Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
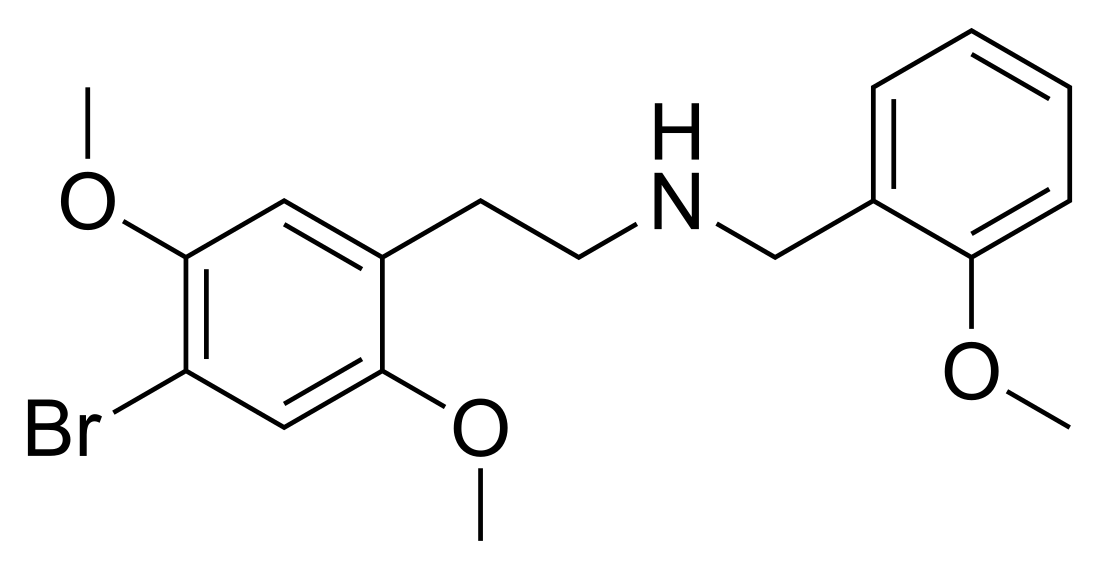
25B-NBOMe
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
25B-NBOMe, also known as NBOMe-2C-B and Cimbi-36, is a psychedelic drug of the 25-NB (NBOMe) family derived from 2C-B. It acts as a potent full agonist for the 5HT2A receptor.[3][4][5] Duration of effects lasts about 3 to 10 hours,[6] although the parent compound is rapidly cleared from the blood when used in the radiolabeled form in tracer doses.[7] Recently, Custodio et al. (2019) evaluated the potential involvement of dysregulated dopaminergic system, neuroadaptation, and brain wave changes which may contribute to the rewarding and reinforcing properties of 25B-NBOMe in rodents.[8]
The carbon-11 labeled version of this compound ([11C]Cimbi-36) was synthesized and validated as a radioactive tracer for positron emission tomography (PET) in Copenhagen.[9][10][11] As a 5-HT2A receptor agonist PET radioligand, [11C]Cimbi-36 was hypothesized to provide a more functional marker of these receptors. Also, [11C]Cimbi-36 is investigated as a potential marker of serotonin release and thus could serve as an indicator of serotonin levels in vivo. [11C]Cimbi-36 is now undergoing clinical trials as a PET-ligand in humans.[12][13][14]
25B-NBOMe was first described in the scientific literature by Ralf Heim and colleagues at the Free University of Berlin by 1999.[15]
Remove ads
Use and effects
The dose range of 25B-NBOMe has been given as 0.05 to 0.7 mg sublingually, with a typical dose estimate of 0.4 mg.[16]
Toxicity and harm potential
Summarize
Perspective
NBOMe compounds are often associated with life-threatening toxicity and death.[17][18] Studies on NBOMe family of compounds demonstrated that the substance exhibit neurotoxic and cardiotoxic activity.[19] Reports of autonomic dysfunction remains prevalent with NBOMe compounds, with most individuals experiencing sympathomimetic toxicity such as vasoconstriction, hypertension and tachycardia in addition to hallucinations.[20][21][22][23][24] Other symptoms of toxidrome include agitation or aggression, seizure, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, hypertonia, rhabdomyolysis, and death.[20][24][18] Researchers report that NBOMe intoxication frequently display signs of serotonin syndrome.[25] The likelihood of seizure is higher in NBOMes compared to other psychedelics.[19]
NBOMe and NBOHs are regularly sold as LSD in blotter papers,[18][26] which have a bitter taste and different safety profiles.[20][17] Despite high potency, recreational doses of LSD have only produced low incidents of acute toxicity.[17] Fatalities involved in NBOMe intoxication suggest that a significant number of individuals ingested the substance which they believed was LSD,[22] and researchers report that "users familiar with LSD may have a false sense of security when ingesting NBOMe inadvertently".[20] While most fatalities are due to the physical effects of the drug, there have also been reports of death due to self-harm and suicide under the influence of the substance.[27][28][20]
Given limited documentation of NBOMe consumption, the long-term effects of the substance remain unknown.[20] NBOMe compounds are not active orally,[a] and are usually taken sublingually.[30]: 3 When NBOMes are administered sublingually, numbness of the tongue and mouth followed by a metallic chemical taste was observed, and researchers describe this physical side effect as one of the main discriminants between NBOMe compounds and LSD.[31][32][33]Neurotoxic and cardiotoxic actions
Many of the NBOMe compounds have high potency agonist activity at additional 5-HT receptors and prolonged activation of 5-HT2B can cause cardiac valvulopathy in high doses and chronic use.[18][23] 5-HT2B receptors have been strongly implicated in causing drug-induced valvular heart disease.[34][35][36] The high affinity of NBOMe compounds for adrenergic α1 receptor has been reported to contribute to the stimulant-type cardiovascular effects.[23]
In vitro studies, 25C-NBOMe has been shown to exhibit cytotoxicity on neuronal cell lines SH-SY5Y, PC12, and SN471, and the compound was more potent than methamphetamine at reducing the visibility of the respective cells; the neurotoxicity of the compound involves activation of MAPK/ERK cascade and inhibition of Akt/PKB signaling pathway.[19] 25C-NBOMe, including the other derivative 25D-NBOMe, reduced the visibility of cardiomyocytes H9c2 cells, and both substances downregulated expression level of p21 (CDC24/RAC)-activated kinase 1 (PAK1), an enzyme with documented cardiac protective effects.[19]
Preliminary studies on 25C-NBOMe have shown that the substance is toxic to development, heart health, and brain health in zebrafish, rats, and Artemia salina, a common organism for studying potential drug effects on humans, but more research is needed on the topic, the doses, and if the toxicology results apply to humans. Researchers of the study also recommended further investigation of the drug's potential in damaging pregnant women and their fetus due to the substance's damaging effects to development.[37][38]Emergency treatment
At present, there are no specific antidotes for NBOMes, and all acute intoxication is managed by symptomatic treatments, such as administration of benzodiazepines, antipsychotic drugs, and antiarrhythmic agents, such as beta blockers; some emergency interventions are intended to specifically treat rhabdomyolysis, which may lead to critical complications such as metabolic acidosis and acute kidney injury.[19]
Remove ads
Interactions
Pharmacology
Summarize
Perspective
Pharmacodynamics
25B-NBOMe is a selective serotonin 5-HT2 receptor agonist.[40] It showed roughly the same affinity for the serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptors in one study (Ki = 0.5–1.7 nM).[40] However, in another study, it showed 12- to 20-fold selectivity for the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor (Ki = 0.5 nM) over the serotonin 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors (Ki = 10 and 6.2 nM, respectively).[54] The drug is highly selective for the serotonin 5-HT2 receptors over a variety of other serotonin receptors, as well as over various other monoamine receptors and over the monoamine transporters (>200-fold selectivity).[40][54] However, 25B-NBOMe is a low-potency partial agonist of the rat and mouse trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) but is inactive at the human TAAR1.[52]
25B-NBOMe has been found to increase levels of glutamate, serotonin, dopamine, and acetylcholine in the frontal cortex, striatum, and nucleus accumbens in rats.[55] Other serotonergic psychedelics like LSD and DOI have also been found to increase glutamate levels in the frontal cortex in rodents, and this effect can be blocked by the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor antagonist volinanserin (MDL-100,907).[55] 25B-NBOMe shows an inverted U-shaped dose–response curve in terms of neurotransmitter elevations in multiple brain areas.[55] This may be due to an inhibitory effect of serotonin 5-HT2C receptors at higher doses.[55] 25B-NBOMe produces the head-twitch response, a behavioral proxy of psychedelic effects, in rodents, and this effect shows an inverted U-shaped dose–response curve similarly to its influences on neurotransmitter levels.[55] The head twitches and hallucinogenic effects of 25B-NBOMe may be due to increased cortical glutamate release secondary to serotonin 5-HT2A receptor activation.[55] The effects of 25B-NBOMe on levels of other neurotransmitters, such as accumbal dopamine concentrations, may also be mediated by activation of serotonin 5-HT2A receptors and glutamate elevation.[55] It has been suggested that the serotonin elevations with 25B-NBOMe may be involved in its production of serotonin syndrome in humans.[54]
Unlike many other serotonergic psychedelics, 25B-NBOMe has been found to produce reinforcing effects in rodents, including conditioned place preference (CPP) and self-administration, and hence may have misuse potential.[56][57][54] Accordingly, 25B-NBOMe robustly increased dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens in rodents similarly to but a lesser extent than methamphetamine, and its reinforcing effects could be blocked by the dopamine receptor antagonists SCH-23390 and haloperidol.[56][57][54] Serotonin 5-HT2A receptor activation is known to increase dopamine release in the mesolimbic pathway.[57] However, the reinforcing effects of 25B-NBOMe were not blocked by the selective serotonin 5-HT2A receptor antagonist ketanserin.[56][57] Similarly to 25B-NBOMe, 25N-NBOMe has also shown reinforcing effects in rodents.[58] More research is needed to elucidate how 25B-NBOMe and other NBOMe drugs produce reinforcing effects in animals.[57]
25B-NBOMe has been found to decrease locomotor activity in rodents.[59][55]
Remove ads
Chemistry
Analogues
Analogues of 25B-NBOMe include 2C-B, DOB, 25B-NB, DOB-NBOMe, 25I-NBOMe, 25C-NBOMe, 25B-NBOH, 25B-NBF, 2CBFly-NBOMe, 2CBCB-NBOMe (NBOMe-TCB-2), DMBMPP, and 25B-NAcPip, among others.
History
25B-NBOMe was first described in the scientific literature, in the form of conference abstracts, by Ralf Heim and colleagues at the Free University of Berlin by 1999.[15]
Society and culture
Legal status
Canada
As of October 31, 2016; 25B-NBOMe is a controlled substance (Schedule III) in Canada.[60]
China
As of October 2015 25B-NBOMe is a controlled substance in China.[61]
Czech Republic
25B-NBOMe is banned in the Czech Republic.[62]
Finland
Scheduled in the "government decree on substances, preparations and plants considered to be narcotic drugs".[63]
Russia
Banned as a narcotic drug since May 5, 2015.[64]
Sweden
In Sweden, the Riksdag added 25B-NBOMe to schedule I ("substances, plant materials and fungi which normally do not have medical use") as narcotics in Sweden as of August 1, 2013, published by the Medical Products Agency in their regulation LVFS 2013:15 listed as 25B-NBOMe 2-(4-bromo-2,5-dimetoxifenyl)-N-(2-metoxibensyl)etanamin.[65]
United Kingdom
This substance is a Class A drug in the United Kingdom as a result of the N-benzylphenethylamine catch-all clause in the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971.[66]
United States
In November 2013, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration placed 25B-NBOMe (along with 25I-NBOMe and 25C-NBOMe) in Schedule I of the Controlled Substances Act, making it illegal to manufacture, buy, possess, process, or distribute.[67]
Remove ads
Notes
- The potency of N-benzylphenethylamines via buccal, sublingual, or nasal absorption is 50- to 100-fold greater (by weight) than oral route compared to the parent 2C-x compounds.[29] Researchers hypothesize the low oral metabolic stability of N-benzylphenethylamines is likely causing the low bioavailability on the oral route, although the metabolic profile of this compounds remains unpredictable; therefore researchers state that the fatalities linked to these substances may partly be explained by differences in the metabolism between individuals.[29]
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads