Portal:Germany
Wikipedia portal for content related to Germany / From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Portal maintenance status: (January 2019)
|
Welcome to the Germany Portal!
Willkommen im Deutschland-Portal!
 |
 |
 | |
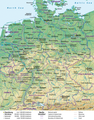
Germany (German: Deutschland), officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central and Western Europe, lying between the Baltic and North Seas to the north and the Alps to the south. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, France to the southwest, and Luxembourg, Belgium and the Netherlands to the west.
Germany includes 16 constituent states, covers an area of 357,578 square kilometres (138,062 sq mi) and has a largely temperate seasonal climate. With 83 million inhabitants, it is the second most populous state of Europe after Russia, the most populous state lying entirely in Europe, as well as the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is a very decentralized country. Its capital and largest metropolis is Berlin, while Frankfurt serves as its financial capital and has the country's busiest airport.
In 1871, Germany became a nation-state when most of the German states unified into the Prussian-dominated German Empire. After World War I and the Revolution of 1918–19, the empire was replaced by the parliamentary Weimar Republic. The Nazi seizure of power in 1933 led to World War II, and the Holocaust. After the end of World War II in Europe and a period of Allied occupation, two new German states were founded: West Germany, formed from the American, British, and French occupation zones, and East Germany, formed from the western part of the Soviet occupation zone, reduced by the newly established Oder-Neisse line. Following the Revolutions of 1989 that ended communist rule in Central and Eastern Europe, the country was reunified on 3 October 1990.
Today, Germany is a federal parliamentary republic led by a chancellor. It is a great power with a strong economy. The Federal Republic of Germany was a founding member of the European Economic Community in 1957 and the European Union in 1993. Read more...
Selected article

The formal unification of Germany into a politically and administratively integrated nation state officially occurred on 18 January 1871 at the Versailles Palace's Hall of Mirrors in France. Princes of the German states gathered there to proclaim Wilhelm of Prussia as Emperor Wilhelm of the German Empire after the French capitulation in the Franco-Prussian War. Unofficially, the transition of the German-speaking states into a federated organization of states occurred over nearly a century of experimentation. Unification exposed several glaring religious, linguistic, and cultural differences between and among the inhabitants of the new nation, suggesting that 1871 represents one moment in a continuum of unification processes.
The Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation had been informally dissolved in 1806 with the abdication of Emperor Francis II during the Napoleonic Wars. Despite the legal, administrative, and political disruption caused by the dissolution of the Empire, the people of the German-speaking areas of the old Empire had a common linguistic, cultural and legal tradition further enhanced by their shared experience in the French Revolutionary Wars. More...
Selected picture
- Image 1Photo credit: Daniel SchwenA portrait of a senior police officer in Hamburg, wearing the new blue uniform in accordance with the policy of using the same colour for police uniforms and vehicles throughout the European Union. Law enforcement in Germany is divided into two groups: the federal police and the state police.
- Image 2Shaft 12 of Zeche Zollverein, a coal mine in Essen
- Image 3Photograph: Thomas WolfThe Bode Museum on Museum Island in Berlin, Germany, named after its founding director, is a museum of antiquities including sculpture, Byzantine art and numismatics. Designed by Ernst von Ihne and completed in 1904, the building was restored extensively from 1997 to 2006.
- Image 4A night shot of the Völkerschlachtdenkmal (Monument of the Battle of the Nations) in Leipzig, Germany.
- Image 5Painting credit: Adolf MosengelAdolf Mosengel (1837–1885) was a landscape painter from Hamburg, Germany, who built a reputation painting Alpine scenes, later turning to scenes from Westphalia. From 1854 to 1857, he studied at the Kunstakademie Düsseldorf under Hans Gude, and from 1858 to 1859 in Paris, after which he moved to Geneva to study under Alexandre Calame. He spent most of his life working in Hamburg, but travelled in 1879 to the lakes of Northern Italy, where he painted en plein air. This oil-on-canvas painting by Mosengel shows a village in the Bernese Alps.
- Image 6The Königsallee (literally "King's Avenue") is an urban boulevard in Düsseldorf, state capital of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. The Königsallee is noted for both the landscaped canal that runs along its center, as well as for the fashion showrooms and luxury retail stores located along its sides.
- Image 8Painting: Caspar David FriedrichCairn in Snow is a landscape painting by Caspar David Friedrich that was completed in 1807. The painting is a Romantic allegorical landscape, showing a pagan burial site between three oaks, near the town Gützkow in Germany. It is held by the Galerie Neue Meister in Dresden, Germany.
- Image 9Photograph: Michael KranewitterThomas Müller (b. 1989) is a German professional footballer who has played for Bayern Munich since 2009; he is also the team's vice-captain. A versatile player, Müller plays as a midfielder or forward but has also been deployed in attacking roles such as attacking midfielder, second striker, centre forward and on either wing. He has represented Germany on its national team since 2010.
- Image 10Photo credit: Daniel SchwenSparrenburg Castle, located in Bielefeld, Germany, as seen from the western lawn. The castle was constructed between 1240 and 1250 by the Counts of Ravensberg. The castle has been rebuilt many times. Although often under siege, it was never stormed. After extensive restoration work, the castle now presents itself as an imposing historic site.
- Image 11Banknote design credit: Deutsch-Ostafrikanische Bank; photographed by Andrew ShivaThe rupie was the unit of currency of German East Africa between 1890 and 1916. During World War I, the colony was cut off from Germany as a result of a wartime blockade and the colonial government needed to create an emergency issue of banknotes. Paper made from linen or jute was initially used, but because of wartime shortages, the notes were later printed on commercial paper in a variety of colours, wrapping paper, and in one instance, wallpaper. This two hundred rupie banknote was issued in 1915, and is now part of the National Numismatic Collection at the Smithsonian Institution.
Other denominations:
'"`UNIQ--templatestyles-00000015-QINU`"' - Image 12Photo credit: Matthias SüßenMorning fog on the plains of East Frisia, a coastal region in the northwest of the German federal state of Lower Saxony. It connects Western Frisia (in the Netherlands) with the district of Nordfriesland ("Northern Frisia") in Schleswig-Holstein, all of which belong to the historic and geographic Frisia.
- Image 14Painting credit: Albert BierstadtAlbert Bierstadt (1830–1902) was a German-American painter best known for his lavish, sweeping landscapes of the American West, such as this oil-on-canvas painting, entitled Among the Sierra Nevada, California, created in 1868. He painted the landscape in his Rome studio, and exhibited it in Berlin and London before shipping it to the United States. His choice of grandiose subjects was matched by his entrepreneurial flair; his exhibitions of individual works were accompanied by promotion, ticket sales, and, in the words of one critic, a "vast machinery of advertisement and puffery". This work is in the collection of the Smithsonian American Art Museum.
- Image 15Photograph: Thomas WolfCharlottenburg Palace is a large palace in Charlottenburg, a part of the Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf borough of Berlin, Germany. The palace was built at the end of the 17th century and expanded during the 18th century. It includes much exotic internal decoration in baroque and rococo styles. It was badly damaged during the Second World War, but has since been reconstructed, becoming a major tourist attraction.
- Image 16Photograph: Henry W. LaurischKadavar are a rock band from Berlin, Germany, founded in 2010. Their retro sound, incorporating psychedelic rock and stoner rock, has been compared to bands of the 1970s hard rock/heavy metal era. Kadavar currently consists of three members: guitarist and lead vocalist Christoph "Lupus" Lindemann, drummer Christoph "Tiger" Bartelt, and bassist Simon "Dragon" Bouteloup.
- Image 17Map credit: Lencer and NordNordWestA general map, showing the geography of Germany, the seventh largest country in Europe and the second most populous. Located in Central Europe, Germany is second only to Russia in the number of borders it shares with other European countries (9).
- Image 18Photo credit: Andreas TilleLichtenstein Castle is a fairy-tale castle located near Honau in the Swabian Alb, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Although there have been previous castles on the site, the current castle was constructed by Duke Wilhelm of Urach in 1840 after being inspired by Wilhelm Hauff's novel Lichtenstein. The romantic Neo-Gothic design of the castle was created by the architect Carl Alexander Heideloff.
- Image 19Design credit: German New Guinea Company; photographed by the National Numismatic CollectionGerman New Guinea was a German colonial protectorate established in 1884 in the northeastern part of the island of New Guinea and several nearby island groups. The German New Guinea Company was founded in Berlin by Adolph von Hansemann and a syndicate of German bankers for the purpose of colonizing and exploiting the protectorate's resources. This gold coin, worth 20 New Guinean marks, was issued by the German New Guinea Company in 1895, and is now part of the National Numismatic Collection at the Smithsonian Institution.
- Image 21Photo credit: Chris 73The Cathedral of Magdeburg (known as Magdeburger Dom in German) is the first gothic cathedral in Germany and with a height of 104 m the highest cathedral in Eastern Germany. The current cathedral was constructed over the period of 300 years starting from 1209, and the completion of the steeples took place only in 1520. In 2004 a funding drive for a new organ that was started in 1997 was completed, collecting 2 Million Euro. The new organ has been ordered from a company near Potsdam, constructing a 36 ton instrument with 93 registers and approximately 5000 pipes. The construction is planned to be completed in 2007, and the new organ will hopefully be used for the first time in 2008.
- Image 22The Einstein Tower, a solar observatory in Potsdam
Related portals
- Parent portals
- Regional
- History
 Holy Roman Empire (900–1806)
Holy Roman Empire (900–1806) East Germany (1949–1990)
East Germany (1949–1990)
- Neighbouring countries
Anniversaries for July 25

- 1790 – Death of educational reformer Johann Bernhard Basedow
- 1802 – Death of Friedrich Karl Joseph von Erthal, Archbishop of Mainz
- 1867 – Birth of author and painter Max Dauthendey
- 2005 – Death of jazz trombonist Albert Mangelsdorff
Did you know...
- ... that during his tenure as the manager of Austria's Burgtheater from 1971 to 1976, Gerhard Klingenberg often directed plays with analogies of a divided Europe?
- ... that Zionist activist Georg Kareski defended the Nuremberg Laws in a Nazi newspaper?
- ... that in Ludwig Krug's rendition of Adam and Eve (pictured), an ape mimics Adam eating the apple?
- ... that Albert Einstein wrote to Joseph Petzoldt in 1914 that he had "long shared his convictions", after reading one of his philosophical books?
- ... that the first public performance of the two songs of Arnold Schoenberg's Zwei Gesänge, Op. 1, was met with hostile audience reactions?
- ... that Margaret Carroux's German translation of The Lord of the Rings contains errors introduced by her editor?
- ... that Samuel Kummer chose for his first recital as the organist of the restored Frauenkirche in Dresden music by Bach, Brahms, Max Reger, Louis Vierne, and himself?
- ... that the Nazis killed more than fifty Dutch nationals in retaliation for the assassinations of Hendrik Seyffardt and Hermannus Reydon by the Dutch resistance?
Selected cuisines, dishes and foods

Pomeranian cuisine generally refers to dishes typical of the area that once formed the historic Province of Pomerania in northeast Germany and which included Stettin (now Szczecin) and Further Pomerania. It is characterised by ingredients produced by Pomeranian farms, such as swede (Wruken) and sugar beet, by poultry rearing, which has produced the famous Pomeranian goose, by the wealth of fish in the Baltic Sea, rivers and inland lakes of the Pomeranian Lake District, and the abundance of quarry in Pomeranian forests. Pomeranian cuisine is hearty. Several foodstuffs have a particularly important role to play here in the region: potatoes, known as Tüften, prepared in various ways and whose significance is evinced by the existence of a West Pomeranian Potato Museum (Vorpommersches Kartoffelmuseum), Grünkohl and sweet and sour dishes produced, for example, by baking fruit.
Pomeranian farmers were self-sufficient: crops were stored until the following harvest, meat products were preserved in the smoke store of the home, or in the smokeries of larger villages such as Schlawin. Fruit, vegetables, lard and Gänseflomen were preserved by bottling in jars. Syrup was made from the sugar beet itself. (Full article...)Topics
Categories
Things you can do

A list of articles needing cleanup associated with this project is available. See also the tool's wiki page and the index of WikiProjects.
Here are some tasks you can do. Please remove completed tasks from the list.
- Requests: German Archaeological Institute at Rome [de], Deutsche Familienversicherung [de], Dietlof von Arnim-Boitzenburg [de], Rolf von Bargen [de], Micky Beisenherz [de], Hennes Bender [de], Georg Bernhard [de] (1875–1944), Eduard Georg von Bethusy-Huc [de], Rolf Brandt [de] (1886–1953), Jan Philipp Burgard [de], Georg Arbogast von und zu Franckenstein [de], Georg Gafron [de], Ferdinand Heribert von Galen [de], Gundula Gause [de], Karl-Heinz Hagen [de], Herbert Helmrich [de], Nils von der Heyde [de], Monty Jacobs [de] (1875–1945), Hans Katzer [de], Siegfried Kauder [de], Matze Knop [de], Wolfgang Kryszohn [de], Claus Larass [de], Isidor Levy [de] (1852–1929), Markus Löning [de], Anke Plättner [de], Hans Heinrich X. Fürst von Pless [de], Gerd Poppe [de], Victor-Emanuel Preusker [de], Günter Prinz [de], Hans Sauer (inventor) [de], Franz August Schenk von Stauffenberg [de], Paul Schlesinger [de] (1878-1928),Oscar Schneider [de], Hajo Schumacher [de], Otto Theodor von Seydewitz [de], Dorothea Siems [de], Werner Sonne [de], Anton Stark [de], Udo zu Stolberg-Wernigerode [de], Christoph Strässer [de], Torsten Sträter, Joseph von Utzschneider [de], Jürgen Wieshoff [de], Hans Wilhelmi [de], Alexandra Würzbach [de]
- Unreferenced: Unreferenced BLPs, Bundesautobahn 93, Benjamin Trinks, Steeler (German band), Amelie Beese, Zoologisches Museum in Kiel, Emil Krebs, Prussian semaphore system, Partenstein, Peter Krieg, Porsche 597, Christa Bauch, Curt Cress, Stefan Beuse
- Cleanup: 53541 issues in total as of 2024-03-03
- Translate: Articles needing translation from German Wikipedia
- Stubs: Albersdorf, Thuringia, Ingo Friedrich, Berndt Seite, Federal Social Court; 116 articles in Category:German MEP stubs
- Update: Deutsches Wörterbuch
- Portal maintenance: Update News, Did you know, announcements and the todo list
- Orphans:
Orphaned articles in Germany

- Photo: Take/Add requested photographs
- Expression error: Unrecognized punctuation character ",".
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus