Loading AI tools
Sinitic language spoken in East Asia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Hokkien (/ˈhɒkiɛn/ HOK-ee-en, US also /ˈhoʊkiɛn/ HOH-kee-en)[8] is a variety of the Southern Min languages, native to and originating from the Minnan region, in the southeastern part of Fujian in southeastern mainland China. It is also referred to as Quanzhang (Chinese: 泉漳; pinyin: Quánzhāng), from the first characters of the urban centers of Quanzhou and Zhangzhou.
| Hokkien | |
|---|---|
| Min Nan, Quanzhang, Amoy | |
 Koa-á books featuring Hokkien written in Chinese characters | |
| Region | China, Taiwan, and Southeast Asia |
| Ethnicity | Hokkien / Hoklo people |
Native speakers | tens of millions (est.)[lower-alpha 1][2] |
Early forms | |
| Dialects | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Taiwan[lower-alpha 3] |
| Regulated by | Taiwan Ministry of Education |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | nan (Southern Min) |
| Glottolog | hokk1242 |
 Distribution of Southern Min languages, with Hokkien in dark green | |
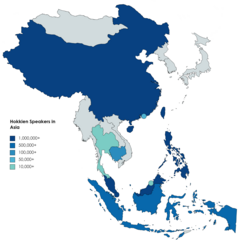 Polities by number of Hokkien speakers
≥1,000,000
≥500,000
≥100,000
≥50,000
Significant minority populations | |
| Hokkien | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 福建話 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 福建话 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hokkien POJ | Hok-kiàn-ōe / Hok-kiàn-ōa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Southern Min / Min Nan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 閩南話/閩南語 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 闽南话/闽南语 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hokkien POJ | Bân-lâm-ōe / Bân-lâm-ōa / Bân-lâm-gú / Bân-lâm-gí / Bân-lâm-gír | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hoklo | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 福佬話 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 福佬话 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hokkien POJ | Ho̍h-ló-ōe / Hô-ló-ōe / Hō-ló-ōe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lanlang | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 咱人話/咱儂話 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 咱人话/咱侬话 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hokkien POJ | Lán-lâng-ōe / Lán-nâng-ōe / Nán-nâng-ōe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Taiwanese Hokkien is one of the national languages in Taiwan. Hokkien is also widely spoken within the overseas Chinese diaspora in Singapore, Malaysia, the Philippines, Indonesia, Cambodia, Myanmar, Hong Kong, Thailand, Brunei, Vietnam, and elsewhere across the world. Mutual intelligibility between Hokkien dialects varies, but they are still held together by ethnolinguistic identity.[6]
In maritime Southeast Asia, Hokkien historically served as the lingua franca amongst overseas Chinese communities of all dialects and subgroups, and it remains today as the most spoken variety of Chinese in the region, including in Singapore, Malaysia, Philippines, Indonesia, Brunei. This applied to a lesser extent to mainland Southeast Asia.[9] As a result of the significant influence and historical presence of its sizable overseas diaspora, certain considerable to ample amounts of Hokkien loanwords are also historically present in the languages it has had historical contact with in its sprachraum, such as Thai. Hokkien Kelantan in northern Malaya of Malaysia and Hokaglish spoken sporadically across the Philippines, especially Metro Manila are also mixed languages with Hokkien as the base lexifier.[excessive detail?]
Hokkien speakers in different regions refer to the language as:
In parts of Southeast Asia and in the English-speaking communities, the term Hokkien ([hɔk˥kiɛn˨˩]) is etymologically derived from the Hokkien pronunciation of Fujian (Hok-kiàn), the province from which the language hails. In Southeast Asia and the English press, Hokkien is used in common parlance to refer to the Southern Min dialects of southern Fujian, and does not include reference to dialects of other Sinitic branches also present in Fujian such as the Fuzhou language (Eastern Min), Pu-Xian Min, Northern Min, Gan Chinese or Hakka.
The term Hokkien was first used by Walter Henry Medhurst in his 1832 Dictionary of the Hok-këèn Dialect of the Chinese Language, According to the Reading and Colloquial Idioms, considered to be the earliest English-based Hokkien dictionary and the first major reference work in POJ, though its romanization system differs significantly from modern POJ. In this dictionary, the word Hok-këèn was used. In 1869, POJ was further revised by John Macgowan in his published book A Manual Of The Amoy Colloquial. In this book, këèn was changed to kien as Hok-kien; from then on, "Hokkien" is used more often.
Historically, Hokkien was also known as "Amoy", after the Zhangzhou Hokkien pronunciation of Xiamen (Ēe-mûi), the principal port in southern Fujian during the Qing dynasty, as one of the five ports opened to foreign trade by the Treaty of Nanking.[11] In 1873, Carstairs Douglas published the Chinese–English Dictionary of the Vernacular or Spoken Language of Amoy, With the Principal Variations of the Chang-chew and Chin-chew Dialects, where the language was referred to as the "Language of Amoy"[12] or as the "Amoy Vernacular"[11] and by 1883, John Macgowan would publish another dictionary, the English and Chinese Dictionary of the Amoy Dialect.[13] Due to possible conflation between the language as a whole with its Xiamen dialect, many proscribe referring to the former as "Amoy", a usage that is more commonly found in older media and some conservative institutions.
In the classification used by the Language Atlas of China, the Quanzhang branch of Southern Min consists of the Min varieties originating from Quanzhou, Zhangzhou, Xiamen and the eastern counties of Longyan (Xinluo and Zhangping).[14]
Hokkien is spoken in the southern seaward quarter of Fujian, southeastern Zhejiang, as well as the eastern part of Namoa in China; Taiwan; Metro Manila, Metro Cebu, Metro Davao and other cities in the Philippines; Singapore; Brunei; Medan, Riau and other cities in Indonesia; and from Perlis, Kedah, Penang and Klang in Malaysia.
Hokkien originated in the southern area of Fujian province, an important center for trade and migration, and has since become one of the most common Chinese varieties overseas. The major pole of Hokkien varieties outside of Fujian is nearby Taiwan, where immigrants from Fujian arrived as workers during the 40 years of Dutch rule, fleeing the Qing dynasty during the 20 years of Ming loyalist rule, as immigrants during the 200 years of rule by the Qing dynasty, especially in the last 120 years after immigration restrictions were relaxed, and even as immigrants during the period of Japanese rule. The Taiwanese dialect mostly has origins with the Tung'an, Quanzhou and Zhangzhou variants, but since then, the Amoy dialect, also known as the Xiamen dialect, has become the modern prestige representative for the language in China. Both Amoy and Xiamen come from the Chinese name of the city (厦门; Xiàmén; Ē-mûi); the former is from Zhangzhou Hokkien, whereas the latter comes from Mandarin.
There are many Min Nan speakers among overseas Chinese communities in Southeast Asia, as well as in the United States (Hoklo Americans). Many ethnic Han Chinese emigrants to the region were Hoklo from southern Fujian, and brought the language to what is now Myanmar, Vietnam, Indonesia (the former Dutch East Indies) and present day Malaysia and Singapore (formerly Malaya and the British Straits Settlements). Most of the Min Nan dialects of this region have incorporated some foreign loanwords. Hokkien is reportedly the native language of up to 80% of the ethnic Chinese people in the Philippines, among which is known locally as Lán-nâng-uē ("Our people's speech"). Hokkien speakers form the largest group of overseas Chinese in Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia and the Philippines.[citation needed]
This section needs additional citations for verification. (May 2021) |
Southern Fujian is home to four principal Hokkien dialects: Chiangchew, Chinchew, Tung'an, and Amoy,[15] originating from the cities of Quanzhou, Zhangzhou, historical Tung'an County (同安縣, now Xiamen and Kinmen) and the Port of Amoy, respectively.
In the late 1800s, the Amoy dialect attracted special attention, because Amoy was one of the five ports opened to foreign trade by the Treaty of Nanking, but before that it had not attracted attention.[16] The Amoy dialect is adopted as the 'Modern Representative Min Nan'. The Amoy dialect cannot simply be interpreted as a mixture of the Zhangzhou and Quanzhou dialects, but rather it is formed on the foundation of the Tung'an dialect with further inputs from other sub-dialects.[17] It has played an influential role in history, especially in the relations of Western nations with China, and was one of the most frequently learned dialects of Hokkien by Westerners during the second half of the 19th century and the early 20th century.
The Modern Representative form of Hokkien spoken around the Taiwanese city of Tainan heavily resembles the Tung'an dialect.[18][19] All Hokkien dialects spoken throughout the whole of Taiwan are collectively known as Taiwanese Hokkien, or Holo locally, although there is a tendency to call these Taiwanese language for historical reasons. It is spoken by more Taiwanese than any Sinitic language except Mandarin, and it is known by a majority of the population;[20] thus, from a socio-political perspective, it forms a significant pole of language usage due to the popularity of Holo-language media. Douglas (1873/1899) also noted that Formosa (Taiwan) has been settled mainly by emigrants from Amoy (Xiamen), Chang-chew (Zhangzhou), and Chin-chew (Quanzhou). Several parts of the island are usually found to be specially inhabited by descendants of such emigrants, but in Taiwan, the various forms of the dialects mentioned prior are a good deal mixed up.[21]
The varieties of Hokkien in Southeast Asia originate from these dialects. Douglas (1873) notes that
Singapore and the various Straits Settlements [such as Penang and Malacca], Batavia [Jakarta] and other parts of the Dutch possessions [Indonesia], are crowded with emigrants, especially from the Chang-chew [Zhangzhou] prefecture; Manila and other parts of the Philippines have great numbers from Chin-chew [Quanzhou], and emigrants are largely scattered in like manner in Siam [Thailand], Burmah [Myanmar], the Malay Peninsula [peninsular Malaysia], Cochin China [Southern Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos], Saigon [Ho Chi Minh City], &c. In many of these places there is also a great mixture of emigrants from Swatow [Shantou].[21]
In modern times though, a mixed dialect descended from the Quanzhou, Amoy, and Zhangzhou dialects, leaning a little closer to the Quanzhou dialect, possibly due to being from the Tung'an dialect, is spoken by Chinese Singaporeans, Southern Malaysian Chinese, and Chinese Indonesians in Riau province and the Riau Islands. Variants include Southern Peninsular Malaysian Hokkien and Singaporean Hokkien in Singapore.
Among Malaysian Chinese of Penang, and other states in northern mainland Malaysia and ethnic Chinese Indonesians in Medan, with other areas in North Sumatra, Indonesia, a distinct descendant dialect form of Zhangzhou Hokkien has developed. In Penang, Kedah and Perlis, it is called Penang Hokkien while across the Strait of Malacca in Medan, an almost identical variant is known as Medan Hokkien.
Many Chinese Filipinos profess ancestry from Hokkien-speaking areas; Philippine Hokkien is also largely derived from the Quanzhou dialect, particularly Jinjiang and Nan'an dialects with some influence from the Amoy dialect.
There are also Hokkien speakers scattered throughout other parts of Indonesia—including Jakarta and the island of Java—Thailand, Myanmar, East Malaysia, Brunei, Cambodia, and Southern Vietnam, though there is notably more Teochew and Swatow background among descendants of Chinese migrants in Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, and Southern Vietnam.
This section needs additional citations for verification. (January 2016) |
Variants of Hokkien dialects can be traced to 2-4 main principal dialects of origin: the original two being, the Quanzhou (泉州; Choân-chiu / Chôaⁿ-chiu) and Zhangzhou (漳州; Chiang-chiu / Cheng-chiu) dialects, and in later centuries Xiamen/Amoy (廈門; Ē-mn̂g / Ēe-mûi) and Tong'an (同安; Tâng-oaⁿ) as well. The Amoy and Tong'an dialects are historically mixtures of Quanzhou and Zhangzhou dialects, since they are the geographic and linguistic midpoint between the two, while the rest of the Hokkien dialects spoken in Taiwan and Southeast Asia are respectively derived from varying proportions of the above principal dialects in southern Fujian.
During the Three Kingdoms period of ancient China, there was constant warfare occurring in the Central Plains of China. Ethnic Han Chinese gradually migrated from Henan to the mouth of the Yangtze to the coasts of Zhejiang and later began to enter into the Fujian region, which in ancient times was originally Minyue country, populated with non-Chinese Baiyue, causing the region for the first time in ancient times to incorporate Old Chinese dialects of which would later become Min Chinese. The massive migration of Han Chinese into Fujian region mainly occurred after the Disaster of Yongjia. The Jìn court fled from the north to the south, causing large numbers of Han Chinese to move into Fujian region. They brought the Old Chinese spoken in the Central Plain of China from the prehistoric era to the 3rd century into Fujian that later became Min, which later split off into its respective branches, of which Hokkien descends from the Southern Min branch of it.
In 677 (during the reign of Emperor Gaozong of Tang), Chen Zheng, together with his son Chen Yuanguang, led a military expedition to suppress a rebellion of the She people. In 885, (during the reign of Emperor Xizong of Tang), the two brothers Wang Chao and Wang Shenzhi, led a military expedition force to suppress the Huang Chao rebellion.[22] Waves of migration from the north in this era brought the language of Middle Chinese into the Fujian region, which gave Hokkien and all the other Min languages its literary readings.
During around the late 17th century when sea bans were lifted, the Port of Xiamen, which overshadowed the old port of Yuegang, became Fujian's main port where trade was legalized. From then, the Xiamen dialect, historically "Amoy", became the main principal dialect spoken overseas, such as in Taiwan under Qing rule, British Malaya, the Straits Settlements (British Singapore), British Hong Kong, Spanish Philippines (then later American Philippines), Dutch East Indies,and French Cochinchina, etc. Historically, Xiamen had always been part of Tung'an County until after 1912.[17] The Amoy dialect was the main prestige form of Hokkien known from the late 17th century to the Republican era. Due to this, dictionaries, bibles and other books about Hokkien from recent centuries and even to this day in certain places, like schools and churches, of certain countries, the Hokkien language is still known as "Amoy".
Several playscripts survive from the late 16th century, written in a mixture of Quanzhou and Chaozhou dialects. The most important is the Romance of the Litchi Mirror, with extant manuscripts dating from 1566 and 1581.[23][24]
In the early 17th century, Spanish friars in the Philippines produced materials documenting the Hokkien varieties spoken by the Chinese trading community who had settled there in the late 16th century:[23][25]
These texts appear to record a primarily Zhangzhou-descended dialect with some attested Quanzhou and Teo-Swa features, from the old port of Yuegang (modern-day Haicheng, an old port that is now part of Longhai).[32]
Chinese scholars produced rhyme dictionaries describing Hokkien varieties at the beginning of the 19th century:[33]
Rev. Walter Henry Medhurst based his 1832 dictionary, "A Dictionary of the Hok-këèn Dialect of the Chinese Language", on the latter work.[34]
Other popular 19th century works are also like those of Rev. John Macgowan's 1883 dictionary, "English and Chinese Dictionary of the Amoy Dialect",[13] and Rev. Carstairs Douglas's 1873 dictionary, "Chinese-English Dictionary of the Vernacular or Spoken Language of Amoy, with the Principal Variations of the Chang-Chew and Chin-Chew Dialects",[35] and its 1899 New Edition with Rev. Thomas Barclay.[15]
Hokkien has one of the most diverse phoneme inventories among Chinese varieties, with more consonants than Standard Mandarin and Cantonese. Vowels are more-or-less similar to that of Mandarin. Hokkien varieties retain many pronunciations that are no longer found in other Chinese varieties. These include the retention of the /t/ initial, which is now /tʂ/ (pinyin zh) in Mandarin (e.g. 竹; 'bamboo' is tik, but zhú in Mandarin), having disappeared before the 6th century in other Chinese varieties.[36] Along with other Min languages, which are not directly descended from Middle Chinese, Hokkien is of considerable interest to historical linguists for reconstructing Old Chinese.
Hokkien has aspirated, unaspirated as well as voiced consonant initials. For example, the word 開; khui; 'open' and 關; kuiⁿ; 'close' have the same vowel but differ only by aspiration of the initial and nasality of the vowel. In addition, Hokkien has labial initial consonants such as m in 命; miā; 'life'.
Another example is 查埔囝; cha-po͘-kiáⁿ / ta-po͘-kiáⁿ / ta-po͘-káⁿ; 'boy' and 查某囝; cha-bó͘-kiáⁿ / cha̋u-kiáⁿ / cha̋u-káⁿ / chő͘-kiáⁿ; 'girl', which for the cha-po͘-kiáⁿ and cha-bó͘-kiáⁿ pronunciation differ only in the second syllable in consonant voicing and in tone.
Unlike Mandarin, Hokkien retains all the final consonants corresponding to those of Middle Chinese. While Mandarin only preserves the [n] and [ŋ] finals, Hokkien also preserves the [m], [p], [t] and [k] finals and has developed the glottal stop [ʔ].
The vowels of Hokkien are listed below:[42]
| Oral | Nasal | Stops | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medial | ∅ | e | i | o | u | ∅ | m | n | ŋ | i | u | p | t | k | ʔ | ||
| Nucleus | Vowel | a | a | ai | au | ã | ãm | ãn | ãŋ | ãĩ | ãũ | ap | at | ak | aʔ | ||
| i | i | io | iu | ĩ | ĩm | ĩn | ĩŋ | ĩũ | ip | it | ik | iʔ | |||||
| e | e | ẽ | ẽŋ* | ek* | eʔ | ||||||||||||
| ə | ə | ə̃m* | ə̃n* | ə̃ŋ* | əp* | ət* | ək* | əʔ* | |||||||||
| o | o | õŋ* | ot* | ok* | oʔ | ||||||||||||
| ɔ | ɔ | ɔ̃ | ɔ̃m* | ɔ̃n* | ɔ̃ŋ | ɔp* | ɔt* | ɔk | ɔʔ | ||||||||
| u | u | ue | ui | ũn | ũĩ | ut | uʔ | ||||||||||
| ɯ | ɯ* | ɯ̃ŋ* | |||||||||||||||
| Diphthongs | ia | ia | iau | ĩã | ĩãm | ĩãn | ĩãŋ | ĩãũ | iap | iat | iak | iaʔ | |||||
| iɔ | ĩɔ̃* | ĩɔ̃ŋ | iɔk | ||||||||||||||
| iə | iə | ĩə̃m* | ĩə̃n* | ĩə̃ŋ* | iəp* | iət* | |||||||||||
| ua | ua | uai | ũã | ũãn | ũãŋ* | ũãĩ | uat | uaʔ | |||||||||
| Others | ∅ | m̩ | ŋ̍ | ||||||||||||||
(*)Only certain dialects
The following table illustrates some of the more commonly seen sound shifts between various dialects. Pronunciations are provided in Pe̍h-ōe-jī and IPA.
| Character | Hokkien | Teochew | Haklau Min | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| operatic | Nan'an | Quanzhou | Xiamen | Zhangzhou | Zhangpu | Zhaoan | Chaozhou | Chaoyang | Haifeng | |
| 二 'two' |
lī | lī | lī | lī | jī | jī | jī | jĭ | jĭ | jĭ |
| [li⁴¹] | [li³¹] | [li⁴¹] | [li²²] | [dʑi²²] | [dʑi²²] | [dʑi²²] | [dʑi³⁵] | [dʑi⁵³] | [dʑi³⁵] | |
| 坐 'to sit' |
chěr | chěr | chěr | chē | chē | chē | chēr | chǒ | chǒ | chě |
| [tsə²²] | [tsə²²] | [tsə²²] | [tse²²] | [tse²²] | [tsɛ²²] | [tsə²²] | [tso³⁵] | [tso⁵³] | [tsɛ³⁵] | |
| 皮 'skin' |
phêr | phêr | phêr | phê | phôe | phôe | phôe | phôe | phôe | phôe |
| [pʰə²⁴] | [pʰə²⁴] | [pʰə²⁴] | [pʰe²⁴] | [pʰuɛ¹³] | [pʰuɛ³¹²] | [pʰuɛ³⁵] | [pʰuɛ⁵⁵] | [pfʰuɛ³³] | [pʰuɛ⁵⁵] | |
| 雞 'chicken' |
kire | koe | koe | koe | ke | kei | kei | koi | koi | kei |
| [kɯe³³] | [kue³³] | [kue³³] | [kue⁴⁴] | [ke³⁴] | [kiei⁴⁴] | [kei⁴⁴] | [koi³³] | [koi³¹] | [kei³³] | |
| 病 'sick' |
pīⁿ | pīⁿ | pīⁿ | pīⁿ | pēⁿ | pēⁿ | pēⁿ | pēⁿ | pēⁿ | pēⁿ |
| [pĩ⁴¹] | [pĩ³¹] | [pĩ⁴¹] | [pĩ²²] | [pɛ̃²²] | [pɛ̃²²] | [pɛ̃²²] | [pɛ̃²¹] | [pɛ̃⁴²] | [pɛ̃³¹] | |
| 飯 'rice' |
pn̄g | pn̄g | pn̄g | pn̄g | pūiⁿ | pūiⁿ | pūiⁿ | pūng | pn̄g | pūiⁿ |
| [pŋ̍⁴¹] | [pŋ̍³¹] | [pŋ̍⁴¹] | [pŋ̍²²] | [puĩ²²] | [puĩ²²] | [puĩ²²] | [puŋ²¹] | [pŋ̍⁴²] | [puĩ³¹] | |
| 自 'self' |
chīr | chīr | chīr | chū | chū | chū | chīr | chīr | chū | chū |
| [tsɯ⁴¹] | [tsɯ³¹] | [tsɯ⁴¹] | [tsu²²] | [tsu²²] | [tsu²²] | [tsɯ²²] | [tsɯ²¹] | [tsu⁴²] | [tsu³¹] | |
| 豬 'pig' |
tir | tir | tir | tu | ti | ti | tir | tir | tu | ti |
| [tɯ³³] | [tɯ³³] | [tɯ³³] | [tu⁴⁴] | [ti³⁴] | [ti⁴⁴] | [tɯ⁴⁴] | [tɯ³³] | [tu³¹] | [ti³³] | |
| 取 'to take' |
chhú | chhú | chhú | chhú | chhí | chhí | chhír | chhú | chhú | chhí |
| [tsʰu⁵⁵] | [tsʰu⁵⁵] | [tsʰu⁵⁵] | [tsʰu⁵³] | [tɕʰi⁵³] | [tɕʰi⁵³] | [tsʰɯ⁵³] | [tsʰu⁵³] | [tsʰu⁴⁵] | [tɕʰi⁵³] | |
| 德 'virtue' |
tirak | terk | tiak | tek | tek | tek | tek | tek | tek | tek |
| [tɯak⁵] | [tək⁵] | [tiak⁵] | [tiɪk³²] | [tiɪk³²] | [tɛk³²] | [tɛk³²] | [tɛk³²] | [tɛk⁴³] | [tɛk³²] | |
| 偶 'idol' |
giró | gió | gió | ngó͘ | ngó͘ | ngóu | ngóu | ngóu | ngóu | ngóu |
| [ɡɯo⁵⁵] | [ɡio⁵⁵] | [ɡio⁵⁵] | [ŋɔ̃⁵³] | [ŋɔ̃⁵³] | [ŋɔ̃u⁵³] | [ŋɔ̃u⁵³] | [ŋou⁵³] | [ŋou⁴⁵] | [ŋou⁵³] | |
| 蝦 'prawn' |
hê | hê | hê | hê | hê͘ | hê͘ | hê͘ | hê | hê | hê |
| [he²⁴] | [he²⁴] | [he²⁴] | [he²⁴] | [hɛ¹³] | [hɛ³¹²] | [hɛ³⁵] | [hɛ⁵⁵] | [hɛ³³] | [hɛ⁵⁵] | |
| 銀 'silver' |
girêrn | gêrn | gûn | gûn | gîn | gîn | gîn | ngîrng | ngîng | ngîn |
| [ɡɯən²⁴] | [ɡən²⁴] | [ɡun²⁴] | [ɡun²⁴] | [ɡin¹³] | [ɡin³¹²] | [ɡin³⁵] | [ŋɯŋ⁵⁵] | [ŋiŋ³³] | [ŋin⁵⁵] | |
| 向 'to face' |
hiòng | hiòng | hiòng | hiòng | hiàng | hiàng | hiàng | hiàng | hiàng | hiàng |
| [hiɔŋ⁴¹] | [hiɔŋ³¹] | [hiɔŋ⁴¹] | [hiɔŋ³¹] | [hiaŋ²¹] | [hiaŋ¹¹] | [hiaŋ¹¹] | [hiaŋ²¹²] | [hiaŋ⁵³] | [hiaŋ²¹²] | |
According to the traditional Chinese system, Hokkien dialects have 7 or 8 distinct tones, including two entering tones which end in plosive consonants. The entering tones can be analysed as allophones, giving 5 or 6 phonemic tones. In addition, many dialects have an additional phonemic tone ("tone 9" according to the traditional reckoning), used only in special or foreign loan words.[43] This means that Hokkien dialects have between 5 and 7 phonemic tones.
Tone sandhi is extensive.[44] There are minor variations between the Quanzhou and Zhangzhou tone systems. Taiwanese tones follow the patterns of Amoy or Quanzhou, depending on the area of Taiwan.
| Tones | level | rising | departing | entering | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dark level | light level | dark rising | light rising | dark departing | light departing | dark entering | light entering | ||
| Tone Number | 1 | 5 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 8 | |
| Tone contour | Xiamen, Fujian | ˦˦ | ˨˦ | ˥˧ | – | ˨˩ | ˨˨ | ˧˨ | ˦ |
| 東 taŋ1 | 銅 taŋ5 | 董 taŋ2 | – | 凍 taŋ3 | 動 taŋ7 | 觸 tak4 | 逐tak8 | ||
| Taipei, Taiwan | ˦˦ | ˨˦ | ˥˧ | – | ˩˩ | ˧˧ | ˧˨ | ˦ | |
| – | |||||||||
| Tainan, Taiwan | ˦˦ | ˨˧ | ˦˩ | – | ˨˩ | ˧˧ | ˧˨ | ˦˦ | |
| – | |||||||||
| Zhangzhou, Fujian | ˧˦ | ˩˧ | ˥˧ | – | ˨˩ | ˨˨ | ˧˨ | ˩˨˩ | |
| – | |||||||||
| Quanzhou, Fujian | ˧˧ | ˨˦ | ˥˥ | ˨˨ | ˦˩ | ˥ | ˨˦ | ||
| – | |||||||||
| Penang, Malaysia[45] | ˧˧ | ˨˧ | ˦˦˥ | – | ˨˩ | ˧ | ˦ | ||
| – | |||||||||
Hokkien is spoken in a variety of accents and dialects across the Minnan region. The Hokkien spoken in most areas of the three counties of southern Zhangzhou have merged the coda finals -n and -ng into -ng. The initial consonant j (dz and dʑ) is not present in most dialects of Hokkien spoken in Quanzhou, having been merged into the d or l initials.
The -ik or -ɪk final consonant that is preserved in the native Hokkien dialects of Zhangzhou and Xiamen is also preserved in the Nan'an dialect (色, 德, 竹) but are pronounced as -iak in Quanzhou Hokkien.[46]
*Haklau Min (Hai Lok Hong, including the Haifeng and Lufeng dialect), Chaw'an / Zhao'an (詔安話), Longyan Min, and controversially, Taiwanese, are sometimes considered as not Hokkien anymore, besides being under Southern Min (Min Nan). On the other hand, those under Longyan Min, Datian Min, Zhenan Min have some to little mutual intelligibility with Hokkien, while Teo-Swa Min, the Sanxiang dialect of Zhongshan Min, and Qiong-Lei Min also have historical linguistic roots with Hokkien, but are significantly divergent from it in terms of phonology and vocabulary, and thus have almost little to no practical face-to-face mutual intelligibility with Hokkien.[excessive detail?]
The Xiamen dialect is a variant of the Tung'an dialect. Majority of Taiwanese, from Tainan, to Taichung, to Taipei, is also heavily based on Tung'an dialect while incorporating some vowels of Zhangzhou dialect, whereas Southern Peninsular Malaysian Hokkien, including Singaporean Hokkien, is based on the Tung'an dialect, with Philippine Hokkien on the Quanzhou dialect, and Penang Hokkien & Medan Hokkien on the Zhangzhou dialect. There are some variations in pronunciation and vocabulary between Quanzhou and Zhangzhou dialects. The grammar is generally the same.
Additionally, extensive contact with the Japanese language has left a legacy of Japanese loanwords in Taiwanese Hokkien. On the other hand, the variants spoken in Singapore and Malaysia have a substantial number of loanwords from Malay and to a lesser extent, from English and other Chinese varieties, such as the closely related Teochew and some Cantonese. Meanwhile, in the Philippines, there are also a few Spanish and Filipino (Tagalog) loanwords, while it is also currently a norm to frequently codeswitch with English, Tagalog, and in some cases other Philippine languages, such as Cebuano, Hiligaynon, Bicol Central, Ilocano, Chavacano, Waray-waray, Kapampangan, Pangasinense, Northern Sorsogonon, Southern Sorsogonon, etc.
Tong'an, Xiamen, Taiwanese, Singaporean dialects as a group are more mutually intelligible, but it is less so amongst the forementioned group, Quanzhou dialect, and Zhangzhou dialect.[47]
Although the Min Nan varieties of Teochew and Amoy are 84% phonetically similar including the pronunciations of un-used Chinese characters as well as same characters used for different meanings,[citation needed] and 34% lexically similar,[citation needed], Teochew has only 51% intelligibility with the Tong'an Hokkien|Tung'an dialect (Cheng 1997)[who?] whereas Mandarin and Amoy Min Nan are 62% phonetically similar[citation needed] and 15% lexically similar.[citation needed] In comparison, German and English are 60% lexically similar.[48]
Hainanese, which is sometimes considered Southern Min, has almost no mutual intelligibility with any form of Hokkien.[47]
Hokkien is an analytic language; in a sentence, the arrangement of words is important to its meaning.[49] A basic sentence follows the subject–verb–object pattern (i.e. a subject is followed by a verb then by an object), though this order is often violated because Hokkien dialects are topic-prominent. Unlike synthetic languages, seldom do words indicate time, gender and plural by inflection. Instead, these concepts are expressed through adverbs, aspect markers, and grammatical particles, or are deduced from the context. Different particles are added to a sentence to further specify its status or intonation.
A verb itself indicates no grammatical tense. The time can be explicitly shown with time-indicating adverbs. Certain exceptions exist, however, according to the pragmatic interpretation of a verb's meaning. Additionally, an optional aspect particle can be appended to a verb to indicate the state of an action. Appending interrogative or exclamative particles to a sentence turns a statement into a question or shows the attitudes of the speaker.
Hokkien dialects preserve certain grammatical reflexes and patterns reminiscent of the broad stage of Archaic Chinese. This includes the serialization of verb phrases (direct linkage of verbs and verb phrases) and the infrequency of nominalization, both similar to Archaic Chinese grammar.[50]
汝
Lí
2SG
去
khì
go
買
bué
buy
有
ū
have
錶仔
pió-á
watch
無?
--bô?
no
"Did you go to buy a watch?"
As in many east Asian languages, classifiers are required when using numerals, demonstratives and similar quantifiers.
Choice of grammatical function words also varies significantly among the Hokkien dialects. For instance, (乞; knit) (denoting the causative, passive or dative) is retained in Jinjiang (also unique to the Jinjiang dialect is 度; thō͘ and in Jieyang, but not in Longxi and Xiamen, whose dialects use 互/予; hō͘ instead.[51]
Hokkien dialects differ in the pronunciation of some pronouns (such as the second person pronoun lí, lú, or lír), and also differ in how to form plural pronouns (such as n or lâng). Personal pronouns found in the Hokkien dialects are listed below:
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| 1st person | 我 góa |
阮1 gún, góan 咱2 or 俺 lán or án 我儂1,3 góa-lâng |
| 2nd person | 汝 lí, lír, lú |
恁 lín 汝儂3 lí-lâng, lú-lâng |
| 3rd person | 伊 i |
𪜶 in 伊儂3 i-lâng |
Possessive pronouns can be marked by the particle 的; ê), in the same way as normal nouns. In some dialects, possessive pronouns can also be formed with a nasal suffix, which means that possessive pronouns and plural pronouns are homophones:[52]
The most common reflexive pronoun is ka-kī (家己). In formal contexts, chū-kí (自己) is also used.
Hokkien dialects use a variety of demonstrative pronouns, which include:
The interrogative pronouns include:
States and qualities are generally expressed using stative verbs that do not require a verb meaning 'to be':
我
goá
1SG
腹肚
pak-tó͘
stomach
枵。
iau.
hungry
"I am hungry."
With noun complements, the verb sī (是) serves as the verb 'to be'.
昨昏
cha-hng
是
sī
八月節。
poeh-ge̍h-choeh.
"Yesterday was the Mid-Autumn festival."
To indicate location, the words tī (佇) tiàm (踮), leh (咧), which are collectively known as the locatives or sometimes coverbs in Chinese linguistics, are used to express '(to be) at':
我
goá
踮
tiàm
遮
chia
等
tán
汝。
lí.
"I am here waiting for you."
伊
i
這摆
chit-mái
佇
tī
厝
chhù
裡
lāi
咧
leh
睏。
khùn.
"They're sleeping at home now."
Hokkien dialects have a variety of negation particles that are prefixed or affixed to the verbs they modify. There are six primary negation particles in Hokkien dialects (with some variation in how they are written in characters):[excessive detail?]
Other negative particles include:
The particle m̄ (毋,呣,唔,伓) is general and can negate almost any verb:
伊
i
3SG
毋
m̄
not
捌
bat
know
字。
jī
character
"They cannot read."
The particle mài (莫,【勿爱】), a concatenation of m-ài (毋愛) is used to negate imperative commands:
莫
mài
講!
kóng
"Don't speak!"
The particle bô (無) indicates the past tense:[dubious – discuss]
伊
i
無
bô
食。
chia̍h
"They did not eat."
The verb 'to have', ū (有) is replaced by bô (無) when negated (not 無有):
伊
i
無
bô
錢。
chîⁿ
"They do not have any money."
The particle put (不) is used infrequently, mostly found in literary compounds and phrases:
伊
i
真
chin
不孝。
put-hàu
They are really unfilial."
The majority of Hokkien vocabulary is monosyllabic.[53][better source needed] Many Hokkien words have cognates in other Chinese varieties. That said, there are also many indigenous words that are unique to Hokkien and are potentially not of Sino-Tibetan origin, while others are shared by all the Min dialects (e.g. 'congee' is 糜 mê, bôe, bê, not 粥 zhōu, as in other dialects).
As compared to Mandarin, Hokkien dialects prefer to use the monosyllabic form of words, without suffixes. For instance, the Mandarin noun suffix 子; zi is not found in Hokkien words, while another noun suffix, 仔; á is used in many nouns. Examples are below:
In other bisyllabic words, the syllables are inverted, as compared to Mandarin. Examples include the following:
In other cases, the same word can have different meanings in Hokkien and Mandarin. Similarly, depending on the region Hokkien is spoken in, loanwords from local languages (Malay, Tagalog, Burmese, among others), as well as other Chinese dialects (such as Southern Chinese dialects like Cantonese and Teochew), are commonly integrated into the vocabulary of Hokkien dialects.
The existence of literary and colloquial readings is a prominent feature of some Hokkien dialects and indeed in many Sinitic varieties in the south. The bulk of literary readings (文讀; bûn-tha̍k), based on pronunciations of the vernacular during the Tang dynasty, are mainly used in formal phrases and written language (e.g. philosophical concepts, given names, and some place names), while the colloquial (or vernacular) ones (白讀; pe̍h-tha̍k) are usually used in spoken language, vulgar phrases and surnames. Literary readings are more similar to the pronunciations of the Tang standard of Middle Chinese than their colloquial equivalents.
The pronounced divergence between literary and colloquial pronunciations found in Hokkien dialects is attributed to the presence of several strata in the Min lexicon. The earliest, colloquial stratum is traced to the Han dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE); the second colloquial one comes from the period of the Northern and Southern dynasties (420–589 CE); the third stratum of pronunciations (typically literary ones) comes from the Tang dynasty (618–907 CE) and is based on the prestige dialect of Chang'an (modern day Xi'an), its capital.[54]
Some commonly seen sound correspondences (colloquial → literary) are as follows:
This table displays some widely used characters in Hokkien that have both literary and colloquial readings:[55][56]
| Chinese character | Reading pronunciations | Spoken pronunciations / †explications | English |
|---|---|---|---|
| 白 | pe̍k | pe̍h | white |
| 面 | biān | bīn | face |
| 書 | su | chu | book |
| 生 | seng | seⁿ / siⁿ | student |
| 不 | put | m̄† | not |
| 返 | hóan | tńg† | return |
| 學 | ha̍k | o̍h | to study |
| 人 | jîn / lîn | lâng† | person |
| 少 | siàu | chió | few |
| 轉 | chóan | tńg | to turn |
This feature extends to Hokkien numerals, which have both literary and colloquial readings.[56] Literary readings are typically used when the numerals are read out loud (e.g. phone numbers, years), while colloquial readings are used for counting items.
| Numeral | Reading | Numeral | Reading | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Literary | Colloquial | Literary | Colloquial | ||
| 1 | it | chi̍t | 6 | lio̍k | la̍k |
| 2 | jī, lī | nn̄g | 7 | chhit | |
| 3 | sam | saⁿ | 8 | pat | peh, poeh |
| 4 | sù, sìr | sì | 9 | kiú | káu |
| 5 | ngó͘ | gō͘ | 10 | si̍p | cha̍p |
Quite a few words from the variety of Old Chinese spoken in the state of Wu, where the ancestral language of Min and Wu dialect families originated, and later words from Middle Chinese as well, have retained the original meanings in Hokkien, while many of their counterparts in Mandarin Chinese have either fallen out of daily use, have been substituted with other words (some of which are borrowed from other languages while others are new developments), or have developed newer meanings. The same may be said of Hokkien as well, since some lexical meaning evolved in step with Mandarin while others are wholly innovative developments.
This table shows some Hokkien dialect words from Classical Chinese, as contrasted to the written Mandarin:
For other words, the classical Chinese meanings of certain words, which are retained in Hokkien dialects, have evolved or deviated significantly in other Chinese dialects. The following table shows some words that are both used in both Hokkien dialects and Mandarin Chinese, while the meanings in Mandarin Chinese have been modified:
| Word | Hokkien | Mandarin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| POJ | Gloss (and Classical Chinese) |
Pinyin | Gloss | |
| 走 | cháu | 'to flee' | zǒu | 'to walk' |
| 細 | sè, sòe | 'tiny', 'small, 'young' | xì | 'thin', 'slender' |
| 鼎 | tiáⁿ | 'pot' | dǐng | 'tripod' |
| 食 | chia̍h | 'to eat' | shí | 'to eat' (largely superseded by 吃) |
| 懸 | kôan, koâiⁿ, kûiⁿ | 'tall', 'high' | xuán | 'to hang', 'to suspend' |
| 喙 | chhùi | 'mouth' | huì | 'beak' |
Some commonly used words, shared by all[citation needed][dubious – discuss] Min Chinese languages, came from the Old Yue languages. Jerry Norman suggested that these languages were Austroasiatic. Some terms are thought be cognates with words in Tai Kadai and Austronesian languages. They include the following examples, compared to the Fuzhou dialect, a Min Dong language:
| Word | Hokkien POJ | Foochow Romanized | Gloss |
|---|---|---|---|
| 骹 | kha [kʰa˥] | kă [kʰa˥] | 'foot and leg' |
| 囝 | kiáⁿ [kjã˥˩] | giāng [kjaŋ˧] | 'son', 'child', 'whelp', 'a small amount' |
| 睏 | khùn [kʰun˨˩] | káung [kʰɑwŋ˨˩˧] | to sleep |
| 骿 | phiaⁿ [pʰjã˥] | piăng [pʰjaŋ˥] | 'back', 'dorsum' |
| 厝 | chhù [tsʰu˨˩] | chuó, chió [tsʰwɔ˥˧] | 'home', 'house' |
| 刣 | thâi [tʰaj˨˦] | tài [tʰaj˥˧] | 'to kill', 'to slaughter' |
| (肉) | bah [baʔ˧˨] | — | 'meat' |
| 媠 | suí [sui˥˧] | — | 'beautiful' |
| 檨 | soāiⁿ [suãi˨˨] | suông [suɔŋ˨˦˨] | 'mango' (Austroasiatic)[58][59] |
Loanwords are not unusual among Hokkien dialects, as speakers readily adopted indigenous terms of the languages they came in contact with. As a result, there is a plethora of loanwords that are not mutually comprehensible among Hokkien dialects.
Taiwanese Hokkien, as a result of linguistic contact with Japanese[60] and Formosan languages, contains many loanwords from these languages. Many words have also been formed as calques from Mandarin, and speakers will often directly use Mandarin vocabulary through codeswitching. Among these include the following examples:
Singaporean Hokkien, Penang Hokkien and other Malaysian Hokkien dialects tend to draw loanwords from Malay, English as well as other Chinese dialects, primarily Teochew. Examples include:
Philippine Hokkien, as a result of centuries-old contact with both Philippine languages and Spanish and due to recent 20th century modern contact with English, also incorporate words from these languages. Speakers today will also often directly use English and Filipino (Tagalog), or other Philippine languages like Bisaya, vocabulary through codeswitching. Examples of loans considered by native speakers to be part of the language already include:
Philippine Hokkien usually follows the 3 decimal place Hindu-Arabic numeral system used worldwide, but still retains the concept of 萬; bān; 'ten thousand' from the Chinese numeral system, so 'ten thousand' would be 一萬; chi̍t-bān, but examples of the 3 decimal place logic have produced words like:
| Gloss | Characters | Mandarin | Yue | Hokkien[63] | Korean | Vietnamese | Japanese |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 'book' | 冊 | cè | caak8 | chheh | chaek | tập/sách | saku/satsu/shaku |
| 'bridge' | 橋 | qiáo | kiu4 | kiô | kyo | cầu/kiều | kyō |
| 'dangerous' | 危險 | wēixiǎn | ngai4 him2 | guî-hiám | wiheom | nguy hiểm | kiken |
| 'flag' | 旗 | qí | kei4 | kî | ki | cờ/kỳ | ki |
| 'insurance' | 保險 | bǎoxiǎn | bou2 him2 | pó-hiám | boheom | bảo hiểm | hoken |
| 'news' | 新聞 | xīnwén | san1 man4 | sin-bûn | shinmun | tân văn | shinbun |
| 'student' | 學生 | xuéshēng | hok6 saang1 | ha̍k-seng | haksaeng | học sinh | gakusei |
| university' | 大學 | dàxué | daai6 hok9 | tāi-ha̍k (tōa-o̍h) | daehak | đại học | daigaku |
Quanzhou was historically the cultural center for Hokkien, as various traditional Hokkien cultural customs such as Nanguan music, Beiguan music, glove puppetry, and the kaoka and lewan genres of Hokkien opera originated from Quanzhou. This was mainly due to the fact that Quanzhou had become an important trading and commercial port since the Tang dynasty and had prospered into an important city. After the Opium War in 1842, Xiamen became one of the major treaty ports to be opened for trade with the outside world. From the mid-19th century onwards, Xiamen slowly developed to become the political and economical center of the Hokkien-speaking region in China. This caused the Amoy dialect to gradually replace the position of dialects from Quanzhou and Zhangzhou. From the mid-19th century until the end of World War II, [citation needed] western diplomats usually learned Amoy as the preferred dialect if they were to communicate with the Hokkien-speaking populace in China or Southeast Asia. In the 1940s and 1950s, Taiwan[who?] also tended towards the Amoy dialect.
The retreat of the Republic of China to Taiwan in 1949 drove party leaders to seek to both culturally and politically assimilate the islanders. As a result, laws were passed throughout the 1950s to suppress Hokkien and other languages in favor of Mandarin. By 1956, speaking Hokkien in ROC schools or military bases was illegal. However, popular outcry from both older islander communities and more recent Mainlander immigrants prompted a general wave of education reform, during which these and other education restrictions were lifted. The general goal of assimilation remained, with Amoy Hokkien seen as less 'native', and therefore preferred.[64]
However, from the 1980s onwards, the development of Taiwanese Min Nan pop music and media industry in Taiwan caused the Hokkien cultural hub to shift from Xiamen to Taiwan.[citation needed] The flourishing Taiwanese Min Nan entertainment and media industry from Taiwan in the 1990s and early 21st century led Taiwan to emerge as the new significant cultural hub for Hokkien.
In the 1990s, marked by the liberalization of language development and mother tongue movement in Taiwan, Taiwanese Hokkien had developed quickly. In 1993, Taiwan became the first region in the world to implement the teaching of Taiwanese Hokkien in Taiwanese schools. In 2001, the local Taiwanese language program was further extended to all schools in Taiwan, and Taiwanese Hokkien became one of the compulsory local Taiwanese languages to be learned in schools.[65] The mother tongue movement in Taiwan even influenced Xiamen (Amoy) to the point that in 2010, Xiamen also began to implement the teaching of Hokkien dialect in its schools.[66] In 2007, the Ministry of Education in Taiwan also completed the standardization of Chinese characters used for writing Hokkien and developed Tai-lo as the standard Hokkien pronunciation and romanization guide. A number of universities in Taiwan also offer Taiwanese degree courses for training Hokkien-fluent talents to work for the Hokkien media industry and education. Taiwan also has its own Hokkien literary and cultural circles whereby Hokkien poets and writers compose poetry or literature in Hokkien.
Thus, by the 21st century, Taiwan had become one of the most significant Hokkien cultural hubs of the world. The historical changes and development in Taiwan had led Taiwanese Hokkien to become the most influential pole of the Hokkien dialect after the mid-20th century. Today, the Taiwanese prestige dialect (台語優勢腔/通行腔) is heard on Taiwanese media.
Hokkien texts can be dated back to the 16th century. One example is the Doctrina Christiana en letra y lengua china, written around 1593 by the Spanish Dominican friars in the Philippines. Another is a Ming dynasty script of a play called Tale of the Lychee Mirror (1566), the earliest known Southern Min colloquial text, which mixes both Hokkien and Teochew.
Hokkien can be written using Chinese characters (漢字; Hàn-jī). However, the written script was and remains adapted to the literary form, which is based on Classical Chinese, not the vernacular and spoken form. Furthermore, the character inventory used for Mandarin (standard written Chinese) does not correspond to Hokkien words, and there are a large number of informal characters (替字; thè-jī, thòe-jī; 'substitute characters') which are unique to Hokkien, as is the case with written Cantonese. For instance, about 20 to 25% of Taiwanese morphemes lack an appropriate or standard Chinese character.[55]
While many Hokkien words have commonly used characters, they are not always etymologically derived from Classical Chinese. Instead, many characters are phonetic loans (borrowed for their sound) or semantic loans (borrowed for their meaning).[67] As example of a phonetic loan character, the word súi meaning "beautiful" might be written using the character 水, which can also be pronounced súi but originally with the meaning of "water". As an example of a semantic loan character, the word bah meaning "meat" might be written using the character 肉, which can also mean "meat" but originally with the pronunciation he̍k or jio̍k. Common grammatical particles are not exempt; the negation particle m̄ is variously represented by 毋, 呣 or 唔, among others. In other cases, new characters have been invented. For example, the word in meaning "they" might be written using the character 𪜶.
Moreover, unlike Cantonese, Hokkien does not have a universally accepted standardized character set. Thus, there is some variation in the characters used to express certain words and characters can be ambiguous. In 2007, the Ministry of Education of the Republic of China formulated and released a standard character set to overcome these difficulties.[68] These standard Chinese characters for writing Taiwanese Hokkien are now taught in schools in Taiwan.
Hokkien can be written in the Latin script using one of several systems. A popular system is POJ, developed first by Presbyterian missionaries in China and later by the indigenous Presbyterian Church in Taiwan. Use of POJ has been actively promoted since the late 19th century, and it was used by Taiwan's first newspaper, the Taiwan Church News. A more recent system is Tâi-lô, which was adapted from POJ. Since 2006, it has been officially promoted by Taiwan's Ministry of Education and taught in Taiwanese schools. Xiamen University has also developed a system based on Pinyin called Bbánlám pìngyīm. The use of a mixed script of Chinese characters and Latin letters is also seen.

Hokkien is registered as "Southern Min" per RFC 3066 as zh-min-nan.[69]
When writing Hokkien in Chinese characters, some writers create 'new' characters when they consider it impossible to use directly or borrow existing ones; this corresponds to similar practices in character usage in Cantonese, Vietnamese chữ Nôm, Korean hanja and Japanese kanji. Some of these are not encoded in Unicode, thus creating problems in computer processing.
All Latin characters required by Pe̍h-ōe-jī can be represented using Unicode (or the corresponding ISO/IEC 10646: Universal Character Set), using precomposed or combining (diacritics) characters. Prior to June 2004, the vowel akin to but more open than o, written with a dot above right, was not encoded. The usual workaround was to use an (stand-alone; spaced) interpunct (U+00B7, ·) or less commonly the combining character dot above (U+0307). As these are far from ideal, since 1997 proposals have been submitted to the ISO/IEC working group in charge of ISO/IEC 10646—namely, ISO/IEC JTC1/SC2/WG2—to encode a new combining character dot above right. This is now officially assigned to U+0358 (see documents N1593, N2507, N2628, N2699 Archived 10 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine, and N2713 Archived 14 January 2006 at the Wayback Machine).
In 2002, the Taiwan Solidarity Union, a party with about 10% of the Legislative Yuan seats at the time, suggested making Taiwanese a second official language.[70] This proposal encountered strong opposition not only from mainland Chinese groups but also from Hakka and Taiwanese aboriginal groups who felt that it would slight their home languages. Because of these objections, support for this measure was lukewarm among moderate Taiwan independence supporters, and the proposal did not pass.
Hokkien was finally made an official language of Taiwan in 2018 by the ruling DPP government.
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.