.[483][484]
- Scientists provide the first scientific assessment of the minimum amount of fossil fuels that would need to be secured from extraction per region as well as globally, to allow for a 50% probability of limiting global warming by 2050 to 1.5 °C.[485][486]
- Scientists report that Earth is reflecting less light – a dimming of ~0.5% in reflectance over two decades may have both been co-caused by climate change as well as substantially increase global warming.[487][488]
- 10 September
- Scientists report what could be the discovery of the oldest rock art, likely dating back to ~169–226,000 years ago, much older than what was previously thought to be the earliest known drawing, made ~73,000[489] years ago. Children likely intentionally placed a series of hands and feet in mud. The findings could also be the earliest evidence of Hominins on the above 4000 m a.s.l. high Tibetan Plateau.[490][491][492]
- 43 expert scientists publish the first scientific framework version that – via integration, review, clarifications and standardization – enables the evaluation of levels of protection of marine protected areas and can serve as a guide for improving, planning and monitoring marine protection-quality and -extents such as in efforts towards the 30%-protection-goal of the "Global Deal For Nature"[493] and the UN's SDG 14.[494][495]
- The CDC reports that despite prevalence of the Delta variant people vaccinated against COVID-19 are ~11 times less likely to die from COVID-19 (age-standardized rates of 1.6 versus 0.1 and 1.1 versus 0.1 weekly deaths per 100,000 U.S. citizens), showing vaccines' effectiveness at preventing severe disease.[496][497]


- 13 September – A scientific review concludes that accumulating data suggests dietary restriction (DR) – mainly intermittent fasting and caloric restriction – results in many of the same beneficial changes in adult humans as in studied organisms, potentially increasing health- and lifespan.[498][499] A review published on 22 September provides an overview of DR as an intervention and develops a framework for a proposed field of "precision nutrigeroscience".[500][501] A study published on 29 September identifies circadian-regulated autophagy as a critical contributor to intermittent time-restricted fasting-mediated lifespan extension in Drosophila and suggests that only certain forms of and/or combinations with intermittent fasting – intervals during which no food but only e.g. water and tea/coffee are ingested[502] – may be effective beyond the benefits of healthy body weight.[503][504]
- 15 September
- Physicists report candidate dark energy particles, Sun-produced local environment-adjusted "chameleon particles", at the dark matter detector XENON1T experiment.[505][506][507]
- Scientists confirm that widespread phytoplankton blooms can be a feedback effect of wildfires. The climate change-exacerbated 2019–2020 Australian wildfires caused oceanic deposition of wildfire aerosols, enhancing marine productivity and thereby increased oceanic carbon dioxide uptake.[508][509] A study using satellite data complements these findings, constraining the amount of CO2 emissions of the fires from November 2019 to January 2020 to around 715 million tons.[510][511]
- Media outlets report that the world's first cultured coffee products have been created by two biotechnology companies, still awaiting regulatory approval for near-term commercialization.[512][513] Such products, for which multiple companies' R&D have acquired substantial funding, may have equal or highly similar effects, composition and taste as natural products but use less water, generate less carbon emissions, require less labor[additional citation(s) needed] and cause no deforestation.[512]
- 16 September – Scientists report evidence of clothes being made 120,000 years ago based on findings in deposits in Morocco, a country in the northwestern part of Africa.[514][515]
- 17 September
- Scientists report that harmful algal blooms, which have been linked to deforestation, global warming and soil erosion, are proliferating in lakes and rivers around the globe. They add that such toxic algal blooms were a prominent feature of previous mass extinction events, in particular of the End-Permian Extinction.[516][517]
- Researchers report in a preprint the discovery of i.a. the so far closest known relative virus, with a 96.8% similarity, to SARS-CoV-2 in samples from wild horseshoe bats in northern Laos – 0.7% more similar than the virus RaTG13 discovered in China in 2013. Their findings indicate that, as of 2021, SARS-CoV-2-like viruses potentially infectious for humans circulate in bats in the Indochinese peninsula and that the pandemic virus may not originate from Wuhan.[518][519] Other scientists complement these findings, reporting in a preprint published on 20 September, that they could not find any SARS-CoV-2 related viruses in any samples collected in China, including from the only two domestic caves where RaTG13 and RmYN02 were detected, indicating such viruses may currently not circulate in bats in the country.[518][520]
- 22 September – Astronomers report the discovery of a nearby spherical structure, a 'superbubble', on the edges of which giant molecular clouds (Perseus and Taurus) with regions of star formation are being formed, the Per-Tau Shell.[521][522]
- 23 September
- Scientists report the discovery of human footprints in the state of New Mexico that are understood to be ~23,000 years old, around the time of the last Ice Age.[523][524]
- Researchers report the world's first artificial synthesis of starch. The material essential for many products and the most common carbohydrate in human diets was made from CO2 in a cell-free process and could reduce land, pesticide and water use as well as greenhouse gas emissions while increasing food security.[525][526]
- After commissioning two impact assessment studies and a technology analysis study, the European Commission proposes the implementation of a standardization – for versions of USB-C – of phone charger products, which may increase device-interoperability, convergence and convenience for consumers while decreasing resource-needs, redundancy and electronic waste.[527][528][529]


- 24 September
- Researchers conclude that projecting effects – such as regional inhabitability, human migration and food insecurity – of greenhouse gas emissions only for up to 2100, as widely practiced in research and policy-making, is short-sighted and model climate change scenarios for up to 2500.[530][531]
- Media outlets report that in Japan the first CRISPR-edited food has gone on public sale. Tomatoes were genetically modified for around five times the normal amount of possibly calming[532] GABA.[533] CRISPR was first applied in tomatoes in 2014.[534]
- Biomedical researchers demonstrate a switchable Yamanaka factors-reprogramming-based approach for regeneration of damaged heart without tumor-formation in mice.[535][536]
- 26 September – Researchers estimate that children born in 2020 (e.g. "Generation Alpha") will experience 2–7 times as many extreme weather events, particularly heat waves, compared to people born in 1960 (e.g. "Baby Boomers" and "Generation X") under current climate policy pledges over their lifetimes, raising issues of intergenerational equity.[537][538]
- 27 September
- Landsat 9, described as the world's most important satellite, is launched by NASA to study the Earth and its environment.[539][540]
- Biochemists and space scientists report that sunlight-, acidity- and water activity-levels in Venus' clouds may have the potential to support Earth-like phototrophy such as photosynthesis.[541][542]
- 28 September
- Medical scientists report that COVID-19 measures may have, apparently, caused the global extinction of the influenza B virus lineage B/Yamagata.[543][544]
- Pathogen researchers report the development of machine learning models for genome-based early detection and prioritization of high-risk potential zoonotic viruses in animals prior to spillover to humans. They conclude that their tool could be used for virus surveillance for pandemic prevention via (i.a.) measures of "early investigation and outbreak preparedness" and would have been capable of predicting SARS-CoV-2 as a high-risk strain.[545][546]
October
- 1 October – A company conducting a preliminary small (~380 patients × 2) clinical trial launched a year ago[547] reports that molnupiravir substantially reduced the risk of hospitalization (7.3% to 14.1%) and death (8 to 0) from COVID-19.[548][549]
- 4 October
- The 2021 Nobel Prize in Medicine is awarded to David Julius and Ardem Patapoutian for their findings about how heat, cold and touch can initiate signals in the nervous system.[550]
- Metascientists report, based on a citation analysis, that "structures fostering disruptive scholarship and focusing attention on novel ideas" could be important as in a growing scientific field citation flows disproportionately consolidate to citing already well-cited papers, possibly slowing and inhibiting canonical progress.[551][552]
- 5 October
- The 2021 Nobel Prize in Physics is awarded to Syukuro Manabe, Klaus Hasselmann and Giorgio Parisi for their work on climate change, resulting from the role of humanity.[553]
- 6 October
- The 2021 Nobel Prize in Chemistry is awarded to Benjamin List and David W.C. MacMillan for their work in creating a tool to build molecules, that may be useful for studies on developing new drugs and reducing the effect of chemicals on the environment.[554]
- The WHO endorses the first malaria vaccine.[555]
- A study of data traffic by popular smartphones running variants of the Android software finds substantial by-default data collection and sharing with no opt-out and implications for users' privacy, control and security.[556][557]
- With 17 studies a consortium of MICrONS[558] researchers concludes the first phase of a long-term project (BICCN) to generate an atlas of the entire mouse (mammalian) brain, releasing an atlas and census of cell types in the primary motor cortex.[559][560][561]
- 7 October – Scientists show experimentally, with brain organoids grown from stem cells, how differences between humans and chimpanzees are also substantially caused by the 98% of DNA outside the protein-coding genes, often discarded as "junk DNA" – in particular via CRE-regulated expression of the ZNF558 gene for a transcription factor.[562][563]
- 8 October – A new eco-friendly way of extracting and separating rare earth elements is described, using a bacteria-derived protein called lanmodulin, which binds easily to the metals.[564][565]

- 11 October
- Scientists report more precise dating of what appear to be the earliest bipedal footprints with hominin-like characteristics, the Trachilos footprints. They are found to be ~6.05 million years old, which is around the time of Orrorin – the previously earliest theorized species of Homininae[566] until these footprints were controversially dated in 2017,[567] despite being discovered outside of Africa in Crete, Greece. However, these apes are not necessarily associated with human evolution.[568][569][570]
- The pilot project of the "world's first automated, driverless train" is launched in the city of Hamburg, Germany. The conventional, standard-track, non-metro train technology could theoretically be implemented for rail transport worldwide and is reported to also be substantially more energy efficient.[571][572]
- Scientists project public health impacts, along with some of the environmental damage, of a, simulated, imminent Red Sea oil spill from the FSO Safer.[573][574]
- 12 October – Scientists report that for 13,115 cities extreme heat exposure of a wet bulb globe temperature above 30 °C tripled between 1983 and 2016. It increased by ~50% when the population growth in these cities is not taken into account. Urban areas are often significantly warmer than surrounding rural areas.[575][576]
- 13 October – Astronomers report the detection of hundreds of Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) from a single system.[577][578]
- 15 October – The first brain metabolome atlas of the mouse brain – and of an animal (a mammal) across different life stages – is released.[579][580]
- 16 October
- The spacecraft Lucy is launched by NASA, the first mission to explore the Trojan asteroids.[581]
- A comprehensive study by Scientists for Future concludes that nuclear fission energy cannot meaningfully contribute to climate change mitigation as it is "too dangerous, too expensive, and too sluggishly deployable" as well as "an obstacle to achieving the social-ecological transformation".[582][583][584]
- 18 October – A study shows for the first time how immunity is inherited, via epigenetic changes, in mice (mammals).[585][586]
- 19 October – Media outlets report about novel technologies for virtual try-ons of clothes for more sustainable fashion and improved online shopping, which increased relatively due to the COVID-19 pandemic.[587][588]

- 20 October
- Astronomers report the first evidence of a giant impact between two exoplanets, which occurred in the HD 172555 system, based on analysis of gas and dust concentrations.[589][590]
- Scientists report that, according to their analysis, today's domestic horses descend from the lower Volga-Don region, Russia. 273 ancient horse genomes further indicate that these populations replaced almost all local populations as they expanded rapidly throughout Eurasia from about 4200 years ago, that certain adaptations were strongly selected for by horse riding, and that equestrian material culture – including Sintashta spoke-wheeled chariots and in the case of Asia Indo-Iranian languages – spread alongside.[591][592]
- Researchers report on the first natural protein that, using lanmodulin, complexes actinium, a natural but radioactive element used in cancer therapy, alongside yttrium-90.[593][594]
- 21 October
- Medical researchers announce that on 25 September the first successful xenotransplantation of a genetically engineered pig kidney, along with the pig thymus gland to make the immune system recognize it as part of the body, to a brain-dead human with no immediate signs of rejection, moving the practice closer to clinical trials with living humans.[595][596]
- A study shows how COVID-19 may inflict long-term brain damage, including in cases of 'long COVID', via endothelial cell-death disrupting the blood–brain barrier.[597][598]
- 22 October
- Researchers describe and substantiate the hypothesis that a recent decrease in brain size "in the last 3,000 years" (previously thought to instead have occurred during the last ~28,000 years) has resulted from externalization of knowledge and group decision-making, partly via social systems of distributed cognition and sharing of information.[599][600] A study by Villmoare et al. (2022) that reanalyzes the used data refutes their findings. It concludes that "the samples need to be specific enough to test the hypothesis across different times and populations".[601][602]
- A study shows that mandatory face masks and social distancing can allow for relatively safe public transport during the COVID-19 pandemic, reducing infection rates by 93.5% and 98.1% in tracking-based simulations of common contemporary forms of public transport during congestion peak-hour.[603][604]
- 25 October
- Astronomers report, with two studies, that 'BLC1' does not appear to be a technosignature or extraterrestrial radio transmission because 15 similar observations were made between 2019 and 2020 that did not originate from around Proxima Centauri – and hence are likely results of forms of local radiofrequency interference – and propose a sequence of "verification checks for narrowband technosignature signals".[605][606][607]
- Another, clearer case of quantum advantage with Zuchongzhi is reported.[608][609][610] A third study reported that Zuchongzhi 2.1 completed a task of classically simulating random circuit sampling that "is about 6 orders of magnitude more difficult than that of Sycamore".[611]

- 27 October
- Astronomers propose a "Confidence of Life Detection" scale (CoLD) for reporting evidence of life beyond Earth.[612][613]
- Astronomers report that the orbits of the detected exoplanets hosted by the star HD 3167 are unusual: two planets (HD 3167 c; HD 3167 d) revolve around the poles of the star, whereas the third planet (HD 3167 b) orbits around the equator of the star instead.[614][615]
- Researchers release a "policy sequencing" framework, in particular for policies of polycentric governance for completely halting and preventing deforestation based on data about already implemented government-designed policies, UN-decided REDD+ initiatives and voluntary private sector initiatives of recent deforestation interventions.[616][617]
- The world's first urban autonomous vessels, 'Roboats', are deployed in the canals of Amsterdam, Netherlands. The ships developed by three institutions could carry up to five people, collect waste, deliver goods, and provide "on-demand infrastructure".[618][619]
- A potentials-assessment study proposes hypothetical portable solar-powered atmospheric water harvesting devices which are under development, along with design criteria, finding they could help a billion people to access safe drinking water, albeit such off-the-grid generation may sometimes "undermine efforts to develop permanent piped infrastructure".[620][621][622]
- 28 October
- An open letter by almost 300 scientists asks the WTO to eliminate increasing harmful fisheries subsidies.[623][624]
- One year after India and South Africa called on WTO to temporarily waive TRIPS vaccine patents for accelerated deployment of COVID-19 vaccines around the world, the WTO reportedly fails to find an accord for doing so.[625] No mechanisms of alternative medical research and development incentive-systems[626] or technical details of proposed "sharing" after certain amounts of profit[627] were reported and some argue that, instead of intellectual property rights, manufacturing know-how is the main barrier to expanding capacity.[626]
- Scientists discover that up to about 20,000 metric tons of microplastics may be stored in coral skeletons worldwide every year, marking the first time that a living microplastic "sink", or long-term storage site, has been quantified.[628][629]
- 30 October – A comprehensive review summarizes scientific research and data about health impacts of climate change.[630][631]
November
- 1 November – Astronomers report detecting, in a "first-of-its-kind" process based on SAM instruments, organic molecules, including benzoic acid, ammonia and other related unknown compounds, on the planet Mars by the Curiosity rover.[632][633]

- 2 November – A study concludes that PM2.5 air pollution induced by contemporary forms of free trade and consumption by the 19 G20 nations (the EU as a whole is not included) causes two million premature deaths annually, suggesting that the average lifetime consumption of about ~28 people in these countries causes at least one premature death (average age ~67) while developing countries "cannot be expected" to implement or be able to implement countermeasures without external support or internationally coordinated efforts.[635][634]

- 3 November
- Astronomers using the ALMA report the presence of water in SPT0311-58, a galaxy nearly 12.9 billion light-years from Earth. This is the most distant detection of a required element for life in a regular star-forming galaxy.[636][637]
- Scientists report that large shares of wild deer in the U.S. have been infected with SARS-CoV-2. The test results showed one "mismatch" for 2019, low inhibition values in 2020 and 152 positive samples (40%) in 2021.[638] A preprint published on 1 November found that ~80% of samples between late November 2020 and January were positive.[639][640] Such spillovers may cause reservoirs for mutating variants that spill back to humans – a possible source for variants of concern other than immunocompromised people.[639]
- A review outlines research and data about COVID-19 vaccinations for children – recommended in the U.S. a day previously (for 5–11 years olds) by the CDC[641] – including about populations-levels factors.[642]

- 4 November
- Astronomers report, in the Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey for the 2020s, recommended scientific priorities and investments for the next decade to help achieve the following primary goals: search for habitable exoplanets and extraterrestrial life, study black holes and neutron stars and study the growth and evolution of galaxies.[643][644]
- A study contributes to a disentangling of the current geopolitical and economic implications of and incentives for a swift renewable energy transition, suggesting i.a. that how fast fossil energy markets decline is primarily decided by the major energy importers China, India, Japan and the EU and that transition dynamics may reverse the free-rider problem in the case of energy sectors, specifically from strategic national standpoints which are not short-term.[645][646]
- Researchers demonstrate a novel X-ray imaging technique, "HiP-CT", for 3D cellular-resolution scans of whole organs, using the ESRF's EBF. The published online Human Organ Atlas includes the lungs from a donor who died with COVID-19.[647][648][649]
- 5 November – A company reports that a phase 2/3 clinical trial shows that Paxlovid can reduce COVID-19 hospitalizations of high-risk adults by 89% when given within three days after symptom onset.[650][651]
- 8 November – Scientists prove that the brain (the insular cortex of mice/mammals) also "remembers" immune activity against past infections, with reactivation – or stimulation – of the neurons being able to cause – or shape – the inflammatory immune response.[652][653]
- 9 November
- Astrophysicists report the discovery of unexplained blockage of high-energy cosmic rays entering the Galactic Center, such as a strong magnetic field.[654][655]
- Scientists report the detection of coronaviruses closely related to SARS-CoV-2 (92.6% nucleotide identity) in two bats sampled in Cambodia in 2010,[656][657][658] complementing i.a. a study published on 17 September.
- 10 November – Researchers report the development of chewing gums that could mitigate COVID-19 spread. The ingredients – CTB-ACE2 proteins grown via plants – bind to the virus.[659][660]
- 11 November
- Astronomers using the Very Large Telescope report the discovery of a black hole in NGC 1850 by viewing its influence on the motion of a star in close proximity, the first direct dynamical detection of a black hole in a young massive cluster.[661][662]
- The first-ever simulation of baryons on a quantum computer is reported by a university.[663][664]
- Astronomers identify a long filament of cold, dense gas connecting two of the Milky Way's spiral arms, the first known observation of such a galactic structure in the Milky Way.[665]
- Bionanoengineers report a novel therapy for spinal cord injury – an injectable gel of nanofibers that contain moving molecules that cause cellular signaling and mimic the matrix around cells in mice.[666][667][668]
- A study investigates how tidal energy could be best integrated into the Orkney energy system.[669] On 3 November, a review assesses the potential of tidal energy in the UK's energy systems, finding that it could, according to their considerations that include economic cost-benefit analysis, deliver 34 TWh/y or 11% of its energy demand.[670][671]
- 14 November – A time-allocation study estimates that in 2020 over 130 million hours of researchers' time were spent on peer review.[672][673]
- 16 November
- A study reports the second case of a person whose immune system apparently cleared the HIV on its own without a therapy.[674][675]
- Biochemists report one of the[clarification needed] first supercomputational approaches for the development of new antibiotic derivatives against antimicrobial resistance.[676][677]
- Scientists report a large extent of alternative splicing – cases of a single gene (a template) being used to create instructions (mRNAs) for building different proteins – in the mouse and human cortex and release the transcriptomes on a public database.[678][679]
- A tech company reveals a new 127 quantum bit processor named 'IBM Eagle', which is the most powerful quantum processor ever made.[680][681]

The image shows one Nextstrain-based visualization of genetic distance of several such variants.
- 17 November
- A systematic review and meta-analysis finds that mask-wearing cuts the incidence of COVID-19 by 53%.[683][684]
- The first 256-qubit quantum computer is announced, by a startup company, founded by scientists and funded by DARPA.[685][686]
- The largest public dataset of whole genomes is made available through a Web platform. The entire genomes of 200,000 UK Biobank participants, linked to anonymized medical information, are made more accessible for biomedical research than prior, less comprehensive datasets.[687][688]
- Scientists call for the creation of space biosecurity measures and inform the creation of planetary protection policies that aim to prevent forward contamination of extraterrestrial bodies as well as backward contamination.[689][690]
- Scientists report the development of a vaccine of mRNAs for the body build 19 proteins in tick saliva which, by enabling quick development of erythema (itchy redness) at the bite site, protects guinea pigs against Lyme disease from ticks.[691][692]
- 19 November
- The first autonomous cargo ship, MV Yara Birkeland is launched in Norway. The fully electric ship is expected to substantially reduce the need for truck journeys.[693]
- A report by Brazil's INPE based on satellite data finds deforestation of the Amazon rainforest has increased by 22% over 2020 and is at its highest level (13,235 km2) since 2006.[694][695][additional citation(s) needed]
- 21 November – Sri Lanka announces that it will lift its import ban on pesticides and herbicides, explained by both a lack of sudden changes to widely applied practices or education systems and contemporary economics and, by extension, food security, protests and high food costs. The effort to become the world's first completely organic farming nation was challenged by effects of the COVID-19 pandemic.[696][697]
- 22 November
- Scientists detect a quantum effect that blocks atoms from scattering light.[698]
- A study using data on ~30,000 patients, for the first time, indicates that aspirin may be associated with an increased (26%) risk for heart failure in persons with at least one cardiovascular risk factor.[699][700] An author notes that the findings require confirmation and the link with heart failure to be clarified.[701]
- 24 November – NASA launches the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART), the first attempt to deflect an asteroid for the purpose of learning how to protect Earth.[702]
- 25 November – Researchers systematically assess impacts of climate change mitigation options on 18 constituents of well-being, finding largely beneficial effects of demand-side solutions based on inputs from 604 studies.[703][704]
- 26 November – The WHO announces the classification of the Omicron variant as a SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern. The variant, that became dominant (74% of samples) in South Africa in November, was detected by the NGS-SA genomic surveillance on 8 November[705][706] and reported to the WHO on 24 November.[682] It has a large number of mutations that, according to early preliminary evidence, appear to increase risk of reinfection,[682] may increase transmissibility compared to Delta and may affect vaccines' efficacies with a key question being whether it causes less severe prognoses.[707][708]
- 29 November – A team of scientists reports a new form of biological reproduction in xenobots that are made up of and are emersed in frog cells.[709][710]
December
- 1 December
- Scientists discover the footprint of an ancient hominid that lived alongside Lucy.[711][712]
- Researchers develop an energy system model for 100% renewable energy, examining feasibility and grid stability in the U.S.[713][714]
- 2 December
- A method of DNA data storage with a hundred times the density of previous techniques is announced.[715]
- A stem cell-based treatment for type 1 diabetes is announced.[716][717]
- 3 December – Scientists demonstrate that grown brain cells integrated into digital systems can carry out goal-directed tasks with performance-scores. In particular, playing a simulated (via electrophysiological stimulation) Pong which the cells learned to play faster than known machine intelligence systems, albeit to a lower skill-level than both AI and humans. Moreover, the study suggests it provides first empirical evidence of information-processing capacity differences between neurons from different species.[718][719]
- 4 December – A total solar eclipse occurs in the Antarctic region.[720]
- 5 December – Researchers report the development of a system of machine learning and hyperspectral camera that can distinguish between 12 different types of plastics such as PET and PP for automated separation of waste of, as of 2020, highly unstandardized[721][additional citation(s) needed] plastics products and packaging.[722][723]
- 6 December
- Scientists show that and how the flavonoid Procyanidin C1 of the antioxidant grape seed extract increases the health- and lifespan of mice and increases the efficacy of mice' chemotherapy.[724][725]
- Sloan Digital Sky Survey's final data release of SDSS-IV including final data products and catalogs.[726][727]

- 7 December
- A study suggests that when two people wear surgical masks, while the infectious one is speaking, the risk of COVID-19 infection at a distance of 1.5 m remains below 30% after one hour, but when both wear a well-fitting FFP2 mask, it is 0.4%.[728]
- Researchers investigating sources of urban PAHs air pollution in Athens report that wood-burning could be causing a third (31%) of such urban air pollution, like diesel and oil combined or gasoline, and, especially during winter days, is responsible for nearly half of PAH cancer-risk.[729][730]
- A study suggests that mutations that promote breakthrough infections or antibody-resistance could be a new mechanism for viral evolution success of SARS-CoV-2 and that such may become a dominating mechanism of its evolution.[731] On 27 December, a preprint finds that "the rapid spread of the Omicron VOC primarily can be ascribed to the immune evasiveness rather than an inherent increase in the basic transmissibility".[732][733] Studies also showed the variant to escape the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies, including of sera from vaccinated and convalescent individuals.[734][735][736][737]
- A scientific review summarizes research and data about telemedicine. Its results indicate that, in general, outcomes of such ICT-use are as good as in-person care with health care use staying similar.[738][739]
- The Reproducibility Project: Cancer Biology shows that of 193 experiments from 53 top papers about cancer published between 2010 and 2012, only 50 replication experiments from 23 papers could be completed with effect sizes of that fraction being 85% smaller on average than the original findings. None of the papers had its experimental protocols fully described and 70% of experiments required asking for key reagents.[740][741]
- 8 December
- Researchers report the development of face masks that glow under ultraviolet light if they contain SARS-CoV-2 when the filter is taken out and sprayed with a fluorescent dye that contains antibodies from ostrich eggs.[742]
- Studies, some of which using large nationwide datasets from either Israel and Denmark, find that vaccine effectiveness of multiple common two-dosed COVID-19 vaccines is substantially lower against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant than for other common variants including the Delta variant, and that a new (often a third) dose – a booster dose – is needed and effective, with it i.a. substantially reducing deaths from the disease compared to cohorts who received two doses.[743][744][745][746][747][748]
- Applied behavioural scientists demonstrate a novel type of intervention studies, a "megastudy", and investigate the efficacy of 54 different designed by separate teams interventions to increase weekly gym-visits of ~60,000 members of a fitness chain, such as digital feedback in the form of redeemable points that are rewarded for returning to the gym after a missed workout.[749][750]
- 9 December
- The Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer, a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency, is launched by SpaceX. It is the first satellite capable of measuring the polarisation of X-rays that come from cosmic sources, such as black holes and neutron stars.[751]
- The Log4Shell security vulnerability in a Java logging framework is publicly disclosed two weeks after its discovery. Because of the ubiquity of the affected software, experts have described it as a most serious computer vulnerability.[752] In a high-level meeting, the importance of security maintenance of open-source software – often also carried out largely by few volunteers – to national security was clarified.[753][754]
- A study reviews modern analytic procedures, including mass spectrometry techniques, for characterization, analysis, and identification of unknown materials and how such were applied to study materials that, according to witnesses, dropped from hovering unknown aerial objects (or UFOs). It suggests that the full range of current capabilities of materials analysis have not been applied so far and, after reviewing a range of proposed explanations, that these materials' purposes and characteristics, such as their isotope ratios,[755] are very odd and remain unexplained.[756]
- Scientists report the development of a genome editing system, called "twin prime editing", which surpasses the original prime editing system reported in 2019 in that it allows editing large sequences of DNA, addressing the method's key drawback.[757][758]
- An mRNA vaccine against HIV with promising results in tests with mice and primates is reported.[759][760]

- 10 December – A vaccine to remove senescent cells, a key driver of the aging process, is demonstrated in mice by researchers from Japan.[761][762]
- 13 December
- Astronomers report that AT 2018cow, an extreme FBOT, "could be a neutron star or black hole with a mass less than 850 solar masses," based on high-time-resolution X-ray observation studies.[763][764]
- Scientists studying the huge Thwaites Glacier in West Antarctica report evidence that it could "shatter like a car windscreen" within five to ten years, potentially adding 65 cm to global sea levels in the long term.[765]
- Observations of 16 years of timing data from the double pulsar PSR J0737−3039 are reported to be in agreement with general relativity by studying the loss of orbital energy due to gravitational waves.[766][767]
- Researchers report the development of a database and analysis tool about perovskite solar cells which systematically integrates over 15,000 publications, in particular data about over 42,400 photovoltaic devices.[768][769]
- 14 December – Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the centre of the Milky Way, is imaged with 20 times greater detail than ever before, by astronomers using the GRAVITY instrument on the Very Large Telescope in Chile.[770][771][772]
- 15 December
- Scientists call for accelerated efforts in the development of broadly protective vaccines, especially a universal coronavirus vaccine that durably protects not just against all SARS-CoV-2 variants but also other coronaviruses, including already identified animal coronaviruses with pandemic potential.[773]
- Researchers report that NOX4 facilitates certain beneficial adaptive responses to exercise mediated by ROS (the opposite of antioxidants), which may be relevant to aging, diabetes, muscle-related and obesity interventions.[774][775]
- 16 December
- Tokamak Energy announces a more efficient design for the cryogenic electronics in fusion reactors. This provides a 50% reduction in the power needed for the cooling of high-temperature superconducting magnets.[776]
- Researchers propose buffer-zones around nature reserves where pesticide-use is drastically reduced, based on Germany-wide field study data which i.a. found insect samples in such areas to be contaminated with ~16 pesticides on average.[777][778]
- Researchers report the development of perovskite solar cells based on self-constructed high-throughput screening of mixtures and contact layers, that – based on the stability tests – are estimated to last for over two years under normal circumstances.[779][780]
- In two separate studies, researchers, using vanadium dioxide, report the development of a "smart-roof coating" for radiative cooling that switches to warming during cold temperatures[781][782] and "smart windows" that self-adapt to heat or cool for energy conservation in buildings.[783][784]
- 20 December – The first known magnetosphere around an exoplanet is reported, surrounding the hot Neptune HAT-P-11b.[785][786]
- 22 December – Japanese scientists announce a key step in the development of a quantum computer using photons, which eliminates the need for an ultracold environment used to cool existing machines.[787][788]
- 23 December – An international team reports the use of an electron microscope to change the chirality of a carbon nanotube, creating a transistor with a length of just 2.8 nanometres.[789][790]
- 24 December – A study suggests that, based on the strength of positive selection pressure, the molecular spectrum of mutations and known mutations for adaptation to mouse hosts, the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant may have evolved in mice and then spilled back to humans.[791][792]
- 25 December – The James Webb Space Telescope, "NASA's most powerful and complex space telescope"[793] and successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, launches successfully.[794]
- 26 December – A third[795] convergent graphical shell and UI framework, based on KDE/Kirigami, for the Linux operating system on phones, desktops and other devices, is released.[796][797]
- 28 December – Scientists report that production of ammonia in the clouds of Venus, possibly by life, may make the environment less acidic and suitable for life, with the atmospheric model matching observations better than earlier ones.[798][799]
- 30 December
- China's EAST tokamak sustains 120 million °C plasma for 17 minutes (1,056 seconds) for the development of fusion energy (which requires i.a. temperatures over 150 million °C).[800][801]
- Researchers report the development of "nanoantennas" made out of DNA that attach to proteins and produce a signal via fluorescence when these perform their biological functions, in particular for distinct conformational changes, i.a. enabling monitoring their motion.[802][803]
- [clarification needed]The first CRISPR-gene-edited marine animals/seafood and second set of CRISPR-edited food has gone on public sale in Japan: two fish of which one species grows to twice the size of natural specimens due to disruption of leptin, which controls appetite, and the other grows to 1.2 the natural size with the same amount of food due to disabled myostatin, which inhibits muscle growth.[804][805]
Remove ads
Predicted and scheduled events
Later date
- Engineering first light of the Vera C. Rubin Observatory's camera was anticipated for 2021 with full science operations to begin a year later.[806][807][808] Delayed to October 2022[809] and later to February 2023[810] due to the COVID-19 pandemic. First light images were released in June 2025.
Awards
- Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine – David Julius and Ardem Patapoutian for their discoveries of receptors for [i.a.] temperature and touch[811] [the discovery/mechanics of TRPV1 and PIEZO2]
- Nobel Prize in Physics – Syukuro Manabe and Klaus Hasselmann (1/2) "for the physical modelling of Earth's climate, quantifying variability and reliably predicting global warming" and Giorgio Parisi (1/2) "for the discovery of the interplay of disorder and fluctuations in physical systems from atomic to planetary scales" – all of which "for groundbreaking contributions to our understanding of complex systems"[812]
- Nobel Prize in Chemistry – Benjamin List and David W.C. MacMillan "for the development of asymmetric organocatalysis"[813]
Deaths
- 4 January – Martinus J. G. Veltman, Dutch theoretical physicist and Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1931)
- 28 January – Paul J. Crutzen, Dutch meteorologist and atmospheric chemist, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1933)
- 16 February – Bernard Lown, Lithuanian-born American inventor and cardiologist (b. 1921)[814]
- 1 April – Isamu Akasaki, Japanese engineer and physicist, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1929)
- 4 April – Robert Mundell, Canadian economist (b. 1932)
- 4 June – Richard R. Ernst, Swiss physical chemist, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1933)
- 6 June – Ei-ichi Negishi, Japanese chemist, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1935)
- 23 July – Toshihide Maskawa, Japanese physicist, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1940)
- 23 July – Steven Weinberg, American physicist, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1933)
Remove ads
See also
- Category:Science events
- Category:Science timelines
- Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on science and technology
- List of technologies
- List of emerging technologies
- List of years in science
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads