Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
ISCU
Mitochondrial protein involved in iron–sulfur cluster biosynthesis From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Iron-sulfur cluster assembly enzyme ISCU, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ISCU gene.[5] It encodes an iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster scaffold protein involved in [2Fe-2S] and [4Fe-4S] cluster synthesis and maturation.[6][7][8][9] A deficiency of ISCU is associated with a mitochondrial myopathy with lifelong exercise intolerance where only minor exertion causes tachycardia, shortness of breath, muscle weakness and myalgia.[10]
Remove ads
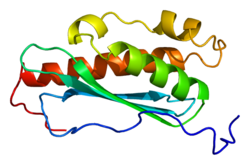
Structure
ISCU is located on the q arm of chromosome 12 in position 23.3 and has 8 exons.[7] ISCU, the protein encoded by this gene, is a member of the NifU family. It is an iron-sulfur transferase that contains binding sites for [2Fe-2S] and [4Fe-4S] clusters. ISCU contains a transit peptide, 4 beta strands, 4 alpha helixes, and 4 turns.[8][9] Alternative splicing results in transcript variants encoding different protein isoforms that localize either to the cytosol or to the mitochondrion. A pseudogene of this gene is present on chromosome 1.[7]
Remove ads
Function
ISCU encodes a component of the iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster scaffold responsible for the synthesis and maturation of [2Fe-2S] and [4Fe-4S] clusters. Fe-S clusters are cofactors that play a role in the function of a diverse set of enzymes, including those that regulate metabolism, iron homeostasis, and oxidative stress response. In one process, the [2Fe-2S] cluster transiently assembles on ISCU and is then transferred to GLRX5 in a cysteine desulfurase complex NFS1-LYRM4/ISD11 dependent process.[7][6][8][9]
ISCU has two isoforms, isoform 1, which is found in the mitochondrion and isoform 2, which is found in the nucleus and cytoplasm.[8][9]
Remove ads
Clinical significance
Summarize
Perspective
ISCU mutations have been found in patients with a mitochondrial myopathy called hereditary myopathy with lactic acidosis (HML).[11] It is also known as hereditary myopathy with exercise intolerance, Swedish type;[11] myopathy with deficiency of succinate dehydrogenase and aconitase;[11] myoglobinuria due to abnormal glycolysis;[11] myopathy with deficiency of ISCU;[10] Larsson–Linderholm syndrome;[12] and Linderholm myopathy.[13]
This disease is a result of a deficiency of ISCU that corresponds to the deficiency of mitochondrial iron-sulfur proteins and impaired muscle oxidative metabolism.[7] Characteristics of mitochondrial myopathy with deficiency of ISCU may include lifelong exercise intolerance in which exertion can cause tachycardia, dyspnoea, cardiac palpitations, shortness of breath, fatigue, pain of active muscles, rhabdomyolysis, myoglobinuria, elevated lactate and pyruvate, decreased oxygen utilization, may have a pseudoathletic appearance of hypertrophic calf muscles, and possibly weakness.[14][15][8][9][10][16] Primarily affecting the skeletal muscles, rarely there is also hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and ptosis (drooping eyelid).[11][17]
Biopsy of skeletal muscle shows deficiency of succinate dehydrogenase and aconitase, abnormal iron deposition and lipid droplet accumulation in the mitochondria. Histochemical studies show impaired respiratory chain complexes I, II, and III, impairing oxidative phosphorylation. Electromyography normal or myopathic increased polyphasic MUAPs. EMG results may be dynamic: more likely to have increased polyphasic MUAPs after exercise.[14] There has been documented temporary restoration of succinate dehydrogenase in regenerating muscle after an episode of rhabdomyolysis; however, the effect does not last.[18]
The disease is limited to muscle, with fibroblasts from skin biopsy being unaffected. As non-muscle tissues are unaffected, this necessitates the need for muscle biopsy when DNA testing using saliva or blood is inconclusive.[19][17]
Genetics
This disorder has been associated with several different mutations and is inherited predominantly in an autosomal recessive manner. It was originally believed to affect only those of northern Swedish ancestry, however the disease has been found in those of Norwegian and Finnish decent as well. The carrier rate in northern Sweden has been estimated at 1:188.[15] ISCU deficiency has been linked to pathogenic variants including intronic variants c.418+382G>C, g.7044G>C,[19] and IVS5+382 G>C[20] as well as a c.149G>A missense mutation in exon 3.[21] The intronic mutations have been suggested to activate a cryptic splice site, resulting in the production of a splice variant that encodes a putatively non-functional protein.[10]
In 2016, an Italian male was found to have a de novo autosomal dominant mutation, c.287G>T (p.Gly96Val) in the ISCU gene, that caused hereditary mitochondrial myopathy with lactic acidosis (HML). This mutation resulted in a similar phenotype as seen in the recessive form of the disease.[17]
Remove ads
Interactions
ISCU has been shown to have 235 binary protein-protein interactions including 79 co-complex interactions. ISCU appears to interact with ISCS, NUP62, SDHB, HPRT1, CCDC172, GOLGA2, IKZF1, KRT40, AGTRAP, NECAB2, FAM9B, BANP, LNX1, MID2, GOLGA6L9, ccdc136, KRT34, SPERT, PICK1, YWHAB, SFN, mbl, E7, dnaX, hscB, MAPk-Ak2, hale, and cv-c.[22]
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads