Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
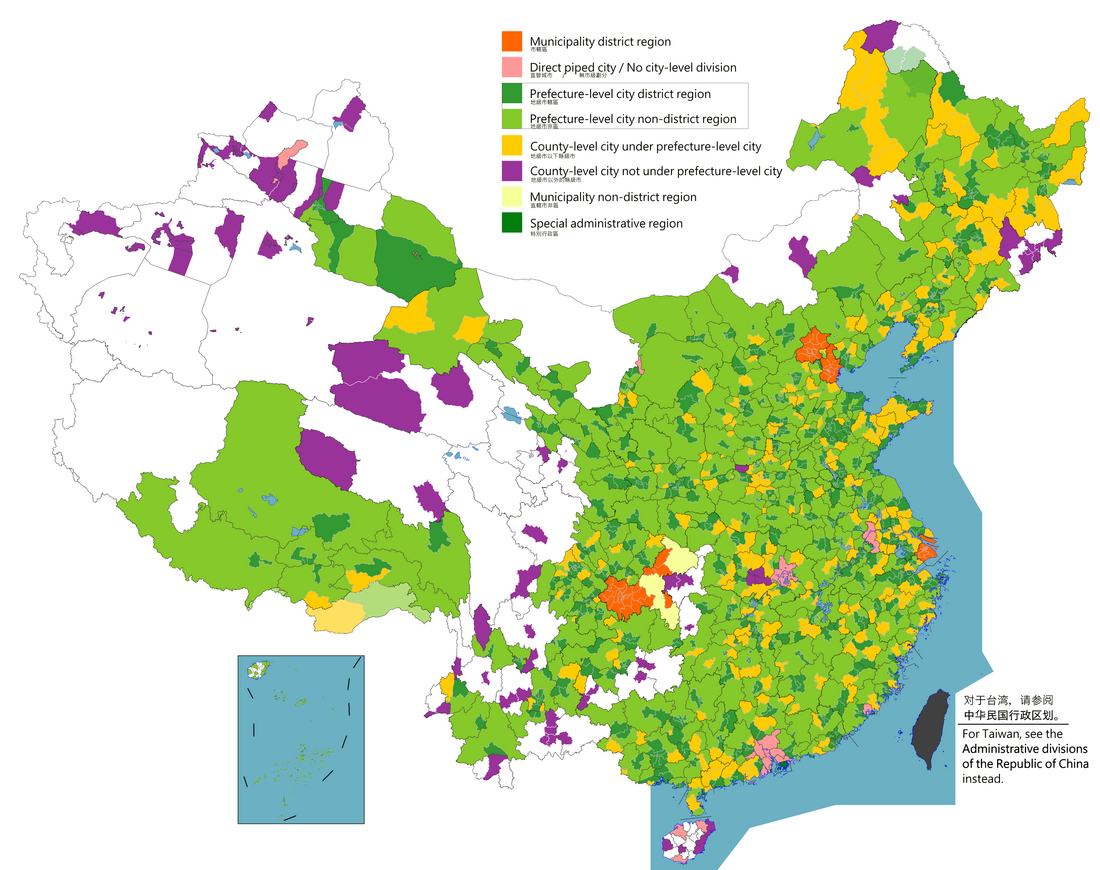
List of cities in China
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
For a list sorted by population, see List of cities in China by population.
This article is about cities in the People's Republic of China (not including Taiwan). For cities in the Republic of China after 1949, see List of cities in Taiwan. For historical prefectural-level divisions of China, see List of fu prefectures of China.
According to the administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China, there are three levels of cities: provincial-level cities[1] (consisting of directly-administered municipalities and the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau[2][3]), prefecture-level cities, and county-level cities. As of January 2024, the PRC has a total of 707 cities: 4 municipalities, 2 SARs, 293 prefecture-level cities (including the 15 sub-provincial cities) and 408 county-level cities (including the 38 sub-prefectural cities and 12 XXPC cities). This list does not include any cities in the disputed Taiwan Province and portions of Fujian Province, which are claimed by the PRC under the One China Policy, as these areas are controlled by the Republic of China (see the List of cities in Taiwan).


Quick facts City (shi), Chinese name ...
| City (shi) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese name | |||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 市 | ||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 市 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Tibetan name | |||||||||||
| Tibetan | གྲོང་ཁྱེར། | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Zhuang name | |||||||||||
| Zhuang | Si | ||||||||||
| Korean name | |||||||||||
| Hangul | 시 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||||||
| Mongolian Cyrillic | хот | ||||||||||
| Mongolian script | ᠬᠣᠲᠠ | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Uyghur name | |||||||||||
| Uyghur | شەھەر | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Manchu name | |||||||||||
| Manchu script | ᡥᠣᡨᠣᠨ | ||||||||||
| Möllendorff | hoton | ||||||||||
| Kazakh name | |||||||||||
| Kazakh | قالا қала qala | ||||||||||
| Kyrgyz name | |||||||||||
| Kyrgyz | شاار шаар şaar | ||||||||||
| Daur name | |||||||||||
| Daur | hotn | ||||||||||
| Xibe name | |||||||||||
| Xibe | ᡥᠣᡨᠣᠨ hoton | ||||||||||
| Evenki name | |||||||||||
| Evenki | HƟTƟNG | ||||||||||
| Oroqen name | |||||||||||
| Oroqen | kutuun | ||||||||||
Close
Prefecture-level cities nearly always contain multiple counties (县), county-level cities, and other such sub-divisions. Because of this, prefecture-level cities often overlap in area with county-level cities.
Four cities are centrally administered municipalities, which include dense urban areas, suburbs, and large rural areas: Chongqing (32.05 million[4]), Shanghai (24.87 million[4]), Beijing (21.89 million[4]), and Tianjin (13.87 million[4]).
In 2024, there were 105 cities governed by the People's Republic of China with an urban population of over 1 million.[5]
Remove ads
List of cities
Contemporary cities
Types of cities
More information Name, Chinese ...
| Name | Chinese | No. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provincial-level city division | |||
| Direct-administered municipality | 直辖市 | 4 | |
| Prefectural-level city divisions | |||
Prefecture-level city
|
地级市
|
293
| |
| County-level city divisions | |||
County-level city
|
县级市
|
397
| |
| Special administrative region | |||
| Special administrative region | 特别行政区 | 2 | |
Close
More information City, Chinese ...
| City | Chinese | Province | Prefecture | Founded (PRC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hong Kong | 香港特别行政區 | ZZZ-SARautonomous | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1997-07-01 |
| Macau | 澳門特别行政區 | ZZZ-SARautonomous | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1999-12-20 |
| Beijing | 北京市 | ZZZ-municipalitymunicipal | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1949-10-01 |
| Chongqing | 重庆市 | ZZZ-municipalitymunicipal | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1997-03-14 |
| Shanghai | 上海市 | ZZZ-municipalitymunicipal | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1949-10-01 |
| Tianjin | 天津市 | ZZZ-municipalitymunicipal | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1967-01-02 |
| Anqing | 安庆市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1979-11-04 |
| Bengbu | 蚌埠市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Bozhou | 亳州市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-05-21 |
| Chaohu | 巢湖市 | Anhui | Hefei | 2011-07-14 |
| Chizhou | 池州市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-25 |
| Chuzhou | 滁州市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1992-12-20 |
| Fuyang | 阜阳市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1996-01-01 |
| Guangde | 广德市 | Anhui | Xuancheng | 2019-07-12 |
| Hefei | 合肥市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Huaibei | 淮北市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1960-04-16 |
| Huainan | 淮南市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1951-01-18 |
| Huangshan | 黄山市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1987-11-27 |
| Jieshou | 界首市 | Anhui | Fuyang | 1989-09-27 |
| Lu'an | 六安市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1999-09-02 |
| Ma'anshan | 马鞍山市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1956-10-12 |
| Mingguang | 明光市 | Anhui | Chuzhou | 1994-05-31 |
| Ningguo | 宁国市 | Anhui | Xuancheng | 1997-03-11 |
| Qianshan | 潜山市 | Anhui | Anqing | 2018-07-02 |
| Suzhou | 宿州市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1998-12-06 |
| Tianchang | 天长市 | Anhui | Chuzhou | 1993-09-18 |
| Tongcheng | 桐城市 | Anhui | Anqing | 1996-08-20 |
| Tongling | 铜陵市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1971-12-11 |
| Wuhu | 芜湖市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1972-12-30 |
| Wuwei | 无为市 | Anhui | Wuhu | 2019-11-20 |
| Xuancheng | 宣城市 | Anhui | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-25 |
| Fu'an | 福安市 | Fujian | Ningde | 1989-11-13 |
| Fuding | 福鼎市 | Fujian | Ningde | 1995-10-13 |
| Fuqing | 福清市 | Fujian | Fuzhou | 1990-12-26 |
| Fuzhou | 福州市 | Fujian | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Jian'ou | 建瓯市 | Fujian | Nanping | 1992-10-20 |
| Jinjiang | 晋江市 | Fujian | Quanzhou | 1992-03-06 |
| Longhai | 龙海市 | Fujian | Zhangzhou | 1993-05-12 |
| Longyan | 龙岩市 | Fujian | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1996-11-20 |
| Nan'an | 南安市 | Fujian | Quanzhou | 1993-05-12 |
| Nanping | 南平市 | Fujian | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1994-09-05 |
| Ningde | 宁德市 | Fujian | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1999-11-14 |
| Putian | 莆田市 | Fujian | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-09-09 |
| Quanzhou | 泉州市 | Fujian | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1985-05-14 |
| Sanming | 三明市 | Fujian | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-04-28 |
| Shaowu | 邵武市 | Fujian | Nanping | 1983-08-17 |
| Shishi | 石狮市 | Fujian | Quanzhou | 1987-12-17 |
| Wuyishan | 武夷山市 | Fujian | Nanping | 1989-08-21 |
| Xiamen | 厦门市 | Fujian | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Yong'an | 永安市 | Fujian | Sanming | 1984-09-12 |
| Zhangping | 漳平市 | Fujian | Longyan | 1990-08-15 |
| Zhangzhou | 漳州市 | Fujian | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1985-05-14 |
| Baiyin | 白银市 | Gansu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1985-05-14 |
| Dingxi | 定西市 | Gansu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2003-04-04 |
| Dunhuang | 敦煌市 | Gansu | Jiuquan | 1987-08-21 |
| Hezuo | 合作市 | Gansu | Gannan | 1996-05-28 |
| Huating | 华亭市 | Gansu | Pingliang | 2018-07-02 |
| Jiayuguan | 嘉峪关市 | Gansu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1971-09-10 |
| Jinchang | 金昌市 | Gansu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1981-02-09 |
| Jiuquan | 酒泉市 | Gansu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2002-06-18 |
| Lanzhou | 兰州市 | Gansu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Linxia | 临夏市 | Gansu | Linxia | 1983-08-31 |
| Longnan | 陇南市 | Gansu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2004-01-11 |
| Pingliang | 平凉市 | Gansu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2002-06-02 |
| Qingyang | 庆阳市 | Gansu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2002-06-22 |
| Tianshui | 天水市 | Gansu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1985-07-08 |
| Wuwei | 武威市 | Gansu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2001-05-09 |
| Yumen | 玉门市 | Gansu | Jiuquan | 1961-11-15 |
| Zhangye | 张掖市 | Gansu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2002-03-01 |
| Chaozhou | 潮州市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1991-12-07 |
| Dongguan | 东莞市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1988-01-07 |
| Enping | 恩平市 | Guangdong | Jiangmen | 1994-02-28 |
| Foshan | 佛山市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1975-11-22 |
| Gaozhou | 高州市 | Guangdong | Maoming | 1993-06-08 |
| Guangzhou | 广州市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1954-06-19 |
| Heshan | 鹤山市 | Guangdong | Jiangmen | 1993-11-08 |
| Heyuan | 河源市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1988-01-07 |
| Huazhou | 化州市 | Guangdong | Maoming | 1994-07-04 |
| Huizhou | 惠州市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1988-01-07 |
| Jiangmen | 江门市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1975-11-22 |
| Jieyang | 揭阳市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1991-12-07 |
| Kaiping | 开平市 | Guangdong | Jiangmen | 1993-01-05 |
| Lechang | 乐昌市 | Guangdong | Shaoguan | 1994-04-28 |
| Leizhou | 雷州市 | Guangdong | Zhanjiang | 1994-04-26 |
| Lianjiang | 廉江市 | Guangdong | Zhanjiang | 1993-12-10 |
| Lianzhou | 连州市 | Guangdong | Qingyuan | 1994-04-22 |
| Lufeng | 陆丰市 | Guangdong | Shanwei | 1995-01-19 |
| Luoding | 罗定市 | Guangdong | Yunfu | 1993-04-08 |
| Maoming | 茂名市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1975-11-22 |
| Meizhou | 梅州市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1988-01-07 |
| Nanxiong | 南雄市 | Guangdong | Shaoguan | 1996-06-17 |
| Puning | 普宁市 | Guangdong | Jieyang | 1993-04-06 |
| Qingyuan | 清远市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1988-01-07 |
| Shantou | 汕头市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1975-11-22 |
| Shanwei | 汕尾市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1988-01-07 |
| Shaoguan | 韶关市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1975-11-22 |
| Shenzhen | 深圳市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1979-03-05 |
| Sihui | 四会市 | Guangdong | Zhaoqing | 1993-11-25 |
| Taishan | 台山市 | Guangdong | Jiangmen | 1992-04-17 |
| Wuchuan | 吴川市 | Guangdong | Zhanjiang | 1994-05-26 |
| Xingning | 兴宁市 | Guangdong | Meizhou | 1994-06-06 |
| Xinyi | 信宜市 | Guangdong | Maoming | 1995-09-11 |
| Yangchun | 阳春市 | Guangdong | Yangjiang | 1994-05-05 |
| Yangjiang | 阳江市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1988-01-07 |
| Yingde | 英德市 | Guangdong | Qingyuan | 1994-01-12 |
| Yunfu | 云浮市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1994-04-05 |
| Zhanjiang | 湛江市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1975-11-22 |
| Zhaoqing | 肇庆市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1988-01-07 |
| Zhongshan | 中山市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1988-01-07 |
| Zhuhai | 珠海市 | Guangdong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1979-03-05 |
| Baise | 百色市 | Guangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2002-06-02 |
| Beihai | 北海市 | Guangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-10-08 |
| Beiliu | 北流市 | Guangxi | Yulin | 1994-04-18 |
| Cenxi | 岑溪市 | Guangxi | Wuzhou | 1995-09-11 |
| Chongzuo | 崇左市 | Guangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2002-12-23 |
| Dongxing | 东兴市 | Guangxi | Fangchenggang | 1996-04-29 |
| Fangchenggang | 防城港市 | Guangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1993-05-23 |
| Guigang | 贵港市 | Guangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1995-10-27 |
| Guilin | 桂林市 | Guangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1961-11-25 |
| Guiping | 桂平市 | Guangxi | Guigang | 1994-05-18 |
| Hechi | 河池市 | Guangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2002-06-18 |
| Hengzhou | 横州市 | Guangxi | Nanning | 2021-02-03 |
| Heshan | 合山市 | Guangxi | Laibin | 1981-06-29 |
| Hezhou | 贺州市 | Guangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2002-06-18 |
| Jingxi | 靖西市 | Guangxi | Baise | 2015-08-01 |
| Laibin | 来宾市 | Guangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2002-09-29 |
| Lipu | 荔浦市 | Guangxi | Guilin | 2018-07-02 |
| Liuzhou | 柳州市 | Guangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1961-11-25 |
| Nanning | 南宁市 | Guangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1961-12-23 |
| Pingguo | 平果市 | Guangxi | Baise | 2019-11-20 |
| Pingxiang | 凭祥市 | Guangxi | Chongzuo | 1961-05-27 |
| Qinzhou | 钦州市 | Guangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1994-06-28 |
| Wuzhou | 梧州市 | Guangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1961-11-25 |
| Yulin | 玉林市 | Guangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1997-04-22 |
| Anshun | 安顺市 | Guizhou | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-23 |
| Bijie | 毕节市 | Guizhou | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2011-10-22 |
| Chishui | 赤水市 | Guizhou | Zunyi | 1990-09-30 |
| Duyun | 都匀市 | Guizhou | Qiannan | 1966-03-09 |
| Fuquan | 福泉市 | Guizhou | Qiannan | 1996-12-02 |
| Guiyang | 贵阳市 | Guizhou | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Kaili | 凯里市 | Guizhou | Qiandongnan | 1983-08-19 |
| Liupanshui | 六盘水市 | Guizhou | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1978-12-18 |
| Panzhou | 盘州市 | Guizhou | Liupanshui | 2017-04-09 |
| Qianxi | 黔西市 | Guizhou | Bijie | 2021-01-20 |
| Qingzhen | 清镇市 | Guizhou | Guiyang | 1992-11-06 |
| Renhuai | 仁怀市 | Guizhou | Zunyi | 1995-11-30 |
| Tongren | 铜仁市 | Guizhou | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2011-10-22 |
| Xingren | 兴仁市 | Guizhou | Qianxinan | 2018-07-02 |
| Xingyi | 兴义市 | Guizhou | Qianxinan | 1987-11-06 |
| Zunyi | 遵义市 | Guizhou | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1997-06-10 |
| Danzhou | 儋州市 | Hainan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2015-02-19 |
| Dongfang | 东方市 | Hainan | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1997-03-12 |
| Haikou | 海口市 | Hainan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1986-05-31 |
| Qionghai | 琼海市 | Hainan | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1992-11-06 |
| Sansha | 三沙市 | Hainan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2012-06-21 |
| Sanya | 三亚市 | Hainan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1987-11-20 |
| Wanning | 万宁市 | Hainan | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1996-08-05 |
| Wenchang | 文昌市 | Hainan | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1995-11-07 |
| Wuzhishan | 五指山市 | Hainan | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1986-06-12 |
| Anguo | 安国市 | Hebei | Baoding | 1991-05-06 |
| Baoding | 保定市 | Hebei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-11-15 |
| Bazhou | 霸州市 | Hebei | Langfang | 1990-01-04 |
| Botou | 泊头市 | Hebei | Cangzhou | 1982-12-13 |
| Cangzhou | 沧州市 | Hebei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-11-15 |
| Chengde | 承德市 | Hebei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-11-15 |
| Dingzhou | 定州市 | Hebei | Baoding | 1986-03-05 |
| Gaobeidian | 高碑店市 | Hebei | Baoding | 1993-04-09 |
| Handan | 邯郸市 | Hebei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-11-15 |
| Hengshui | 衡水市 | Hebei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1996-05-31 |
| Hejian | 河间市 | Hebei | Cangzhou | 1990-10-18 |
| Huanghua | 黄骅市 | Hebei | Cangzhou | 1989-07-27 |
| Jinzhou | 晋州市 | Hebei | Shijiazhuang | 1991-11-30 |
| Langfang | 廊坊市 | Hebei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1988-09-13 |
| Luanzhou | 滦州市 | Hebei | Tangshan | 2018-07-02 |
| Nangong | 南宫市 | Hebei | Xingtai | 1986-03-05 |
| Pingquan | 平泉市 | Hebei | Chengde | 2017-04-09 |
| Qian'an | 迁安市 | Hebei | Tangshan | 1996-10-10 |
| Qinhuangdao | 秦皇岛市 | Hebei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-03-03 |
| Renqiu | 任丘市 | Hebei | Cangzhou | 1986-03-05 |
| Sanhe | 三河市 | Hebei | Langfang | 1993-03-03 |
| Shahe | 沙河市 | Hebei | Xingtai | 1987-02-20 |
| Shenzhou | 深州市 | Hebei | Hengshui | 1994-07-04 |
| Shijiazhuang | 石家庄市 | Hebei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1978-03-11 |
| Tangshan | 唐山市 | Hebei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1978-03-11 |
| Xinji | 辛集市 | Hebei | Shijiazhuang | 1986-03-05 |
| Wu'an | 武安市 | Hebei | Handan | 1988-09-01 |
| Xingtai | 邢台市 | Hebei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-11-15 |
| Xinle | 新乐市 | Hebei | Shijiazhuang | 1992-10-08 |
| Zhangjiakou | 张家口市 | Hebei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-11-15 |
| Zhuozhou | 涿州市 | Hebei | Baoding | 1986-09-24 |
| Zunhua | 遵化市 | Hebei | Tangshan | 1992-02-17 |
| Anda | 安达市 | Heilongjiang | Suihua | 1984-11-17 |
| Bei'an | 北安市 | Heilongjiang | Heihe | 1982-12-18 |
| Daqing | 大庆市 | Heilongjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1965-12-28 |
| Dongning | 东宁市 | Heilongjiang | Mudanjiang | 2015-12-15 |
| Fujin | 富锦市 | Heilongjiang | Jiamusi | 1988-08-30 |
| Fuyuan | 抚远市 | Heilongjiang | Jiamusi | 2016-01-13 |
| Hailin | 海林市 | Heilongjiang | Mudanjiang | 1992-07-28 |
| Hailun | 海伦市 | Heilongjiang | Suihua | 1989-12-23 |
| Harbin | 哈尔滨市 | Heilongjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1954-06-19 |
| Hegang | 鹤岗市 | Heilongjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1966-02-08 |
| Heihe | 黑河市 | Heilongjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1993-02-08 |
| Hulin | 虎林市 | Heilongjiang | Jixi | 1996-10-11 |
| Jiamusi | 佳木斯市 | Heilongjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-10-08 |
| Jixi | 鸡西市 | Heilongjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1966-02-08 |
| Mishan | 密山市 | Heilongjiang | Jixi | 1988-11-17 |
| Mohe | 漠河市 | Heilongjiang | Daxing'anling | 2018-02-22 |
| Mudanjiang | 牡丹江市 | Heilongjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-10-08 |
| Muling | 穆棱市 | Heilongjiang | Mudanjiang | 1995-03-07 |
| Nehe | 讷河市 | Heilongjiang | Qiqihar | 1992-09-02 |
| Nenjiang | 嫩江市 | Heilongjiang | Heihe | 2019-07-12 |
| Ning'an | 宁安市 | Heilongjiang | Mudanjiang | 1993-02-12 |
| Qiqihar | 齐齐哈尔市 | Heilongjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1964-01-15 |
| Qitaihe | 七台河市 | Heilongjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-10-08 |
| Shangzhi | 尚志市 | Heilongjiang | Harbin | 1988-09-14 |
| Shuangyashan | 双鸭山市 | Heilongjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1966-02-08 |
| Suifenhe | 绥芬河市 | Heilongjiang | Mudanjiang | 1975-08-15 |
| Suihua | 绥化市 | Heilongjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1999-12-28 |
| Tieli | 铁力市 | Heilongjiang | Yichun | 1988-09-13 |
| Tongjiang | 同江市 | Heilongjiang | Jiamusi | 1987-02-24 |
| Wuchang | 五常市 | Heilongjiang | Harbin | 1993-06-01 |
| Wudalianchi | 五大连池市 | Heilongjiang | Heihe | 1983-10-08 |
| Yichun | 伊春市 | Heilongjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1979-12-14 |
| Zhaodong | 肇东市 | Heilongjiang | Suihua | 1986-09-08 |
| Anyang | 安阳市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1982-03-10 |
| Changge | 长葛市 | Henan | Xuchang | 1993-12-14 |
| Changyuan | 长垣市 | Henan | Xinxiang | 2019-07-12 |
| Dengfeng | 登封市 | Henan | Zhengzhou | 1994-05-30 |
| Dengzhou | 邓州市 | Henan | Nanyang | 1988-11-17 |
| Gongyi | 巩义市 | Henan | Zhengzhou | 1991-06-12 |
| Hebi | 鹤壁市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1974-01-19 |
| Huixian | 辉县市 | Henan | Xinxiang | 1988-10-11 |
| Jiaozuo | 焦作市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1974-01-19 |
| Jiyuan | 济源市 | Henan | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1988-06-25 |
| Kaifeng | 开封市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1961-12-25 |
| Lingbao | 灵宝市 | Henan | Sanmenxia | 1993-05-12 |
| Linzhou | 林州市 | Henan | Anyang | 1994-01-24 |
| Luohe | 漯河市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1986-01-18 |
| Luoyang | 洛阳市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1964-04-30 |
| Mengzhou | 孟州市 | Henan | Jiaozuo | 1996-04-29 |
| Nanyang | 南阳市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1994-07-01 |
| Pingdingshan | 平顶山市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1969-03-15 |
| Puyang | 濮阳市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-09-01 |
| Qinyang | 沁阳市 | Henan | Jiaozuo | 1989-09-27 |
| Ruzhou | 汝州市 | Henan | Pingdingshan | 1988-06-25 |
| Sanmenxia | 三门峡市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1986-01-18 |
| Shangqiu | 商丘市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1997-06-10 |
| Weihui | 卫辉市 | Henan | Xinxiang | 1988-10-08 |
| Wugang | 舞钢市 | Henan | Pingdingshan | 1990-09-04 |
| Xiangcheng | 项城市 | Henan | Zhoukou | 1993-12-16 |
| Xingyang | 荥阳市 | Henan | Zhengzhou | 1994-04-05 |
| Xinmi | 新密市 | Henan | Zhengzhou | 1994-04-05 |
| Xinxiang | 新乡市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1982-03-10 |
| Xinyang | 信阳市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1998-06-09 |
| Xinzheng | 新郑市 | Henan | Zhengzhou | 1994-05-16 |
| Xuchang | 许昌市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1986-01-18 |
| Yanshi | 偃师市 | Henan | Luoyang | 1993-12-15 |
| Yima | 义马市 | Henan | Sanmenxia | 1981-04-04 |
| Yongcheng | 永城市 | Henan | Shangqiu | 1996-10-11 |
| Yuzhou | 禹州市 | Henan | Xuchang | 1988-06-25 |
| Zhengzhou | 郑州市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Zhoukou | 周口市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-08 |
| Zhumadian | 驻马店市 | Henan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-08 |
| Anlu | 安陆市 | Hubei | Xiaogan | 1987-09-04 |
| Chibi | 赤壁市 | Hubei | Xianning | 1986-05-27 |
| Dangyang | 当阳市 | Hubei | Yichang | 1988-10-22 |
| Danjiangkou | 丹江口市 | Hubei | Shiyan | 1983-08-19 |
| Daye | 大冶市 | Hubei | Huangshi | 1994-02-18 |
| Enshi | 恩施市 | Hubei | Enshi | 1981-11-07 |
| Ezhou | 鄂州市 | Hubei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-08-19 |
| Guangshui | 广水市 | Hubei | Suizhou | 1988-10-11 |
| Hanchuan | 汉川市 | Hubei | Xiaogan | 1997-03-12 |
| Honghu | 洪湖市 | Hubei | Jingzhou | 1987-07-31 |
| Huanggang | 黄冈市 | Hubei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1995-12-23 |
| Huangshi | 黄石市 | Hubei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1950-08-30 |
| Jianli | 监利市 | Hubei | Jingzhou | 2020-06-12 |
| Jingmen | 荆门市 | Hubei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-08-19 |
| Jingshan | 京山市 | Hubei | Jingmen | 2018-02-22 |
| Jingzhou | 荆州市 | Hubei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1994-09-29 |
| Laohekou | 老河口市 | Hubei | Xiangyang | 1979-11-16 |
| Lichuan | 利川市 | Hubei | Enshi | 1986-05-27 |
| Macheng | 麻城市 | Hubei | Huanggang | 1986-05-27 |
| Qianjiang | 潜江市 | Hubei | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1988-05-25 |
| Shishou | 石首市 | Hubei | Jingzhou | 1986-05-27 |
| Shiyan | 十堰市 | Hubei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1973-02-17 |
| Suizhou | 随州市 | Hubei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-25 |
| Songzi | 松滋市 | Hubei | Jingzhou | 1995-12-29 |
| Tianmen | 天门市 | Hubei | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1987-08-03 |
| Wuhan | 武汉市 | Hubei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1954-06-19 |
| Wuxue | 武穴市 | Hubei | Huanggang | 1987-10-23 |
| Xiangyang | 襄阳市 | Hubei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1979-06-21 |
| Xianning | 咸宁市 | Hubei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1998-12-06 |
| Xiantao | 仙桃市 | Hubei | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1986-05-27 |
| Xiaogan | 孝感市 | Hubei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1993-04-10 |
| Yichang | 宜昌市 | Hubei | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1979-06-21 |
| Yicheng | 宜城市 | Hubei | Xiangyang | 1994-06-10 |
| Yidu | 宜都市 | Hubei | Yichang | 1987-11-30 |
| Yingcheng | 应城市 | Hubei | Xiaogan | 1986-05-27 |
| Zaoyang | 枣阳市 | Hubei | Xiangyang | 1988-01-08 |
| Zhijiang | 枝江市 | Hubei | Yichang | 1996-07-30 |
| Zhongxiang | 钟祥市 | Hubei | Jingmen | 1992-05-20 |
| Changde | 常德市 | Hunan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1988-01-23 |
| Changning | 常宁市 | Hunan | Hengyang | 1996-11-26 |
| Changsha | 长沙市 | Hunan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Chenzhou | 郴州市 | Hunan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1994-12-17 |
| Hengyang | 衡阳市 | Hunan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1980-02-20 |
| Hongjiang | 洪江市 | Hunan | Huaihua | 1979-09-01 |
| Huaihua | 怀化市 | Hunan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1997-11-29 |
| Jinshi | 津市市 | Hunan | Changde | 1979-12-19 |
| Jishou | 吉首市 | Hunan | Xiangxi | 1982-08-03 |
| Leiyang | 耒阳市 | Hunan | Hengyang | 1986-11-11 |
| Lengshuijiang | 冷水江市 | Hunan | Loudi | 1983-07-13 |
| Lianyuan | 涟源市 | Hunan | Loudi | 1987-06-10 |
| Liling | 醴陵市 | Hunan | Zhuzhou | 1985-05-24 |
| Linxiang | 临湘市 | Hunan | Yueyang | 1992-09-01 |
| Liuyang | 浏阳市 | Hunan | Changsha | 1993-01-16 |
| Loudi | 娄底市 | Hunan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1999-01-20 |
| Miluo | 汨罗市 | Hunan | Yueyang | 1987-09-23 |
| Ningxiang | 宁乡市 | Hunan | Changsha | 2017-04-09 |
| Shaoshan | 韶山市 | Hunan | Xiangtan | 1990-12-26 |
| Shaodong | 邵东市 | Hunan | Shaoyang | 2019-07-12 |
| Shaoyang | 邵阳市 | Hunan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1980-02-20 |
| Wugang | 武冈市 | Hunan | Shaoyang | 1994-02-18 |
| Xiangtan | 湘潭市 | Hunan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1980-02-20 |
| Xiangxiang | 湘乡市 | Hunan | Xiangtan | 1986-09-12 |
| Yiyang | 益阳市 | Hunan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1994-03-07 |
| Yongzhou | 永州市 | Hunan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1995-11-21 |
| Yuanjiang | 沅江市 | Hunan | Yiyang | 1988-10-11 |
| Yueyang | 岳阳市 | Hunan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-02-08 |
| Zhangjiajie | 张家界市 | Hunan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1988-05-18 |
| Zhuzhou | 株洲市 | Hunan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1956-11-30 |
| Zixing | 资兴市 | Hunan | Chenzhou | 1984-12-20 |
| Arxan | 阿尔山市 | Inner Mongolia | Hinggan | 1996-06-10 |
| Baotou | 包头市 | Inner Mongolia | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1950-02-13 |
| Bayannur | 巴彦淖尔市 | Inner Mongolia | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2003-12-01 |
| Chifeng | 赤峰市 | Inner Mongolia | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-10-10 |
| Erenhot | 二连浩特市 | Inner Mongolia | Xilingol | 1966-01-18 |
| Ergun | 额尔古纳市 | Inner Mongolia | Hulunbuir | 1994-07-13 |
| Fengzhen | 丰镇市 | Inner Mongolia | Ulanqab | 1990-11-15 |
| Genhe | 根河市 | Inner Mongolia | Hulunbuir | 1994-04-28 |
| Hohhot | 呼和浩特市 | Inner Mongolia | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1950-01-18 |
| Holingol | 霍林郭勒市 | Inner Mongolia | Tongliao | 1985-11-09 |
| Hulunbuir | 呼伦贝尔市 | Inner Mongolia | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2001-10-10 |
| Manzhouli | 满洲里市 | Inner Mongolia | Hulunbuir | 1954-05-21 |
| Ordos | 鄂尔多斯市 | Inner Mongolia | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2001-02-26 |
| Tongliao | 通辽市 | Inner Mongolia | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1999-01-13 |
| Ulanhot | 乌兰浩特市 | Inner Mongolia | Hinggan | 1980-07-26 |
| Ulanqab | 乌兰察布市 | Inner Mongolia | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2003-12-01 |
| Wuhai | 乌海市 | Inner Mongolia | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1975-08-30 |
| Xilinhot | 锡林浩特市 | Inner Mongolia | Xilingol | 1983-10-10 |
| Yakeshi | 牙克石市 | Inner Mongolia | Hulunbuir | 1983-10-10 |
| Zhalantun | 扎兰屯市 | Inner Mongolia | Hulunbuir | 1983-10-10 |
| Changshu | 常熟市 | Jiangsu | Suzhou | 1983-01-18 |
| Changzhou | 常州市 | Jiangsu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1962-06-25 |
| Danyang | 丹阳市 | Jiangsu | Zhenjiang | 1987-12-15 |
| Dongtai | 东台市 | Jiangsu | Yancheng | 1987-12-17 |
| Gaoyou | 高邮市 | Jiangsu | Yangzhou | 1991-02-06 |
| Hai'an | 海安市 | Jiangsu | Nantong | 2018-02-22 |
| Huai'an | 淮安市 | Jiangsu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-01-18 |
| Jiangyin | 江阴市 | Jiangsu | Wuxi | 1987-04-23 |
| Jingjiang | 靖江市 | Jiangsu | Taizhou | 1993-07-14 |
| Jurong | 句容市 | Jiangsu | Zhenjiang | 1995-04-06 |
| Liyang | 溧阳市 | Jiangsu | Changzhou | 1990-08-15 |
| Lianyungang | 连云港市 | Jiangsu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1962-06-25 |
| Kunshan | 昆山市 | Jiangsu | Suzhou | 1989-07-27 |
| Nanjing | 南京市 | Jiangsu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1953-12-17 |
| Nantong | 南通市 | Jiangsu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1962-06-25 |
| Pizhou | 邳州市 | Jiangsu | Xuzhou | 1992-07-07 |
| Qidong | 启东市 | Jiangsu | Nantong | 1989-11-13 |
| Rugao | 如皋市 | Jiangsu | Nantong | 1991-02-06 |
| Suqian | 宿迁市 | Jiangsu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1996-07-19 |
| Suzhou | 苏州市 | Jiangsu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1962-06-25 |
| Taicang | 太仓市 | Jiangsu | Suzhou | 1993-01-08 |
| Taixing | 泰兴市 | Jiangsu | Taizhou | 1992-09-21 |
| Taizhou | 泰州市 | Jiangsu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1996-07-19 |
| Wuxi | 无锡市 | Jiangsu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Xinghua | 兴化市 | Jiangsu | Taizhou | 1987-12-22 |
| Xinyi | 新沂市 | Jiangsu | Xuzhou | 1990-02-05 |
| Xuzhou | 徐州市 | Jiangsu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1962-06-25 |
| Yancheng | 盐城市 | Jiangsu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-01-18 |
| Yangzhong | 扬中市 | Jiangsu | Zhenjiang | 1994-05-18 |
| Yangzhou | 扬州市 | Jiangsu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-01-18 |
| Yixing | 宜兴市 | Jiangsu | Wuxi | 1988-01-09 |
| Yizheng | 仪征市 | Jiangsu | Yangzhou | 1986-04-21 |
| Zhangjiagang | 张家港市 | Jiangsu | Suzhou | 1986-09-16 |
| Zhenjiang | 镇江市 | Jiangsu | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-01-18 |
| Dexing | 德兴市 | Jiangxi | Shangrao | 1990-12-26 |
| Fengcheng | 丰城市 | Jiangxi | Yichun | 1988-10-04 |
| Fuzhou | 抚州市 | Jiangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-23 |
| Ganzhou | 赣州市 | Jiangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1998-12-24 |
| Gao'an | 高安市 | Jiangxi | Yichun | 1993-12-08 |
| Gongqingcheng | 共青城市 | Jiangxi | Jiujiang | 2010-09-10 |
| Guixi | 贵溪市 | Jiangxi | Yingtan | 1996-05-28 |
| Ji'an | 吉安市 | Jiangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-05-11 |
| Jingdezhen | 景德镇市 | Jiangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1953-06-15 |
| Jinggangshan | 井冈山市 | Jiangxi | Ji'an | 1984-12-13 |
| Jiujiang | 九江市 | Jiangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1980-03-28 |
| Leping | 乐平市 | Jiangxi | Jingdezhen | 1992-07-27 |
| Longnan | 龙南市 | Jiangxi | Ganzhou | 2020-06-12 |
| Lushan | 庐山市 | Jiangxi | Jiujiang | 2016-03-20 |
| Nanchang | 南昌市 | Jiangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Pingxiang | 萍乡市 | Jiangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1970-03-10 |
| Ruichang | 瑞昌市 | Jiangxi | Jiujiang | 1989-12-20 |
| Ruijin | 瑞金市 | Jiangxi | Ganzhou | 1994-05-18 |
| Shangrao | 上饶市 | Jiangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-23 |
| Xinyu | 新余市 | Jiangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-07-27 |
| Yichun | 宜春市 | Jiangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-05-22 |
| Yingtan | 鹰潭市 | Jiangxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-07-27 |
| Zhangshu | 樟树市 | Jiangxi | Yichun | 1988-10-13 |
| Baicheng | 白城市 | Jilin | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1993-06-14 |
| Baishan | 白山市 | Jilin | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1985-02-04 |
| Changchun | 长春市 | Jilin | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1954-06-19 |
| Da'an | 大安市 | Jilin | Baicheng | 1988-08-30 |
| Dehui | 德惠市 | Jilin | Changchun | 1994-07-06 |
| Dunhua | 敦化市 | Jilin | Yanbian | 1985-02-28 |
| Fuyu | 扶余市 | Jilin | Songyuan | 2013-01-24 |
| Gongzhuling | 公主岭市 | Jilin | Changchun | 1985-12-19 |
| Helong | 和龙市 | Jilin | Yanbian | 1993-07-05 |
| Huadian | 桦甸市 | Jilin | Jilin | 1988-05-25 |
| Hunchun | 珲春市 | Jilin | Yanbian | 1988-05-25 |
| Ji'an | 集安市 | Jilin | Tonghua | 1988-03-16 |
| Jiaohe | 蛟河市 | Jilin | Jilin | 1989-08-15 |
| Jilin | 吉林市 | Jilin | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Liaoyuan | 辽源市 | Jilin | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-08-30 |
| Linjiang | 临江市 | Jilin | Baishan | 1993-11-28 |
| Longjing | 龙井市 | Jilin | Yanbian | 1988-05-25 |
| Meihekou | 梅河口市 | Jilin | Tonghua | 1985-12-19 |
| Panshi | 磐石市 | Jilin | Jilin | 1995-08-30 |
| Shuangliao | 双辽市 | Jilin | Siping | 1996-04-29 |
| Shulan | 舒兰市 | Jilin | Jilin | 1992-10-08 |
| Siping | 四平市 | Jilin | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-08-30 |
| Songyuan | 松原市 | Jilin | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1992-06-06 |
| Taonan | 洮南市 | Jilin | Baicheng | 1987-05-21 |
| Tonghua | 通化市 | Jilin | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1985-02-04 |
| Tumen | 图们市 | Jilin | Yanbian | 1965-03-27 |
| Yanji | 延吉市 | Jilin | Yanbian | 1953-05-04 |
| Yushu | 榆树市 | Jilin | Changchun | 1990-12-26 |
| Anshan | 鞍山市 | Liaoning | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1954-06-19 |
| Benxi | 本溪市 | Liaoning | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1954-06-19 |
| Beipiao | 北票市 | Liaoning | Chaoyang | 1985-01-17 |
| Beizhen | 北镇市 | Liaoning | Jinzhou | 1995-03-21 |
| Chaoyang | 朝阳市 | Liaoning | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1984-06-30 |
| Dalian | 大连市 | Liaoning | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1954-06-19 |
| Dandong | 丹东市 | Liaoning | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Dashiqiao | 大石桥市 | Liaoning | Yingkou | 1992-11-03 |
| Dengta | 灯塔市 | Liaoning | Liaoyang | 1996-08-27 |
| Diaobingshan | 调兵山市 | Liaoning | Tieling | 1986-09-12 |
| Donggang | 东港市 | Liaoning | Dandong | 1993-06-18 |
| Fengcheng | 凤城市 | Liaoning | Dandong | 1994-03-08 |
| Fushun | 抚顺市 | Liaoning | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1954-06-19 |
| Fuxin | 阜新市 | Liaoning | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Gaizhou | 盖州市 | Liaoning | Yingkou | 1992-11-03 |
| Haicheng | 海城市 | Liaoning | Anshan | 1985-01-17 |
| Huludao | 葫芦岛市 | Liaoning | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1989-06-12 |
| Jinzhou | 锦州市 | Liaoning | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Kaiyuan | 开原市 | Liaoning | Tieling | 1988-12-27 |
| Liaoyang | 辽阳市 | Liaoning | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1965-12-27 |
| Linghai | 凌海市 | Liaoning | Jinzhou | 1993-11-16 |
| Lingyuan | 凌源市 | Liaoning | Chaoyang | 1991-12-21 |
| Panjin | 盘锦市 | Liaoning | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1984-06-05 |
| Shenyang | 沈阳市 | Liaoning | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1954-06-19 |
| Tieling | 铁岭市 | Liaoning | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1984-06-30 |
| Wafangdian | 瓦房店市 | Liaoning | Dalian | 1985-01-17 |
| Xingcheng | 兴城市 | Liaoning | Huludao | 1986-09-12 |
| Xinmin | 新民市 | Liaoning | Shenyang | 1993-06-14 |
| Yingkou | 营口市 | Liaoning | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Zhuanghe | 庄河市 | Liaoning | Dalian | 1992-09-21 |
| Guyuan | 固原市 | Ningxia | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2001-07-07 |
| Lingwu | 灵武市 | Ningxia | Yinchuan | 1996-04-29 |
| Qingtongxia | 青铜峡市 | Ningxia | Wuzhong | 1984-12-17 |
| Shizuishan | 石嘴山市 | Ningxia | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1975-11-23 |
| Wuzhong | 吴忠市 | Ningxia | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1998-05-11 |
| Yinchuan | 银川市 | Ningxia | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1958-08-11 |
| Zhongwei | 中卫市 | Ningxia | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2003-12-31 |
| Delingha | 德令哈市 | Qinghai | Haixi | 1988-04-19 |
| Golmud | 格尔木市 | Qinghai | Haixi | 1980-06-14 |
| Haidong | 海东市 | Qinghai | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2013-02-08 |
| Mangnai | 茫崖市 | Qinghai | Haixi | 2018-02-22 |
| Tongren | 同仁市 | Qinghai | Huangnan | 2020-06-12 |
| Xining | 西宁市 | Qinghai | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1956-07-14 |
| Yushu | 玉树市 | Qinghai | Yushu | 2013-07-04 |
| Ankang | 安康市 | Shaanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-23 |
| Baoji | 宝鸡市 | Shaanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1971-10-05 |
| Binzhou | 彬州市 | Shaanxi | Xianyang | 2018-02-22 |
| Hancheng | 韩城市 | Shaanxi | Weinan | 1983-09-09 |
| Hanzhong | 汉中市 | Shaanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1996-02-21 |
| Huayin | 华阴市 | Shaanxi | Weinan | 1990-12-27 |
| Shangluo | 商洛市 | Shaanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2001-08-31 |
| Shenmu | 神木市 | Shaanxi | Yulin | 2017-04-09 |
| Tongchuan | 铜川市 | Shaanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1966-06-24 |
| Weinan | 渭南市 | Shaanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-09-09 |
| Xi'an | 西安市 | Shaanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1954-06-19 |
| Xianyang | 咸阳市 | Shaanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-09-09 |
| Xingping | 兴平市 | Shaanxi | Xianyang | 1993-06-18 |
| Xunyang | 旬阳市 | Shaanxi | Ankang | 2021-01-20 |
| Yan'an | 延安市 | Shaanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1996-11-05 |
| Yulin | 榆林市 | Shaanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1999-12-05 |
| Zichang | 子长市 | Shaanxi | Yan'an | 2019-07-12 |
| Anqiu | 安丘市 | Shandong | Weifang | 1994-01-18 |
| Binzhou | 滨州市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-10 |
| Changyi | 昌邑市 | Shandong | Weifang | 1994-06-10 |
| Dezhou | 德州市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1994-12-17 |
| Dongying | 东营市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1982-11-10 |
| Feicheng | 肥城市 | Shandong | Tai'an | 1992-08-01 |
| Gaomi | 高密市 | Shandong | Weifang | 1994-05-18 |
| Haiyang | 海阳市 | Shandong | Yantai | 1996-04-29 |
| Heze | 菏泽市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-23 |
| Jiaozhou | 胶州市 | Shandong | Qingdao | 1987-02-12 |
| Jinan | 济南市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Jining | 济宁市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-08-30 |
| Laixi | 莱西市 | Shandong | Qingdao | 1990-12-18 |
| Laiyang | 莱阳市 | Shandong | Yantai | 1987-02-20 |
| Laizhou | 莱州市 | Shandong | Yantai | 1988-02-24 |
| Leling | 乐陵市 | Shandong | Dezhou | 1988-09-01 |
| Liaocheng | 聊城市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1997-08-29 |
| Linqing | 临清市 | Shandong | Liaocheng | 1983-08-30 |
| Linyi | 临沂市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1994-12-17 |
| Longkou | 龙口市 | Shandong | Yantai | 1986-09-23 |
| Pingdu | 平度市 | Shandong | Qingdao | 1989-07-27 |
| Qingdao | 青岛市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Qingzhou | 青州市 | Shandong | Weifang | 1986-03-01 |
| Qixia | 栖霞市 | Shandong | Yantai | 1995-11-30 |
| Qufu | 曲阜市 | Shandong | Jining | 1986-06-02 |
| Rizhao | 日照市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1989-06-12 |
| Rongcheng | 荣成市 | Shandong | Weihai | 1988-11-01 |
| Rushan | 乳山市 | Shandong | Weihai | 1993-07-17 |
| Shouguang | 寿光市 | Shandong | Weifang | 1993-06-01 |
| Tai'an | 泰安市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1985-03-27 |
| Tengzhou | 滕州市 | Shandong | Zaozhuang | 1988-03-07 |
| Weifang | 潍坊市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-08-30 |
| Weihai | 威海市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1987-06-15 |
| Xintai | 新泰市 | Shandong | Tai'an | 1983-08-30 |
| Yantai | 烟台市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-08-30 |
| Yucheng | 禹城市 | Shandong | Dezhou | 1993-09-09 |
| Zaozhuang | 枣庄市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1961-09-12 |
| Zhaoyuan | 招远市 | Shandong | Yantai | 1991-12-21 |
| Zhucheng | 诸城市 | Shandong | Weifang | 1987-04-20 |
| Zibo | 淄博市 | Shandong | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1961-09-12 |
| Zoucheng | 邹城市 | Shandong | Jining | 1992-10-04 |
| Zouping | 邹平市 | Shandong | Binzhou | 2018-07-02 |
| Changzhi | 长治市 | Shanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1975-07-09 |
| Datong | 大同市 | Shanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1972-03-09 |
| Fenyang | 汾阳市 | Shanxi | Lüliang | 1996-08-20 |
| Gaoping | 高平市 | Shanxi | Jincheng | 1993-05-12 |
| Gujiao | 古交市 | Shanxi | Taiyuan | 1988-02-24 |
| Hejin | 河津市 | Shanxi | Yuncheng | 1994-01-12 |
| Houma | 侯马市 | Shanxi | Linfen | 1971-06-05 |
| Huairen | 怀仁市 | Shanxi | Shuozhou | 2018-02-22 |
| Huozhou | 霍州市 | Shanxi | Linfen | 1989-12-23 |
| Jiexiu | 介休市 | Shanxi | Jinzhong | 1992-02-10 |
| Jincheng | 晋城市 | Shanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1985-04-30 |
| Jinzhong | 晋中市 | Shanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1999-09-24 |
| Linfen | 临汾市 | Shanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-23 |
| Lüliang | 吕梁市 | Shanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2003-10-23 |
| Shuozhou | 朔州市 | Shanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1988-03-24 |
| Taiyuan | 太原市 | Shanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Xiaoyi | 孝义市 | Shanxi | Lüliang | 1992-02-10 |
| Xinzhou | 忻州市 | Shanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-14 |
| Yangquan | 阳泉市 | Shanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1972-03-09 |
| Yongji | 永济市 | Shanxi | Yuncheng | 1994-01-12 |
| Yuncheng | 运城市 | Shanxi | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-14 |
| Yuanping | 原平市 | Shanxi | Xinzhou | 1993-06-17 |
| Barkam | 马尔康市 | Sichuan | Ngawa | 2015-11-02 |
| Bazhong | 巴中市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-14 |
| Chengdu | 成都市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Chongzhou | 崇州市 | Sichuan | Chengdu | 1994-06-20 |
| Dazhou | 达州市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1999-06-20 |
| Deyang | 德阳市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-08-18 |
| Dujiangyan | 都江堰市 | Sichuan | Chengdu | 1988-03-03 |
| Emeishan | 峨眉山市 | Sichuan | Leshan | 1988-09-01 |
| Guang'an | 广安市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1998-07-31 |
| Guanghan | 广汉市 | Sichuan | Deyang | 1988-02-24 |
| Guangyuan | 广元市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1985-02-08 |
| Huaying | 华蓥市 | Sichuan | Guang'an | 1985-02-04 |
| Huili | 会理市 | Sichuan | Liangshan | 2021-02-01 |
| Jiangyou | 江油市 | Sichuan | Mianyang | 1988-02-24 |
| Jianyang | 简阳市 | Sichuan | Chengdu | 1994-04-05 |
| Kangding | 康定市 | Sichuan | Garzê | 2015-02-17 |
| Langzhong | 阆中市 | Sichuan | Nanchong | 1991-01-12 |
| Leshan | 乐山市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1985-02-11 |
| Longchang | 隆昌市 | Sichuan | Neijiang | 2017-04-09 |
| Luzhou | 泸州市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-03-03 |
| Mianzhu | 绵竹市 | Sichuan | Deyang | 1996-10-15 |
| Meishan | 眉山市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-10 |
| Mianyang | 绵阳市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1985-02-08 |
| Nanchong | 南充市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1993-07-02 |
| Neijiang | 内江市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1985-02-11 |
| Panzhihua | 攀枝花市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1965-04-22 |
| Pengzhou | 彭州市 | Sichuan | Chengdu | 1993-12-01 |
| Qionglai | 邛崃市 | Sichuan | Chengdu | 1994-06-19 |
| Shifang | 什邡市 | Sichuan | Deyang | 1995-11-08 |
| Shehong | 射洪市 | Sichuan | Suining | 2019-07-12 |
| Suining | 遂宁市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1985-02-08 |
| Wanyuan | 万源市 | Sichuan | Dazhou | 1993-07-14 |
| Xichang | 西昌市 | Sichuan | Liangshan | 1979-07-19 |
| Ya'an | 雅安市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-14 |
| Yibin | 宜宾市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1996-10-05 |
| Zigong | 自贡市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Ziyang | 资阳市 | Sichuan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-06-14 |
| Lhasa | 拉萨市 | Tibet | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1960-01-07 |
| Nagqu | 那曲市 | Tibet | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2017-07-18 |
| Nyingchi | 林芝市 | Tibet | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2015-03-16 |
| Qamdo | 昌都市 | Tibet | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2014-10-29 |
| Shannan | 山南市 | Tibet | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2016-01-07 |
| Xigazê | 日喀则市 | Tibet | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2014-06-26 |
| Aksu | 阿克苏市 | Xinjiang | Aksu | 1983-08-19 |
| Alashankou | 阿拉山口市 | Xinjiang | Bortala | 2012-12-17 |
| Altay | 阿勒泰市 | Xinjiang | Altay | 1984-11-17 |
| Aral | 阿拉尔市 | Xinjiang (XPCC) | ZZZZ-nonenone | 2002-09-17 |
| Artux | 阿图什市 | Xinjiang | Kizilsu | 1986-06-07 |
| Beitun | 北屯市 | Xinjiang (XPCC) | ZZZZ-nonenone | 2011-12-27 |
| Bole | 博乐市 | Xinjiang | Bortala | 1985-06-24 |
| Changji | 昌吉市 | Xinjiang | Changji | 1983-07-21 |
| Fukang | 阜康市 | Xinjiang | Changji | 1992-11-03 |
| Hami | 哈密市 | Xinjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2016-01-07 |
| Hotan | 和田市 | Xinjiang | Hotan | 1983-09-09 |
| Huyanghe | 胡杨河市 | Xinjiang (XPCC) | ZZZZ-nonenone | 2019-11-06 |
| Karamay | 克拉玛依市 | Xinjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1982-02-16 |
| Kashgar | 喀什市 | Xinjiang | Kashgar | 1952-05-22 |
| Khorgas | 霍尔果斯市 | Xinjiang | Ili | 2014-06-26 |
| Kokdala | 可克达拉市 | Xinjiang (XPCC) | ZZZZ-nonenone | 2015-03-16 |
| Korla | 库尔勒市 | Xinjiang | Bayingolin | 1979-09-02 |
| Kunyu | 昆玉市 | Xinjiang (XPCC) | ZZZZ-nonenone | 2016-01-07 |
| Kuqa | 库车市 | Xinjiang | Aksu | 2019-11-20 |
| Kuytun | 奎屯市 | Xinjiang | Ili | 1975-08-29 |
| Shawan | 沙湾市 | Xinjiang | Tacheng | 2021-01-20 |
| Shihezi | 石河子市 | Xinjiang (XPCC) | ZZZZ-nonenone | 1976-01-02 |
| Shuanghe | 双河市 | Xinjiang (XPCC) | ZZZZ-nonenone | 2014-01-25 |
| Tacheng | 塔城市 | Xinjiang | Tacheng | 1984-11-17 |
| Tiemenguan | 铁门关市 | Xinjiang (XPCC) | ZZZZ-nonenone | 2012-12-17 |
| Tumxuk | 图木舒克市 | Xinjiang (XPCC) | ZZZZ-nonenone | 2002-09-17 |
| Turpan | 吐鲁番市 | Xinjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2015-03-16 |
| ÜrümqiÜrümqi | 乌鲁木齐市 | Xinjiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Wujiaqu | 五家渠市 | Xinjiang (XPCC) | ZZZZ-nonenone | 2002-09-17 |
| Wusu | 乌苏市 | Xinjiang | Tacheng | 1996-07-10 |
| Xinxing | 新星市 | Xinjiang (XPCC) | ZZZZ-nonenone | 2021-02-04 |
| Yining | 伊宁市 | Xinjiang | Ili | 1952-05-22 |
| Anning | 安宁市 | Yunnan | Kunming | 1995-10-13 |
| Baoshan | 保山市 | Yunnan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-12-30 |
| Chengjiang | 澄江市 | Yunnan | Yuxi | 2019-11-20 |
| Chuxiong | 楚雄市 | Yunnan | Chuxiong | 1983-09-09 |
| Dali | 大理市 | Yunnan | Dali | 1983-09-09 |
| Gejiu | 个旧市 | Yunnan | Honghe | 1958-09-16 |
| Jinghong | 景洪市 | Yunnan | Xishuangbanna | 1993-12-22 |
| Kaiyuan | 开远市 | Yunnan | Honghe | 1981-01-18 |
| Kunming | 昆明市 | Yunnan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Lincang | 临沧市 | Yunnan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2003-12-26 |
| Lijiang | 丽江市 | Yunnan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2002-12-26 |
| Lufeng | 禄丰市 | Yunnan | Chuxiong | 2021-01-20 |
| Lushui | 泸水市 | Yunnan | Nujiang | 2016-06-16 |
| Mangshi | 芒市 | Yunnan | Dehong | 1996-10-28 |
| Mengzi | 蒙自市 | Yunnan | Honghe | 2010-09-10 |
| Mile | 弥勒市 | Yunnan | Honghe | 2013-01-24 |
| Pu'er | 普洱市 | Yunnan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2003-10-30 |
| Qujing | 曲靖市 | Yunnan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1997-05-06 |
| Ruili | 瑞丽市 | Yunnan | Dehong | 1992-06-26 |
| Shangri-La | 香格里拉市 | Yunnan | Dêqên | 2014-12-16 |
| Shuifu | 水富市 | Yunnan | Zhaotong | 2018-07-02 |
| Tengchong | 腾冲市 | Yunnan | Baoshan | 2015-08-01 |
| Wenshan | 文山市 | Yunnan | Wenshan | 2010-12-02 |
| Xuanwei | 宣威市 | Yunnan | Qujing | 1994-02-18 |
| Yuxi | 玉溪市 | Yunnan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1997-12-13 |
| Zhaotong | 昭通市 | Yunnan | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2001-01-13 |
| Cixi | 慈溪市 | Zhejiang | Ningbo | 1988-10-13 |
| Dongyang | 东阳市 | Zhejiang | Jinhua | 1988-05-25 |
| Haining | 海宁市 | Zhejiang | Jiaxing | 1986-11-22 |
| Hangzhou | 杭州市 | Zhejiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-10-01 |
| Huzhou | 湖州市 | Zhejiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-07-27 |
| Jiande | 建德市 | Zhejiang | Hangzhou | 1992-04-01 |
| Jiangshan | 江山市 | Zhejiang | Quzhou | 1987-11-27 |
| Jiaxing | 嘉兴市 | Zhejiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-07-27 |
| Jinhua | 金华市 | Zhejiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1985-05-15 |
| Lanxi | 兰溪市 | Zhejiang | Jinhua | 1985-05-15 |
| Linhai | 临海市 | Zhejiang | Taizhou | 1986-03-01 |
| Lishui | 丽水市 | Zhejiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 2000-05-20 |
| Longgang | 龙港市 | Zhejiang | Wenzhou | 2019-08-16 |
| Longquan | 龙泉市 | Zhejiang | Lishui | 1990-12-26 |
| Ningbo | 宁波市 | Zhejiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-12-20 |
| Pinghu | 平湖市 | Zhejiang | Jiaxing | 1991-06-15 |
| Quzhou | 衢州市 | Zhejiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1985-05-15 |
| Ruian | 瑞安市 | Zhejiang | Wenzhou | 1987-04-15 |
| Shaoxing | 绍兴市 | Zhejiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1983-07-27 |
| Shengzhou | 嵊州市 | Zhejiang | Shaoxing | 1995-08-30 |
| Taizhou | 台州市 | Zhejiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1994-08-22 |
| Tongxiang | 桐乡市 | Zhejiang | Jiaxing | 1993-03-26 |
| Wenling | 温岭市 | Zhejiang | Taizhou | 1994-02-18 |
| Wenzhou | 温州市 | Zhejiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1949-11-06 |
| Yiwu | 义乌市 | Zhejiang | Jinhua | 1988-05-25 |
| Yongkang | 永康市 | Zhejiang | Jinhua | 1992-08-24 |
| Yueqing | 乐清市 | Zhejiang | Wenzhou | 1993-09-18 |
| Yuhuan | 玉环市 | Zhejiang | Taizhou | 2017-04-09 |
| Yuyao | 余姚市 | Zhejiang | Ningbo | 1985-07-16 |
| Zhoushan | 舟山市 | Zhejiang | ZZZ-direct administrationdirect administration | 1987-01-23 |
| Zhuji | 诸暨市 | Zhejiang | Shaoxing | 1989-09-27 |
Close
Renamed cities
More information Before, Chinese ...
| Before | Chinese | After | Chinese | Renamed date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weihaiwei | 威海卫市 | Weihai | 威海市 | 1949-11-01 |
| Xingshan | 兴山市 | Hegang | 鹤岗市 | 1950-03-23 |
| Xi'an | 西安市 | Liaoyuan | 辽源市 | 1952-04-03 |
| Nanzheng | 南郑市 | Hanzhong | 汉中市 | 1953-10-24 |
| Dihua | 迪化市 | Ürümqi | 乌鲁木齐市 | 1953-11-20 |
| Guisui | 归绥市 | Hohhot | 呼和浩特市 | 1954-04-20 |
| Xinhailian | 新海连市 | Lianyungang | 连云港市 | 1961-09-02 |
| Andong | 安东市 | Dandong | 丹东市 | 1965-01-20 |
| Suixi | 濉溪市 | Huaibei | 淮北市 | 1971-03-30 |
| Anda | 安达市 | Daqing | 大庆市 | 1979-12-14 |
| Sucheng | 宿城市 | Suzhou | 宿州市 | 1980-02-29 |
| Lüda | 旅大市 | Dalian | 大连市 | 1981-02-09 |
| Dukou | 渡口市 | Panzhihua | 攀枝花市 | 1987-01-23 |
| Meixian | 梅县市 | Meizhou | 梅州市 | 1988-01-07 |
| Daxian | 达县市 | Dazhou | 达州市 | 1993-07-05 |
| Hunjiang | 浑江市 | Baishan | 白山市 | 1994-01-31 |
| Dayong | 大庸市 | Zhangjiajie | 张家界市 | 1994-04-04 |
| Jinxi | 锦西市 | Huludao | 葫芦岛市 | 1994-09-20 |
| Jingsha | 荆沙市 | Jingzhou | 荆州市 | 1996-11-20 |
| Puqi | 蒲圻市 | Chibi | 赤壁市 | 1998-06-11 |
| Zhicheng | 枝城市 | Yidu | 宜都市 | 1998-06-11 |
| Huaiyin | 淮阴市 | Huai'an | 淮安市 | 2000-12-21 |
| Tongza | 通什市 | Wuzhishan | 五指山市 | 2001-07-05 |
| Tiefa | 铁法市 | Diaobingshan | 调兵山市 | 2002-02-20 |
| Beining | 北宁市 | Beizhen | 北镇市 | 2006-02-08 |
| Simao | 思茅市 | Pu'er | 普洱市 | 2007-01-21 |
| Luxi | 潞西市 | Mangshi | 芒市 | 2007-12-30 |
| Xiangfan | 襄樊市 | Xiangyang | 襄阳市 | 2010-11-26 |
Close
Dissolved cities
More information City, Chinese ...
| City | Chinese | Founded | Dissolved | Merged division | Former status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acheng | 阿城市 | 1987-02-24 | 2006-08-15 | merge into Harbin | County-level city |
| Anjiang | 安江市 | 1961-07-09 | 1962-10-20 | merge into Huaihua Prefecture | |
| Bayangol | 巴彦郭勒市 | 1960-01-07 | 1964-07-20 | merge into Bayannur League | |
| Bayanhot | 巴彦浩特市 | 1954-06-19 | 1956-04-03 | merge into Alxa League | |
| Beibei | 北碚市 | 1951-11-05 | 1953-03-13 | merge into Chongqing | |
| Boshan | 博山市 | 1949-10-01 | 1950-05-09 | merge into Zibo Prefecture | |
| Changle | 长乐市 | 1994-02-18 | 2017-07-18 | merge into Fuzhou, Fujian | County-level city |
| Chaohu | 巢湖市 | 1999-07-09 | 2011-07-14 | merge into Hefei | Prefecture-level city |
| Chaoyang | 潮阳市 | 1993-04-09 | 2003-01-29 | merge into Shantou | County-level city |
| Chenghai | 澄海市 | 1994-04-18 | 2003-01-29 | merge into Shantou | County-level city |
| Conghua | 从化市 | 1994-03-26 | 2014-02-12 | merge into Guangzhou | County-level city |
| Dafeng | 大丰市 | 1996-08-01 | 2015-07-23 | merge into Yancheng | County-level city |
| Da Qaidam | 大柴旦市 | 1960-11-17 | 1964-06-05 | merge into Haixi Prefecture | |
| Dêwolu | 德乌鲁市 | 1958-12-20 | 1961-12-15 | merge into Gannan Prefecture | |
| Dongchuan | 东川市 | 1958-10-20 | 1998-12-06 | merge into Kunming | Prefecture-level city |
| Dongjiang | 东江市 | 1961-07-09 | 1962-10-20 | merge into Binzhou | |
| Dongsheng | 东胜市 | 1983-10-10 | 2001-02-26 | merge into Ordos | County-level city |
| Echeng | 鄂城市 | 1960-11-17 | 1961-12-15 | merge into Huanggang Prefecture | |
| Fengfeng | 峰峰市 | 1955-05-06 | 1956-10-12 | merge into Handan | |
| Fenghua | 奉化市 | 1988-10-13 | 2016-09-14 | merge into Ningbo | County-level city |
| Fengnan | 丰南市 | 1994-04-05 | 2002-02-01 | merge into Tangshan | County-level city |
| Fuling | 涪陵市 | 1995-11-05 | 1997-03-14 | merge into Chongqing | Prefecture-level city |
| Fuyang | 富阳市 | 1994-01-18 | 2014-12-13 | merge into Hangzhou | County-level city |
| Gaocheng | 藁城市 | 1989-07-02 | 2014-09-09 | merge into Shijiazhuang | County-level city |
| Gaoming | 高明市 | 1994-04-18 | 2002-12-08 | merge into Foshan | County-level city |
| Gaoyao | 高要市 | 1993-09-28 | 2015-05-07 | merge into Zhaoqing | County-level city |
| Haibowan | 海勃湾市 | 1961-07-09 | 1975-08-30 | merge into Wuhai | |
| Hailar | 海拉尔市 | 1949-10-01 | 2001-10-10 | merge into Hulunbuir | County-level city |
| Haimen | 海门市 | 1994-04-26 | 2020-06-05 | merge into Nantong | County-level city |
| Hangu | 汉沽市 | 1953-11-06 | 1958-06-06 | merge into Tianjin | |
| Hankou | 汉口市 | 1949-10-01 | 1949-10-01 | merge into Wuhan | |
| Hanyang | 汉阳市 | 1949-10-01 | 1949-10-01 | merge into Wuhan | |
| Hechuan | 合川市 | 1952-04-04 | 2006-10-22 | merge into Chongqing | County-level city |
| Hekou | 河口市 | 1950-06-10 | 1955-01-03 | merge into Honghe Prefecture | |
| Huadu | 花都市 | 1993-06-18 | 2000-05-21 | merge into Guangzhou | County-level city |
| Huangyan | 黄岩市 | 1989-09-27 | 1994-08-22 | merge into Taizhou, Zhejiang | County-level city |
| Huangzhou | 黄州市 | 1990-12-26 | 1995-12-23 | merge into Huanggang | County-level city |
| Huiyang | 惠阳市 | 1994-05-06 | 2003-03-06 | merge into Huizhou | County-level city |
| Jiangdu | 江都市 | 1994-04-26 | 2011-11-14 | merge into Yangzhou | County-level city |
| Jiangjin | 江津市 | 1992-08-04 | 2006-10-22 | merge into Chongqing | County-level city |
| Jiangyan | 姜堰市 | 1994-07-17 | 2012-12-20 | merge into Taizhou, Jiangsu | County-level city |
| Jiaojiang | 椒江市 | 1981-07-21 | 1994-08-22 | merge into Taizhou, Zhejiang | County-level city |
| Jianyang | 建阳市 | 1994-03-04 | 2014-05-15 | merge into Nanping | County-level city |
| Jiaonan | 胶南市 | 1990-12-18 | 2012-12-01 | merge into Qingdao | County-level city |
| Jimo | 即墨市 | 1989-07-27 | 2017-07-18 | merge into Qingdao | County-level city |
| Jintan | 金坛市 | 1993-11-10 | 2015-04-29 | merge into Changzhou | County-level city |
| Jingpohu | 镜泊湖市 | 1986-07-01 | 1987-11-27 | merge into Mudanjiang | |
| Jining | 集宁市 | 1954-06-19 | 2003-12-01 | merge into Ulanqab | County-level city |
| Jiutai | 九台市 | 1988-08-30 | 2014-11-02 | merge into Changchun | County-level city |
| Jizhou | 冀州市 | 1993-09-22 | 2016-06-08 | merge into Hengshui | County-level city |
| Laiwu | 莱芜市 | 1992-11-22 | 2019-01-09 | merge into Jinan | Prefecture-level city |
| Lenghu | 冷湖市 | 1960-11-17 | 1964-06-05 | merge into Haixi Prefecture | |
| Lengjiang | 冷江市 | 1961-07-09 | 1962-10-20 | merge into Loudi | |
| Lengshuitan | 冷水滩市 | 1961-07-09 | 1962-10-20 | merge into Yongzhou Prefecture | |
| Lin'an | 临安市 | 1996-10-28 | 2017-07-18 | merge into Hangzhou | County-level city |
| Linchuan | 临川市 | 1987-08-22 | 2000-06-23 | merge into Fuzhou, Jiangxi | County-level city |
| Linhe | 临河市 | 1984-12-11 | 2003-12-01 | merge into Bayannur | County-level city |
| Lishi | 离石市 | 1996-04-02 | 2003-10-23 | merge into Lüliang | County-level city |
| Liuzhi | 六枝市 | 1960-05-26 | 1962-10-20 | merge into Anshun Prefecture | |
| Lucheng | 潞城市 | 1994-04-26 | 2018-06-18 | merge into Changzhi | County-level city |
| Luquan | 鹿泉市 | 1989-07-02 | 2014-09-09 | merge into Shijiazhuang | County-level city |
| Lüshun | 旅顺市 | 1949-10-01 | 1960-01-07 | merge into Lüda | |
| Malipo | 麻栗坡市 | 1950-06-10 | 1955-01-03 | merge into Wenshan Prefecture | |
| Miquan | 米泉市 | 1996-12-30 | 2007-06-30 | merge into Ürümqi | County-level city |
| Nanchuan | 南川市 | 1994-06-10 | 2006-10-22 | merge into Chongqing | County-level city |
| Nanhai | 南海市 | 1992-09-02 | 2002-12-08 | merge into Foshan | County-level city |
| Nankang | 南康市 | 1995-03-07 | 2013-10-18 | merge into Ganzhou | County-level city |
| Panyu | 番禺市 | 1992-05-20 | 2000-05-21 | merge into Guangzhou | County-level city |
| Penglai | 蓬莱市 | 1991-11-30 | 2020-06-05 | merge into Yantai | County-level city |
| Pulandian | 普兰店市 | 1991-11-30 | 2015-10-13 | merge into Dalian | County-level city |
| Qingjiang | 清江市 | 1950-12-18 1964-08-18 | 1958-09-05 1983-01-18 | rename as Huaiyin | |
| Qiongshan | 琼山市 | 1994-01-24 | 2002-10-16 | merge into Haikou | County-level city |
| Runan | 汝南市 | 1950-05-09 | 1951-04-26 | merge into Xinyang Prefecture | |
| Sanshui | 三水市 | 1993-03-29 | 2002-12-08 | merge into Foshan | County-level city |
| Shangyu | 上虞市 | 1992-08-24 | 2013-10-18 | merge into Shaoxing | County-level city |
| Shangzhou | 商州市 | 1988-05-24 | 2001-08-31 | merge into Shangluo | County-level city |
| Shanhaiguan | 山海关市 | 1949-10-01 | 1953-01-02 | merge into Qinhuangdao | |
| Shashi | 沙市市 | 1979-06-21 | 1994-09-29 | merge into Jingsha | Prefecture-level city |
| Shayang | 沙洋市 | 1960-11-17 | 1961-12-15 | merge into Jingzhou | |
| Shuangcheng | 双城市 | 1988-09-14 | 2014-05-15 | merge into Harbin | County-level city |
| Shidao | 石岛市 | 1949-10-01 | 1950-05-09 | merge into Rongcheng | |
| Shiqi | 石岐市 | 1953-03-12 | 1959-03-20 | merge into Zhongshan | |
| Shunde | 顺德市 | 1992-03-26 | 2002-12-08 | merge into Foshan | County-level city |
| Taishan | 泰山市 | 1958-06-01 | 1958-11-01 | merge into Tai'an | |
| Tongguanshan | 铜官山市 | 1956-07-02 | 1958-09-05 | merge into Tongling | |
| Tongzhou | 通州市 | 1953-11-06 | 1958-03-07 | merge into Beijing | |
| Tongzhou | 通州市 | 1993-01-08 | 2009-03-31 | merge into Nantong | County-level city |
| Tunxi | 屯溪市 | 1975-12-19 | 1987-11-27 | merge into Huangshan | |
| Wanding | 畹町市 | 1985-01-31 | 1999-01-02 | merge into Dehong Prefecture | County-level city |
| Wanxian | 万县市 | 1992-12-11 | 1997-03-14 | merge into Chongqing | Prefecture-level city |
| Wuchang | 武昌市 | 1949-10-01 | 1949-10-01 | merge into Wuhan | |
| Wendeng | 文登市 | 1988-10-24 | 2014-03-18 | merge into Weihai | County-level city |
| Wuda | 乌达市 | 1961-07-09 | 1975-08-30 | merge into Wuhai | |
| Wujiang | 吴江市 | 1992-02-17 | 2010-09-01 | merge into Suzhou, Jiangsu | County-level city |
| Wujin | 武进市 | 1995-06-08 | 2002-04-03 | merge into Changzhou | County-level city |
| Wutongqiao | 五通桥市 | 1952-04-04 | 1985-02-11 | merge into Leshan | |
| Wuxian | 吴县市 | 1995-06-08 | 2000-12-31 | merge into Suzhou, Jiangsu | County-level city |
| Xiaguan | 下关市 | 1951-03-14 1962-03-27 | 1960-09-13 1983-09-09 | merge into Dali Prefecture | |
| Xiaoshan | 萧山市 | 1987-11-27 | 2001-02-02 | merge into Hanzhou | County-level city |
| Xifeng | 西峰市 | 1986-01-01 | 2002-06-22 | merge into Qingyang | County-level city |
| Xinhui | 新会市 | 1992-10-08 | 2002-06-22 | merge into Jiangmen | County-level city |
| Xinwen | 新汶市 | 1960-03-28 | 1983-08-30 | merge into Xintai | |
| Xishan | 锡山市 | 1995-06-08 | 2000-12-21 | merge into Wuxi | County-level city |
| Xuanhua | 宣化市 | 1952-11-05 | 1955-08-08 | merge into Zhengjiakou | |
| Yangkou | 杨口市 | 1949-10-01 | 1950-05-09 | merge into Qinghe | |
| Yanzhou | 兖州市 | 1992-08-01 | 2013-10-18 | merge into Jining | County-level city |
| Yizhou | 宜州市 | 1993-09-09 | 2016-11-24 | merge into Hechi | County-level city |
| Yongchuan | 永川市 | 1992-03-09 | 2006-10-22 | merge into Chongqing | County-level city |
| Yuci | 榆次市 | 1954-04-09 | 1999-09-24 | merge into Jinzhong | County-level city |
| Yuhang | 余杭市 | 1994-04-05 | 2001-02-02 | merge into Hangzhou | County-level city |
| Zengcheng | 增城市 | 1993-12-08 | 2014-02-12 | merge into Guangzhou | County-level city |
| Zhangqiu | 章丘市 | 1992-08-01 | 2016-09-14 | merge into Jinan | County-level city |
| Zhangzhou | 张周市 | 1950-11-18 | 1954-12-09 | merge into Zibo | |
| Zhuji | 朱集市 | 1949-10-01 | 1951-08-03 | merge into Shangqiu |
Close
Remove ads
Tier system
Main article: Chinese city tier system
The Chinese central government introduced a ranking system in the 1980s to facilitate the staged rollout of infrastructure and urban development throughout the country. Cities were ranked by tier according to the government's development priorities.[6] The tier system began as a bureaucratic classification, but has since the later 1990s acquired new salience from the perspectives of real estate development, commercial vitality and cosmopolitanness, besides the old notions of population, economic size, and political ranking. It has now become a proxy for demographic and social segmentation in China, especially relevant to those college-educated seeking non-governmental employment.[7][8][9]
It is the general consensus that four cities, namely Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, belong to the first tier, while tier II includes other major cities. Small and medium cities are grouped into tier III or IV.[10]
Remove ads
Republic of China (1912–1949)
Summarize
Perspective
- Note: All names are transliterated in pinyin.
- Fu (府) cities
More information City, Chinese ...
| City | Chinese | Province | Administration period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nanjing | 南京府 | Nanjing | 1914–1927 |
| Shuntian | 順天府 (顺天府) | Shuntian | 1914–1921 |
Close
- Shi (市) cities
More information Type, No. ...
| Type | No. | |
|---|---|---|
| Special/Yuan/Direct-controlled* | 16 | |
| Province-controlled | 70 | |
Close
More information City, Chinese ...
| City | Chinese | Province | Type | Administration period | Founded (ROC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangzhou | 廣州市 (广州市) | Guangdong
Guangzhou |
Province-controlled (de facto)
Ordinary (de jure) Yuan-controlled Direct-controlled |
15 Feb. 1921 – Jan. 1930; 20 June 1930 – 7 June 1947
3 July 1921 – 29 December 1928 Jan. 1930 – 20 June 1930 Jan. 1930 – 20 June 1930; 7 June 1947 – 1 October 1949 |
1921-02-15 |
| Shantou | 汕頭市 (汕头市) | Guangdong | Province-controlled | Mar. 1921 – 1 October 1949 | 1921-03- |
| Beiping
|
北平市
京都市 北平市 |
Hebei
Jingdu Beiping |
Province-controlled (claimed)
Special (de jure) Yuan-controlled Direct-controlled |
Apr 1921 – 20 June 1928; 20 June 1930 – Dec. 1930
3 July 1921 – 29 December 1928 20 June 1928 – 30 May 1930 30 May 1930 – 20 June 1930; Dec. 1930 – 1 October 1949 |
1921-04- |
| Chengdu | 成都市 | Sichuan | Province-controlled | June 1921 – 1 October 1949 | 1921-06- |
| Qingdao | 青島市 (青岛市) | Qingdao | Special
Yuan-controlled Direct-controlled |
3 July 1921 – 29 December 1928
July 1929 – 30 May 1930 30 May 1930 – 1 October 1949 |
1921-07-03 |
| Harbin | 哈爾濱市 (哈尔滨市) | Harbin | Special
Direct-controlled |
3 July 1921 – 29 December 1928
5 June 1947 – 1 October 1949 |
1921-07-03 |
| Wuxi | 無錫市 (无锡市) | Jiangsu | Ordinary
Province-controlled |
3 July 1921 – 29 December 1928
1929 – Apr. 1930 |
1921-07-03 |
| Hangzhou | 杭州市 | Zhejiang | Ordinary (de jure)
Province-controlled (de facto) |
3 July 1921 – 29 December 1928
Apr. 1927 – 1 October 1949 |
1921-07-03 |
| Ningbo | 寧波市 (宁波市) | Zhejiang | Ordinary (de jure)
Province-controlled (de facto) |
3 July 1921 – 29 December 1928
Apr. 1927– Feb. 1931 |
1921-07-03 |
| Anqing | 安慶市 (安庆市) | Anhui | Ordinary (de jure)
Province-controlled (de facto) |
3 July 1921 – 29 December 1928
1927 – Sep. 1930 |
1921-07-03 |
| Wuchang | 武昌市 | Hubei | Ordinary
Province-controlled |
3 July 1921 – 29 December 1928
July 1935 – 1 October 1949 |
1921-07-03 |
| Nanchang | 南昌市 | Jiangxi | Ordinary
Province-controlled |
3 July 1921 – 29 December 1928
July 1935 – 1 October 1949 |
1921-07-03 |
| Wuzhou | 梧州市 | Guangxi | Ordinary (de iure)
Province-controlled (de facto) |
3 July 1921 – 29 December 1928
Dec. 1927 – June 1932 |
1921-07-03 |
| Jingu
|
津沽市
天津市 |
Jingu
Hebei Tianjin |
Special (de jure)
Province-controlled (claimed) Yuan-controlled Direct-controlled |
3 July 1921 – 29 December 1928
6 Oct. 1923 – 20 June 1928; Dec. 1930 – June 1935 20 June 1928 – 30 May 1930 30 May 1930 – Dec. 1930; June 1935 – 1 October 1949 |
1921-07-03 |
| Jiangmen | 江門市 (江门市) | Guangdong | Province-controlled | Aug. 1925 – Feb. 1931 | 1925-08- |
| Foshan | 佛山市 | Guangdong | Province-controlled | 1925–1927 | 1925– - |
| Jiujiang | 九江市 | Guangdong | Province-controlled | 1925–1936 | 1925– - |
| Beihai | 北海市 | Guangdong | Province-controlled | 1925 – May 1930 | 1925– - |
| Hankou
|
漢口市 (汉口市)
武漢市 (武汉市) 漢口市 (汉口市) |
Hankou
Hubei Wuhan Hankou |
Special (de jure)
Province-controlled (de facto) Yuan-controlled Direct-controlled |
3 July 1921 – 29 December 1928
Oct. 1926-10 – Apr. 1927; Jan. 1929 – Apr. 1929; July 1931 – 7 June 1947 Apr. 1927 – Jan. 1929 Apr. 1929 – 30 May 1930 30 May 1930 – July 1931; 7 June 1947 – 1 October 1949 |
1921-07-03 |
| Haikou | 海口市 | Guangdong | Province-controlled | Dec. 1926 – Feb. 1931; Apr. 1949 – 1 October 1949 | 1926-12- |
| Chencun | 陳村市 (陈村市) | Guangdong | Province-controlled | 1926 (failed) | (failed) |
| Meilu | 梅菉市 | Guangdong | Province-controlled | 1926–1932 | 1926– - |
| Wuhu | 蕪湖市 (芜湖市) | Anhui | Province-controlled | 1927 – Mar. 1930 | 1927– - |
| Songhu
|
淞滬市 (淞沪市)
上海市 |
Songhu
Shanghai |
Special (de jure)
Yuan-controlled (de facto) Direct-controlled |
3 July 1921 – 29 December 1928
Mar. 1927 – 30 May 1930 30 May 1930 – 1 October 1949 |
1921-07-03 |
| Jiujiang | 九江市 | Jiangxi | Province-controlled | Mar. 1927 – Sep. 1930 | 1927-03- |
| Zigong | 自貢市 (自贡市) | Sichuan | Province-controlled | Mar. 1927 – 1 October 1949 | 1927-03- |
| Chongqing | 重慶市 (重庆市) | Sichuan | Province-controlled
Direct-controlled |
Mar. 1927 – 5 May 1939
5 May 1939 – 1 October 1949 |
1927-03- |
| Nanjing | 南京市 | Nanjing | Yuan-controlled
Direct-controlled |
May 1927 – 30 May 1930
30 May 1930 – 1 October 1949 |
1927-05- |
| Shilong | 石龍市 (石龙市) | Guangdong | Province-controlled | Aug. 1927 (failed) | (failed) |
| Zhengzhou | 鄭州市 (郑州市) | Henan | Province-controlled | 1928–1931 | 1928– - |
| Xijing / Xi'an | 西京市
西安市 |
Shaanxi
Xijing Xi'an |
Province-controlled
Direct-controlled |
1928 – 7 June 1947
1933 (failed) 7 June 1947 – 1 October 1949 |
1928– - |
| Changsha | 長沙市 (长沙市) | Hunan | Province-controlled | Jan. 1928 – 1 October 1949 | 1928-01- |
| Liuzhou | 柳州市 | Guangxi | Province-controlled | Apr. 1928– Oct. 1928 | 1928-04- |
| Nanning | 南寧市 (南宁市) | Guangxi | Province-controlled | Apr. 1928 – Oct. 1932 | 1928-04- |
| Kunming | 昆明市 | Yunnan | Province-controlled | Aug. 1928 – 1 October 1949 | 1928-08- |
| Wanxian | 萬縣市 (万县市) | Sichuan | Province-controlled | Nov. 1928 – 1935 | 1928-11- |
| Suzhou | 蘇州市 (苏州市) | Jiangsu | Province-controlled | Nov. 1928 – Apr. 1930 | 1928-11- |
| Kaifeng | 開封市 (开封市) | Henan | Province-controlled | 1929–1930 | 1929– - |
| Guilin | 桂林市 | Guangxi | Province-controlled | Nov. 1932 (failed); June 1940 – 1944; 1945 – 1 October 1949 | 1940– - |
| Baotou | 包頭市 (包头市) | Suiyuan | Province-controlled | Apr. 1933 – 1 October 1949 | 1933-04- |
| Fuzhou | 福州市 | Fujian | Province-controlled | May 1933 – July 1934; Jan. 1946 – 1 October 1949 | 1933-05- |
| Lianyun | 連雲市 (连云市) | Jiangsu | Province-controlled | Feb. 1935 – 1 October 1949 | 1935-02- |
| Xiamen | 廈門市 (厦门市) | Fujian | Province-controlled | Apr. 1935 – 1 October 1949 | 1935-04- |
| Lanzhou | 蘭州市 (兰州市) | Gansu | Province-controlled | May 1941 – 1 October 1949 | 1941-05- |
| Hengyang | 衡陽市 (衡阳市) | Hunan | Province-controlled | July 1941 – 1 October 1949 | 1941-07- |
| Guiyang | 貴陽市 (贵阳市) | Guizhou | Province-controlled | July 1941 – 1 October 1949 | 1941-07- |
| Taiyuan | 太原市 | Shanxi | Province-controlled | Nov. 1941 – 1 October 1949 | 1941-11- |
| Shanba | 陝壩市 (陕坝市) | Suiyuan | Province-controlled | Mar. 1943 – 1 October 1949 | 1943-03- |
| Shaoguan | 韶關市 (韶关市) | Guangdong | Province-controlled | Oct. 1943 – 1944 | 1943-10- |
| Yinchuan | 銀川市 (银川市) | Ningxia | Province-controlled | Jan. 1944 – 1 October 1949 | 1944-01- |
| Weihaiwei | 威海衛市 (威海卫市) | Shandong | Province-controlled | 1945 – 1 October 1949 | 1945– - |
| Dihua | 迪化市 | Xinjiang | Province-controlled | Aug. 1945 – 1 October 1949 | 1945-08- |
| Zhanjiang | 湛江市 | Guangdong | Province-controlled | Sep. 1945 – 1 October 1949 | 1945-09- |
| Xuzhou | 徐州市 | Jiangsu | Province-controlled | Oct. 1945 – 1 October 1949 | 1945-10- |
| Xining | 西宁市 | Qinghai | Province-controlled | Nov. 1945 – 1 October 1949 | 1945-11- |
| Keelung | 基隆市 | Taiwan | Province-controlled | 25 Oct. 1945 – … (List of cities in Taiwan) | 1945-10-25 |
| Hsinchu | 新竹市 | Taiwan | Province-controlled | 25 Oct. 1945 – … (List of cities in Taiwan) | 1945-10-25 |
| Taichung | 臺中市 (台中市) | Taiwan | Province-controlled | 25 Oct. 1945 – … (List of cities in Taiwan) | 1945-10-25 |
| Chiayi City | 嘉義市 | Taiwan | Province-controlled | 25 Oct. 1945 - … (List of cities in Taiwan) | 1945-10-25 |
| Tainan | 臺南市 (台南市) | Taiwan | Province-controlled | 25 Oct. 1945 – … (List of cities in Taiwan) | 1945-10-25 |
| Changhua City | 彰化市 | Taiwan | Province-controlled | 25 Oct. 1945 – … (List of cities in Taiwan) | 1945-10-25 |
| Pingtung City | 屏東市 | Taiwan | Province-controlled | 25 Oct. 1945 - … (List of cities in Taiwan) | 1945-10-25 |
| Taipei | 臺北市 (台北市) | Taiwan | Province-controlled | 25 Oct. 1945 – … (List of cities in Taiwan) | 1945-10-25 |
| Kaohsiung | 高雄市 | Taiwan | Province-controlled | 25 Oct. 1945 -… (List of cities in Taiwan) | 1945-10-25 |
| Tangshan | 唐山市 | Hebei | Province-controlled | Apr. 1946 – 1 October 1949 | 1946-04- |
| Shimen | 石門市 (石门市) | Hebei | Province-controlled | Apr. 1946 – 1 October 1949 | 1946-04- |
| Jinan | 濟南市 (济南市) | Shandong | Province-controlled | Sep. 1946 – 1 October 1949 | 1946-09- |
| Yantai | 煙臺市 (烟台市) | Shandong | Province-controlled | 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947– - |
| Bengbu | 蚌埠市 | Anhui | Province-controlled | Apr. 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-04- |
| Zhangyuan | 張垣市 (张垣市) | Qahar | Province-controlled | June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06- |
| Yingkou | 營口市 (营口市) | Liaoning | Province-controlled | June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06- |
| Lüshun | 旅順市 (旅顺市) | Liaoning | Province-controlled | June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06- |
| Tonghua | 通化市 | Andong | Province-controlled | June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06- |
| Andong | 安東市 (安东市) | Andong | Province-controlled | June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06- |
| Siping | 四平市 | Liaobei | Province-controlled | June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06- |
| Jilin | 吉林市 | Jilin | Province-controlled | June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06- |
| Changchun | 長春市 (长春市) | Jilin | Province-controlled | June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06- |
| Mudanjiang | 牡丹江市 | Songjiang | Province-controlled | June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06- |
| Yanji | 延吉市 | Songjiang | Province-controlled | June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06- |
| Jiamusi | 佳木斯市 | Hejiang | Province-controlled | June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06- |
| Bei'an | 北安市 | Heilongjiang | Province-controlled | June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06- |
| Qiqihar | 齊齊哈爾市 (齐齐哈尔市) | Nenjiang | Province-controlled | June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06- |
| Hailar | 海拉爾市 (海拉尔市) | Xing'an | Province-controlled | June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06- |
| Dalian | 大連市 (大连市) | Dalian | Direct-controlled | 5 June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06-05 |
| Shenyang | 瀋陽市 (沈阳市) | Shenyang | Direct-controlled | 5 June 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-06-05 |
| Jinzhou | 錦州市 (锦州市) | Liaoning | Province-controlled | July 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-07- |
| Guisui | 歸綏市 (归绥市) | Suiyuan | Province-controlled | Nov. 1947 – 1 October 1949 | 1947-11- |
Close
Remove ads
See also
- List of capitals in China
- List of top Chinese cities by GDP
- List of top Chinese cities by GDP per capita
- List of prefecture-level divisions of China by GDP
- List of cities in China by population
- List of cities in the Republic of China (Taiwan)
- List of fu prefectures of China
- List of villages in China
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
Remove ads